Dentists recommend undergoing preventive examinations at least once a year and, if caries is detected, treating it at an early stage. Unfortunately, many patients go to the doctor with an advanced form of the disease. In this article we will tell you why and how deep caries occurs, and we will tell you about treatment methods.
In this article
- Areas affected by caries and stages of the disease
- Deep caries and its features
- Risk factors for deep caries
- Forms of deep caries
- Features of diagnosing deep caries
- How can deep caries be cured?
- Conclusion
Areas affected by caries and stages of the disease
Caries is a dental disease in which, under the influence of microorganisms and other factors, the structure of dental tissues is destroyed.
The mechanism of development of the disease is due to the vital activity of bacteria Streptococcus mutans and some other species. They have a cariogenic effect and create conditions for the development of the carious process. It goes like this. Bacteria accumulate on teeth and form a biological film called plaque. When we eat foods rich in carbohydrates, plaque bacteria actively process the sugars they contain and produce organic acids that are dangerous to our teeth. They destroy the enamel structure, deprive it of minerals, and penetrate deep into the tooth. The more acids produced by oral microorganisms, the more active and rapid the destruction of dental tissue.
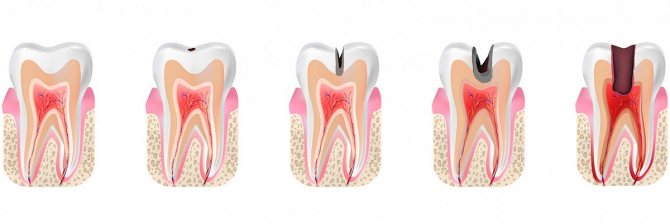
Damage to teeth by caries does not occur instantly; it can take several months from a small spot to the appearance of a hole in the tooth. Based on how deeply the carious process penetrates, several stages of the disease are distinguished.
- The earliest is the spot stage.
A small focus of demineralization appears on the surface of the enamel. It looks like a whitish dot or streak. It is almost impossible to notice such changes with the naked eye. And provided that there are no other symptoms (pain or discomfort) at this stage, a person often misses the onset of caries and does not see a doctor.
- Superficial caries.
If the stain was not noticed in time, it gradually grows, the enamel tissue is destroyed, and a cavity is formed in it - a small hole. As a rule, there is still no pain, although food may get into the cavity or tooth sensitivity may increase.
- Average caries.
The form of average caries is characterized by the penetration of the pathological process into dentin - the bone tissue under the enamel. At this stage, a carious cavity forms in the dentin, pain becomes severe, and the tooth reacts to temperature or taste stimuli. Most often, people go to the dentist with the listed symptoms.
- Deep caries.
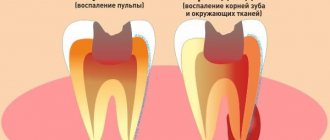
If for some reason you do not treat average caries, the pathology progresses and approaches the pulp - the dental nerve. This is the most complex and dangerous form of caries, because there is a high risk of infection spreading to the pulp, periodontium and the development of complications.
How does the caries process proceed?
Caries is a destructive process that occurs in the hard tissues of teeth (dentine with a cavity, covered on the outside with enamel and cement). The onset of the disease affects the outer protective shell of the tooth crown - enamel. Enamel demineralization occurs. In the absence of proper treatment, destruction (Latin destructio - decomposition, destruction) “goes deeper” - dentin (Latin dentinum) - the hard tissue of the tooth, constituting its bulk in the area of the crown, neck and root - begins to soften, as it were, and the formation of carious cavity. The root part of the dentin is covered with cement; between the cement of the tooth root and the alveolar plate there is a complex of tissues - periodontium (lat. periodontium). Periodontal fibers and pulp (lat. pulpis dentis) - the fibrous connective tissue that fills the tooth cavity - are the next objects of destruction. Inflammations occurring in the periodontium and pulp are complicated by the carious process and are called periodontitis and pulpitis.
Caries susceptibility (caries resistance) of a tooth (teeth) depends on many factors, which include: the property of greater or lesser resistance of the anatomical surface of the tooth to dental plaque; degree of saturation of tooth enamel with fluoride; a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements in the food taken; quality and quantity of saliva; genetic factor; general condition of the body.
The speed of the caries process will be greater the later the patient receives qualified dental care.
Deep caries and its features
Deep caries is always an advanced pathological process. It cannot arise instantly, in a few days. As a rule, the deep form of caries develops over many months, sometimes years. In this case, the person does not consult a doctor and does not take measures to treat the carious process.
