What do leukocytes in urine indicate during pregnancy?
It is not the white blood cells themselves in the urine that are of concern. Their presence is a marker of certain pathological conditions that can be dangerous for both the pregnant woman and the unborn baby. The most common causes of white blood cells in urine during pregnancy include the following pathologies.
- Acute and chronic cystitis. Acute inflammation of the bladder is quite difficult to ignore, as it manifests itself as cutting and pain in the lower abdomen, as well as frequent painful urination. But chronic cystitis can last almost asymptomatically, occasionally manifesting itself as exacerbations, similar in symptoms to the acute process. In pregnant women, cystitis often accompanies the 1st trimester of gestation due to a slight decrease in immunity, as well as the 3rd trimester, when the growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder.
- Pyelonephritis. Inflammation of the renal pelvis. The acute period is characterized by fever and pain in the lumbar region; in chronically ill patients, pyelonephritis manifests itself only by prolonged headaches, high fatigue and rises in body temperature to subfebrile levels. In pregnant women, an exacerbation of the process often occurs in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, when the load on the kidneys increases due to the intensive growth of the fetus, and the enlarged uterus compresses the ureters and prevents the outflow of urine.
- Glomerulonephritis. Inflammation of the renal glomeruli of an autoimmune nature. A fairly serious disease in which, in addition to leukocytes, red blood cells are also found in the urine. Glomerulonephritis is a serious contraindication to pregnancy, since the affected kidneys often cannot cope with double load, which carries risks not only for the fetus, but also for the life of the woman.
- Kidney cyst. It does not show itself for a long time, but when the outflow of urine is disrupted, and this is possible in the later stages of pregnancy, a bacterial infection is noted. The cyst may fester with corresponding symptoms (lower back pain, fever, weakness).
- Chronic and acute urethritis. Manifested by inflammation of the urethra. Acute urethritis is characterized by sharp pain when urinating, cloudy urine is visually detected; symptoms of chronic urethritis are rarely seen, but pregnancy of any stage can be a provoking factor.
- Severe pathologies of the urinary system. For example, tumors, renal amyloidosis, renal tuberculosis, systemic lupus erythematosus. These diseases can be diagnosed both during pregnancy and outside of it. Each case is examined individually and, as a rule, leukocyturia is far from the only and not at all defining symptom.
- Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. Against the background of weakened immunity, pregnant women may experience the onset of diseases such as vulvovaginitis and adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine appendages). Thrush often worsens and a cheesy discharge appears. These same diseases can be caused by specific sexually transmitted pathogens. To find out the causes of inflammation, it is necessary to take a smear from the woman’s cervical canal.
- Preeclampsia. A terrible disease characteristic of the second half of pregnancy. Develops as a result of pathology of the placenta and generalized spasm of microvessels. Gestosis is characterized by the following set of symptoms: increased blood pressure, swelling, changes in the composition of urine (leukocytes increase slightly, but protein appears in the urine).
- Asymptomatic leukocyturia. Very often accompanies pregnancy. As the name implies, it is not accompanied by disturbances in the woman’s well-being, but is a sign of a latent inflammatory process, possibly outside the genitourinary system of the pregnant woman.
- Errors when collecting analysis. Insufficient hygiene of the external genitalia can lead to the release of white blood cells into the urine from the vagina. If there is any doubt, the doctor will recommend retaking the test as soon as possible.
If it is found that leukocytes in the urine are elevated during pregnancy, then all the causes can be divided into several groups: infectious-inflammatory in nature, not related to infection (aseptic) and resulting from pregnancy (preeclampsia). Their effect on the fetus depends on the severity of these reasons.
Separately, we can note the importance of correct urine collection for analysis and the need for a retake to clarify the diagnosis.
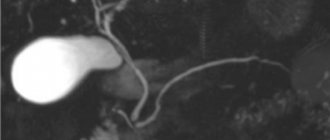
Pyelonephritis
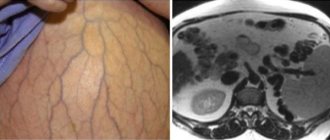
During pregnancy, women in 7% of cases develop such an unpleasant and dangerous disease as pyelonephritis, or gestational pyelonephritis. Pyelonephritis is a kidney disease, during which the kidney tissue first becomes inflamed, and subsequently the calyces and pelvis may also be affected. Typically, this disease develops at the end of the second - third trimester of pregnancy, when the uterus is already quite large and puts pressure on neighboring organs, including the ureters. In this case, urine cannot pass through them normally, and inflammation begins. Another reason may be a change in hormone levels, which affects the peristalsis of the ureters, and as a result, a deterioration in urine excretion. As a result, urine stagnates in the pelvis and forms an excellent environment for the development of pathogenic microflora.
