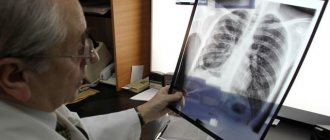
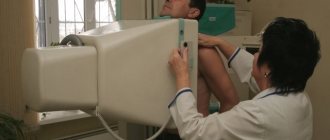
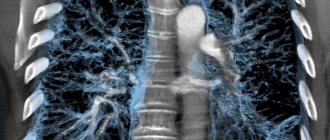
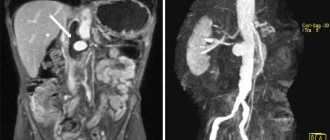
MRI is one of the most informative ways to identify various tumors in the body, as well as monitor their condition. MRI in oncology, even with severe pathology in the patient, is harmless, and the resulting images allow doctors to obtain a clear image of the tumor, which is important for its competent interpretation and treatment.
Palpation of the prostate gland through the rectum for prostate cancer
Due to the proximity of the prostate to the rectum, a urologist can perform a digital rectal examination. A simple method allows you to detect the presence of a tumor, since it differs from other tissues in its immobility and increased density. In most cases, tumors are located in the peripheral zone, so the doctor can feel them through the rectum.
A healthy gland has an elastic consistency, symmetrical contours and reacts when pressed. During palpation, the doctor pays attention to:
- asymmetry and blurred contours;
- surface roughness;
- immobility when pressed;
- the presence of a dense tumor protruding into the intestinal lumen.
Digital examination is the primary diagnostic method, which must be carried out when examining a man. The result is supported by laboratory and instrumental studies.
What else needs to be considered?
Before you sign up for an MRI, find out which machine will be used to perform the procedure. MRI for cancer should be performed on a device capable of accurately and clearly visualizing organs, tissues and other structures of the body. For example, MRI scans obtained using low-field tomographs will not have sufficient diagnostic accuracy for the early detection of tumors. Therefore, when diagnosing cancer using MRI, it is worth giving preference to high-field devices with a power of 1.5 T or more, since the higher the power of the device, the better the quality of the images, the shorter the procedure time and the thinner the sections. Thanks to this, high-field expert-class MRI scanners are able to detect cancer at an early stage.
| apparatus/indicators | low-pole | mid-field | high-field |
| power | from 0.1 T | from 1 Tl | from 1.5 T |
| time | from 40 minutes | from 25 minutes | from 15 minutes |
| slice thickness in photographs | 5-7 mm | 3-4 mm | 1-2 mm |
It is important to understand that, despite all its information, magnetic resonance imaging is not a way to make a histological diagnosis of cancer. MRI allows you to identify a tumor and provides the necessary information about its structure, growth pattern, and a full clinical diagnosis is made by the attending physician, depending on the patient’s clinical picture and the results of additional examinations. In addition to MRI, the results of laboratory and instrumental studies, the key of which is a biopsy, followed by a histological conclusion, will be important. Therefore, after receiving the MRI results, you should not try to make a diagnosis yourself. It is necessary to immediately consult a specialist, because timely treatment begins increases the prognosis for recovery.
PSA blood test
Prostate-specific antigen is a substance that is found in the serum and prostate gland of a man. With an abnormal increase in organ volume, the PSA level increases because the integrity of the cell structure is disrupted. Under normal conditions, the prostate is protected by a cellular barrier.
PSA also increases in other diseases not related to cancer. A cancer process is indicated by a PSA level higher than normal - from 4 ng/ml or more. Also, when studying the antigen, the ratio of total to free PSA is taken into account. If it is less than 15%, then the likelihood of cancer is high.
Digital rectal examination, bladder catheterization, biopsy and prostate massage increase the antigen concentration for 3 weeks. Therefore, the analysis is carried out some time after the described studies in order to obtain reliable results.
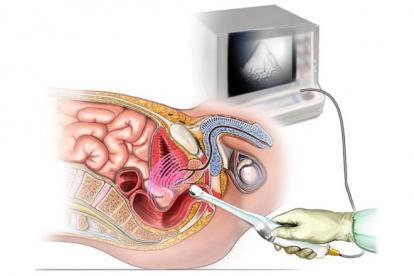
Transrectal ultrasound examination
To diagnose prostate cancer, transrectal ultrasound is used, which is performed through the rectum. The study makes it possible to more accurately determine the presence of a tumor, in contrast to the abdominal one, since there is a very thin wall between the rectum and the prostate.