The main feature and at the same time the danger of deep caries is that it is located in close proximity to the pulp - the neurovascular bundle - and creates a threat of the development of pulpitis and periodontitis. The risk of infection spreading to other organs and tissues, as well as tooth loss, increases.
The following symptoms are characteristic of deep caries:
- Aching pain in the area of the affected tooth, which intensifies from hot, cold or when biting. Acute pain with deep caries can occur when a lot of food debris accumulates in the carious cavity.
- Bad breath. Even regular brushing of teeth in compliance with all the rules does not lead to the disappearance of the odor, since it arises due to decay processes in the affected tooth.
- A large hole in the crown of a tooth is the most obvious sign of deep caries.
Dentists note that often with deep caries the patient has no complaints. But this does not reduce the risk of complications.
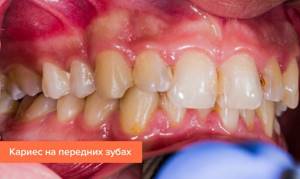
Why is caries on the front teeth dangerous?
Caries on the front teeth has a number of distinctive features that affect the course of the disease and treatment. Here are the key ones:
- the enamel of the front teeth is thinner than that of the molars, so the process spreads much faster;
- it is with the appearance of a white or yellowish stain that caries of the front teeth most often begins;
- a carious cavity, as a rule, grows in depth: even a small caries on the front tooth in the form of a point can affect the pulp, which is why the result largely depends on the timeliness of visiting a doctor;
- due to anatomical features and increased aesthetic requirements, treatment of anterior teeth is more difficult and more expensive compared to treatment of chewing teeth;
- the process is accompanied by noticeable pain and reaction to irritants even in the early stages of carious lesions;
- aesthetic drawback: on the front teeth the process is immediately visible.
Caries is caused by the activity of acid-forming bacteria, and in this regard, the front teeth are no different from the rest. Poor hygiene and consumption of harmful products greatly increase the risk of developing the disease. Tight spaces between teeth can also be an additional risk factor, as it makes it difficult to remove food debris.
Despite the fact that the disease in the frontal zone develops rapidly, it is easier to diagnose. Here it is not at all difficult to notice a carious cavity or a chalk spot (excluding lesions on the inside). In addition, pain is often the main stimulus for going to the doctor, so severe pain in the context of diagnosis can be considered a conditionally positive signal.
All types of diseases can be divided into two categories: according to the degree of spread and the place of occurrence.
Risk factors for deep caries
Deep tooth decay with caries most often occurs in the presence of the following risk factors:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Abuse of sweet and carbohydrate foods.
- Lack of calcium, fluorine, phosphorus, vitamin D in the body.
- Chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine and immune systems.
- Genetic background.
And, of course, one of the main reasons for the development of deep caries is late diagnosis and untimely treatment.
How does caries form?
The causes of caries are poor hygiene and the presence of bacteria in the oral cavity.
There are many bacteria in the human oral cavity. These bacteria feed on food debris that remains on the surface of the enamel after eating. Bacteria “love” foods high in carbohydrates: sweets, flour. During their life, bacteria produce acid, which destroys teeth.
Caries occurs in both adults and children. This disease spreads in each person at a different rate.
Factors contributing to the rapid development of caries:
- insufficient or lack of oral hygiene;
- excess carbohydrate foods: flour products, sweets, carbonated drinks;
- low buffering capacity of saliva, when acids and alkalis are not sufficiently neutralized in the oral cavity;
- insufficient fluorine and calcium content in enamel;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- severe somatic pathologies suffered in childhood (tuberculosis, rickets);
- reduced immunity.
Answering a frequent question from patients: “Why do caries form on teeth?”, we note that the most important factor is insufficient hygiene. All dentists strongly recommend brushing your teeth regularly and using floss to clean the gaps. Without careful hygiene, bacteria will destroy teeth one by one, leading to serious complications.
Forms of deep caries
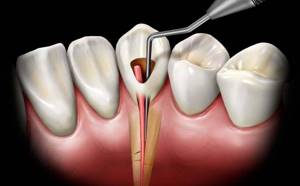
Deep caries can occur in two forms - acute and chronic. Each has its own characteristics. Acute deep caries is characterized by rapid development and can affect a large area of the tooth in a short time. Upon superficial examination, the cavity in the tooth appears small. But further diagnostics show that this is deep-stage caries, and it has almost reached the tooth root. It is acute caries that is most often accompanied by a complication in the form of pulpitis. Therefore, when treating it, the dentist has to not only prepare the tooth and put a filling on the dental crown, but also remove the nerve and fill the canals.
