Hemoglobin norms during pregnancy
If in normal conditions the hemoglobin norm for women under 40 years of age is 120-140 g/l, then for expectant mothers the threshold norm values are slightly lower. Hemoglobin levels decrease during pregnancy for natural reasons. Blood volume in women at this time increases by more than 30%. Iron consumption increases as the placenta forms and grows, and the fetal circulatory system forms and develops.
The lower limit of normal hemoglobin during pregnancy is 110 g/l. At a level of 109 g/l, the pregnant woman is already diagnosed with a mild degree of anemia and is prescribed iron supplements.
Hemoglobin in the range of 89-70 g/l indicates moderate anemia, and below 70 g/l - severe anemia. Pregnant women with severe anemia require hospital treatment.
Treatment options
During pregnancy, correction of iron protein levels is not always carried out. If the excess of the norm is insignificant, the indicator does not require reduction. Treatment is carried out in case of pronounced clinical symptoms or in the presence of other diseases that affect the state of hemoglobin. All deviations in blood flow are perceived as a symptom of other diseases. To treat pregnant women, gentle methods are used - diet correction, traditional medicine. Medicines are used as a last resort.
Therapeutic diet
A high hemoglobin level is the reason for following a special diet. A woman is recommended to drink a lot of clean water throughout the day. The liquid helps normalize the rheological properties of blood. Red meat and products made from it are excluded from the diet. This is necessary to reduce exogenous sources of iron-containing protein production. Instead, they eat white meat. It contributes to the gradual normalization of hemoglobin levels.

To reduce the concentration of iron-binding protein, adhere to the following recommendations:
- The menu is varied. It includes products containing beneficial microelements, except iron.
- Drink a lot of clean water. The required volume of liquid is calculated at the rate of 30 ml for every 1 kg of body weight.
- Fried and fatty foods are excluded from the menu. The diet is supplemented with fruits and berries.
- Products are boiled or stewed, excluding frying.
If the hemoglobin level is slightly exceeded, a therapeutic diet is sufficient for correction. Gradually, the woman’s condition returns to normal. If symptoms threaten, drug treatment is necessary.
How does anemia manifest during pregnancy?
Anemia is a condition in which the number of red cells in the blood decreases - red blood cells, and therefore hemoglobin. The insidiousness of anemia during pregnancy is that its symptoms can easily be mistaken for manifestations of toxicosis: increased fatigue, drowsiness, pale skin, lack of appetite, memory loss, irritability, shortness of breath, sometimes tinnitus - fits perfectly into the picture of pregnancy, doesn’t it? In this case, a mild degree of anemia can be completely asymptomatic.

That is why, to monitor hemoglobin levels, a woman is given a general blood test three times during pregnancy. And if anemia is confirmed, then more often to monitor the dynamics.
What symptoms suggest low hemoglobin in pregnant women?
The disease can manifest itself:
- asthenovegetative symptoms (constant weakness, frequent dizziness, drowsiness, tachycardia, shortness of breath, muscle weakness, decreased performance, fatigue);
- sideropenic symptoms (atrophic changes in the mucous membranes and skin, atrophy of the papillae on the tongue, blue sclera, yellowing of the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle, a grayish tint to the face, alopecia, brittle hair, delamination of the nail plates, concavity of the nails), cheilitis, stomatitis, perversion of taste perception - patients feel the desire to eat raw meat products, chalk, sand, earth, etc. and a perverted sense of smell - patients like the smell of gasoline, solvents, etc.;
- neurological symptoms (urinary incontinence, irritability, tearfulness, nausea, impaired skin sensitivity, chilliness, cold extremities, swallowing disorders (discomfort when swallowing solid food)).
In isolated cases, swelling may occur.
How to increase hemoglobin?