A typical condition in prostate cancer is the presence of nodes of a hypoechoic structure, mainly in the peripheral zone of the prostate. With TRUS it is impossible to determine the nature of the tumor, so the study is always supplemented by palpation, PSA analysis and other diagnostic methods.
In what cases is MRI effective?
- Prevention and initial diagnosis of suspected cancer. As a rule, cancer screening is prescribed in the presence of risk factors, as well as when specific and nonspecific symptoms of the tumor process appear. If a tumor is suspected, contrast-enhanced MRI is performed. This is very important for differential diagnosis between malignant and benign processes.
- Observation if a diagnosis has already been made. Since the method is harmless and does not provoke the progression of the tumor, MRI can be performed as many times as necessary for adequate treatment. This method will help the doctor give an opinion about the changing state of the tumor over time.
- Evaluation of treatment results. After a course of radiation or chemotherapy or another treatment option, including surgery, has been completed, the results of treatment must be monitored. The timing of MRI control is determined by the attending physician, based on many factors (size and location of the tumor, type of treatment, etc.).
MRI of the pelvis with contrast
Magnetic resonance imaging is an accurate diagnostic method that is used to clarify the results of ultrasound examination. To determine the nature of the tumor, an MRI is performed with a statement - a drug with paramagnetic substances is injected into the vein, which makes images of tissues and blood vessels clearer. A malignant tumor quickly accumulates contrast, after which it is easily recognized in the image. Multiparametric MRI is safe for the body; the administered substances do not cause allergic reactions. Tomography allows you to determine the location of tumors and the extent of damage to surrounding tissues. MRI is prescribed in preparation for fusion biopsy.
Suspicious lesions are classified according to the Pirads scale:
- 1-2 points – no cancer.
- 3-4 points – possible oncology.
- 5 points – high risk of cancer.
Does MRI show cancer?
Tomography allows us to examine the focus of a malignant neoplasm at all stages of the oncological process. Metastases are also visible in the images, regardless of the characteristics of their localization.
It is important that MRI allows you to see cancer even at the stage of the formation of atypical cells - during this period the lesions do not exceed one millimeter, and the neoplasm itself has not yet formed.
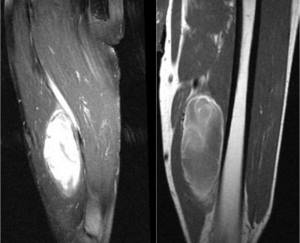
When it is necessary to assess the process of spread of metastases, doctors use MRI with contrast, which allows them to create a three-dimensional model of the tumor. This allows you to find out:
- tumor size and location;
- degree of "expansion";
- pathological changes in the blood supply to the area being studied;
- feasibility of surgical intervention;
- features of the “interaction” of the tumor with elements of the nervous and vascular systems;
- type of neoplasm.
Important!
If we are not talking about the primary detection of cancer, but about monitoring a previously diagnosed pathology, the research method helps doctors track the results of surgical or therapeutic effects on the body.
Probability of error
MRI detects oncology with a probability of 90-95%, which makes the study the most advanced tool in terms of hardware diagnostics of cancer. Errors happen in three cases:
- insufficient qualifications of personnel;
- study of “difficult” areas to analyze, which include lungs and bones due to their special structure;
- poor quality of the tomograph.
Cancer detected in time can often be defeated using a conservative method. Only tomography can timely detect a malignant process in the early stages.
Important!
The most clearly visible during the study are blood vessels and soft tissues and organs, so almost 100% accuracy can be achieved when analyzing the condition of the liver, kidneys, spleen, brain, as well as the cardiovascular, nervous and lymphatic systems.
Additional research methods
To diagnose prostate cancer for certain indications, computed tomography, PET-CT, and radioisotope scanning are additionally prescribed
- PET-CT is performed by injecting a radiopharmaceutical into a vein to detect tumors and metastases. In the early stages, the method is uninformative. The study is done in cases of moderate and high cancer risk, also in addition to osteoscintigraphy or in order to exclude relapse after prostatectomy.
