X-ray, fluorography, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are hardware diagnostic methods. The foundations for the use of fluorography and radiography were laid immediately after the discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Roentgen back in 1895. In 1896, X-rays were first used in surgery. CT and MRI are more modern diagnostic methods. The use of computed tomography was proposed in 1972 by engineer Godfrey Hounsfield and physicist Allan Cormack . The founding year of MRI is considered to be 1973, when chemistry professor Paul Lauterbur published an article about this technique in the journal Nature.
Article on the topic X-ray. The Doctor Who Made the Invisible Visible
What are the main differences between these four research methods?
Three techniques - fluorography, radiography and CT - x-ray. They are based on X-ray radiation. MRI is performed using radiofrequency signals under conditions of an increased magnetic field.
Fluorography is a screening test of the lungs, and radiography is a study performed using a standard X-ray machine. “A fluorograph can only perform examinations of the lungs; an X-ray machine can conduct examinations of all permissible scanning zones. Fluorographs cannot perform additional research in a non-standard projection. Thus, their scope of application is limited only to screening,” explained Kirill Kharlamov, a radiologist and head of the radiology service at the capital’s clinic ,
In MRI, the patient is placed in a magnetic field and radio frequency signals are applied. According to Kharlamov, this study is considered harmless. CT scan uses x-rays; this study is carried out only according to the indications of the attending physician.
The second important difference between the four research methods is the resulting image. X-ray and fluorography are techniques in which, as a result of exposure to X-rays on organs and tissues, two-dimensional images of them are obtained with the effect of summing up the contours and structure of the organs through which the X-ray beam passes. When using CT and MRI, a layer-by-layer and/or three-dimensional image is formed without the effect of summation. The device studies the area under study layer by layer, resulting in a series of images that can then be reconstructed in different planes.
What diseases does fluorography reveal? More details
Advantages and disadvantages of both methods
Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of MRI. The advantages include the highest image quality, the resulting three-dimensional image, in which many organs and systems, areas of the brain with different slice thicknesses of 4-5 mm can be clearly seen. Such good visualization makes it possible to find tumors in different parts of the brain even at the earliest stages of their development. Another advantage is the safety of this research method, which allows you to repeat the procedure several times. Disadvantages include the higher cost compared to radiography and the length of the procedure, during which you need to remain motionless for a long time.
The advantages of radiography include simplicity, cost, and functionality. The disadvantage is relative unsafety. It is recommended to undergo such examination with significant breaks. The resulting image is static, which complicates the assessment of the condition. Without contrast agents, radiography of soft tissues is not very informative.
If we compare which is better, an MRI or an X-ray of the spine, for example, then even in this case it is impossible to answer for sure. It all depends on the damage. X-ray will allow the doctor to assess the condition of the bone tissue - to see fractures, cracks, etc. And MRI will visualize the nerves, spinal cord, surrounding soft tissues, and will allow to see the tumor.
How else do these methods differ?
The methods also differ in information content and dose load (the amount of exposure to ionizing radiation on a person). “If we compare these indicators for X-ray and fluorography, a lot depends on the generation of the equipment and its condition. The general trend is that analog devices provide a higher radiation dose and less information content than digital ones. The dose loads of modern digital fluorographs and digital X-ray machines are comparable, and the information content of a standard study (in frontal and lateral projections) is also comparable,” says the radiologist.
According to the expert, CT is more informative than radiography, but it also has a higher dose load. “CT also provides new opportunities: it allows for examinations using contrast agents (a special substance that is injected into an organ, body cavity or bloodstream). CT with contrast is performed in cases where it is necessary to very clearly separate normal and pathological structures in the human body or to conduct functional studies. For example, if we look at the contractility of the heart muscle. The dose load with CT is greater than with radiography if we compare the study of the same organs. But modern developments in radiation diagnostics are aimed at reducing the maximum dose load. There is a low-dose CT scan of the lungs, which gives a dose load of less than one millisievert, while radiography of the abdominal organs in several projections can give more than one millisievert,” explains Kharlamov.
Unlike X-ray diagnostic methods, MRI does not have a dose load. The patient is placed in the device in a high-intensity magnetic field, where there is no ionizing radiation.
Article on the topic
IVF, MRI, “chemistry”. What kind of medical services seem to be paid?
What is radiography
X-rays are most often used to diagnose musculoskeletal injuries, but can also detect pneumonia, cancer and other degenerative changes.
During the test, an X-ray machine sends individual X-ray particles through the body, which are recorded as digital images on a computer. These images (x-rays) are the result of a shadow being cast between the x-ray source and the detector. This diagnosis is painless, and the radiation dose is negligible. The radiation exposure standard for preventive studies is 1 mSv per year, with the average dose per procedure being 0.001-0.5 mSv.
In what cases what techniques are used?
According to the radiologist, one or another diagnostic method is selected based on the clinical question of the doctor who referred the patient for examination. “In my opinion, MRI is the most promising diagnosis. But that doesn't mean it's always better. Radiography is a good method for studies that do not create too many differential diagnoses. If we understand that there are many more questions about the patient’s condition, then CT will be more helpful in clarifying the clinical situation,” says the specialist.