It is believed that you can increase hemoglobin by eating apples and meat. Unfortunately, this is unlikely. A balanced diet with the obligatory inclusion of animal products: red meat, liver, eggs, as well as iron-rich plant foods is indeed the basis for the prevention of anemia. But it is unlikely that it will be possible to cure it only with the help of “correct” food: iron from foods is not completely absorbed, and what is absorbed does not meet the needs of the pregnant woman’s body.
It is important!
In addition, iron from food is absorbed worse if the expectant mother drinks strong tea and coffee, eats chocolate, rice, and corn.
All these products, as well as calcium from milk and fermented milk products, interfere with the absorption of iron. A therapeutic diet is a mandatory step to treat anemia, but it alone will not be enough. Low hemoglobin during pregnancy can lead to serious consequences, as mentioned above.
Therefore, even with a mild degree of anemia, a pregnant woman is prescribed iron supplements in the form of tablets and multivitamins, which help iron to be absorbed. If a woman does not tolerate such drugs well or there is no effect from them, as well as in case of severe anemia, the medicine is administered to her intravenously.
Thus, anemia is a common complication of pregnancy:
- hemoglobin of 109 g/l and below indicates the development of iron deficiency in the expectant mother;
- signs of anemia may be subtle, since they are similar to the symptoms of toxicosis, the diagnosis is made only by the results of a blood test;
- anemia is dangerous for both mother and child; in the worst case, a miscarriage may occur, premature birth may occur, and postpartum hemorrhage may develop;
- hemoglobin is increased with the help of a proper diet, as well as by taking iron supplements: in the form of tablets or intravenously.
(0 ratings; article rating 0)
Share Share Share
Causes of anemia and low hemoglobin
In most cases, anemia in pregnant women is caused by unevenly increased volumes of plasma and erythrocyte blood components.
It should also be taken into account that during pregnancy there is a significant increase in the body’s need for proteins, iron, etc. Additionally, the development of iron deficiency anemia is facilitated by changes in hormonal levels, the development of toxicosis, etc.
Risk factors for decreased Hb are:
- history of heavy menstrual bleeding;
- multiple pregnancies;
- early or late pregnancy;
- a new pregnancy following a short period of time from the previous one;
- insufficient or unhealthy nutrition;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- long-term lactation during a previous pregnancy;
- the patient has helminth infections, gastrointestinal bleeding, hemorrhoids;
- bleeding disorders;
- severe pathologies of the liver, accompanied by a violation of its protein synthetic function;
- kidney pathologies accompanied by impaired erythropoiesis;
- bone marrow pathologies;
- malignant neoplasms;
- excessive production of estradiol, leading to inhibition of erythropoiesis;
- iron deficiency that occurred before pregnancy;
- deficiency of folic acid and cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12);
- excessive antigenic stimulation of the maternal body from fetal tissues (impaired T-cell immune links, lymphocytopenia, increased anti-tissue sensitization, etc.),
- infectious diseases and intoxications accompanied by the development of erythrocyte hemolysis;
- various hemoglobinopathies;
- postpartum bleeding.
Predictions and prevention

Since a high level of iron-containing protein in pregnant women is a concomitant condition, all complications develop as a consequence of the underlying disease. Therefore, prevention of exceeding the permissible norm of the hemoglobin indicator is nonspecific. It is enough for a woman to monitor her well-being, switch to proper nutrition, give up bad habits and be physically active. Following these simple recommendations greatly reduces the likelihood of worsening the pathology.
With elevated levels of iron-containing protein, the prognosis is usually favorable. Drug therapy is not required if there are no obvious symptoms. To bring the hemoglobin indicator back to normal, it is enough to eliminate blood viscosity and the tendency to form blood clots and rehydrate the body. Treatment consists of following a special diet and using folk remedies.
Pregnant women rarely develop high hemoglobin. Normalizing its level involves following a special diet and adjusting your lifestyle. Drug therapy to correct iron-containing protein in pregnant women is rarely used and only in case of significant excess of the norm.
What is hemoglobin?
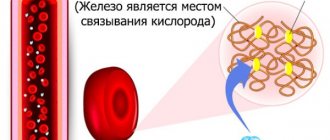
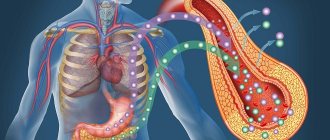
The term “hemoglobin” should be understood as special blood cells of protein origin that are part of red blood cells (red cells). Its main function is to deliver oxygen to all cells of the body from the lungs. But in addition to this, hemoglobin’s responsibilities also include the removal of carbon dioxide, which is delivered directly to the respiratory organs, and they, in turn, get rid of it.
The proteins themselves contain iron, which is why our blood is red. Thanks to this structure, hemoglobin fulfills its direct duties. In case of successful conception, a need for iron arises in the female body, and a significant one.
The role of an important protein compound
What hemoglobin should a pregnant woman have? To answer this question, it is worth understanding a little about some features of physiology. All life processes taking place inside the human body, regardless of the person’s age, occur with the participation of oxygen! This is a natural catalyst that is necessary for any reactions that occur every second.
A lack of this element or its supply in small quantities results in a rather dangerous pathology - hypoxia. This condition seriously impedes the development of the child, and if no action is taken, it can cause a number of intrauterine anomalies in the fetus.
And since iron is part of hemoglobin, it is very important to control its levels. If this trace element in the blood is more or less than normal, this can lead to undesirable consequences.