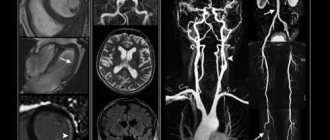
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels
CT angiography of cerebral vessels allows one to study the state of arterial and venous circulation in the brain. This diagnostic method is used by introducing a certain contrast agent into the bloodstream, which makes it possible to visualize the vessels in the area under study. There is also a technique for creating a three-dimensional model of the vascular bed, which facilitates diagnosis and analysis of the data obtained. Thanks to CT of the brain vessels, it is possible to analyze and assess the condition of arteries and veins, as well as identify pathological conditions of the blood supply.
When is a CT scan of the brain vessels prescribed?
This diagnostic method is widely used by specialists when they suspect the presence of abnormalities in the structure of the brain or the vascular bed of the cranial cavity. It is also used for diagnosing brain tumors of various origins, in cases of tissue ischemia, and in the presence of suspected stroke or thrombosis. CT scan of the vessels of the brain and neck is prescribed in the presence of neurological symptoms, which indicate abnormalities and pathological phenomena in the bloodstream of the brain. Also performed before vascular operations.
Indications
- Obstructive atherosclerotic lesions
- Aortic expansion
- Vascular emergencies
- Visualization of atherosclerotic plaques
- Diagnosis of vasculitis
- Diagnosis of vasculopathy (for example, fibromuscular dysplasia).
- External pathologies affecting blood vessels
- Degenerative aneurysms of the abdominal aorta
- Chronic dissection with aneurysm formation
- Infection (mycotic aneurysm)
- Injury
- Connective tissue diseases
- Congenital anomalies
- Bleeding
What does a brain CT scan show?
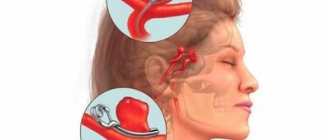
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels is a fairly indicative method for diagnosing vascular pathologies and is widely used in medical clinics. This type of study clearly visualizes the structure of the vascular bed and the condition of the walls of veins and arteries, therefore it is used to diagnose aneurysms (pathological protrusion of the wall of a blood vessel that occurs as a result of changes or damage).
CT angiography of cerebral vessels reflects the movement of blood in the bloodstream. Thanks to this, it is possible to diagnose blood flow disorders, determine the localization of thrombosis, atherosclerotic plaques or emboli that impede normal blood flow. Also, the described angiography method makes it possible to diagnose various vascular malformations, kinks, pathological looping and narrowing of the lumen.
This method allows you to determine the presence and location of brain tumors and the degree of their vascularization.
Advantages of the method
— Angiography of the abdominal vessels facilitates the study of formations that are inaccessible through other research methods, and therefore rarely provides false results. For example, CT of the splenic artery reveals even very small aneurysms that can be treated.
— The study is characterized by a small radiation dose, so it can be carried out several times.
— Computed tomography is performed in emergency situations, and the study has a minimum of contraindications.
Preparing the patient for CT scan of cerebral vessels
When conducting a study such as CT angiography of the vessels of the neck and brain
, there is no need for preliminary preparation. However, when contrast is introduced into the bloodstream to visualize the condition of the vessels, a number of clinical tests are necessary: a blood test to determine the level of creatinine and urea, to determine whether the patient has renal failure or claustrophobia. An important step in preliminary preparation is conducting an allergy test for iodine-containing drugs, since the contrast agent administered for diagnostics contains iodine.
On the eve of the study, experts recommend drinking plenty of fluids. This event will speed up the removal of the contrast agent from the body. You should also avoid eating food 5-6 hours before the procedure, so as not to provoke possible vomiting during the diagnosis.
Before a CT scan, the patient must remove all metal devices and jewelry (to prevent interference in the images), and also undress. They provide a disposable set of special cotton clothing.
What sensations does the patient experience?
No negative sensations, pain or discomfort are felt during the examination. Patients hear only the hum and clicks produced by the device.
Sometimes after the administration of contrast, nausea, vomiting and dizziness occur. However, these sensations are quite tolerable and pass quickly.
What are the risks of the procedure?
The radiation dose that the body receives during such an examination is very small and amounts to only 0.29 mSv. For comparison, the background radiation of a person per year is 1 mSv, that is, much more. Therefore, computed tomography does not harm the body.
The only thing that can create a problem is an allergic reaction to the contrast agent. But conducting a preliminary test for intolerance makes this situation extremely rare.
Carrying out the procedure
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels with contrast is a diagnostic method that is based on the use of X-rays generated in a special tube of the device. X-ray radiation affects a specific area under study, and tomograph sensors receive and analyze the data, building them into a single picture. Thanks to this, the specialist, reviewing the results obtained, draws a conclusion about the state of the department being studied. In the future, this allows you to make a correct and accurate diagnosis, select individual treatment and improve the patient’s quality of life.
