MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain allows you to analyze the state of all brain tissue using an electromagnetic field to obtain a three-dimensional image. The method allows for detailed visualization of brain structures and detection of tissue and vascular defects.
This is one of the newest and “young” research methods, so it is safe and highly informative. The procedure for diagnosing the state of the central nervous system using nuclear magnetic resonance, subsequently processed on a computer to obtain data, has no analogues and is the “gold standard” of examination for the overwhelming number of possible pathologies.
Philips Intera MRI scanner
Progress of the procedure: how does an MRI of the brain with contrast work?
The NMR tomography method allows you to examine and study human organs based on the saturation of tissues of various structures with hydrogen atoms. The characteristics of their magnetic properties are also important. This procedure is most often prescribed in difficult clinical situations: for cancer patients, for a detailed and clear examination of the tumor and the affected organ, for demyelinating diseases, for some types of strokes.
During the procedure, the condition of all parts of the brain is monitored, as well as the cerebellum, basal ganglia, ventricles, the ratio of gray and white matter and other structural indicators.
The method is safe, since the patient is not exposed to x-rays during diagnosis.
The contrast agent is injected into a vein using a syringe system. Within 10-30 seconds, the substance penetrates all vessels and tissues and illuminates the areas necessary for diagnosis.
The implementation consists of several stages:
- Before administering the drug, a native study is performed, without the use of contrast;
- After this, the patient is given an injection with a contrast agent in the required volume;
- Then you need to re-set the scanning programs.
Most patients do not notice any deterioration in their health or side effects.
What is MR angiography
MR angiography is a study of blood vessels using magnetic resonance.
It can be contrasting or non-contrasting. Non-contrast testing is possible due to the presence of native contrast from blood moving through the vessels. MRA (both contrast and non-contrast) is indispensable in cases where the identification or exclusion of pathological changes in blood vessels can affect the treatment or medical tactics, and the use of iodinated radiocontrast agents and X-ray radiation is undesirable.
The use of contrast can significantly increase the amount of diagnostic information obtained during the study. Almost all drugs used in MRI contain gadolinium and are called paramagnetic agents (there are also superparamagnetic agents based on iron, which are practically not used). Due to their high hydrophilicity, they do not penetrate cell membranes, including the blood-brain barrier, and are quickly excreted by the kidneys, causing virtually no adverse reactions.
Initially, contrasts were used only to study the brain and spinal cord, and then the whole body. They are approved for use in children (including newborns), as well as for administration in significant (triple) doses required for angiography. During pregnancy, use is undesirable due to the lack of reliable data on penetration through the placenta and effects on the fetus.
Highly concentrated contrast agents in combination with ultra-fast pulse sequences on powerful devices make it possible to determine in real time the slightest changes in blood flow in any part of the human body.
Why is an MRI of the brain done with contrast agent?
MR contrast agents are used to detect tumors, autoimmune inflammation and other pathological changes. Most often used in neurosurgery and neurology to enable more informative and high-quality research.
The substance allows you to visualize the exact boundaries, structure and localization of the tumor, the activity of the demyelinating process, the severity of the blood supply to the area under MRI observation.
The advantages of MRI of the brain are that it preserves a clear picture of all structures, even if the tissues are at different depths, and also provides the opportunity to examine all areas of the brain that are covered by the skull.
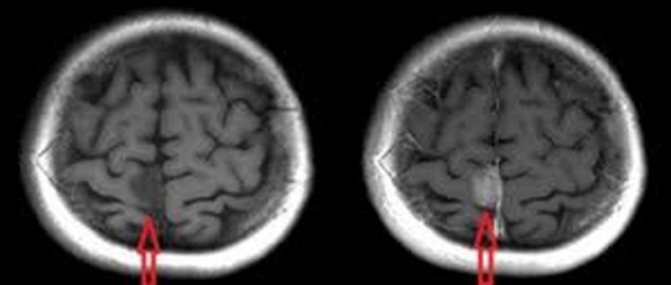
Differences in imaging with contrast-enhanced MRI
Types of contrast enhancement in MRI
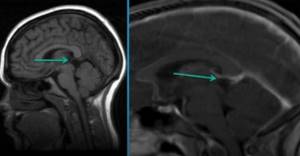
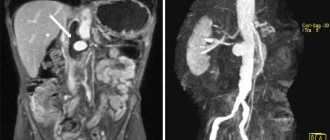
Pre- and post-contrast images of the brain on MRI (the arrow indicates the difference in the signal from the cyst and the cerebrospinal fluid)
The distribution of gadolinium in various diseases is not the same. In some cases, the very fact of drug accumulation is an indicator of pathology. In MRI diagnostics of the brain, the distribution of the substance distinguishes between foci of demyelination (“attract” contrast) and vascular changes (here gadolinium preparations are not concentrated), etc.
Based on the specific accumulation of the amplifier, doctors receive preliminary information about the nature of tumor structures. Benign formations concentrate gadolinium drugs in the capsule area. This provides a hyperintense signal. Malignant tumors are characterized by penetrating growth with destruction of nearby tissues. In this case, the accumulation of contrast will show an irregular shape, complex structure, uneven density of formation and the development of inflammatory changes along the periphery.