Chronic deep caries, unlike acute caries, is a slow, sluggish process. Although most of the tooth with this form is destroyed, the carious cavity is smaller in area than with acute caries. The patient may complain of periodic aching pain, which does not depend on external stimuli and occurs on its own.
Depending on the affected area, deep caries can be divided into cervical, fissure or located on the front incisors.
Based on the speed of development of the pathological process, it is divided into compensated (relatively slow development), subcompensated (with an average speed of development) and decompensated (with a high speed of development). Objectively, any form of deep caries can be cured, but it will require varying amounts of time and effort.
Treatment of deep dental caries with pulp damage
When infection penetrates into the pulp chamber, in the vast majority of cases, tooth depulpation and root canal cleaning are performed. There are methods for complete or partial preservation of the pulp (biological and vital methods of treating pulpitis), however, conservative treatment is possible only at the very early stages of the disease and does not always guarantee a 100% result. After depulpation of the canals, depending on the extent of the damage, the doctor chooses the method of treatment.
- Classic filling of deep caries.
- Installation of filling and stump inlay.
- Crown installation (orthopedic treatment).
Features of diagnosing deep caries
Advanced caries often has the same clinical picture as pulpitis and some other dental diseases. Therefore, before starting treatment, the doctor must conduct a differential diagnosis and understand which pathology to treat.
Deep caries can be distinguished from focal pulpitis by a number of symptoms. With pulpitis, probing the cavity with a dental probe will cause pain only in one area - in the area of the pulp, while with deep caries pain occurs over the entire surface of the tooth.
The probing procedure will also help to distinguish deep caries from medium ones. On average, it is almost painless, because a fairly thick layer of dentin remains between the sensitive pulp and the bottom of the carious cavity. With a deep form, the tooth reacts to probing with severe pain. The method of electroodontodiagnostics helps to distinguish deep caries from fibrous pulpitis. In most cases, the doctor will order an x-ray to confirm the diagnosis.
DIAGNOSIS OF DENTIN CARIES
A dentist-therapist makes a diagnosis of “Dentine caries” based on subjective and objective data. Subjective data (what one person says) for dentin caries are complaints. Diagnosis of dentin caries is based on the following complaints:
- Pain from thermal stimuli (hot and cold);
- Unpleasant sensations when chewing (when the cavity is located on the contact and chewing surfaces);
- Food getting stuck between teeth with approximal dentin caries;
- Complicated use of floss;
- Aesthetic defect;
- Bad breath (due to accumulation of food between the teeth);
- No pain with the existing defect.

Correct interpretation and understanding of pain by the patient is important for the correct diagnosis of dentin caries. Depending on the nature of the pain and its frequency, subsequent treatment has some features. Medium dentin caries is characterized by pain in response to temperature stimuli, such as hot and cold (a reaction to chemical stimuli is also possible: sour/sweet). The duration of pain plays an important role here: medium dentin caries is characterized by rapidly passing pain, with large pain-free intervals; Deep dentin caries is characterized by more intense long-term pain, with short painless intervals. Also, with dentin caries, there may be no pain. This is explained by the destruction of the dentin-enamel boundary with the formation of replacement (secondary) dentin.
Methods for diagnosing dentin caries
After listening to the patient, the doctor proceeds to an objective assessment. With the help of objective data and high-quality diagnostics, the dentist-therapist can more specifically understand the essence of the problem that the patient has addressed and choose the right treatment. To make a diagnosis, a doctor can use the following methods for diagnosing dentin caries:
- BASIC:
- Probing;
- Percussion;
- Palpation;
- ADDITIONAL:
- Thermometry;
- Electroodontometry;
- Radiography;
- Transillumination (transillumination).
When probing the affected tooth, the dentist notes:
- The softened bottom has a light brown tint in case of acute dentin caries;
- Dense pigmented dark bottom with chronic dentin caries;
- Overhanging enamel edges;
- The enamel is fragile and can chip (undermined enamel)
- Softened walls, fissures, smooth surface;
- In the case of acute dentin caries, the probe can enter the cavity from the approximal side.
- Pain on probing. This method will help the specialist to correctly determine the depth of caries damage. If, upon probing, pain was noted along the enamel-dentin border, therefore, this is medium dentin caries (mantle dentin is affected). If probing was painful at one point, it means that the caries is located in the peripulpal dentin - deep dentin caries.