According to Kharlamov, MRI and CT very often compete with each other when studying certain areas in terms of information content, speed and cost. But the final decision in favor of one or another technique is made by the attending physician together with the radiologist.
“Initially, MRI was considered the gold standard for examining the central nervous system, as well as joints and soft tissues. This method is developing extremely dynamically, and now it allows performing research in almost any area, conducting functional studies, assessing the composition of metabolites of certain organs (so-called MR spectroscopy), studying the heart and blood vessels (including without the introduction of a contrast agent), seeing conductive brain pathways and much more. CT scan allows you to evaluate the lungs, bone structures, abdominal organs, heart and blood vessels. This method is indispensable in urgent (requiring urgent medical intervention, often surgical - note AiF.ru) traumatology and so on,” explains the doctor.
How harmful are x-rays and ultrasound? More details
Indications for X-ray diagnostics
Dental targeted X-rays may be needed in the following cases:
- to determine the depth, severity, nature of the disease process to determine treatment tactics for periodontal disease, caries, pulpitis;
- to identify the presence of a tooth root cyst, granuloma;
- after tooth extraction to identify complications, the presence of tooth root fragments;
- to identify defects and bite pathologies;
- when teething is delayed, to determine the presence of rudiments, the direction of growth;
- to control the quality and effectiveness of treatment, the correct filling of canals, installation of fillings, prostheses, implants;
- to determine the condition of bone structures;
- before prosthetics to determine the structure of supporting dental units;
- to assess the severity of maxillofacial trauma.
What are the contraindications for hardware diagnostics?
Kharlamov points out that there are contraindications for MRI and CT. For the first type of study, these are pacemakers incompatible with MRI, other electronic implants, the presence of large ferromagnetic metal structures and foreign objects in the body. Also relative contraindications are the first trimester of pregnancy, claustrophobia, and the inability to remain still. The main contraindication for CT is pregnancy.
In addition, there is a separate group of contraindications for the administration of contrast agents used in CT and MRI (the drugs are different for different methods). The main ones are allergic reactions and decreased kidney function. Therefore, before each examination and each administration of a contrast agent, a doctor’s consultation is necessary.
What is computed tomography (CT)
Doctors use CT scans to study the body's soft tissues and various organs. CT scanning uses data from multiple X-ray images of structures inside the body and converts them into CT scan images. CT scans can also diagnose infections and help identify tumors and tumors, including cancer. The method may be necessary to determine the desired area for biopsy.
During a CT scan procedure, the patient will be asked to lie on a table that extends from the CT scanner. Once the patient is inside the scanner, they are exposed to X-rays. The computer creates many different CT scan images of the body that the radiologist can view on a monitor. During the test, you must remain still so that the image does not turn out blurry.
In some cases, a computed tomography scan with contrast is performed. Contrast is a special dye that the x-ray technician injects into the patient intravenously. The technology allows the radiologist to highlight specific areas for a clearer image.
A full scan usually takes only a few minutes. If a new study is required, at least 4-5 weeks should pass between procedures.
Fluorography
Another type of examination that all residents of our country regularly undergo. Fluorography was “invented” almost a hundred years ago. This is a kind of accelerated radiography. Scientists proposed photographing a screen with an image obtained from radiography. This made the procedure faster and more widespread. Screening tests began to be administered to everyone in order to detect latent pulmonary tuberculosis.
Main plus
The procedure is fast,
the main disadvantage
is the image quality. The patient also receives a dose of radiation, and the doctor has a rather blurry picture, so fluorography is recommended to be supplemented with questionnaires and laboratory tests for the presence of tuberculosis.
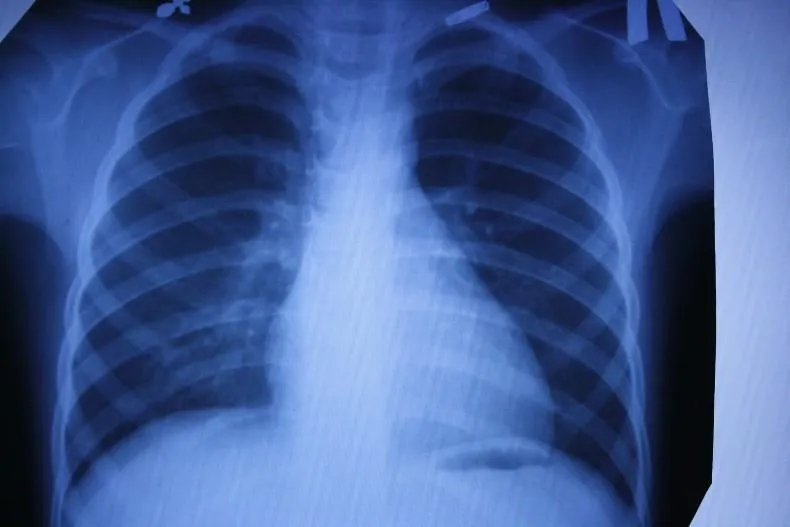
X-ray
The oldest and most common method of visualizing the human body. X-rays are used everywhere, from surgery to dentistry. The method is simple and clear: a person is irradiated with special rays that easily pass through soft tissues and linger in hard ones. Thanks to this principle, an image is transmitted to a photographic film or sensor located on the side opposite the ray source, and radiography or fluoroscopy is available to the doctor.