The difference between a healthy kidney and a kidney affected by pyelonephritis
What to do if there is an increase in leukocytes in the urine?
What do leukocytes in a child’s urine mean?
First of all, don’t panic! The appearance of leukocytes in the urine is an important diagnostic criterion, but does not yet determine the absolute presence of pathology. An increase in leukocytes in the urine to 20 units in the field of view requires mandatory rechecking. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- To do this, a repeat general urine test is required. If there are signs of leukocyturia in it, then a study according to Nechiporenko should be carried out. Deviations from the norm in this analysis require mandatory monitoring by the therapist.
- During the consultation, the doctor will conduct a clinical examination and collect anamnesis. It often happens that during such a simple study, kidney or urinary tract diseases are detected.
- The appearance of leukocyturia is also a mandatory reason for examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist. The appearance of a moderate number of leukocytes also occurs during exacerbation of diseases of the genital organs. If the pathology has developed for this reason, then the doctor can easily establish this.
- If more advanced diagnostics are necessary, auxiliary ultrasound examination is performed. In the early stages of pregnancy, doctors usually prefer transvaginal ultrasound.
For some pathologies of the kidneys and urinary tract, special laboratory diagnostic methods are used:
- One of these specific tests is the Zimnitsky urine test. Using this method, doctors can get a good look at the filtration capacity of the kidneys. For this purpose, samples collected every three hours are assessed.
- In certain situations, bacterial culture may also be required. It is prescribed in cases where the expectant mother's leukocytes were detected in a general urine test. Bacteriological research allows you to determine the type of bacterial cells more accurately. This method can also be used to determine the sensitivity of microbes to various antibacterial drugs.

After making a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe an appropriate treatment regimen for a pregnant woman with signs of leukocyturia. To compile it, the doctor uses quite a few different criteria. It necessarily takes into account the severity of the inflammatory process, the period of pregnancy, the level of functioning of the expectant mother’s immune system, as well as her age and the presence of concomitant diseases of internal organs.
Mild forms of leukocyturia are usually treated by prescribing various uroseptic agents. It should be noted that doctors try to rarely resort to prescribing various antibiotics during pregnancy.

Complex treatment prescribed by a doctor is usually the following:
- Various herbal remedies are well suited as uroseptic drugs. These include: chamomile, cranberry, lingonberry leaf, currant, as well as various ready-made pharmaceutical preparations. They should be brewed according to the instructions on the package. Typically, such infusions are prescribed 2-3 times a day, 40-60 minutes after meals.
- The combination drug “Canephron” is also suitable as a complex treatment. It contains a whole complex of various plant components that have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect on the kidneys and urinary tract. As a rule, after taking this drug, leukocytes in the urine normalize.
- During the acute period of the disease, doctors prescribe that expectant mothers must observe bed rest. This simple measure helps normalize the flow of urine and reduces the severity of intoxication syndrome. If there is a unilateral lesion, you should lie on the healthy side.
- To improve urine levels, expectant mothers should be sure to follow nutritional recommendations. All salted and pickled foods should be completely excluded from the daily menu. Excessive amounts of salt can aggravate the course of kidney pathology, which will only intensify the manifestations of leukocyturia.
- In severe cases of pathology, the prescription of antibacterial drugs may be required. This treatment is usually carried out in a hospital setting. In this case, the potential risk to the fetus must be assessed. Antibiotics that do not cause teratogenic effects are selected for treatment.
For more information about why leukocytes in the urine increase, see the following video.
Additional examination
To confirm the diagnosis, the woman will be prescribed a series of tests that will help determine the severity of the disease. In addition to a general blood and urine test, you will need to undergo a urine test according to Zinitsky and Nechiporenko, bacteriological urine culture, undergo an ultrasound of the kidneys, consult with a nephrologist, and perhaps chromocystoscopy or catheterization of the ureters will be prescribed.
In rare cases, an X-ray examination with contrast is prescribed; it is safe for the woman, but can harm the fetus.
Pregnancy is a very important period in the life of every woman, and you need to treat yourself especially carefully at this time. Register with the antenatal clinic on time, take all tests, follow your doctor’s recommendations, eat right, walk more, beware of colds, and at the slightest sign of any disease, be sure to visit a doctor, and then your pregnancy will go smoothly, and you won’t face any complications will bother you.
