MRI or magnetic resonance imaging is the most accurate diagnostic test that provides greater detail of the internal structures of the body without the use of radiation. MRI uses a magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create clear, exceptionally detailed “images” of the area being examined. The MRI itself is a painless procedure.
Anatomy of the wrist joint
The wrist joint is one of the most mobile and complex articulations in the human body, formed by three small carpal bones (scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum), the articular surface of the radius and a cartilage disc. Normal wrist joint function is essential for the precise, intricate hand movements needed in many areas of human activity. This is a rather fragile joint, easily damaged by injuries, which is due to the not very powerful ligaments and complex structure.
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications:
- artificial pacemaker;
- cochlear implant;
- built-in implants made of metal material;
- ferromagnetic fragments;
- Shevtsov-Matsukatov apparatus.
Relative contraindications:
- insulin injection device;
- artificial heart valve;
- hemostatic clamps on blood vessels;
- heart failure;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- claustrophobia;
- mental disorder;
- tattoos applied with dyes containing metallic components;
- braces.
Prosthetic products made of titanium are not ferromagnetic and are not a contraindication to tomography.
Contraindications for MRI with contrast:
- hemolytic anemia (increased destruction of red blood cells);
- allergic reaction to contrast agent;
- renal failure;
- pregnancy and lactation (the effect of contrast agents on the fetus is poorly studied).
Diseases of the wrist joint
The most common injuries to the wrist joint are fractures of the head of the radius and ulna, subluxations and dislocations. The most common mechanism of fracture is a fall on outstretched arms. Dislocations of the wrist joint most often occur in children under 5 years of age, which is due to the weakness and high extensibility of the ligaments that strengthen the joint. The most common mechanism for dislocation of the wrist joint in children is a tug on the hand with simultaneous rotation along the longitudinal axis of the joint, which occurs when an accompanying adult tries to keep the child from falling.
The wrist joint is susceptible to inflammatory processes, for example in rheumatoid or other arthritis. The cause of the disease can be specific infections (gonorrhea, chlamydia, tuberculosis), autoimmune diseases (rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis), metabolic disorders (gout). Less commonly, the cause of inflammation of the wrist joint is a direct hit of a nonspecific infection during injury or through the bloodstream (purulent arthritis). The inflammatory process may involve the synovial bursa of the joint and tendon.
With age, the risk of degenerative-dystrophic phenomena increases. Osteoarthritis of the wrist joint occurs as a result of metabolic disorders in the articular cartilage. Professional activity may be a predisposing factor - most often PC operators, artists, workers who use jackhammers, rotary hammers and drills, and musicians encounter osteoarthritis.
Space-occupying formations of the wrist joint are a large group of benign (synovial cysts, hygromas, fibromas, chondromas) and malignant neoplasms. MRI of the wrist joint is ideal for diagnosing all possible diseases in this area, due to the ability of the method to “see” soft tissue, unlike radiography or computed tomography. The latter methods are good for diagnosing fractures, but not other diseases.
What diseases can be diagnosed using MRI of the hand?
Traumatic hand injuries
The contrast resolution of thin soft tissue MRI allows the evaluation of tendons, ligaments, and complex interconnection systems of the fingers. Normal tendons and ligaments of the hands usually show low signal intensity on MRI. In contrast, these structures exhibit increased signal intensity or abnormal morphology upon injury.
Tendon injuries
Flexor tendon injuries most often occur secondary to a palmar tear or sports-related injury. Tendon rupture or partial damage usually occurs due to resistance to forced stretching or other types of injury. MRI can accurately differentiate partial from complete rupture, and can easily display the length of tendon retraction. This injury can occur anywhere along the flexor tendon and is classified according to the location of the injury.
Extensor tendon wounds
Extensor tendon injuries can occur anywhere along the extensor tendons. A common example is a distal extensor tear from the distal phalanx. This occurs during forced flexion of the joint during active contraction of the extensor.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disease in the hand, and the prevalence of the disease increases with age. More than 50% of men and women over 60 years of age have evidence of OA using radiographs of the hands. Osteoarthritis is usually a slowly progressive disorder characterized by uneven narrowing of articular cartilage, periarticular sclerosis, osteophytosis, and subchondral cysts. Erosive OA has the additional features of synovitis, tenosynovitis and erosions, and is most often observed in postmenopausal women. When synovitis is observed in the presence of OA, the current theory is that synovitis is a marker of a secondary inflammatory response to damage to cartilage and loose particles in the joint. Detection of synovitis in a patient with OA can help diagnose patients who are at risk for OA erosion, allowing for early preventive treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an uncommon chronic systemic inflammatory arthropathy, affecting approximately 0.5–1.0% of the population, although the prevalence appears to be increasing. RA manifests as a proliferative, hypertrophied synovitis that leads to bone breakdown and cartilage breakdown. Within the upper extremity, RA predominantly involves the wrist joints. Characteristic radiographic findings of symmetrical or concentric narrowing of articular erosions indicate the presence of irreversible damage to cartilage and bone. The greater availability and positive results associated with disease-modifying agents necessitate the use of MRI to recognize RA very early before irreversible damage occurs. MRI allows you to more quickly and accurately detect synovitis, tenosynovitis, bursitis, early or minor erosion and osteitis. Proliferating synovitis is the earliest recognized pathological finding in RA and is an indicator of poor prognosis for the patient.