How is the procedure done? In the absence of contraindications, and after a series of clinical tests and preparatory measures, the patient is placed on a special tomograph table. In this case, a contrast agent is injected into the bloodstream. Next, the tomograph is put into operation. The tomograph table automatically moves to the required position. During the diagnosis, the patient should lie still so that the resulting picture is not blurry. The duration of the procedure is 15-25 minutes.
Using Contrast
The use of contrast is a prerequisite when performing computed tomography of cerebral vessels. This substance allows you to accurately visualize the vascular bed of the area under study, identify pathological abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels and determine the presence of neoplasms in the cranial cavity. The contrast agent is a safe compound, does not cause harm and is quickly eliminated from the body.
How is the examination carried out?
The patient lies down on a table attached to the tomograph. The device is made in the form of a wide ring, inside of which there is an X-ray tube that sends radiation and a receiving detector.
The table then gradually moves through this ring, and the technique takes pictures without contrast (native). After which a contrast agent is injected and the procedure is repeated.
While passing through the tomograph, X-rays are scanned through the patient's head and neck. The results are transferred to a computer, where they are processed using a special program. Multi-slice images are obtained, allowing the vessels of this area to be examined in different projections.
During the examination, the specialist is in the next room and monitors the diagnostics on the computer screen. However, if the patient becomes unwell, he can call a doctor - the tomography room is equipped with a microphone.
The data is provided to the patient in the form of images or recordings on magnetic media. The duration of the study takes approximately 20-30 minutes.
Alternative methods for studying cerebral vessels
Alternative ways to study the condition of cerebral vessels are represented by the following diagnostic methods:
Lymphography
It is an indicative method for studying the elements of the lymphatic system and is widely used in oncology. This diagnostic method allows you to determine deviations in the functioning of lymphatic and venous drainage and determine the presence of neoplasms.
Arteriography
It is also a widely used method for diagnosing arterial diseases using a contrast agent.
Cerebral angiography
A special type of angiography that allows identifying pathological changes in the cerebral vascular bed.
Venography
Allows you to assess the condition of superficial and deep veins through exposure to X-ray radiation. Often used to diagnose venous diseases of the upper and lower extremities.
MR angiography
It is carried out using an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) machine. It is a highly informative method for diagnosing veins and arteries, providing an opportunity to qualitatively assess the condition of the vascular bed of the area under study. It is worth noting that the price for this study may be higher than previous ones.
All presented diagnostic methods are also widely used in various treatment centers.
MSCT of the aorta at the Innovative Vascular Center
Multislice computed tomography angiography of the abdominal aorta is widely used by doctors at our clinic for preoperative diagnosis of problems with the aorta and its branches. This technology allows you to plan a surgical intervention, select the correct size of stent graft for an aortic aneurysm and an instrument for passing chronic occlusions. We also use MSCT to evaluate postoperative results after stenting or resection of an aortic aneurysm, and the status of vascular reconstructions in the long-term period.
Contraindications and possible complications
Like all diagnostic methods, CT scan of cerebral vessels has its contraindications. Situations that do not allow the use of CT angiography include:
- allergic reactions that develop as a result of exposure to a contrast agent;
- severe liver and kidney disease (inability to properly remove the contrast agent from the body);
- severe degrees of phlebitis - a contrast agent can provoke a worsening of the pathological process in this disease;
- pregnancy, because there is a risk of intrauterine development disorders of the fetus.
Frequent and regular use of X-rays for diagnostic purposes (with CT) increases the likelihood of developing malignant tumors. However, with a single or rare use of cerebral CT with contrast, there are almost no risks.
CT angiography on a multislice tomograph (MSCT angiography)
In multislice (multi-layer, multi-slice) computed tomographs (MSCT), unlike tomographs of previous generations, not one, but two or more rows of detectors are located around the circumference. This technology significantly increases the speed and information content of studies, and also reduces the radiation dose to the patient. MSCT has a number of advantages over conventional computed tomography:
- improved time resolution;
- improved spatial resolution along the longitudinal z-axis;
- increasing scanning speed;
- improved contrast resolution;
- increase in signal-to-noise ratio;
- effective use of the X-ray tube;
- large anatomical coverage area;
- reducing radiation exposure to the patient;
Multislice CT angiography in Volyn hospital
The computed tomography room of the Volyn Hospital is equipped with a modern spiral tomograph “Bright Speed Elite”. Doctors at the CT office are at the forefront of the development of computed tomography in Russia and have unique, enormous experience and original research methods. Highly qualified personnel and the latest software allow us to conduct the widest range of research.
The department has extensive experience in computed tomography (CT) of the spine and extremities for degenerative diseases, trauma, tumors and inflammatory diseases. Three-dimensional and multiplanar image reconstructions are widely used.