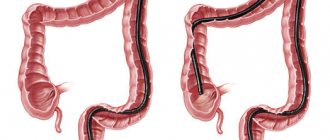
Indications
The group of patients who need high-quality bowel preparation includes those who are prescribed1:
Instrumental studies:
- colonoscopy,
- endoscopic polypectomy,
- biopsy,
- video capsule endoscopy,
- colposcopy,
- transrectal ultrasound;
Minimally invasive treatment:
- hemorrhoids,
- anal fissure,
- polyps,
- gynecological diseases,
- colorectal cancer located within the anal access.
Possible complications
Sigmoidoscopy is considered a safe diagnostic method - with proper preparation and implementation of the procedure, it does not pose a risk to the patient’s health. In rare cases, injuries, ruptures and perforations of the intestinal walls are possible. If after the examination there is pain in the anus or abdomen, bleeding from the rectum or fever, you should immediately consult a doctor. Such signs may indicate the need for emergency surgery.
Quality criteria
Poor bowel preparation may result in poor mucosal visualization, diagnostic misdiagnosis and missed pathology,2 as well as an increased risk of postoperative infectious complications.
Criteria for adequate bowel preparation: cleansing the intestinal lumen from various organic deposits, foamy contents, solid and liquid feces. She also must not:
- aggravate the clinical symptoms of the underlying disease,
- cause side effects from other organs and systems,
- distort the image,
- limit the use of additional products (dyes and others),
- damage the equipment.
The quality of bowel cleansing before elective surgery may affect the postoperative prognosis. If feces remain in the intestinal lumen, this can complicate the course of the operation, influence the surgeon’s decisions, and force him to change the outcome of the operation. In addition, the quality of preparation affects the likelihood of developing postoperative complications of an infectious nature.
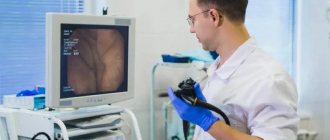
Carrying out sigmoidoscopy
The procedure is carried out in an office designed for such manipulations. Most patients do not require anesthesia - anesthesia or light sedation is done only in rare cases. Before performing sigmoidoscopy, the doctor must palpate the anus for damage, hemorrhoids or neoplasms.
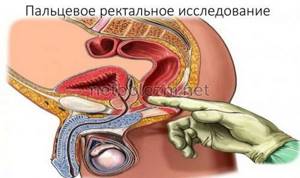
If there is fecal matter in the rectum or sigmoid colon that interferes with the examination, the patient is given an enema again.
The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes, and the result is given to the patient immediately after its completion.
The sigmoidoscope, with which the examination is performed, is a long tube with an air supply system and optics. The patient takes a knee-elbow position or lies on his left side with his legs tucked. The tip of the sigmoidoscope is lubricated with petroleum jelly and inserted into the patient’s anus, while pumping up air.
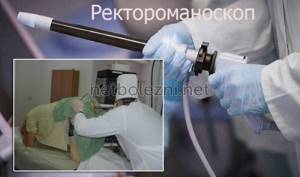
As we move forward, the doctor assesses the condition of the internal walls of the intestine, after which he draws appropriate conclusions and gives a conclusion. To avoid discomfort and complications, the patient should lie absolutely still, completely relax and breathe deeply through the mouth.
Contraindications
Comprehensive bowel preparation is not performed in patients1:
- with severe forms of inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, pseudo-obstruction of the colon);
- with contraindications to endoscopic examinations - with diverticulitis, colon perforation, acute stroke and myocardial infarction;
- requiring special approaches - pregnant women, children, acute intestinal obstruction, intestinal bleeding, etc.
Analogs
To date, no drugs have been developed that could be classified as analogues of the active component. But there are analogues that are similar in the principle of influence and the list of indications for use. These products include glycerin suppositories, which can be given to adults and children from infancy. The cost of many analogues is lower.
Analogs based on the principle of action also include Glycerin and Norgalax. These drugs also have a laxative effect and are used rectally. Glycerin is also available in solution form for topical and external use.
Preparation method
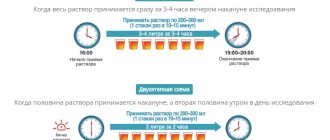
The most effective is comprehensive bowel preparation.
An important condition is the absence of coarse fiber in the intestines. To prevent its accumulation, a slag-free diet is prescribed 1-2 days before the examination or surgery. It consists of eating foods without plant fiber.
Diet
What is allowed:
- Liquid: clear broth without vegetables, tea, compote and other uncolored drinks, juice without pulp, water.
- Boiled protein: fish, poultry, eggs.
- Cheese, cottage cheese, low-fat dairy products, butter, honey, sugar, crackers
What not to do:
- Vegetables, fruits, berries in any form, greens.
- Coffee, alcohol, juices with pulp and other colored drinks, compote.
- Whole milk, bread, mushrooms, millet, pearl barley and oatmeal, fried, smoked foods, nuts, legumes.
