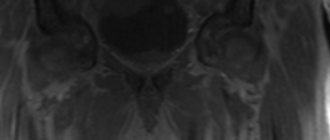
February 3, 2021 Computed tomography (CT) is a diagnostic method that combines X-rays and digital reconstruction of data. X-rays pass through the human body, and a computer system forms an image of transverse and longitudinal layers (sections). The method is often compared with MRI and conventional x-rays. CT has a very high sensitivity - about 0.5-0.8 cm. In urology, CT helps to detect diseases of the prostate, kidneys, bladder, ureters and a number of other organs.
What does a CT scan of the bladder show?
CT scan of the bladder, as diagnostic practice shows, allows us to identify many diseases: urolithiasis, cystitis, nephritis, pyelonephritis, bladder cancer, kidney prolapse, kidney cysts, thrombosis and thrombophlebitis of the pelvic vessels, renal colic and others.
CT images can also show the lumbar spine and abdominal aorta. Such information will become valuable in diagnosing vascular pathologies associated with impaired nutrition and blood supply to the kidneys or the occurrence of malignant kidney tumors.
Indications for use
Acute undiagnosed abdominal pain without a clear etiology, which is accompanied by symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or problems with urine output, is the main indication for CT of the bladder.
Many conditions can be associated with signs and symptoms in this area. These include, but are not limited to, intestinal obstruction, gallstones or bladder stones, malignant tumors, and complications of inflammation or infection.
Where applicable, contrast media can be used to obtain a detailed description of the organ and to identify anatomical abnormalities. CT makes it possible to obtain detailed and complete information about the bladder. This study visualizes all its walls and cavities, makes it possible to see the presence of neoplasms in a given organ, and accurately assess the degree of damage to the organ.
Your doctor may order a CT scan of your bladder if you have the following features, symptoms, or dysfunction:
- if there is a burning sensation or sharp pain during urination;
- urinary incontinence unless there is a known cause (eg pregnancy);
- periodic appearance of shooting pains in the pelvic area;
- when a symptom of nocturia appears (frequent urination at night);
- when the consistency or smell of urine changes;
- the presence of impurities in the urine;
- if you suspect the presence of a neoplasm in the bladder.
The absolute indication for a computed tomography scan of the bladder is its injury, as well as the presence of strictures.
How to prepare for a CT scan of the bladder and urinary system
CT scanning of the bladder and urinary system requires certain preparation. The day before the study, the patient must limit food intake that promotes increased gas formation. 6-8 hours before the CT scan, you must avoid eating completely.
Typically, before a CT scan, the doctor may prescribe a laxative or enema to cleanse the intestines. Diagnosis is carried out with a full bladder, so 2-3 hours before the scan you need to drink a glass of water (if the CT scan is performed with contrast, an iodine-containing drug is added to the water).
What can you see with a CT scan?
Simultaneous examination of the seminal vesicles, urinary tract and intestines allows us to assess their condition, see tumor neoplasms, clarify their size and the extent of metastasis.
Answering the question of what a CT scan of the prostate gland shows, we can name the following pathologies:
- BPH;
- cancer of the gland;
- benign hyperplasia;
- acute prostatitis;
- chronic prostatitis;
- abscesses and inflammatory processes in the gland;
- anatomical changes.
A CT scan may be a planned test before preparation for surgery. A highly detailed image allows the surgeon to see not only the size, but also the geometry of the tumor, and clarify the course of the intervention.
Assessing post-traumatic changes is another answer to the question of what a prostate CT scan shows in men. Open and closed pelvic injuries can lead to loss of integrity of the prostate gland and other organs and disrupt their physiological functions. This method allows you to assess the condition of the rectum, the functioning of the bladder, and the viability of the seminal vesicles. Based on the study, the doctor decides on the need for surgical intervention or treatment with conservative methods.
CT is useful for monitoring recovery processes after surgery. It allows you to determine the success of the intervention and monitors rehabilitation in the postoperative period.
How does the procedure work?
Before the study begins, the doctor talks with the patient, tells him about how the CT scan is performed, what results it can give and how the patient should behave during the scan. After this, the patient must remove all jewelry, put on loose clothing and take a stationary position on the retractable tomograph table.
