X-ray, fluorography, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are hardware diagnostic methods. The foundations for the use of fluorography and radiography were laid immediately after the discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Roentgen back in 1895. In 1896, X-rays were first used in surgery. CT and MRI are more modern diagnostic methods. The use of computed tomography was proposed in 1972 by engineer Godfrey Hounsfield and physicist Allan Cormack . The founding year of MRI is considered to be 1973, when chemistry professor Paul Lauterbur published an article about this technique in the journal Nature.
Article on the topic X-ray. The Doctor Who Made the Invisible Visible
Fluorography: essence, features, application
Fluorography is the simplest and most accessible screening method, which is used mainly for preventive examinations. It helps to identify:
- pathologies of the lungs, bronchi,
- tuberculosis,
- oncology in the chest area.
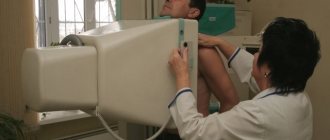
To conduct the study, a special apparatus with a fluorescent screen is used. X-rays are passed through the patient's chest. The image obtained due to the uneven absorption of rays by different tissues and organs is displayed on the screen and then photographed on film. The image is only 11x11 cm in size. It is then enlarged and examined by a radiologist, who makes a conclusion about the presence of pathologies.
The screen of a fluorographic apparatus is less sensitive compared to X-ray equipment, so the radiation dose for such an examination is higher. For example, when undergoing chest fluorography, the radiation dose is 0.8, and an x-ray of a diseased tooth can be taken with a beam of no more than 0.1 m3v. To avoid unnecessary exposure of the body, fluorography is recommended to be done only once a year.
The following categories of people should undergo fluorography every six months:
- patients with chronic diseases,
- people who have had tuberculosis (during the first 3 years),
- medical workers, teachers, educators, people employed in hazardous/harmful industries,
- persons with HIV,
- people living with pregnant women and newborn children,
- people released from prison (in the first 2 years).
Which procedure should I choose?
When specialists prescribe one of the types of diagnostics, they always focus on the goals that such a study will help solve. It should not be forgotten that X-rays are not advisable for pregnant women and children. osteopath or chiropractor, who can establish a diagnosis by palpation can refuse X-ray diagnostics
When choosing between x-rays and fluorography, you need to consider the differences:
- X-ray gives high accuracy;
- fluorography irradiates more strongly;
- Fluorography makes it possible to obtain an image of the lungs;
- X-rays take local pictures and record the dynamics of changes;
- the x-ray is taken immediately on a special film;
- The fluorography image is displayed immediately on the screen, then a photograph is taken from it;
- X-rays are more expensive than fluorography.
Based on a number of these differences, the doctor decides which type of examination to choose in a particular situation.
Radiography: main differences from fluorography
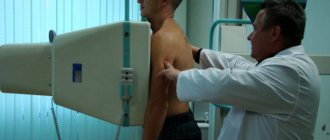
Classic radiography is carried out in a similar way - by illuminating a certain area of the body with X-rays. But unlike fluorography, this equipment does not have a fluorescent screen. The photograph is taken immediately in full size. Because of this, it turns out to be clearer and more detailed, which allows you to identify any pathological changes, determine the size, contours, localization of foci of inflammation, the presence of cavities and much more. Thus, it becomes clear that fluorography can always be replaced with x-rays , but it is very difficult to replace x-rays with fluorography.
Using X-ray equipment, you can examine not only the chest, but also other parts of the body. Such an examination is not carried out for preventive purposes; radiography is prescribed only if it is necessary to clarify or make the correct diagnosis.
It is not necessary to irradiate the entire person during the examination. Special protective aprons, collars, skirts, and caps with a lead layer reliably protect those parts of the body that do not need examination. This is especially important for children and other categories of patients.
At the KIT multidisciplinary medical center, we perform radiography using modern digital equipment . The radiation dose is minimal and similar to the dose you might receive from short periods of direct sunlight. Digital radiography is used to diagnose diseases and pathologies of the respiratory, cardiovascular systems, musculoskeletal system, as well as various injuries to the chest.