To quickly undergo an MRI of any anatomical area, sign up at the Magnit DC. Radiologists with extensive practical experience, candidates of medical sciences, and regular participants in international conferences and congresses work here. You can make an appointment by phone, during a visit to the DC or through the feedback form on the website.
What does a brain MRI with contrast show?
There are many symptoms of brain disorders, in which it is better not to postpone a visit to specialists and get a tomography. If you observe: atypical behavior, movement disorders, general health, often neurologists or other clinicians after examination will advise you to do an MRI as the most revealing diagnostic method. MRI of the brain with contrast is prescribed when making a diagnosis is difficult and additional examination is required.
Indications for MRI:
- tumors;
- acute vascular diseases of the nervous system;
- epilepsy;
- severe headaches;
- multiple sclerosis;
- pathology of cerebral vessels;
- bruises and injuries of the skull and brain and their consequences.
As a result of the procedure, inflammatory processes can be detected, indicating their exact location. Examinations are also prescribed after brain surgery. An MRI can help determine whether the tumor has shrunk or recurred.
For a clear and detailed image, the doctor prescribes the injection of a special substance that will help to examine the patient’s problem in more detail. It is worth noting that the contrast agent is safe for health, since it is eliminated from the body within 3-4 hours.
The main advantages of contrast in brain MRI include:
- minimum contraindications;
- obtaining slices in any plane;
- high contrast and image resolution;
- the ability to obtain images of all brain structures covered by bone tissue;
- good tolerability of the drug.
This technique uses several types of substances; they differ in composition and method of application. Most often, doctors prescribe a contrast agent, which is administered intravenously and contains the rare earth paramagnetic metal gadolinium.
The procedure has no contraindications, the exception may be a peculiarity of the body with individual intolerance. In some cases, side effects are possible: rash, nausea, slight dizziness. Complications are observed in less than one percent of clinical cases.

Preparing for an MRI with contrast
What can you eat before an MRI?
When preparing for magnetic resonance imaging of any anatomical area, except the abdominal cavity and pelvis, it is allowed to consume familiar foods. There are no restrictions regarding the frequency of meals. It is better to refrain from eating exotic foods and overeating (to avoid causing indigestion), and not to drink too much coffee (to prevent frequent urination).
Before an MRI of the abdominal cavity and pelvis, you need to follow a diet to prevent constipation and excess gas formation. 2-3 days before the procedure you should exclude from your diet:
- sweets;
- dairy products;
- baked goods;
- black bread;
- legumes;
- berries and fruits;
- alcohol;
- mushrooms;
- starchy foods (rice, potatoes, pasta).
You can eat meat, eggs, fish, cereals, stewed vegetables, day-old bread, biscuits. These same foods are allowed to be eaten on the day of the examination, taking into account the need to withstand fasting 4 hours before the start of the scan.

Snack options on the eve of an intensified tomography scan
If you are planning an MRI of any anatomical area with contrast, you should arrange a light snack 40-45 minutes before the procedure. This measure reduces the risk of autonomic reactions of the body to the contrast agent.
Preparing for an MRI of the brain with contrast
No special preparation is required before administering contrast, but experts advise avoiding heavy meals, regardless of which organ is being scanned. This will help avoid side effects such as nausea and vomiting.
During the procedure, you should remove all products made from ferromagnetic alloys. It is also necessary to remove any metal, even non-magnetic, from the face and head (earrings, chains, etc.) to avoid interference.
Women are advised to remove make-up from their face as some dyes contain metallic particles which may distort images.
The question of the frequency and frequency of MRI depends primarily on the disease for which this examination is prescribed. It is worth addressing this issue individually with your doctor, neurologist or neurosurgeon. The MRI procedure, regardless of the frequency of use, is completely safe and can be performed as often as necessary.
MRI: rules of passage
Simple preparation is necessary on the day of scanning. At the DC you need to take your passport and available medical documentation (referral, results of other diagnostic procedures, certificate for the implant).
It is better to come to the clinic 5 minutes before the appointed time. This will allow you to fill out the forms without haste. You should arrive 15 minutes early for your pelvic scan so you can drink extra water.
Preparation for an MRI procedure includes a preliminary consultation with a radiologist. The conversation helps to identify contraindications to scanning and clarify the purpose of tomography. The specialist is warned about:
- pregnancy (if you suspect, you should do a test);
- feeling unwell (due to a recent ARVI, cold, etc.);
- acute pain;
- drinking alcohol on the eve of diagnosis;
- fear of equipment or fear of confined spaces.
Before entering the diagnostic room, you should prepare for tomography: remove jewelry, metal products, and items of clothing with locks, hooks, or buttons. Personal items and gadgets are left in the dressing room.
In the MRI room, the patient lies down on the tomograph platform. To prevent movement, the subject's body is secured with soft straps. During the scanning process, you can communicate with a clinic employee via two-way speakerphone or give a signal by pressing a special button.
Contraindications
There are relative and absolute contraindications. In the first case, research is possible under certain conditions, in the second it is unacceptable.
