For certain conditions, your doctor may order a CT scan of the ear. CT uses X-ray technology and advanced computer analysis to visualize structures in the ear area. The scan produces images of tissue sections, which are then transformed into three-dimensional images of morphological structures in the ear area. CT scans can detect changes in bone tissue and diagnose various diseases or injuries. Typically, a CT scan of the temporal bone (ear area) is used only for certain clinical indications, such as to determine the cause of hearing loss or chronic infections of the middle and inner ear.
Indications
- Hearing impairment or loss
- Otitis
- Cholesteatoma
- Temporal bone injury
- Tumors of the presbycus, internal auditory canal and cerebellopontine angle
- Labyrinthitis
- Otosclerosis
- Exostoses
- Osteomas
- Keratosis obturans
- Incudostapedial joint dislocation
- Maleoincudal dislocation
- Acquired cholesteatomas
- Tympanosclerosis
- Paragangliomas (in particular, glomus tympanicum),
- Congenital cholesteatomas,
- Schwannomas
- Infection or inflammation
Contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging
Before you sign up for the procedure, you should pay attention to the contraindications to its implementation. During scanning, the patient is exposed to a magnetic field, which should not be exposed to objects containing metals that react to the magnet with displacement or heating (iron, steel, cobalt, nickel), as well as magnetic devices.
Internal implants containing a magnet may fail under the influence of a tomograph and lead to irreversible consequences. Such devices include:
- pacemakers;
- stimulants of nervous and muscle activity;
- drug dispensers (pumps for administering insulin, analgesics, parenteral nutrition);
- cochlear implant.
Some cochlear implants have a removable magnet that allows for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanning if necessary.
An obstacle to the procedure may be the presence of metal objects in the body:
- endoprostheses containing a high percentage of ferromagnetic materials;
- Ilizarov apparatus;
- clips on cerebral vessels;
- artificial heart valves;
- fragments, bullets, metal shavings or dust remaining in the body as a result of injury.
When visiting a radiologist, you must bring with you all the technical documentation describing the implant or prosthesis located inside the body. After studying the composition of the implanted material, the doctor decides on the possibility of carrying out the procedure.
Relative contraindications and restrictions include early pregnancy, claustrophobia, mental and severe somatic illnesses, severe pain, convulsions, epilepsy, age under 7 years, body weight more than 120 kg.
The contrast agent is not administered at any stage of pregnancy, as well as for people with renal failure, since the drug is excreted through the kidneys. For healthy people, an obstacle to contrast research is an allergic reaction to its components.
Preparation
- Before your CT scan, you should leave your jewelry at home and wear comfortable clothing.
- Considering that a CT scan scans the head area, it is necessary to remove dentures and various metal objects.
- If it is planned to use a contrast agent, the patient is advised to refrain from eating for several hours before the CT scan.
- The patient should inform the radiologist about the presence of any allergies, including to contrast or iodine, as well as the presence of pregnancy or kidney disease.
Indications for MRI of the inner and outer ear
The ear is an organ that captures and conducts sound with the further formation of the auditory sensation. In addition, it performs the function of the vestibular apparatus - it perceives and analyzes the position of the body and its parts in space to maintain balance.
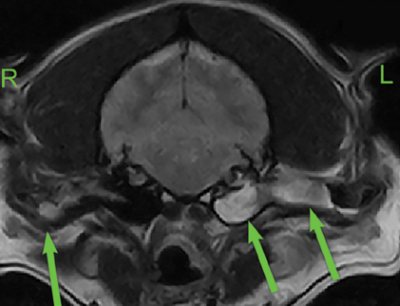
An MRI of the ear is prescribed by an otolaryngologist, neurologist or oncologist if the following indications exist:
- congenital anomalies of the external ear;
- suspicion of benign or malignant neoplasms - early diagnosis, assessment of the stage and extent of the process is possible;
- signs of vascular disorders;
- inflammatory processes that cannot be treated for a long time;
- identification of complications of otitis media;
- carrying out differential diagnosis of head diseases;
- decreased or loss of hearing;
- noise in ears;
- swelling, redness, ear pain, pathological discharge (pus, blood, effusion);
- signs of damage to the vestibular system - unsteady gait, dizziness, nausea unrelated to food intake, unexplained fainting.
In complex diagnostic cases, when the studies and analyzes do not provide convincing results, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed. Timely diagnosis allows you to prescribe correct and effective treatment, adjust already started therapy, determine further treatment tactics and monitor the dynamics of the process.
During the procedure
- While placing the patient on the scanner table, the x-ray technician will explain the procedure and answer the patient's questions.