Main advantages
such an examination: speed and cost. Almost all hospitals are equipped with X-ray machines; the procedure is quick and inexpensive.
Main disadvantages:
exposure and image quality. When performing radiography, the patient is irradiated, and the picture is two-dimensional. The doctor can hardly see the internal organs individually, since their shadows overlap each other. It is also impossible to see the cartilage tissue and brain in detail. The cartilage practically does not block the rays, the brain is securely closed by the skull. X-rays are not suitable for their examination.
It will be most effective to carry out radiography for damage to bones, joints and teeth.
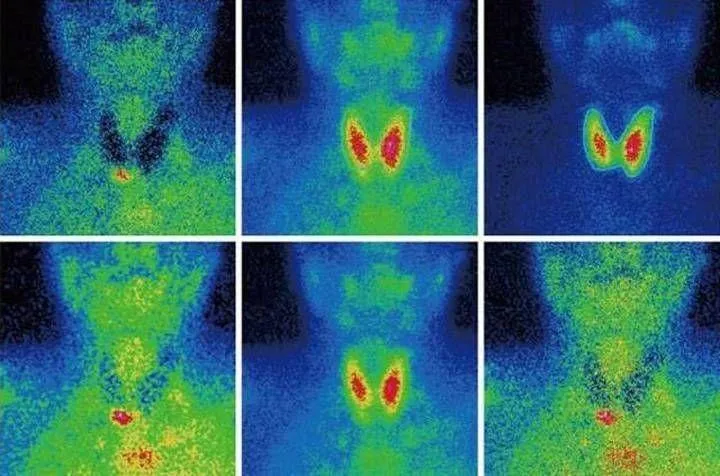
Scintigraphy, SPECT, PET
Perhaps these are one of the rarest procedures on our list. These examination methods are based on radiation diagnostics, but it is used in reverse. The patient is not irradiated from the outside, but a special radioactive drug is injected into him to make him “glow from the inside.” First, scientists invented and tested scintigraphy. With its help, it was possible to obtain two-dimensional images. Then research went further and single photon emission computed tomography ( SPECT)
), followed by positron emission tomography (
PET
). The difference between these methods is rather technical; they use different radiopharmaceuticals and different types of detectors that record radiation from the patient’s body.
The question arises: “Why such difficulties?” The fact is that thanks to these procedures, you can see formations in the pictures that are not visible in pictures obtained by external irradiation. Metastases and tumors can appear inside bones or organs and remain silent for a long time. The radiopharmaceutical is injected into the body and accumulates in the tissues, which allows it to “illuminate” certain areas.
Main disadvantage
of this examination method is the cost. The radiopharmaceutical is developed individually for each patient; in addition, the patient receives radiation exposure, and the procedure itself is more complex than those we described earlier. However, in some cases it cannot be avoided, for example, in cases of oncological and neurological diseases, diagnosis of heart and thyroid diseases.
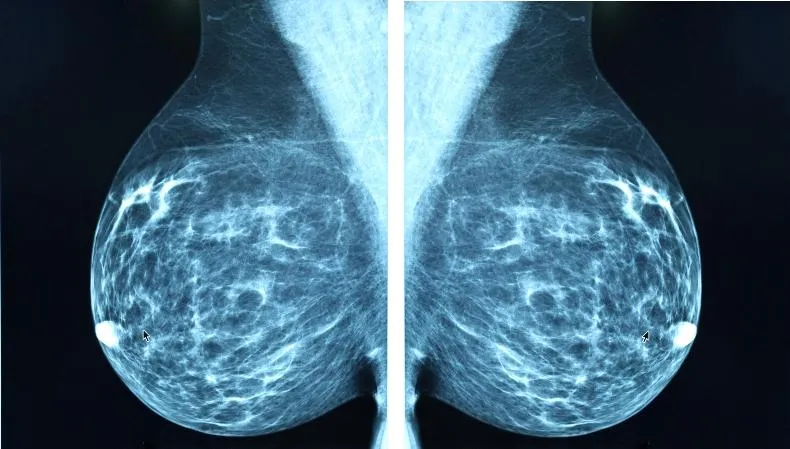
Mammography
A separate type of radiography designed to diagnose breast diseases, which is why women undergo mammography. There is no consensus on the recommended age for the procedure. Mammography helps ensure the absence of a malignant tumor with an accuracy of 89%. It is believed that women should be screened regularly starting at age 39, although some cancer societies recommend screening at a younger age.
Mammography is prescribed to diagnose breast cancer, the procedure is quick
, this is a plus, but the patient
is irradiated
, and the risk of an incorrect diagnosis remains, this is a minus. Mammography can be digital or film; digital mammography provides a clearer image.