The main diagnostic methods are, as described above, percussion and palpation. These methods are carried out only to determine the vitality of the pulp, that is, for the differential diagnosis of dentin caries and periodontitis. For periodontitis, these methods will have a positive effect; for dentin caries, they are negative.
Thermometry for dentin caries gives the doctor information about the vitality (viability) of the pulp. For a more qualitative analysis, it is necessary to carry out thermometry on adjacent teeth and teeth on the opposite side, that is, conduct a comparative analysis. And it is best to start the test with the teeth of the opposite side so that the patient can specifically and accurately understand his sensations. To begin the procedure, it is necessary to isolate the tooth from saliva and dry it using cotton rolls (you cannot dry it with a gun, as a reaction to hypothermia may occur). There are the following methods of thermometry:
- Irrigation of the tooth with water from a pistol;
- Irrigation of the tooth using wet rollers;
- Inserting a swab moistened with warm or cold water into the tooth cavity;
- Heat test. For this test you will need a stick of gutta-percha or a rubber-like filling material. The material is heated, preventing it from smoking, after which it is applied to the middle third of the crown of the affected tooth and pain is noted.
- Test with a piece of ice, using chloroethyl, carbon dioxide - "dry ice"
During the tests, the doctor evaluates the patient's reaction:
- Lack of reaction - the pulp has died (necrosis, perioontitis) or a false reaction with significant obliteration;
- Rapidly passing pain – dentin caries, non-carious lesions;
- Slowly passing pain, pain after eliminating the stimulus - pulpitis;
I repeat once again that dentin caries is characterized by quickly passing pain from temperature stimuli.
Electroodontometry should always be performed, especially in asymptomatic dentin caries. The threshold value of indicators for dentin caries is from 2 to 10 μA.
Radiography
Radiography for dentin caries is carried out to determine the location of the cavity and its extent. Any of its types can be used to diagnose dentin caries.
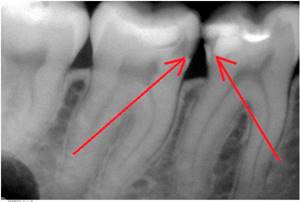
Transillumination
Transillumination (transillumination) for dentine caries is used most often when the cavity is localized on the approximal surface or when the course of dentine caries is hidden. The tissues of a healthy tooth, when transilluminated, appear transparent; when damaged by caries, a shadow appears that clearly demarcates the tissue affected and not affected by caries.
After making a preliminary diagnosis, for specification it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of dentin caries and other forms of diseases.
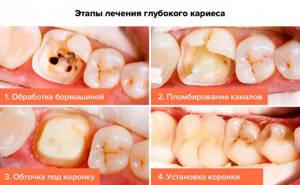
How can deep caries be cured?
A disease such as deep caries can be treated in one or two visits.
The first option is carried out according to this scheme:
- The doctor numbs the affected tooth with a local anesthetic.
- Opens the carious cavity and, using a drill, cleans it of dead and diseased tissue until dense walls and bottom remain.
- If caries is complicated by pulpitis, endodontic treatment is carried out, that is, the dental canals are filled.
- To treat inflammation, isolate the sensitive pulp from the effects of filling material, and build up dentin, a therapeutic or insulating pad is placed at the bottom of the cavity.
- After all the above manipulations, the tooth is closed with a filling.
Treatment in two visits is carried out according to this scheme.
During the first visit, pain relief is performed, the cavity is opened and the affected tissue is removed. A medical pad is placed in the cavity and closed with a temporary filling. On the second visit after a few days or weeks, if the patient has no complaints, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one.
Treatment in two visits is considered preferable because it is possible to observe the condition of the tooth before installing a permanent filling. If pain, discomfort and other symptoms occur, additional therapeutic procedures can be performed to ensure that the affected tissue is completely removed. When treating a tooth in two visits, complications and relapses of caries occur much less frequently.
How is caries on the front teeth treated?
If you have caries on your front teeth, you need to start treatment as soon as possible. Therapeutic methods directly depend on the location of the disease and stage. In addition, the treatment of caries on the front teeth is complicated by various factors.
Relatively new methods for treating caries on the front teeth
- Filling. The most common therapeutic technique. Due to increased aesthetic requirements (especially if caries has occurred on the front surface of the tooth), light (photopolymer) fillings are used. Treatment of caries between the front teeth requires special precision: it is necessary not only to choose the correct color of the material, but also to recreate the natural shape of the teeth and the interdental space.