- If contrast is used, it will be injected into a vein.
- During the injection, the patient may feel a feeling of warmth throughout the body and a metallic taste in the mouth.
- If during the administration of contrast the patient feels shortness of breath, sneezes, nasal congestion, or discomfort in the throat, then this must be immediately reported to the x-ray technician.
- This CT procedure is performed in two projections. In both cases, the head is in a fixed position and the patient must remain motionless.
- In the first position, the patient lies on his back, with his arms at his sides. In the second position, the patient lies on his stomach, with the head fixed on the chin.
- The table the patient is on will slide into the scanner. Only the patient's head will be in the scanner. The scanner is open at the back and front, reducing the likelihood of claustrophobia
- The x-ray technician can see and hear the patient during the scan
- After the first series of images is taken, the patient will be repositioned and a second series of images will be taken.
- This CT scan usually takes about 30 minutes.
CT scan of the temporal bones: when is this study needed?
Computed tomography of the skull bones is a fairly common study. However, some diseases may require targeted images of individual bones of the skull.
We talk about the features of one of these studies - computed tomography of the temporal bones - with Roman Aleksandrovich Strokov, a radiologist at the Expert Clinic Kursk.
— Roman Aleksandrovich, where are the temporal bones located and what is their function?
- They are located in the base of the skull and participate in the formation of its lateral part. The temporal bones contain the organ of hearing and balance. In addition, the bone canals of the temporal bones contain important nerve structures such as the facial and vestibular-cochlear nerves, and the trigeminal ganglion is located.
— What can be a reason for a CT scan of the temporal bones? For what diseases is this diagnosis effective?
— Computed tomography of the temporal bones is a technique that is carried out according to a special protocol. This helps to clearly detail all the anatomical formations that are located in the temporal bone. Therefore, doctors refer patients with damage to the organ of hearing and balance, or with traumatic brain injury (TBI), when, in particular, a fracture of the base of the skull is suspected, for a CT scan of the temporal bones.
The study is also recommended for patients with neurological symptoms that correspond to damage to the nerves located in the temporal bones. A CT scan of the temporal bones may also be needed when planning surgical treatment, for example, for a disease such as otosclerosis. This is done to evaluate the anatomical features of the temporal bone in a particular patient and to select the appropriate cochlear prosthesis (prosthesis of the cochlea of the inner ear).
CT scan of the temporal bones is also informative for inflammatory processes of the ear (acute and chronic otitis media), injuries, and tumors of this area.
Read materials on the topic:
Is there noise in your ear? Rule out otosclerosis What is otitis media and how to avoid it?
— What does a CT scan of the temporal bones show?
— On a CT image we observe the structures of the outer, middle and inner ear (auditory ossicles, configuration of the ear canal). In addition, it is possible to evaluate the bone elements, as well as the air cavities of the temporal bone for violations of their pneumatization (filling with air). Based on these data, we conclude whether the identified changes are the cause of the illness that worries the patient.
— Roman Aleksandrovich, please tell us how a CT scan of the temporal bones is done
— A standard examination of the temporal bones is performed without contrast (that is, without the use of a contrast agent). The patient enters the office, undergoes instructions, undresses, lies down on the tomograph table and lies motionless throughout the entire procedure. It usually takes a few minutes.
The tomograph is equipped with means of communication with personnel. If during the study the patient experiences discomfort or deteriorates in health, he can report this to the staff.
At the end of the scan, the radiologist checks the quality of the images obtained and their information content. The patient receives pictures on film, a disk with a recording of the procedure and a doctor’s report.
— Do I need to prepare for this procedure?
— There is no special preparation for CT scanning of the temporal bones. The only condition is that the patient must remove all metal-containing jewelry from the outer ear.
— What are the contraindications to this research method?
— CT scanning of the temporal bones, like computed tomography of any other area, is not recommended for pregnant women and children due to ionizing radiation.
— Are there cases in which this study can be performed on pregnant women or children?
— For children, it is performed according to the necessary indications and when other diagnostic methods and clinical examination data do not provide sufficient information to make a diagnosis. Most often, the indications for doing a CT scan of the temporal bones are:
- inflammatory diseases of the ear, congenital anomalies of its development;
- traumatic brain injury;
- planning of surgical treatment.
For pregnant women, this study is carried out strictly according to indications if there is a life-threatening condition.
— Do I need a referral to take this test?
