The hepatobiliary system (HBS) - the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (intra- and extrahepatic) - is very important for human health. These organs are directly involved in many metabolic processes, in particular in regulating the absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, the functioning of the small intestine, the neutralization of many toxins, etc. Not only health, but also human life depends on the state of this system.
Therefore, GBS diseases must be identified as early as possible and treated before the changes become irreversible or affect the functioning of other organs and systems. Ultrasound for the organs of the hepatobiliary system is an important diagnostic measure, because it allows the gastroenterologist to assess its condition at the appointment and take timely measures if there are any deviations.
Our advantages
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system at the Alfa Health Center clinic is:
- high information content and accuracy . The diagnostic base of our centers is equipped with General Electric ultrasound equipment. Expert-class equipment provides image detail and allows you to evaluate various indicators of the condition of the liver, gall bladder and ducts (size, location relative to other organs, contours, density, presence of tumors, etc.);
- quick results . The duration of the procedure is about 30 minutes. The doctor writes down the ultrasound report on a special form and gives it to you;
- A complex approach . Considering that GBS affects almost all systems and organs, its diseases may make it necessary to carry out diagnostics in other directions. Thus, based on the results of ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system, consultation with specialized specialists (endocrinologist, hepatologist, gastroenterologist, etc.) may be required and/or their participation in prescribing treatment and monitoring its effectiveness. All these services are available to you in our clinic, which eliminates the need to waste time and money on visiting other medical and diagnostic institutions;
- affordable prices . The developed network of our medical centers and a clear work schedule is your opportunity to undergo an ultrasound scan without wasting extra money and time.
In what cases is ultrasound of the abdominal organs prescribed?
In comparison with other studies - x-rays and CT scans, ultrasound is completely safe and can be prescribed to children from birth, and in adults it can be carried out without time intervals between diagnostics. Ultrasound gives an idea not only of pathologies in a specific organ, but also allows you to measure it, assess the condition of tissues and structure. Referrals for this study are issued by therapists, general practitioners and almost all specialized specialists: from gynecologists and urologists to neurologists.
Ultrasonic waves allow you to determine:
- size;
- shape;
- integrity;
- compliance with anatomical standards;
- location;
- contractility;
- level of peristalsis of the abdominal organs.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs may be required in the process of comprehensive diagnosis of the following systems of the human body:
| Functional systems of the body | Organs examined using abdominal ultrasound |
| hepatobiliary system | gallbladder bile ducts liver |
| urinary system | kidneys renal tubules collecting ducts ureter bladder |
| digestive system | small and large intestine rectum pancreas duodenum |
| hematopoietic and circulatory system | spleen veins arteries |
When is ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system prescribed?
Indications for ultrasound examination of the GBS organs:
- any unusual or unpleasant sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium (pain, heaviness, discomfort, colic, etc.);
- symptoms indicating possible dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system (bitterness and/or unpleasant taste in the mouth not associated with the intake of bitter foods, flatulence, indigestion, undigested food particles in stool, etc.);
- results of blood tests indicating dysfunction of the GBS organs (high levels of AST, ALT, bilirubin);
- yellowness of the mucous membranes, skin or sclera;
- acute or chronic intoxication (poisoning with food, drugs, household chemicals, etc.);
- abdominal injuries;
- professional employment in production that uses toxic compounds, etc.;
- treatment of diseases of the GBS organs and the need to monitor its effectiveness.
An ultrasound examination of the GBS organs can be prescribed as part of the diagnosis of a number of other diseases to determine the causes of already identified pathologies and/or assess the extent to which they have affected the liver and gall bladder.
Indications for liver ultrasound
Patients are referred for examination:
- with pain in the right hypochondrium;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- injuries of the abdominal organs;
- suspected abnormalities in the structure of the gallbladder;
- abnormalities in blood tests indicating liver disease;
- acute and chronic diseases of the gallbladder and liver;
- chronic liver diseases;
- suspected tumors and metastases;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- alcohol abuse.
How to prepare for the procedure
Preparation for ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is an important stage on which the accuracy of the results largely depends. General preparation requirements:
- diet correction . 3-4 days before the scheduled ultrasound date, you should stop eating foods that cause increased gas formation in the intestines: legumes, whole milk, black bread, raw vegetables and fruits, confectionery, baked goods made from yeast dough, carbonated drinks;
- performing an ultrasound on an empty stomach . Routine ultrasound examination is carried out in the morning. Before visiting the ultrasound room, you should not have breakfast or drink tea/coffee, and your last meal should be no later than 10–12 hours before the ultrasound.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe additional preparation measures if necessary:
- administering a cleansing enema or taking laxatives on the eve of an ultrasound scan if the patient has persistent constipation;
- taking enzyme preparations and enterosorbents with an increased tendency to form gas in the intestines (the doctor will inform you individually about the names of the drugs and the specifics of their use).