What to do if there is salt in your urine?
Leukocyturia (leukocytes in urine): classification, causes, diagnosis
Of the salts during pregnancy, oxalates are most often found. Less commonly, folates and phosphates.
Calcium binds to oxalates and precipitates as salts in the urine. In non-pregnant women, if oxalates are detected, calcium intake is limited. But during pregnancy, foods containing calcium are not limited, as it is necessary for the development of the fetus. Also, a diet high in calcium has a positive effect if prescribed to prevent preeclampsia.
What can you do if there is salt in your urine:
- limit the amount of table salt consumed, complete exclusion is not required;
- avoid drinking mineral waters unless they are intended for the treatment of kidney diseases;
- do not overuse vitamin C;
- Maintain proper nutrition and drinking regime.
Treatment, how to return to normal?
Causes of white flakes in a child's urine. Why does a child have sediment in his urine?

Leukocyturia is one of the pathological conditions that require immediate response and correction. Naturally, each clinical case of the disease is unique, so the doctor prescribes additional tests for the patient to confirm the diagnosis and determine its main causes.
Treatment for an increase in leukocytes in urine should be individual and aimed at normalizing laboratory parameters, eliminating other symptoms of the disease and preventing its relapses.
The most adequate treatment option for high levels of leukocyte cells in the urine will be treatment in a specialized hospital, which will allow medical personnel to constantly monitor the health of a pregnant woman, minimize the risk of complications and normalize the functioning of all the patient’s vital organs.
Treatment should consist exclusively of medications that are safe for the fetus and include additional therapeutic measures aimed at improving its condition. An important point is to follow a special diet, according to which unhealthy foods, processed foods, salt, smoked meats and fatty foods should be excluded from the pregnant woman’s diet.

The expectant mother needs to eat food enriched with vitamins and microelements, in particular, introduce a lot of fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy products, and cereals into her daily diet.
Modern doctors do not deny the effectiveness of folk remedies in the treatment of leukocyturia in pregnant women, so they often prescribe diuretic teas based on violet tricolor to their patients.
This is necessary so that the organs of the urinary system do not experience increased stress and are emptied on time, especially in the evening before bedtime. Herbs with an antibacterial effect, in particular rosemary, chamomile, mint, which also have a sedative effect, will greatly help prevent harm to the fetus.
It is important to remember that the only competent treatment in the event of the appearance of leukocytes in the urine can only be prescribed by an experienced, qualified specialist, based on data from the research results, the individual characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body and general disorders of her health. Treatment will depend on the duration of pregnancy, the sensitivity of the pathogen (if leukocyturia is provoked by microbial agents) to medications
Treatment will depend on the duration of pregnancy, the sensitivity of the pathogen (if leukocyturia is provoked by microbial agents) to drugs.
Unfortunately, sometimes it is not easy to determine the pathogen, or local treatment does not have a positive effect. In this case, patients are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics according to a standard regimen, taking into account the duration of pregnancy.
Naturally, many expectant mothers react negatively to antibiotic therapy, believing that it can harm the child. Some even voluntarily refuse such treatment, fearing the negative effects of medications.

It is worth noting that refusal of treatment and progression of inflammatory processes in the body can cause enormous damage to both the pregnant woman and the fetus and even provoke death.
Therefore, one should not give in to doubts. In such cases, it is necessary to completely trust the specialists, which will allow you to avoid sad consequences and irreparable results of the underlying illness.
Advanced leukocyturia often causes miscarriage, symptoms of preeclampsia, intrauterine infection of the fetus, and much more.
Symptoms of pyuria (leukocyturia)
Pyuria symptoms are identical to the underlying disease, which provokes the appearance of pus in the urine. Pyuria is almost always combined with bacteriuria (the presence of microorganisms - bacteria in urine), therefore a typical symptom of a pathological increase in leukocytes in the urine is painful urination. Frequent urge to urinate, small portions of urine, hyperthermia (increased body temperature), pain and aches in the lumbar region, headache - this is not a complete list of signs of infectious inflammation of the genitourinary area. Pyuria also exhibits obvious symptoms - the urine becomes cloudy and purulent inclusions are clearly visible in it.
Typical signs of a UTI - urinary tract infection include the following:
- Dysuria is a violation of normal urination, which can be as follows: Frequent - pollakiuria, frequent urge to urinate as a sign of possible diabetes, cystitis, prostatic hyperplasia (mainly at night), urethritis and other inflammatory processes of the lower urinary tract.