— I believe that it is always advisable to have a referral for a computed tomography scan, not only for children, but also for adults. Why? Because in the referral, the attending physician (otorhinolaryngologist, audiologist, therapist, traumatologist) indicates a preliminary diagnosis made on the basis of the examination. And to confirm or refute his opinion, he sends him for a computed tomography scan. For example, a doctor suspects a patient has an inflammatory process in the middle or inner ear and points this out. That is, the radiologist is asked whether there is inflammation or not. Accordingly, the radiologist must answer this question, specifically describing changes in the structures of interest to the attending physician.
In the vast majority of cases, patients come to our clinic for a CT scan of the temporal bones with a referral. If the patient comes on his own, it is difficult for the radiologist to give a clear answer. Often such a subsequent study is not informative enough for the attending physician.
Interviewed by Sevilya Ibraimova
You can sign up for a CT scan of the temporal bones here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
The editors recommend:
When is CT indispensable? Why can't my ear hear?
For reference:
Strokov Roman Alexandrovich
Graduate of the medical faculty of the Tashkent State Medical Academy in 2011. In 2012, he completed his internship in the field of Radiology. He currently holds the position of radiologist at Clinic Expert Kursk. Receives at the address: st. Karl Liebknechta, 7
After the procedure
- After a CT scan, there are no restrictions for the patient to return to normal life and nutrition.
- If the patient has been injected with a contrast agent, it is recommended to drink six to eight glasses of water after the scan to help remove the contrast from the body more quickly.
- The CT results will be analyzed by a radiologist and a description of the images will be sent to the attending physician, who will compare the obtained data on morphological changes with the clinical picture.
- If necessary, other tests (eg MRI) may be recommended.
Which is better: MRI or CT
During MRI, the patient is not exposed to ionizing radiation, as with X-ray methods, and there are no restrictions on the number of procedures performed. Computed tomography gives a large radiation dose to the body and is not recommended for children and pregnant women.
In each clinical case, the choice of method remains with the doctor, so it is important to consult a specialist if symptoms appear. After examining the complaints and checking the ear using available methods, the doctor gives a referral for the most appropriate examination.
Computed tomography is more informative for injuries and damage to the skull, damage to bone structures, and accumulation of pathological fluid in the middle ear cavity. MRI will more accurately show the condition of soft tissues, tumors, inflammatory processes, and vascular diseases.
Procedure for implementing CT
Diagnosis of pathologies and disorders associated with the functioning of the middle ear is carried out in the medical center using modern equipment.
The procedure for performing computed tomography:
- the patient is placed on a specialized mobile table;
- the head is fixed to prevent sudden movements during diagnosis;
- the table is placed in the tomograph, after which a specialized ring rotates around the person’s head;
- diagnostic results are displayed on the PC screen.
Doctors of the medical diagnostic center provide a professional approach to the implementation of activities. The research results are interpreted and deciphered as competently as possible. The most important aspect of correct diagnosis is high-quality diagnostics. Therefore, doctors perform their work responsibly, providing highly accurate computed tomography results.
At the clinic you will be able to undergo a CT scan of the middle ear, as well as other ENT systems. On the website you can sign up for diagnostics, as well as calculate the cost of diagnostic procedures.
Bone diseases
The skeleton is the support of the whole organism. It is not surprising that most bone pathologies relate to musculoskeletal disorders. They can be:
- Genetically determined. These are diseases that are inherited. These include Paget's disease and osteogenesis imperfecta.
- Inflammatory. The entry of pathological microorganisms into bone tissue leads to osteomyelitis. It causes necrotic changes in the skeletal structure.
- Dystrophic lesions include osteoporosis and rickets. They are caused by a lack of phosphorus and calcium in the diet. Disruption of the ovaries and thyroid gland also interferes with the absorption of these elements from food.
- Tumor lesions.
- Mechanical damage.
- Degenerative – ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis. They are classified as autoimmune lesions.
Safety
The examination has been used in clinical medicine for decades. Sufficient data have been accumulated on the proven safety of diagnostics. In the absence of contraindications and compliance with the rules, it does not cause harm to health.
CT refers to x-ray methods. Requires a recovery period. Without good reason, you should not resort to it more often than once every six months. Before and after the examination, you must observe an increased drinking regime.
Operating principle
The tomograph scans the area under study layer by layer. On the computer screen, based on the received data, a three-dimensional model is built in different projections. The received information is written to disk or printed in the form of snapshots. For this purpose, the device includes a high-tech set of devices. This is an X-ray unit, a computerized station, a mobile couch.
During the examination, the X-ray camera rotates continuously. It generates ionizing radiation into the area being studied. The rays passing through the body are recorded and processed. This allows you to create a multi-dimensional, detailed picture.