Osteolysis, typically seen on MRI as a edematous bone marrow signal when synovial membrane is injected, is increasingly recognized as an early feature of RA that predicts cartilage and bone damage. Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules are present in 30-40% of patients and may be seen on imaging of the arm.
Psoriatic arthritis and other inflammatory arthropathies
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Psoriatic arthritis is an uncommon inflammatory arthropathy associated with psoriasis. Up to 30% of patients with psoriasis may be affected by this complication. On radiographs, arthritis usually appears as isolated tenosynovitis, especially of the flexor tendons, with associated soft tissue swelling that can be easily identified on MRI. A signal resembling cerebral edema is the earliest bone sign on MRI and tends to occur with involvement of the joint capsule at the phalanx. This signal becomes more extensive as the disease progresses. Erosion eventually forms at the edge of the bone, leading to the deformity characteristic of psoriatic arthritis. Other systemic inflammatory diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, may have evidence of tenosynovitis, synovitis, and a bone marrow edema signal as well, which may be indistinguishable from early or seronegative RA.
Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis
Septic arthritis is an arthropathy caused by intra-articular infection that leads to joint destruction. Risk factors include bacteremia, immunocompromised status, rheumatoid arthritis, and previous penetrating trauma. Septic arthritis should be considered in the setting of acute uniarticular arthritis, especially with accompanying clinical signs and symptoms of joint pain and fever. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential when making a diagnosis of septic arthritis with articular cartilage still intact to prevent the immediate risk of irreversible damage and subsequent secondary osteoarthritis. On MRI, the presence of septic arthritis and synovitis with an associated subchondral bone marrow edema signal is typical of septic arthritis in the corresponding clinical presentation. Osteomyelitis usually occurs in the presence of a skin defect or previous penetrating injury and is characterized by edema and cortical destruction. MRI is the most reliable method for accurately detecting osteomyelitis, since fluid-sensitive sequences can show similar signal changes to both non-infectious reactive changes and osteomyelitis.
Tumors
A wide variety of growths can be found in the hand, although they are less common than in other areas of the body. Injuries involving the bones of the hands and fingers account for 6% of all benign and 0.5% of all malignant bone injuries. Lesions associated with the soft tissues of the hand and fingers account for 15% of all benign and 4% of all malignant soft tissue neoplasms. MRI can be a useful adjunct to radiographs of the hand and fingers given its ability to accurately delineate and differentiate tissue characteristics. MRI also provides multidimensional ability to accurately localize lesions in all planes. Soft tissue injuries are ideally suited for MRI evaluation because this examination can accurately localize the injury and determine its relationship to surrounding structures. Tissue characterization with MRI is often sufficient to allow specific diagnoses of hand and finger injuries to be made.
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the wrist joint
Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist joint is indicated in the presence of the following complaints:
- pain;
- limited mobility, inability to bend or straighten the hand;
- swelling, redness of the skin in the wrist area;
- deformity of the wrist joint;
- nodes, swelling, tumor-like formations in the area of the wrist joint.
MR imaging of the wrist joint is contraindicated:
- children under 5 years of age (the study is carried out only in departments specially created for this, since MRI in children under 5 years of age requires sedation and medicated sleep due to the inability of small patients to remain still during the examination);
- patients with defibrillators, pacemakers, neurostimulators, cochlear implants and other electronic devices implanted into the body (magnetic fields disable implants);
- patients with metal foreign bodies (bullets, shot, shrapnel, metal shavings in the eyes) or medical devices (vascular clips, stents, prostheses) in the body (risk of injury or bleeding due to the displacement of a metal object under the influence of a magnetic field);
- patients with excess body weight, weighing more than 130 kg and torso girth more than 150 cm (physically do not fit into the tomograph);
- pregnant women during the 1st trimester (in the 2nd and 3rd trimester without restrictions).