Digital X-rays are considered less dangerous to human health than examinations using film equipment or FLG. It is allowed to take x-rays several times a year if this is necessary to make a diagnosis and the radiation dose will not exceed the maximum permissible. Our specialists do not prescribe unnecessary procedures and carefully monitor compliance with safe standards.
X-ray: how not to harm your health?
Medicine notes that you can protect yourself from X-ray equipment with a protective shield. This role may include an “apron” for the abdomen, a “collar” for the neck, a “skirt” to protect the abdominal cavity and genitals, and a “cap” for the head. All these protective screens have a solid lead layer.
At young childbearing ages, experts recommend protecting the genitals and abdominal area from radiation, since the greatest negative impact of the device affects the germ cells and blood.
Particular attention should be paid to children. Their protective screen should cover the entire body, leaving only the area being examined.
X-ray images make the examination quite informative and allow you to observe the dynamics of the body’s reaction to treatment. Doctors do not recommend doing several x-rays in one day (for example, additional fluorography or mammography). It is also important that the patient has a radiation passport, where the radiologist enters the dates of the examination and the doses received.
Which is better: x-ray or fluorography?
Compared to digital radiography, fluorographic examination is considered simpler and cheaper, but at the same time an outdated screening method. Let us note the main differences between these 2 survey options:
- Accuracy. Fluorography is a superficial study. From such an image, the doctor can only determine the presence of pathology or signs of an advanced disease. An X-ray is more accurate and detailed. It allows you to get a clear picture of the current state of internal organs, bones, tissues, notice pathologies and diseases in the early stages of development, begin treatment faster, and record the dynamics of changes. For comparison, we note that the shadows on an x-ray image can be about 2 millimeters, while on a fluorographic image they occupy as much as 5 centimeters, which significantly complicates decoding.
- Radiation dose . Digital X-ray is safer for the patient, since the device operates with less radiation exposure. Especially considering that many public clinics still use old film FLG equipment.
- The area of fluorography examination is limited only to the chest, while x-rays are carried out in relation to almost any area of the body (limbs, head, teeth, etc.).
- Price . Fluorography is cheaper than x-rays, and this is the only reason why it is still used. It is worth considering the fact that if any pathologies are detected on the FLG, the patient may be referred for radiography to obtain a more accurate result and confirm the diagnosis.
In what cases what techniques are used?
According to the radiologist, one or another diagnostic method is selected based on the clinical question of the doctor who referred the patient for examination. “In my opinion, MRI is the most promising diagnosis. But that doesn't mean it's always better. Radiography is a good method for studies that do not create too many differential diagnoses. If we understand that there are many more questions about the patient’s condition, then CT will be more helpful in clarifying the clinical situation,” says the specialist.
According to Kharlamov, MRI and CT very often compete with each other when studying certain areas in terms of information content, speed and cost. But the final decision in favor of one or another technique is made by the attending physician together with the radiologist.
“Initially, MRI was considered the gold standard for examining the central nervous system, as well as joints and soft tissues. This method is developing extremely dynamically, and now it allows performing research in almost any area, conducting functional studies, assessing the composition of metabolites of certain organs (so-called MR spectroscopy), studying the heart and blood vessels (including without the introduction of a contrast agent), seeing conductive brain pathways and much more. CT scan allows you to evaluate the lungs, bone structures, abdominal organs, heart and blood vessels. This method is indispensable in urgent (requiring urgent medical intervention, often surgical - note AiF.ru) traumatology and so on,” explains the doctor.
How harmful are x-rays and ultrasound? More details
What to choose: X-ray or fluorography
We have already talked about the advantages and disadvantages of each x-ray examination method, now let’s summarize. X-rays can easily replace conventional fluorography and give a more complete picture of your health, confirming the absence of pathologies and symptoms of diseases. Fluorography can only act as the simplest, most basic research method. It is not suitable for more accurate diagnosis and diagnosis. If it is necessary to clarify the data, the doctor will still send you for an x-ray.
If you intend to undergo a medical examination and make sure that everything is fine with you, then it is better to sign up for a chest x-ray. By modern standards, the study will cost a little more, but possible pathology can be detected at an earlier stage. The procedure takes only a few minutes, and is interpreted by an experienced radiologist at our medical center.