Intestinal lavage
The lavage method is the mechanical flushing of intestinal contents. The ideal cleansing scheme implies the absence of residual feces, maintaining a minimum amount of liquid that is removed during the study, and relatively rapid bowel movement.
Preparation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures should be easy to perform, well tolerated by patients, and not cause changes in water and electrolyte balance, especially in the elderly and children.
The complex product Microlax® in microenemas copes with this task painlessly. The drug provides a mild cleansing effect, does not irritate or injure the intestinal walls, which does not distort the research results4. It includes:
- sodium citrate - breaks down feces, displacing bound water and facilitating their removal from the intestines;
- sorbitol solution - significantly increases the release of water with the help of citrate;
- Sodium lauryl sulfate acetate is a non-toxic humectant that helps soften stool conglomerates.
The action of a microenema can begin within 5-15 minutes4. The tip is inserted to its full length; 5 ml (1 microenema) on the eve of the procedure and another one in the morning on the day of manipulation are enough.
Ascending lavage with cleansing enemas with cold water is now used less and less, as it is a labor-intensive procedure that can cause electrolyte disturbances, tissue swelling, and mucosal hyperemia, which subsequently leads to overdiagnosis of colitis1.
Descending lavage has a number of advantages, which include: no negative impact on the intestines, aesthetic aspects and greater patient compliance1.
Descending colon cleansing
For the top-down method, various pharmacological drugs are used. An ideal cleaning product3 should meet the following criteria:
- does not leave liquid or solid fecal residues in the intestinal lumen,
- does not interact with the intestinal mucosa,
- quickly induce bowel movement,
- be easy to make, use at home,
- well tolerated, does not cause discomfort,
- do not affect the acid-base balance.
The most common medications included in cleansing regimens include osmotic laxatives, such as magnesium sulfate, mannitol, polyethylene glycol and sodium phosphate, and lactulose-based products. These may be supplemented with simethicone to reduce gas formation, senna extract to enhance peristalsis, or metoclopramide, which speeds up gastric emptying2.
The method of colon cleansing is selected individually for each patient, taking into account indications, contraindications, preliminary diagnosis and the presence of concomitant pathology.
Modern techniques for performing endoscopic manipulations and minor invasive interventions in outpatient practice require optimization of patient preparation schemes. A careful choice of remedy makes it possible to better prepare the intestines and avoid purulent-septic complications6.
Literature:
- N.V. Topchiy, A.S. Toporkov. Sodium phosphate solution for preparing the intestines for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in outpatient practice. Outpatient surgery. Hospital-replacing technologies, 2017, 3-4 (67-68), pp. 88-93.
- P.L.Shcherbakov, G.Yu.Knorring. Modern possibilities of preparation for endoscopic examination of the intestine. Internal Medicine Cardiology Rheumatology. 2015, No. 8(109)-9(110), pp.54-61.
- P.L. Shcherbakov and others. Comparison of various bowel preparation schemes for instrumental research methods. Gastroenterology, 2021, No. 1(118), pp.59-65.
- Instructions for use Microlax®.
- Gas O.C. Comparative clinical evaluation of a new microenema, clinical study. 1965.
- V.T. Kokhnyuk, I.V. Anufrenok. Preparation of the colon for examinations and operations in patients with colorectal cancer. RMZh, No. 21 from 10/23/2006, p. 1520.
How to use Microlax
The medicine is used rectally. Before giving an enema, you need to wash your hands well and thoroughly clean the area around the anus. The seal must be broken off immediately before insertion. After removing the seal, you need to press on the tube so that the solution comes out. After this, the tip is inserted into the anus and the entire contents of the tube are squeezed out. You need to take out the enema with the walls of the tube compressed.
From the age of 3, the tip must be inserted completely. For younger children, half will be enough. One enema will be enough for a one-time dose.
The frequency of use and dosage can only be determined by a specialist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Many people wonder about the emergence of addiction. Doctors say that you should not take the medicine for a long time. If a person has chronic constipation, then it is worth making an appointment with a doctor to undergo an examination and prescribe further treatment.
It is not recommended to take the medicine in parallel with alcoholic beverages.
Reviews about the drug are in most cases positive. In 95% of cases, the treatment takes place without any adverse reactions or discomfort. Parents note that Microlax has a much better and more effective effect on young children than other medications.
Sigmoidoscopy without discomfort
Sigmoidoscopy is an effective diagnostic method that allows you to identify serious gastrointestinal diseases in the early stages. This is a painless but unpleasant procedure that requires the patient to have proper preparation and an appropriate psychological attitude.
There are alternative methods for examining the intestines, but they cannot give a complete and accurate picture of the condition of the rectum and sigmoid colon. Accordingly, if there are indications for sigmoidoscopy, it is better to agree to the procedure and strictly follow medical recommendations. Compliance with the rules will reduce discomfort, allow you to make an accurate diagnosis and eliminate the need to undergo repeated examinations.