How is an ultrasound of the gallbladder performed?
The person lies down on the couch on his back, exposing his stomach. For better signal conductivity during an ultrasound, the doctor applies a special gel to the skin. Using the device's sensor, an examination is performed, starting from the area of the right hypochondrium; if necessary, the entire abdominal area is scanned.
An ultrasound can also be performed lying on your left side. During the examination, the doctor may ask you to hold your breath and take several deep breaths. Scanning of the organ is carried out in three projections: longitudinal, transverse, oblique.
The gel is then removed using a napkin. The study takes about 20 minutes.
Cost of the procedure
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is a common technique. It is available to public hospitals and private centers. The cost is determined by the region of residence.
Price table for ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system.
| City | Price |
| Moscow | 480-1000 rubles |
| Saint Petersburg | 350-1100 rubles |
| Ekaterinburg | 500-1500 rubles |
| Novosibirsk | 450-1200 rubles |
| average cost | 445-1225 rubles |
Ultrasound examination of the liver system, gall bladder, ducts of adults and children is aimed at primary diagnosis or control of existing diseases. The procedure is safe, painless, and requires preparation. It is carried out taking into account indications in public hospitals or private centers.
Leave comments on the article and share your opinion. Tell your friends about what you read on social networks. All the best.
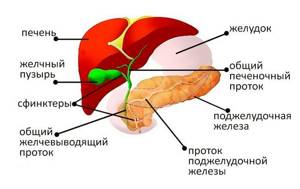
Organs of the hepatobiliary system
The hepatobiliary system (HBS) consists of three main components: the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts.
The liver is one of the largest organs in the human body and performs many functions simultaneously:
- blood detoxification, that is, neutralization and removal of allergens, poisons, toxins, excess hormones, and so on;
- synthesis and secretion of bile;
- protein synthesis;
- regulation of carbohydrate metabolism.
That is why the liver is a vital organ.
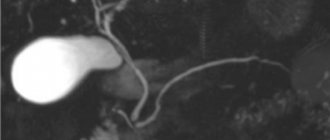
The gallbladder is a small reservoir for storing bile, which comes from the liver through the hepatic duct.
The bile ducts form a complex system with several valves that prevent bile from flowing in the opposite direction.
The ducts are built in such a way that the bile accumulated in the bladder enters the intestines only under the influence of the hormone cholecystokinin, released during meals.
From the bladder, bile enters the common bile duct, which then unites with the main pancreatic duct and opens through the sphincter of Oddi into the duodenum.
Technique
Ultrasound examination compares favorably with other manipulations in its simplicity and painlessness. The person is asked to lie down on the couch and take off his upper part of his clothes. A hypoallergenic gel is applied to the skin of the abdomen, which increases the speed of ultrasound. Using a sensor, the doctor examines the necessary organs of the hepatobiliary system, all parameters are immediately read by a computer and displayed on the screen.
In children, examination of the hepatobiliary system is carried out in the same way. It is recommended to first explain to the child that there is nothing to be afraid of, the manipulation is painless. Very young children are examined in the presence of their mother.
Examination of the gallbladder takes place in two stages. First, a routine examination of the entire system is performed, then the person is given a choleretic breakfast. Usually this is chicken yolk or a glass of sour cream. For an hour, every 15 minutes, the doctor examines the bladder, its peristalsis and fullness.
Watch the video to see how the hepatobiliary system looks on the monitor:
Possible contraindications
Ultrasound examination of any body system is safe. It is allowed for newborns, pregnant women, and the elderly. But contraindications still exist - these are conditions that will interfere with the reliability of the procedure. These include:
- damage or inflammation of the skin of the abdomen;
- pronounced flatulence;
- state of alcohol or drug intoxication;
- psychosis.
After eliminating these conditions, a study of the liver system is carried out.
Interpretation of the ultrasound result
Only an ultrasound diagnostic specialist – a sonologist – should evaluate the ultrasound result. It is also important to take into account that when conducting diagnostics for children, certain difficulties may arise due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the child’s body. Therefore, a specialist who understands and knows age norms will handle deciphering a children’s ultrasound.
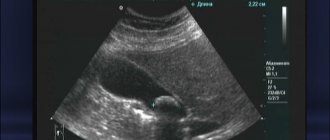
Interpretation of an ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder begins with an assessment of the shape, size and location of the organs. The liver is not assessed as a whole, but by its individual lobes. It is usually located in the right hypochondrium. The right lobe normally does not exceed 15 cm in thickness, length and oblique vertical dimension. The left lobe is smaller, up to 7 cm in thickness and up to 10 cm in length. Next, echogenicity must be assessed, that is, the ability of the tissue to reflect ultrasound, which normally should be uniform throughout the entire organ. An important factor when examining the liver is its contours. In a healthy organ they are clear and even.