Next, the work table slides into the cylinder of the CT machine, and the scanner sensors begin to move around the area of the body being examined.
During the study, communication between the doctor and the patient is carried out via voice communication.
The procedure lasts approximately 20 minutes. The patient does not feel any pain.
CT scan of the bladder and urinary system with contrast
The contrast helps to more clearly visualize the organs of the urinary system and evaluate their structural changes. After contrast is administered, the patient may experience headache, dizziness, or nausea. This is not scary, since such unpleasant symptoms will go away after the study.
What happens during the procedure
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Any names of medications taken by the patient in the previous days should be reported to the doctor to ensure that they are not contraindicated for the procedure. In addition, the possibility of pregnancy should be excluded to avoid negative effects on the developing child from the teratogenic effects of radiation.
The patient is placed in a supine position in the CT scanner and must remain still during the procedure. The advantage of the supine position is that it allows for better assessment of urinary stones at the vesicoureteral junction. The results of the study are assessed by a radiologist, who then creates a report and sends it to the doctor who is responsible for the patient's care.
Contraindications for
CT scanning should not be performed on pregnant women or nursing mothers. Also, a contraindication to tomography is the patient’s excess weight – more than 130 kg.
Contrast-enhanced CT scan of the bladder has the following contraindications:
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes;
- allergy to iodine-containing drugs;
- renal and liver failure;
- asthma;
- severe heart defects.
Since in order to obtain high-quality images it is necessary that the patient remain motionless during the scan, it is not recommended to administer CT scans to small children, since it is quite difficult for them to lie still.
In addition to general analysis, the following can be carried out:
| Analysis name | Features of the study |
| According to Nechiporenko | With the help of the study, inflammatory processes are diagnosed, the exact number of red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders in one milliliter of liquid is determined. Urine collection is carried out in the same way as for general analysis. |
| According to Zimnitsky | The analysis allows us to determine the concentration ability of organs - not only the bladder, but also the kidneys. To do this, the density of urine, the daily norm, and the distribution of its entire volume over 24 hours are determined. To collect throughout the day, eight portions are collected in sterile containers, carefully cleaning the genitals each time |
| Bacteriological | The study involves urine culture and subsequent determination of the causative agents of pathological processes. Urine that contains no infectious agents is considered normal. Urine collection is normal; each container is sown on different nutrient substrates. The same method determines the sensitivity of pathogens to certain antimicrobial drugs |
Ultrasound provides the most reliable information when filling the bladder - the volume of fluid should reach at least 150 or 200 ml. This approach allows us to consider the shape of the organ, its size, and wall thickness.
Alternative methods for examining the bladder
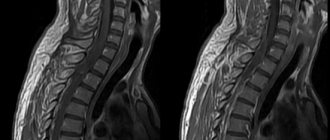
If a CT scan with contrast did not provide an informative picture of the condition of the bladder and urinary system, the attending physician may prescribe an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to clarify the complexity of the disease. This method will allow you to examine the thinnest sections of organs and tissues and help identify the disease at the initial stage of its development.
In addition, MRI has virtually no restrictions on the number of scans, since during the scanning process there is no harmful effect of ionizing radiation on the human body. In this regard, if it is necessary to track the course of the disease over a short period of time (for example, 1-2 months), MRI is preferable.
What will a multislice CT scan of the kidneys show?
The study can be carried out to find out the causes of pain in the lumbar region, increased body temperature in combination with pain in the lower back, urination problems, the presence of blood in the urine, poor results of a urine test, and also in cases where alternative research methods cannot identify this or that other violation and provide dubious information.
MSCT urography is performed to diagnose the following disorders:
- consequences of injuries to the lower abdomen or back;
- infectious disorders;
- anomalies of kidney development, in particular, hypoplasia, polycystic disease, aplasia, duplication, pelvic, cross, thoracic and other dystopias, rudimentary kidney, accessory, horseshoe-shaped kidney and others;
- necrotic and dystrophic processes;
- stones;
- abscesses;
- pyelonephritis, other inflammations;
- benign and malignant tumors, as well as metastases from other organs;
- cystic formations.