- Orthopedic treatment. If the damage is severe, it is often impossible to install a filling. In this case, veneers and crowns come to the rescue, allowing you to restore the aesthetics and functionality of the tooth. In particularly severe situations, removal is required. For example, classical treatment of root caries of the front teeth at the last stage is often not possible, so the most effective solution is implantation.
- Infiltration method. We are talking primarily about Icon technology, however, removal of caries on the front teeth is possible only at the initial stage.
Prevention of caries
Even strict adherence to hygienic rules for oral care does not mean that you can ignore visiting the dentist once every six months. Regular, thorough teeth cleaning alone is not enough; special professional cleaning is necessary to completely remove plaque and formed stones. The doctor also carries out a procedure that is effective for disease prevention to restore the mineral balance of tooth tissue. Remineralization increases resistance to disease and is a mandatory step in teeth whitening - before and after.
Of particular importance in preventive measures is the sealing of dental fissures. Today in dental practice, the use of sealants that cover fissures and blind dental pits is widely accepted. It is painless and is usually prescribed for children and adolescents.
Incorrect bite and misaligned teeth can also trigger the development of caries, so treating these deficiencies is not just a solution to the issue of attractiveness, it is a matter of dental health. It is necessary to consult an orthodontist and carry out treatment with him if necessary.
What to do if caries appears on teeth
First of all, you need to immediately contact your dentist. When a tooth is destroyed due to caries, treatment cannot be delayed. Otherwise, the complications described above arise. It is worth noting that no available means at home will relieve the patient of this problem. Only a dentist can cure this disease.
You should also pay attention to your oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day.
- Use floss and mouth rinses.
- Visit your dentist for a checkup every six months.
- Come for professional hygiene every 6 months.
Dentists will help you select individual hygiene products (brushes, pastes, threads, rinses) at your appointment. The doctor will also determine why dental caries appears in your particular case and give the necessary recommendations.
POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS AFTER TREATMENT
Deep caries is the last stage of caries, which is closest to pulpitis, and this can cause some complications during treatment:
- Pulpitis. Dental procedures performed at the wrong time or of insufficient quality lead to the development of caries into pulpitis. In this case, more serious treatment is required.
- Repeated caries. Usually provoked by the negligence of the dentist at the border of the filling and the tooth.
- Opening the tooth cavity. Also, the “culprit” is the carelessness of the doctor. If the autopsy is not noticed in time, then sooner or later the question of treating pulpitis will arise.
- Fracture of the tooth crown. Most often observed if the walls of the tooth are very thin. Treatment involves either strengthening the tooth with an artificial crown or re-filling.
TREATMENT OF DEEP CARIES IN OUR CLINIC
Modern dentistry allows us to provide the highest level of treatment for any type of caries, including such complex varieties as deep cervical caries, root caries, and so on. If you are interested in the latest methods for treating deep caries, please contact our clinic. Our premises are equipped with modern dental equipment, which allows us to quickly, efficiently and painlessly solve any problems. We will perform fluoridation, preparation, and laser treatment of the nerve at an affordable cost.
What happens if caries is not treated?
- For a long time, the disease may not bother the patient in any way. When the destruction of hard tissue has reached a significant extent, sensitivity appears during eating.
- If you do not consult a doctor at the first stage, the carious process will go further and reach the pulp (nerve). Spontaneous severe pain appears. Treatment of pulpitis will be required.
- If the patient does not seek help at this stage, the infection spreads beyond the root. Periodontitis occurs. The prognosis here is unfavorable, since such a tooth often needs to be removed to eliminate the infection.
Therefore, timely visit to the dental clinic will help to avoid acute pain and complications.
Caries in children
Since acute forms of dental caries are more common in children, special attention should be paid to oral care from the moment the first tooth erupts. A properly formulated diet, hygiene and systematic examinations with a doctor will help to avoid many problems.
Classification of childhood caries is based on the place of origin and degree of development. It is not easy to detect carious changes in teeth in preschoolers, especially at the initial stage. A dental examination using special equipment is required. If a preschooler has a toothache, this indicates a medium or deep stage of development of the disease. Symptoms of the disease do not appear at all for a long time, which is why routine medical examinations by the dentist are needed.
Bottle caries
Bottle caries (another name is circular) caries appears in children under 3 years of age, negatively affecting baby teeth during eruption. The damage to the upper front teeth begins, the disease is detected by the formation of white spots in the area where the tooth adheres to the gum or where the teeth touch.
Experts believe that the appearance and development of bottle tooth caries is facilitated by feeding children before bedtime - no matter whether it is during the day or at night. This does not mean only breastfeeding and bottle feeding: the beginning of carious destruction can be caused by any cariogenic product (confectionery, sweet drinks). After eating, food remains get stuck between the child’s teeth, which leads to the onset of the disease.
If the slightest signs of disease are detected, you should visit a pediatric dentist. Treatment of a child’s teeth is successful, regardless of the stage of development of the disease.
The equipment of modern clinics and the use of innovative diagnostic methods make it possible to identify the disease at any stage of development. The use of computed tomography, targeted and panoramic images provide a complete picture of the condition of the oral cavity.
Do baby teeth need to be treated?
You should not think that if baby teeth are going to fall out anyway, then there is no need to treat them. The fact is that carious lesions in milk teeth will not allow permanent teeth to develop normally. Often, untreated teeth in childhood can result in serious diseases. Regular dental checkups are necessary, and treatment must be carried out in a timely manner. This is the key to healthy teeth and a beautiful smile as an adult.
Panoramic dental x-ray
If pulpitis or another disease is suspected, the dentist sends the patient to take a photo of the diseased tooth. But sometimes it is difficult to determine exactly which tooth is the source of the problem. If the gums are inflamed, a person simply cannot understand where exactly it hurts.
Previously, in such cases it was necessary to take x-rays of nearby teeth. Today, the doctor will definitely refer you for an orthopantomogram - a panoramic image. This method allows you to get a “picture” of the entire oral cavity at one time. Moreover, from such an image it is possible to determine not only caries or periodontal destruction. A panoramic x-ray of the teeth will reflect the condition of the alveoli, sinuses and even maxillofacial bones.
Experts also advise periodically taking panoramic dental x-rays for prevention. This diagnostic method will allow you to identify inflammatory processes at the tops of the roots of the teeth even before toothache begins to torment you. And having seen the general picture of the state of your dental system, the dentist will prescribe a targeted photo of the questionable tooth in case of any deviation.
After the therapy, especially if it took place in several stages, you may need to repeat dental x-rays. This will allow you to notice and eliminate defects in the canal filling in a timely manner.
If, according to indications, you are offered to remove a wisdom tooth, a panoramic photograph will also be useful. The surgeon needs to see the entire area around the problem area - the area of the upcoming operation.
If you decide to have prosthetics, install braces or implant an implant, be sure to take a panoramic photo. Such an X-ray of the teeth in this case will allow the doctor to fully assess the condition of your oral cavity and decide on a treatment regimen.
So, if you are determined to correct your bite, the orthodontist will ask you to do an orthopantomogram in order to use it to analyze at what angle the roots of the teeth are, and whether there are teeth that are not visible, but they are located inside the jaw bone - the so-called impacted teeth. This information will allow you to perform bite correction as successfully as possible.
If you are going to have dental prosthetics, it is necessary to exclude hidden problems - a dental cyst, granuloma or tumor. The size and boundaries of these neoplasms are quite clearly visible on a panoramic photograph of the teeth. With a traditional x-ray, when only 1-2 teeth are reflected in the image, the doctor risks missing the threat.
When placing an implant in the upper jaw, the implantologist will use this image to estimate the distance to the maxillary sinuses. This is necessary so that during the procedure the implant does not enter the maxillary sinus. If you need to place an implant in the lower jaw, it is important to make sure that it does not touch the nerve.
How is a panoramic dental x-ray performed?
Everything is elementary simple: you just need to stand at a special installation for a few seconds. And within a couple of minutes the photo is in your hands. Before starting the procedure, be sure to remove all metal objects from yourself. They interfere with the passage of the X-ray beam, which means they can cause image distortion. The most modern devices are digital, they allow you to store your pictures in the computer's memory. After all, they can be useful to you at an appointment with a variety of doctors - dental therapists, maxillofacial surgeons, orthodontists, implantologists, and so on.
Another plus is the price. A panoramic dental x-ray will cost you much less than taking pictures of several problem areas. In addition, modern technologies make this procedure as safe as possible, even for young patients. After all, the radiation dose is reduced to a minimum. But do not forget that for some chronic diseases, as well as during pregnancy, any x-ray is contraindicated. Therefore, before the procedure, be sure to discuss all the nuances with your doctor.