Causes of pain in the joints of the fingers
There are a large number of diseases and conditions that can lead to pain in the joints of the hands. This:
- Arthritis is an inflammatory process that affects the joint itself and nearby tissues. How to suspect: swelling, redness and local hyperthermia, limited mobility, persistent pain at rest, crunching.
- Injury. Pain is a consequence of mechanical damage. May be accompanied by ligament rupture, severe swelling, redness or cyanosis, and bone fracture.
- Osteomyelitis. Infectious joint damage is accompanied by headache, fever, and general poor health.
- Gout. Develops when uric acid crystals accumulate. With this pathology, the joints become swollen, painful and lose mobility, and a burning sensation is possible. The disease is caused by improper functioning of the kidneys.
- Bursitis. With this pathology, the joint capsules become inflamed. The fingers swell, do not bend, the pain is almost unbearable.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. With this disease, the connective tissue is first affected, and symmetrically on both hands. The pain gets worse at night.
- Psoriasis. Aching sensations affect all fingers, and if left untreated, visible deformation occurs.
- Osteoarthritis (destruction of cartilage tissue). Pathology can be suspected by the following signs: pain in the joint on the finger when bending, crunching, increased pain with exertion, limited mobility.
- Stenosing ligamentitis. Swelling, cyanosis, inability to bend fingers, burning and numbness, occurring mainly in the morning, are the main signs of pathology.
- Polyosteoarthrosis. They develop mainly in older people. It is characterized by limited mobility of the fingers, stiffness of movement and severe pain.
Some other pathologies can also lead to pain in the joints of the hands. These are neuropathy, vascular disorders, tunnel syndrome (pain in the joint of the index finger in people who spend a long time at the computer) and some others.
Important!
Polyosteoarthrosis and arthritis can lead to disability, and osteomyelitis causes limb loss in 30% of cases. You can prevent the development of serious complications by promptly consulting a doctor.
Preparing for MRI of the wrist joint
MRI of the wrist joint is performed without prior preparation. The procedure does not require a special diet or fasting, pre-medication or other measures. However, due to the magnetic field, magnetic resonance imaging requires compliance with safety regulations. The presence of foreign objects in pockets or on the body, such as jewelry, body jewelry, piercings, cell phones, and other wearable electronics, can cause burns or injury. Magnetic fields cause heating of metal products, disable and lead to fire of devices and gadgets.
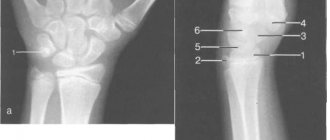
Tomography for wrist fracture
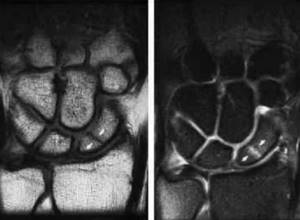
Scaphoid fracture on MRI
Traumatologists often prescribe diagnostics for fractures of the hard structures of the hand. A fall or direct blow can lead to partial or complete disruption of the integrity of the scaphoid, lunate, pisiform and other bones. Symptoms include:
- acute pain;
- increasing swelling;
- pathological bone mobility;
- hemorrhage/hematoma due to vascular damage;
- wrist deformity;
- limitation of movements in the hand;
- crepitation (characteristic crunching), etc.
In an open wrist fracture, bone fragments are visible. A cold limb with a bluish tint is suspicious for insufficient blood circulation due to a violation of the anatomy.
In an emergency, the victim will undergo a CT scan. The results of the CT examination will be ready almost immediately. Often the patient is transferred from the diagnostic room to the operating room.
An MRI of the hand is done a little later to assess the consequences of the injury: a computer scan does not always demonstrate damage to soft tissue structures.
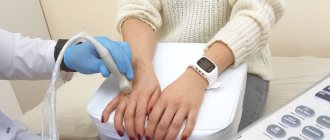
How to do an MRI of the wrist joint
MRI examination of the wrist is performed using an MRI scanner. This is a large cylindrical device with a hole in the center, forming a tunnel 60 cm long and wide. This is the working part of the installation; the patient lies in the tunnel during the examination. Before the procedure begins, the patient is positioned, with the arms either extended above the head or folded along the body, depending on which additional coil is used.

Before starting the examination, the patient needs to wear headphones, since the tomograph makes quite loud sounds during operation. Headphones are also needed to communicate with the operator and listen to music - it helps you relax and make the procedure more comfortable. The duration of an MRI examination of the wrist joint is 30 minutes. In some cases, with inflammatory processes or neoplasms, contrast is used to increase diagnostic accuracy. Contrast drugs are administered intravenously in the middle of the study - the contrast is evenly distributed throughout the body, accumulating exclusively where there are signs of disease. When using contrast enhancement, the duration of the procedure increases to 45 minutes.