What are the contraindications for hardware diagnostics?
Kharlamov points out that there are contraindications for MRI and CT. For the first type of study, these are pacemakers incompatible with MRI, other electronic implants, the presence of large ferromagnetic metal structures and foreign objects in the body. Also relative contraindications are the first trimester of pregnancy, claustrophobia, and the inability to remain still. The main contraindication for CT is pregnancy.
In addition, there is a separate group of contraindications for the administration of contrast agents used in CT and MRI (the drugs are different for different methods). The main ones are allergic reactions and decreased kidney function. Therefore, before each examination and each administration of a contrast agent, a doctor’s consultation is necessary.
Purpose and features of obtaining a certificate
It is important for the management of the educational institution that students monitor their health, and the educational process cannot negatively affect the development of identified chronic diseases. There are a number of diseases, the presence of which imposes some restrictions on the performance of professional and job duties. It makes no sense for a person with such a diagnosis to study at a university, college or technical school to master such a profession if in the future he will not be able to get a job. There are few such restrictions, but they exist.
A certificate in form 086/у is issued on a prescribed form, which contains the following information:

- name of the subject;
- Date of Birth;
- registration address;
- place of study where the document will be sent;
- information about confirmed chronic diseases, certain diseases suffered in the past;
- information about vaccination;
- results of fresh fluorography;
- individual reference number;
- information about the medical institution where the document was issued, seal, signature of the chief physician.
How is the research going?
The procedure is carried out in a specially prepared x-ray room. First, the patient must remove clothing from the upper body and remove all metal jewelry from the area being examined. After this, the subject takes a place in front of the shield, where the film cassette is located, and leans his chest tightly against it. Next, you should follow the recommendations of the x-ray technician: take a full breath and hold your breath for a while. At this time, a photo is taken. In some cases, diagnosis is carried out on exhalation.
X-rays are taken in one or two projections: anterior and lateral. If detailed examination of individual areas is necessary, the patient can take other positions. The procedure is absolutely painless and lasts no more than one minute. Ready images with descriptions are delivered within 15–30 minutes; more time may be required when taking a series of images.
When performing a chest x-ray, a radiologist examines the data obtained in real time on a monitor screen.
Preparation
Typically, preparation involves freeing the area of the body that will be examined from clothing, as well as removing other “obstacles” to the passage of rays such as bandages, tubes, patches, etc. In addition, it is important to remove all metal objects from yourself and provide protection for those areas that are not subject to study (due to a special apron). For examination of a specific system or organ, there are preparation measures, which the doctor who prescribed the procedure will tell you about.
What are the harms of radiography?
X-rays must pass through an organ, structure, or body of a person to produce the final image on film. They, penetrating every cell of the body, have a destructive effect, the degree of which depends on the duration and, of course, the power of the radiation itself. In addition, it is not perceived by our senses in the form of the skin, eyes and ears, nose and tongue, as well as the vestibular apparatus, which is, in fact, dangerous. But it is worth noting that this danger is often exaggerated.
Of course, ionizing radiation can provoke a temporary change in the composition of the blood, premature aging of cells, the resumption or emergence of pathological conditions, disruption of the normalization of the process of maturation and vital activity of cells, as well as changes in the structure of proteins. That is why, to the question of how often you can do an x-ray without harm, we will answer - no way, it is there, but still not as great as it seems. Moreover, different tissues of the body have different sensitivity to this radiation.

Indications and contraindications for the study
Absolute contraindications to fluorography are childhood (up to 15 years), severe respiratory failure and the inability to stay in an upright position (bedridden patients). Fluorography is prohibited for pregnant women at any stage, and lactating women should also use radiography - it has a lower radiation dose and is more informative than fluorography. Indications for radiography for pregnant women are determined only by a doctor.
Indications for the examination are: preventive examination once a year, conscription for military service, employment, suspicion of an inflammatory process in the lungs (urgent need for fluorography), contact with a tuberculosis patient, suspicion of HIV infection, living together with a pregnant woman or newborns.