- CT can exclude the presence of metastases in the bone, abdominal cavity, lungs and other organs. Often, if there are contraindications to MRI, patients undergo a CT scan of the pelvic organs with contrast to assess the extent of the process.
- Radioisotope scanning (scintigraphy) is a diagnostic method that is prescribed for moderate and high cancer risk in order to exclude the presence of metastases. For the procedure, a radioactive drug is injected into a patient's vein. After three hours, the body is scanned using a gamma camera, which transmits the information to a computer.
Why choose MRI?
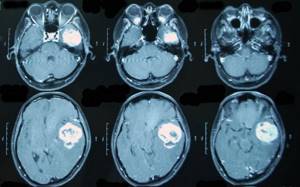
Magnetic resonance imaging is a safe and accurate method for diagnosing malignant diseases. MRI for cancer can help identify structural changes in almost any part of the body. An MRI scanner can be used to examine the head, spine, blood vessels, joints, mammary glands, pelvis, parenchymal organs (liver, pancreas, etc.), as well as soft tissues of any location.
In addition, the magnetic field is harmless to humans. The patient is not exposed to radiation, and the procedure itself is non-invasive and completely painless. Accordingly, no additional health risks are created by factors that could provoke tumor growth.
Using MRI, you can make an initial assumption about whether a neoplasm is malignant or not, as well as determine the stage of cancer.
MR imaging during a malignant process gives an idea not only of the tumor (its size, shape, structure), but also allows one to judge its interaction with surrounding organs and tissues, nearby vessels and nerves, and also reveals distant and local metastases.
After the patient undergoes an MRI, the attending physician will have a more complete understanding of the tumor process, which will allow him to subsequently choose the most optimal method of correction (treatment) of the identified changes and predict the outcome of the disease. Thus, MRI for cancer is one of the most effective diagnostic methods.
The gold standard is transrectal biopsy.
A common method for taking biopsies from a man's prostate gland. Features of transrectal biopsy:
- It is carried out under ultrasound control through the rectum.
- The doctor makes 12 punctures with a needle with cutting ends, on which particles of tissue remain. They are preserved and sent for examination.
- Transrectal intervention causes minimal tissue trauma.
The disadvantage is that there is a possibility of obtaining an insufficient number of biopsies, which leads to the need for a repeat biopsy.
Fusion biopsy is the most informative method for diagnosing prostate cancer
Fusion biopsy involves performing targeted punctures in 3-4 suspicious points. The procedure is carried out under ultrasound and MRI control with ascertaining. The images are superimposed to create a three-dimensional image of the prostate. This allows you to accurately determine the location of the site for tissue sampling. Advantages of fusion biopsy:
- Targeted punctures at suspicious points.
- High diagnostic accuracy – 95%.
- No pain due to epidural anesthesia.
- Preserving the integrity of the intestinal walls
Features of diagnosing prostate cancer in old age
Men over 70 years of age do not need to undergo early diagnosis of prostate cancer. At this age, a slowly progressing pathology is more often detected, which does not entail serious consequences.
A biopsy for elderly patients is dangerous because it can lead to side effects such as problems with urination, infection, bleeding, etc. In this case, urologists focus on PSA levels and accompanying symptoms. In case of mild symptoms, invasive diagnostics are often abandoned and observation tactics are chosen using MRI and PSA.
The doctor individually determines the necessary methods for examining the condition of the prostate gland. It is important for men to closely monitor their body and, at the first suspicion of problems with the prostate, contact a specialist.
Oncological search is a highly effective method for diagnosing cancer
Oncological search using magnetic resonance imaging has no alternative, since only this diagnosis can reliably identify a tumor, as well as the presence of metastases. Also, this diagnosis is in demand during the treatment process, since it allows specialists to monitor all the changes occurring in the patient’s body.
MRI24 centers invite you to undergo highly informative diagnostics in Moscow using a tomograph at a convenient time and guarantee the optimal cost of services. We work around the clock, you can see the addresses and prices on the website. Full body MRI, performed using the latest equipment installed in our centers, will provide your treating specialist with all the information you need.
With us you have the opportunity to do an MRI, the affordable price of which is combined with a high level of reliability. By providing diagnostic services, we strive to set prices at a level acceptable to a wide audience.