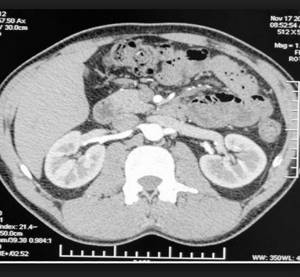
A comprehensive CT scan of the kidneys and bladder is often performed, which also shows bladder development abnormalities, cystitis, squamous cell carcinoma, bladder adenocarcinoma, bladder neck obstruction, metastatic lesions and other pathologies.
For differential diagnosis of cysts, tumors, inflammations, a CT scan of the kidneys with a contrast agent is performed. Differentiation of such formations is based on the property of malignant formations to accumulate a radiocontrast agent, while the density of the tumor increases by more than 5-15 units on the Hounsfield scale. Computed tomography without contrast is not performed when diagnosing tumors; contrast enhancement is required to obtain the most detailed information.
The main signs of benign cysts on CT are a round shape of the formation with a smooth wall, clear contours, as well as homogeneous content with a density of less than 20 units. An exception is hyperdense cysts, the density of which can be more than 20 units due to the content of a large amount of protein or hemorrhagic components. Also, CT signs of cysts are the presence of nodular seals in the wall, internal septa and multi-chamber formation. After administration of a contrast agent, the density, shape and size of a simple cyst do not change, while the density of the renal parenchyma increases.
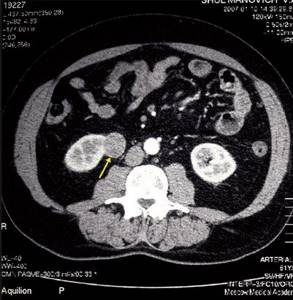
In modern practice, the main method for verifying calcifications is CT. The presence of calcifications in the cyst may indicate a possible malignancy of the process. However, small linear calcifications can occur in the septum or wall of benign cysts.
The contrast procedure also makes it possible to determine areas of growth of secondary tumors from the pelvic organs, structures of the abdominal cavity and chest, to diagnose stones in the kidneys and ureters, as well as vascular disorders. For example, with angiomyolipoma, an unenhanced CT photo shows areas of adipose tissue with reduced density. On post-contrast images in the cortical phase, a hyperdense formation is visualized, the degree of which depends on the size and vascularization of the tumor.
For a comprehensive assessment of the extent of the pathological process, a CT scan of the kidneys and abdominal cavity is often performed, which shows the mutual relationships of the structures of a given anatomical region, the condition of the blood vessels and the lymphatic system.
Why do CT angiography of the kidneys?
A CT examination of renal vessels is carried out to identify pathologies of the renal arteries, veins, as well as oncological processes that affect the blood vessels. Angiography makes it possible to detect abnormalities in the development of renal arteries, stenoses, vasorenal conflicts, arteriovenous malformations, and the degree of compression of vessels by germinating tumors.
Diagnosis is carried out with contrast enhancement, since without the administration of the drug such a scan will not be informative enough.
Preparing for a CT scan of the kidneys with contrast
The study requires compliance with simple preparation measures. So, the patient should not eat 3-4 hours before screening. Diagnosis of the bladder is carried out in an average or full degree of fullness; for this, the patient needs to drink 1 glass of clean water half an hour before the examination and not urinate. This is necessary in order to smooth out the folds of the bladder as much as possible.
If possible, the patient should take with him a doctor’s referral, data from previous diagnostics, hospital extracts or medical records and other documents to the study.
The contrast procedure requires the patient to undergo a blood test to determine creatinine and urea levels. If these parameters deviate from the norm, the decision about the possibility of conducting a contrast study will be made by the attending physician or radiologist.
How to do a CT scan of the kidneys
During the procedure, the patient is placed horizontally on his back on the moving table of the tomograph. If contrast is necessary, the laboratory assistant installs a catheter into the antecubital vein, through which a contrast solution will be supplied in the future.
After this, the table with the patient moves into the ring of the device, while the abdominal area is located at the level of this ring. During screening, the ring will perform rotational movements around the patient, and the tabletop will move progressively, while the speed of its movement depends on the diagnostic purposes.
A CT scan of the kidneys without contrast usually takes 15 minutes, with contrast it lasts up to 25-30 minutes, taking into account the patient’s positioning and other preparatory measures.
After screening, the patient receives a series of black-and-white images, printed on film or recorded onto a medium, and later receives a written description from the radiologist.