After completing the MRI scan, the radiologist begins interpreting the images. This process lasts no more than 30 minutes. After decoding, the patient is given the images on a CD and a specialist’s report. They must be handed over to the attending physician. In addition, the radiologist at our center will definitely tell you about the results of the study and show the problems found in the images, and recommend a doctor to whom you can contact if the patient comes without a referral.
Advantages
The level of diagnostic equipment plays a huge role in the diagnosis of various hand diseases. The MART clinic pays special attention to this, so MRI of the hand is performed on a German high-field tomograph Siemens Espree, which allows you to visualize minor disorders and pathological processes at an early stage of the disease.
Its main difference from older models is the ultra-short length and large diameter of the tunnel pipe. This eliminates the possibility of developing attacks of claustrophobia. Wider options have been created for heavier patients. The limit for them is up to 160 kg versus 120 kg compared to older models.
Internal quality control
Burn to disc for free
Patient weight up to 160 kg
MRI for children
What will an MRI of the wrist joint show?
MRI images are a series of 1 mm thick sections taken through the examination area in several planes. They clearly show the bones that form the wrist joint, the articular cavity and articular cartilage, the membrane of the articulation, ligaments, muscles and their tendons.
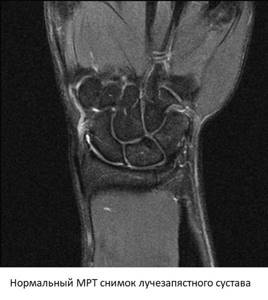
When interpreting the images, the doctor pays attention to the width of the joint space, the condition of the cartilage and articular membrane, and the integrity of the ligamentous apparatus. In the presence of space-occupying formations, MRI allows one to determine with high accuracy whether it is a cyst or a tumor. By studying the dynamics of contrast accumulation, early signs of inflammation or a malignant process can be identified.
Types of vascular MRI
Currently, there are several types of magnetic resonance examination of cerebral vessels:
- Arteriography of vessels with contrast
- Venography - a detailed examination of the venous network
- Comprehensive examination of veins and arteries
In the resulting image, the doctor is able to examine every part of the circulatory system, detect the slightest defects and disorders, including tumors, atherosclerotic manifestations, and so on.
This type of MRI is an indispensable stage in diagnosing a patient after a stroke, to assess the degree of brain damage after an injury, and also makes it possible to identify thrombosis and abnormalities in the structure and location of the vascular network.
A general examination is prescribed for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the brain, for example, before or after surgery. Using the resulting image, the doctor can reliably assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment method and correct it in time if necessary.
Make an appointment now!
The essence of MRI and why it is performed
MRI allows you to assess the condition of organs and tissues due to exposure to a magnetic field. During the procedure, a cross-sectional scan of the area of the body that is being examined is performed. Each of the resulting images simultaneously reveals bone structures, blood vessels and nerves, as well as soft tissue. From these images, the doctor can get an accurate idea of the structure of the area being examined and changes in it.
MRI in Moscow and other cities is used primarily to identify pathologies of the spine and central nervous system, heart and blood vessels, brain and spinal cord, joints, and some pelvic and abdominal organs. However, the examination is not used to examine the lungs, bones, intestines and stomach.
MRI makes it possible to accurately assess the structure of organs, detect tumors, pathologies, and traumatic changes. This method is used in oncology, urology, angiology and other fields of medicine. It is often carried out with a contrast agent, which allows for a more detailed examination of the tissue structure.
How is diagnostics carried out?
The patient lies down on the tomograph table and tries to lie still. Children are required, but adults are provided with headphones or earplugs if they wish to drown out the clicks, noise and crackles of the tomograph. If contrast is required, the substance is administered intravenously before the examination.
Having prepared a person for the MRI procedure, the table is pushed into the tomograph tunnel. The feedback system allows the patient to contact the staff if their health worsens: nausea, pain, panic reactions. The capsule of the device is illuminated and ventilated, which makes the diagnostic procedure comfortable.
Diagnostics lasts 40 minutes, if a contrast agent is used - 60 minutes.
The need for a combination of several zones
Comprehensive studies are the best way to make an early diagnosis. The human body is unique, but at the same time quite simple. Everything in it is interconnected. Therefore, if a pathological process occurs in one place, it is highly likely that it will soon spread to neighboring tissues.
A combination of several zones is most often used when there is a suspicion of a rapidly growing tumor or its metastases to other parts of the body. Often the need for complex studies arises in cases of nerve pathology. Remember that the more information, the higher the likelihood of making a correct diagnosis and prescribing adequate treatment.