- Difficulty urinating - strangury, as a possible sign of stones in the urinary tract, acute stage of prostatitis, polycystic kidney disease, phimosis.
Pyuria may have symptoms characteristic of kidney disease, among which the following are typical:
Stones in the kidneys:
- Turbid urine, which may contain pus and blood (a combination of pyuria and hematuria).
- Periodic pain in the lower back or below the ribs, radiating down to the groin.
- If the stone has moved, there is a bacterial infection and pus, and urination is interrupted. Frequent urge and small portions of cloudy urine.
- Nausea, even vomiting.
- Burning in the ureter.
- Feverish state during an acute process and purulent infection.
Pyelonephritis:
- The acute stage is characterized by high fever, pain in the lower back, joints, pain when urinating, cloudy urine with pus, uncharacteristic odor of urine, high body temperature, nausea, vomiting.
- Chronic pyelonephritis (latent) - pyuria as the main symptom, transient dull pain in the lower back, transient dysuria, weakness, possible anemia, loss of appetite.
Pyuria exhibits symptoms typical of the disease that causes it; pyuria can also develop latently, asymptomatically and is detected only through laboratory tests of urine.
The three-glass test (Stamey test) more accurately reflects the topical diagnosis for the inflammatory process in the prostate and posterior urethra between the external and internal sphincters. Naturally, this test is applicable exclusively to males. In this case, the first two portions of urine are not changed, and the last portion, with a volume of 50-70 ml, formed during the final contraction of the detrusor and muscles of the pelvic diaphragm, turns out to be cloudy; Microscopy of the sediment reveals leukocytes. The true degree of activity of the inflammatory process in the urinary tract can be assessed only on the basis of the detection of bacteriuria in a diagnostically significant titer.
If the disease is chronic and does not have pronounced symptoms, treatment is carried out as sparingly as possible, especially in pregnant women, children and elderly patients. In such cases, immunomodulators and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
Acute urinary tract infections are usually treated with fluoroquinolones, drugs of the cephalosporin group (new generation). Along with these drugs, the prescription of antibiotics - carbalenems - bactericidal inhibitors of the synthesis of the cell wall of microorganisms is indicated. Classic penicillins can also be used in combination with fluoroquinolones.
Treatment for pyuria involves a rather long period of time, which depends on the timing of elimination of the main cause, that is, the source of inflammation. As a symptom, pyuria can be neutralized within 7-10 days, but if the prescribed course of treatment is not followed, it can recur and become chronic. It is believed that the course of antibiotic therapy for UTIs should be at least two weeks.
Leukocyturia and pregnancy
A slight increase in the number of leukocytes in urine during pregnancy (10–15 cells per field of view) may be a physiological process - this is how the mother’s body reacts to the appearance of a “foreign” fetus. However, you should still remember that pregnancy itself increases the risk of developing diseases of the urinary system. This happens for several reasons.
- From the first days of pregnancy, changes occur throughout a woman’s body to ensure normal growth and development of the baby. The urinary system is no exception. For example, the size of the kidneys increases by 1–2 cm, the ureters expand, the tone of the walls of the bladder decreases, the speed of blood flow passing through the kidneys increases, the pH of urine changes, etc. The urinary system works under increased load, which naturally weakens it .
- During pregnancy, the hormone progesterone is produced in huge quantities. It helps relax the muscles of not only the uterus, but also other organs. At the same time, all kinds of congestion occur in the urinary system, the backflow of urine from the ureter into the bladder, etc. All this leads to the fact that it is easier for infections from the vagina or external genitalia to penetrate into the bladder, and from there into the ureters and kidneys.
- As the uterus grows, intra-abdominal pressure increases, which leads to prolapse of the right kidney (the ligaments of which are already relaxed under the influence of progesterone) and disruption of its function.
One of the most serious complications for pregnant women is pyelonephritis (occurs in approximately 10–20% of expectant mothers). It can be chronic or gestational, i.e. associated directly with pregnancy (usually the woman has never had any inflammatory diseases of the urinary system before).
Urolithiasis is much less common - less than 1% of pregnant women. Recognizing this diagnosis during pregnancy is quite difficult, since conventional radiographic examination cannot be performed. Therefore, most often you have to rely on clinical tests and the doctor’s experience.
Approximately 10% of expectant mothers experience cystitis. Its danger lies primarily in the fact that pyelonephritis very often develops against the background of cystitis in pregnant women.
Diseases of the urinary system, one of the symptoms of which is leukoceturia, in the absence of adequate treatment are very dangerous for both a pregnant woman and her unborn baby. Therefore, in no case should you self-medicate, be it with medications or folk remedies; consultation with an experienced doctor is necessary.
The most unfavorable consequences of advanced diseases of the urinary system include:
Recent Posts Is it possible to give a mirror as a gift: how to protect yourself from bad omens It became known about the influence of cell phone towers on human health Is it possible to eat bananas bought in Russia?
- Placental abruption.
- Severe oxygen starvation of the fetus.
- Premature birth.
- Stillbirth.
- Acute renal failure in a woman.
- More severe gestosis.
- Sepsis in the mother in the postpartum period, etc.
Depending on the causes of leukocyturia, various treatment regimens are prescribed:
- When pyelonephritis develops, antibiotics approved during pregnancy, nitrofurans, antispasmodics to improve renal blood flow, and drugs to cleanse the body of accumulated toxins are prescribed.
- In case of urolithiasis, first of all, they try to relieve renal colic using medicinal methods. For this purpose, antispasmodics and analgesics are prescribed. However, if the condition cannot be alleviated or if stones interfere with the flow of urine, surgical treatment is performed.
- Cystitis is most difficult to treat in the early stages of pregnancy, when most medications are contraindicated. During this period, some uroantiseptics are used (for example Monural), No-shpa, herbal preparations (Canephron, Urolesan, etc.). After 20 weeks, cystitis can be treated with antibiotics, and the condition can be alleviated with local thermal procedures (a heating pad on the lower abdomen) and physiotherapy. In case of chronic cystitis in the later stages, instillation of the bladder is also possible, i.e., administration of the medicine directly into the bladder using a catheter.
Cystitis
Approximately 10% of pregnant women develop cystitis during pregnancy. The risk increases if the woman has already had this disease.
Cystitis is an inflammation of the lining of the bladder and disruption of its functioning, which is caused by microorganisms and some other factors.
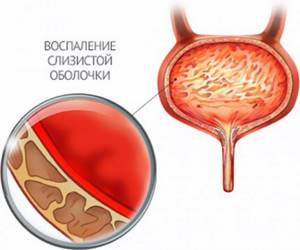
This is what cystitis looks like - inflammation of the bladder mucosa
What to do if leukocytes are elevated during pregnancy
If leukocytes are elevated, you should first do a repeat urine test to rule out a possible error. If leukocytosis persists after 2-3 times, and other signs of pathology are also present, additional methods are used to make a diagnosis.
Additional examinations
To clarify the pathology of the urinary tract, the following is carried out:
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- three-glass sample;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder;
- vaginal smear;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs;
- tests for specific infections.
In some cases, you may need to consult a therapist, allergist, surgeon, nephrologist, and undergo additional tests and instrumental studies.
What treatment is needed
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause or reducing the provoking factor of the pathological condition:
- Antibiotics are used for inflammation of the kidneys and bladder. They are prescribed only by a doctor.
- To overcome stagnation of urine, it is recommended to drink fluid (1.5 liters or more per day), if there is no tendency to edema.
- It is useful to drink rosehip decoction, which saturates the body with vitamins and has a diuretic effect.
- Mild inflammation can be relieved by washing the genitals with chamomile infusion. If the cause is a fungus (thrush), then soda baths will help.
- Preeclampsia, glomerulonephritis, and neoplasms require constant hospitalization. In complex, severe and life-threatening conditions, artificial termination of pregnancy may be required.
The appearance of leukocytes in a pregnant woman's urine requires special attention. Leukocyturia can be a sign of a serious illness, so the analysis should be repeated and additional research done.
Reasons for the development of cystitis
Cystitis can be infectious, medicinal, allergic, thermal. Infectious cystitis is caused by various bacteria. The main causative agent of such cystitis is Escherichia coli. Typically, this type of cystitis occurs in women due to the structure of the genital organs (where the urethra is located close to the anus).
Drug-induced cystitis occurs due to certain drugs, the altered substances of which are excreted in the urine, thereby irritating the mucous membrane of the bladder.
Allergic cystitis occurs in people with hypersensitivity to certain substances contained, for example, in bubble baths, hygiene sprays, condoms and certain products.
Thermal cystitis occurs due to hypothermia or exposure to hot liquids to the bladder mucosa.