Interpretation of GBS ultrasound also includes an assessment of liver vessels. The portal vein normally has a diameter of less than 1.3 cm, and the hepatic artery has a diameter of up to 0.7 cm.
Normally, the common bile duct is about 0.7-0.8 cm in diameter. The gallbladder is 30-50 mm wide and 60-100 mm long. The shape is round or oval (on an empty stomach it is often oval), but a pear-shaped bladder is also a normal variant. When diagnosing diseases of the gallbladder, the thickness of its walls plays an important role - normally they are up to 0.4 cm with clear and smooth edges. The contents of the bladder are assessed - normally it is filled with hypoechoic homogeneous fluid.
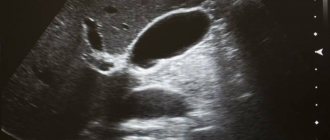
GBS pathology, which is visible on ultrasound
Based on knowledge of what an ultrasound scan of the liver and gallbladder shows, we will consider the manifestations of pathology.
During inflammatory processes, for example, hepatitis, the echogenicity of the liver may change. It ceases to be homogeneous, hypoechoic foci appear that do not have clear contours. The contours of the organ itself may also become uneven. If the appearance of neoplasms is suspected, these two factors also need to be assessed. The tumor can be detected due to unclear contours and changes in the structure of the liver (more often - increased echogenicity). Liver cirrhosis is characterized by a decrease in the overall size of the organ and an increase in the echogenicity of the tissue.
Impaired hepatic blood flow may play an important role in the development of certain diseases. In such cases, it is more rational to conduct Doppler ultrasound - a special type of ultrasound that allows you to assess the speed and direction of blood flow in the vessels. But even on a regular ultrasound, you can see the expansion and contraction of liver vessels.
Liver cysts are visualized by ultrasound as clear cavities. They are filled with anechoic fluid. The only exception is an hydatid cyst, inside of which there is a hyperechoic inclusion.
Inflammation of the biliary tract (cholangitis) or gall bladder (cholecystitis) is determined by the thickening of their walls, for the gall bladder more than 0.4 cm, and an increase in the diameter of the ducts. With calculous cholecystitis, hyperechoic inclusions are also found in the cavity of the bladder or duct - gallstones. It is they who, when the ducts are blocked, give severe pain in the right side of the abdomen.
If there are stones in the main duct of the pancreas, it is necessary to check the gland itself. Because bile does not enter the intestine through the main duct, it can flow in the opposite direction, enter the pancreas and lead to the development of pancreatitis. The manifestation of pancreatitis on ultrasound is similar to hepatitis - blurred contours and decreased echogenicity.
Obtained results
Since ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is usually prescribed in the presence of complaints, the results reveal changes characteristic of diseases. The doctor issues a normal conclusion if a person was examined by this system not for health reasons, but during employment or for military service.
Norm
Normal criteria for the hepatobiliary system include:
- organ sizes corresponding to age;
- acceptable level of tissue density - the liver is the standard for comparison;
- homogeneous structure;
- good contractility of the gallbladder;
- absence of foreign inclusions, cysts, tumors;
- the size of the portal vein is no more than 13 mm.
An indicator of the health of the hepatobiliary zone is compliance with all specified criteria. Mild diffuse changes in the liver are also allowed.
Liver diseases
Ultrasound can detect any disease of the liver system.
- Hepatitis. The inflammatory process is determined by an increase in the size of the liver - hepatomegaly. Diffuse tissue changes of varying severity are visible. Moderate hepatomegaly of the liver in a child under 5 years of age is normal.
- Cirrhosis. Destruction of hepatocytes and the appearance of scars in their place. The liver tissue becomes denser, the size of the organ decreases.
- Cysts. Parasitic or gall. They are represented by a round formation that does not reflect ultrasound.
- Tumor. Benign ones have clear contours and a capsule around them. Malignant ones look vague, there is no capsule.
Sometimes a computed tomography scan is required to clarify the diagnosis using this system.
Gallbladder diseases
Ultrasound evaluates the anatomy and function of the gallbladder.
- Cholecystitis. Non-calculous - simple inflammation of the organ wall, represented by its thickening. Calculous - stones are found that look like very dense round formations.
- Polyp. The growth of the bladder wall looks like a protrusion into the cavity and has an increased density.
- Bubble bend. A change from its normal pear-shaped shape, it becomes like an hourglass.
Bladder tumors are identical to those of the liver.
Pathology video
Watch the video where the pathologies of the hepatobiliary system are clearly shown: