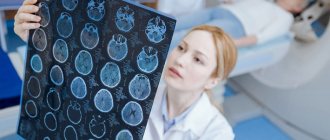
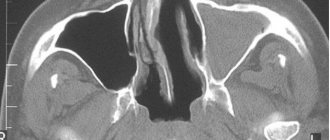
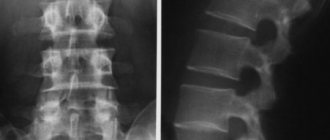
MRI is a popular and reliable technique for studying internal organs. This diagnostic method is considered safe because it uses electromagnetic waves that do not harm the human body. For scanning, special devices called tomographs are used. The main components of the design of such devices are:
- Software that receives and processes information;
- Magnet;
- Cooling system;
- RF, gradient, shimming coils;
- Protective screen.
There is a wide variety of MRI equipment with different characteristics. The question of which device is better and what is the difference between them is quite popular, it requires an answer.
Operating principle
X-rays have a high penetrating ability, that is, they pass unhindered through human organs and tissues. Each tissue absorbs them at different rates and rates. The denser the medium (for example, bone), the more X-ray energy is absorbed.
The computed tomography method is based on measuring the difference in attenuation of the energy of X-ray radiation as it passes through tissues of the human body of different densities, followed by processing the results with a computer program.
The tomograph consists of:
- rings (gantry), in which one or more radiation sources - X-ray tubes - are mounted on one side, and receiving devices - detectors - on the other;
- the table on which the patient is placed during the examination;
- a computer that reconstructs the received data into an image.
During scanning, the X-ray tube begins to rotate around the patient's body. X-rays, penetrating through the body, are captured by sensitive detectors located on the opposite side of the ring.
The difference in the density of different biological tissues of the body that X-ray radiation encounters along its path causes a change in its intensity, which is recorded by detectors. Next, the radiation energy is converted into electrical signals, which, after amplification, are converted into digital pulses.
After analyzing the data, a computer program constructs layer-by-layer images of the structures of the area under study.
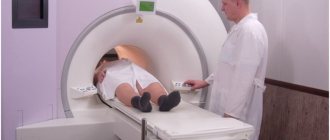
Open type devices and closed devices
Tomographs can be open or closed. The first ones are like a canopy over a couch with magnets placed in the device at the top and bottom. The second type is a chamber that has a closed annular part into which the viewing platform slides. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. So, the advantages of an open tomograph are:
- Affordable scanning price;
- Possibility of conducting examinations for people who do not feel well in a closed space, patients with significant body weight, with plastered limbs, as well as children - parents can be nearby and, if necessary, calm the child;
- Minimal noise when the device operates.
Among the disadvantages are not very detailed images due to the low field power, the duration of the procedure, the impossibility of a high-quality examination of organs and soft tissues. The main advantages of closed-type equipment are diagnostics of any degree of complexity on all parts of the body, speed of examination and obtaining images in which the smallest details are visible. Such devices also have disadvantages:
- Loud noise;
- Problems with screening people with significant weight;
- Risk of claustrophobia;
- Increased sensitivity of the device to the presence of metal elements.
To examine women in late stages of pregnancy, open-type equipment is more often used, where the stomach does not interfere with the placement of the patient.
Noise during operation of a closed tomograph is associated with vibration of the spirals in the gradient coil due to fast electrical pulses. Such a knock does not indicate a malfunction of the device. On the contrary, it is an integral part of the operation of the device. To prevent patients from being frightened by loud noises, they are usually offered earplugs or headphones.
What does the number of slices affect?
A CT slice is an image produced by a tomograph during one rotation of the X-ray tube around the area of the body being examined. The number of slices depends on the detectors installed in the gantry. The more detectors, the more slices can be obtained during the study.
The increased number of slices reduces scanning time and allows for complex tasks such as examination of the brain and heart.
The level of detail and quality of the examination depends on the cutting capabilities of the device. The more slices the setup makes per ring rotation, the more accurate the image reconstruction will be.
After the reconstruction process is completed, the computer program displays the image on the screen. Bones on tomograms look white, gas and air look black, all other tissues have gray shades of varying intensity.
Equipment quality and settings
The next criterion is the quality of the tomograph and its novelty. Not every medical center can afford new equipment, so in clinics you can find used devices from Europe and America. Some of them cope with the assigned tasks quite adequately, but there is a chance that the equipment is morally and physically outdated.

The quality of the study also depends on what kind of machine the clinic has in terms of scanning settings. To study various tissues and organs, special software and a set of modes are provided. These modes differ from each other:
- The presence of certain pulse sequences;
- Thickness of slices;
- Number of slices;
- Spatial resolution;
- The ratio of noise and signal;
- Scan plane.
The regimen is chosen by the doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the area being studied and the type of disease being diagnosed. It is worth considering that carefully setting up the device may take some time, so the duration of the procedure increases. But this is necessary to obtain informative images, otherwise the examination loses its meaning.
Types of CT
Depending on the type of scanning, there are three types of computed tomographs.
A step-by-step or single-slice tomograph belongs to the first generation devices. Equipped with one X-ray tube and detector. Scanning is carried out step by step, depending on the selected mode (2, 5, 10 mm), making one revolution per layer. Nowadays it is rarely used due to the low information content, the duration of the procedure and the significant radiation exposure the patient receives during the study.
Spiral tomograph. The movement of the circuit around the patient resembles a spiral, and the radiation beam is formed in the form of a thin fan. With the spiral type of scanning, the constant rotation of the X-ray tube around the patient's body is accompanied by the translational movement of the table through the gantry ring. A special computer program reconstructs the obtained data in any plane, and also reproduces a three-dimensional image of the organ under study. At the same time, the scanning process is significantly accelerated, and the volume of ionizing radiation becomes smaller.
Multislice spiral computed tomograph (MSCT). The main difference between MSC tomographs and spiral ones is that they have not one, but two or more rows of detectors around the gantry circumference. The scanning trajectory takes a spiral shape. How many rows of detectors are installed in the tomograph, so many optical sections are obtained simultaneously: if there are 2 rows - 2 slices, if there are 4 rows - 4 slices. The scanning time is reduced, the radiation dose is reduced due to reduced exposure
320-, 512-, 640-slice computed tomographs have been developed that provide the most detailed images of the organs being studied, and also allow real-time study of the processes occurring in the blood vessels and heart.
Advantages of the MRI method
Magnetic tomography is a safe, painless and most informative type of diagnostics for a wide range of diseases:
- blood vessels;
- brain;
- thyroid and mammary glands;
- joints;
- internal organs;
- soft tissues;
- spine;
- tumor processes.
MRI eliminates radiation exposure to the body, does not require special preparation, and has only the presence of metal implants in the body as contraindications. This type of study can be carried out during pregnancy and at a very early age. There are no restrictions on the frequency of tomography repetitions. It is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Which CT machine is better?
The attending physician decides which equipment is best for diagnostics. If to study bone tissue it is enough to do a CT scan on a 16- or 32-slice machine, then for examining blood vessels, the heart, and internal organs, a 64-slice tomograph will be optimal.
In clinical practice, 16-, 32-, 64-slice devices are used for most diagnostic studies using computed tomography.
Diagnostic centers in St. Petersburg are equipped with spiral and multispiral tomographs with a number of sections from 8 to 64. Highly specialized medical clinics use 128-slice equipment.
Modern computed tomographs have a system for recording the examination process in digital format, which allows you to reproduce the study if necessary (consultation with other specialists, study of the dynamics of the disease).
Equipment of centers and cost of services
We use modern PHILIPS ACHIEVA tomographs, expert-class equipment with a power of 1.5 Tesla. This makes it possible to make scanning as accurate and effective for diagnosis as possible. Our prices are truly affordable - at least 25% lower than the average market price for MRI in Moscow.
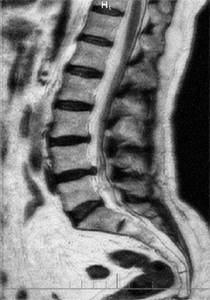
Approximate image quality at 0.3-0.5 Tesla.
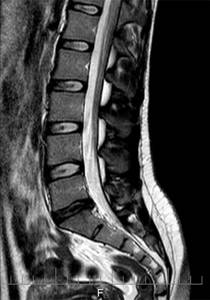
Image quality is 1.5 tesla. Higher quality means lower probability of error.
What types of tomographs are there?
Now there are several classifications of MRI machines.
By type of magnet used:
- with a permanent magnet - the most common type of tomograph, as it is used by open-type MRI machines;
- with a resistive magnet - also found in open tomographs, but the expensive maintenance of this type of magnet has made such equipment rare;
- with a superconducting magnet - an undoubted advantage is the power of the created magnetic field (up to 4 Tesla), but the disadvantage is the high price and the fact that it is cooled with liquid helium.
Closed-type MRI machine Open-type MRI machine
According to the design of the tomograph, there are: closed-type and open-type MRI machines. The former are not suitable for patients suffering from claustrophobia due to long periods of immobility in a kind of closed tube.
There are 5 classes of tomographs, distinguished by magnetic field power:
- Class 1 - ultra-low (power less than 0.1 T).
- Class 2 - low (0.1-0.5 T).
- Class 3 - medium (from 0.5 to 1 T).
- Class 4 - high (1-2 Tesla).
- Class 5 - ultra-high (power more than 2 Tesla).
Each tomograph is equipped with: a magnet (creates a powerful magnetic field); magnetic gradients (create a low-power alternating magnetic field in the center of the main magnet); transmitter (creates excitation in the patient’s body) and receiver (records the response of excited areas) of impulses; computer system for recording and processing the received data, image reconstruction; cooling and energy-saving equipment.
Summarizing
Magnetic resonance imaging devices are complex technological complexes that have a number of characteristics that influence their choice as a diagnostic tool for patients. After analyzing the medical history and contraindications, the attending physician decides which tomograph is best for MRI in each specific case.
Closed devices make it possible to conduct deep and high-quality diagnostics of human organs. For example, for MRI of the brain, only high-field, or even better, ultra-high-field tunnel-type devices are used. However, they are expensive and are not suitable for overweight people or patients with phobias. Open or low-field devices are suitable in cases of analysis of gross pathology, when images with moderate organ visualization characteristics are sufficient for the doctor.