Absolute contraindications:
- pacemaker;
- middle ear implants;
- metal body prostheses made of ferromagnetic alloys;
- presence of insulin pumps;
- pregnancy in the early trimester;
- Ilizarov apparatus.
Relative contraindications:
- claustrophobia;
- mental disorders in the patient;
- prosthetic heart valves;
- Bracket system;
- patients under 5 years of age.
The examination is performed as prescribed by a doctor to clarify the diagnosis, as well as to monitor the dynamics of treatment. In most cases, MRI of the brain makes it possible to correctly diagnose and identify diseases at an early stage.
MRI of the brain with or without contrast
The difference between the procedures is the information content of the image, because the use of contrast allows a detailed examination of the pathological focus under study. Standard MRI is performed without enhancing substances. There is no preparation before the usual procedure.
MRI with the drug takes longer than tomography without enhancement, since after the end of the umbrella tomography it takes about 15 more minutes to complete the contrast protocol.
The difference in price is noticeable - the cost of the substance increases the cost of scanning. The required amount of medicine is calculated based on the patient’s weight and varies between approximately 2500-5000 thousand rubles.
The substance is completely safe for the body - scientists have proven the low toxicity of gadolinium, which is part of the drug. This drug does not cause an allergic reaction and leaves the body without difficulty. The drug plays a significant role in identifying malignant tumors.
When is vascular MRI with contrast prescribed?
Contrast is most often prescribed for the diagnosis of neoplasms of various locations, diseases of the brain (including perfusion studies), spinal cord, spine, neck and face, chest organs, heart, liver, pancreas, rectum, kidneys and adrenal glands, bladder, abdominal cavity, uterus, prostate, musculoskeletal system, bone marrow, joints. Slightly less commonly used for examining the vessels themselves and for performing three-dimensional MRA of the whole body. Sometimes these examinations are combined into one.
To conduct contrast MRA, the drug is used at a rate of 0.1–0.2 ml/kg and is administered intravenously at a rate of 1–2 ml/sec.
Using MR angiography, without the use of catheters, it is possible to obtain contrast images of vessels in almost all anatomical areas and diagnose vascular pathologies such as narrowings (stenoses), pathological dilations (aneurysms) or malformations (shunts).
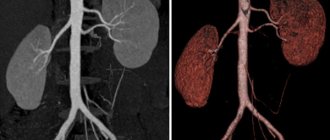
Study of the aorta
In patients with aortic diseases, contrast MRA allows one to assess the degree of mural thrombosis and the maximum diameter of the aneurysm, its proximal extension and relationship with the renal arteries, the size of the affected area in the iliac arteries, as well as the condition of the ostia of the renal arteries. In addition, this study makes it possible to determine the extent of vessel occlusion, study the structure of vessels above and below the occlusion, evaluate collateral circulation, and identify irregularities in the vessel wall.
Use in the study of cardiac vessels
Contrast has proven to be very useful in detecting coronary stenoses and myocardial infarctions. Compared to traditional methods - radiography, CT or ultrasound, MRI allows more accurately identifying differences in myocardial structures. Contrast is administered to diagnose coronary heart disease, contrast the coronary arteries and especially shunts, and is also widely used in the diagnosis of congenital anomalies of the structure of the heart and blood vessels.
The introduction of contrast-enhanced MRI has significantly increased the quality of diagnosis of acute and chronic myocardial ischemia. Now two methods are used - determination of perfusion and contrast study in later periods after contrast injection.
Measuring perfusion during the initial passage of the drug allows one to judge myocardial blood flow. This method is used primarily for the primary detection of coronary artery diseases. Contrast-enhanced MRI can be used in myocardial infarction to determine the exact size of the ischemic area. 15 minutes after administration, areas of necrosis and scar changes can be detected. According to experimental studies, contrast accumulates precisely in scar tissue formed after a heart attack. The reason for this is a change in the pharmacokinetics of the drug and an increase in extracellular spaces in the scar area.
Cardiac wall motion disorders often occur secondary to myocardial infarction. The reason for this may be a scar - a non-viable area of the myocardium or a viable one, but not contracting at the moment. The purpose of this diagnosis is to predict the possibility of restoring myocardial contractile function after revascularization. The accumulation of gadolinium in the tissue of the myocardial wall to a thickness exceeding 50% indicates its non-viability.
Detection of pathology in the blood supply to the liver
In most cases, with malignant liver tumors and its metastatic lesions, the signal intensity increases immediately after administration of the drug with its further washout, which indicates the presence of increased blood supply to the tumor.
Other common indications for circulatory testing
As a rule, the amount of diagnostic information obtained using contrast can be significantly increased by monitoring the contrast over time. This is most often used in cases of:
- metastases of tumors in the brain - they do not have a blood-brain barrier, which is normally impenetrable to contrast agents; additional metastases are detected in 52% of patients;
- metastases in different parts of the body - such formations have both a larger number of vessels and the vessels themselves with increased permeability, which leads to rapid accumulation and faster leaching of the drug;
- scar tissue changes - extracellular space is increased in them and contrast accumulates more