Blood tests
– the most accurate way to diagnose problems related to human health, as well as a necessary condition for the prevention of possible diseases. Under the influence of external and internal influences, blood is able to change its composition, which helps to see an objective picture of the patient’s health status, make a correct diagnosis and draw up the most correct plan for combating the disease.
There are many types of laboratory tests of blood, consisting of plasma and formed elements suspended in it. Pathological processes occurring in the body cause sudden changes in all indicators. Quite often, specialists resort to a series of studies to monitor the dynamics of the disease, as well as evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen therapy.
Clinical (general) analysis
Clinical (general) analysis
blood is prescribed both for preventive purposes and during illness. The required amount of biomaterial can be collected from a finger or a vein. Before the procedure, you must completely avoid eating and drinking 8 hours before the procedure. You can only drink drinking water without gas. The patient is advised to refrain from sports and strenuous physical activity.
A clinical blood test determines:
- The state of the body's immune system.
- Hemoglobin level.
- The presence and severity of the inflammatory process.
- The presence of allergic or parasitic diseases.
- Disorders of the blood clotting process.
Blood chemistry
Blood chemistry
gives the most complete picture of the functioning of all human organs and systems, as well as the speed of metabolic processes occurring in his body. It is recommended to conduct a biochemical blood test annually. The biomaterial for research is taken from a vein in an amount of no more than 5 ml and distributed into several test tubes. Blood sampling is performed exclusively in the morning. Before analysis it is necessary to prepare:
Sign up for blood tests
Make an appointment
Blood grouping and determination of Rh factor
Blood grouping and determination of the Rh factor is one of the important studies that can save the life of a patient as a result of an accident. This laboratory analysis is also carried out:
Biomaterial is collected from a vein in the morning. Before the procedure, the patient should follow simple recommendations - do not consume food or alcoholic beverages for 4 hours, avoid smoking, and reduce the intensity of physical activity 12 hours before the test.
Decoding the results
If the patient receives the laboratory test results in person, it is necessary to contact their doctor. Only he will be able to decipher why the leukocyte ratio has changed. It is important to consider the relationship between young and mature cells, this is of great importance. The doctor indicates why certain cells increase, decrease, or why the leukocyte formula shifts.
Any doctor who prescribed it can decipher the analysis. For example, a surgeon, oncologist, therapist, endocrinologist, cardiologist and other specialists. But it is not recommended to do this yourself; you may make mistakes.
Coagulogram (hemostasiogram) or blood test
A coagulogram (hemostasiogram) or blood clotting test helps determine the quantity and quality of prothrombins, as well as their ability to form blood clots and prevent serious blood loss, as evidenced by the rate of formation of blood clots. If clotting rates are reduced, then there is a possibility of extensive bleeding even with minor injuries, which, in turn, can lead to serious health problems. Excessive blood clotting (increased thickness) can lead to the formation of blood clots that can block the most important vessels and arteries. Most often, a coagulogram is prescribed before surgery, for the diagnosis and treatment of thrombosis, during planning of pregnancy or its pathologies, for diseases of the hematopoietic organs, bleeding, diseases of the liver and cardiovascular system. To obtain reliable parameters for this type of study, the patient must follow some rules:
Blood is drawn from a vein in the morning. Before the procedure, you can drink a glass of plain water without carbon.
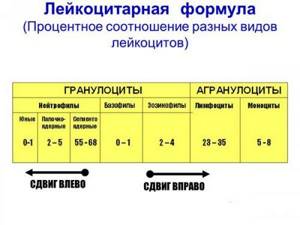
Leukocyte formula
Leukocyte formula is the percentage of various forms of leukocytes in the blood serum and the calculation of their number per unit volume. If atypical forms of cells are present, the blood is examined under a microscope. Unlike red blood cells, the population of which is homogeneous, leukocytes are divided into 5 types, differing in appearance and functions: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils.
Synonyms Russian
The ratio of different forms of leukocytes in the blood, differentiated leukocyte count, leukocytogram, leukogram, blood formula, leukocyte formula count.
English synonyms
Leukocyte differential count, Peripheral differential, WBC differential.
Research method
Flow cytometry.
Units
*10^9/l (10 in st. 9/l).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet the day before donating blood.
- Do not eat food 2-3 hours before the test (you can drink clean still water).
- Avoid physical and emotional stress and do not smoke 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
White blood cells, like other blood cells, are produced in the bone marrow. Their main function is to fight infection and respond to tissue damage.
Unlike red blood cells, the population of which is homogeneous, leukocytes are divided into 5 types, differing in appearance and functions: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils.
White blood cells are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow. They do not live long, so they are constantly renewed. White blood cell production in the bone marrow increases in response to any tissue damage, as part of the normal inflammatory response. Different types of leukocytes have slightly different functions, but they are capable of coordinated interactions by “communicating” using certain substances - cytokines.
For a long time, the leukocyte formula was calculated manually, but modern analyzers make it possible to carry out the study much more accurately in automatic mode (the doctor looks at 100-200 cells, the analyzer looks at several thousand). If the analyzer detects atypical forms of cells or detects significant deviations from reference values, then the leukocyte formula is supplemented by a microscopic examination of a blood smear, which makes it possible to diagnose certain diseases, such as, for example, infectious mononucleosis, determine the severity of the infectious process, and describe the type of atypical cells identified in leukemia .
Neutrophils, the most numerous of the white blood cells, are the first to fight infection and are the first to appear at the site of tissue damage. Neutrophils have a nucleus divided into several segments, which is why they are also called segmented neutrophils or polymorphonuclear leukocytes. These names, however, refer only to mature neutrophils. Maturing forms (young, rod-nucleated) contain a solid core.
At the site of infection, neutrophils surround bacteria and eliminate them by phagocytosis.
Lymphocytes are one of the most important parts of the immune system; they are of great importance in destroying viruses and fighting chronic infection. There are two types of lymphocytes - T and B (the leukocyte formula does not count the types of leukocytes separately). B-lymphocytes produce antibodies - special proteins that bind to foreign proteins (antigens) found on the surface of viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. Surrounded by antibodies, cells containing antigens are accessible to neutrophils and monocytes, which kill them. T lymphocytes are able to destroy infected cells and prevent the spread of infection. They also recognize and destroy cancer cells.
There are not very many monocytes in the body, but they perform an extremely important function. After a short circulation in the bloodstream (20-40 hours), they move into tissues, where they turn into macrophages. Macrophages are capable of destroying cells, just like neutrophils, and keeping foreign proteins on their surface, to which lymphocytes react. They play a role in maintaining inflammation in some chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
There are small amounts of eosinophils in the blood; they are also capable of phagocytosis, but they mainly play a different role - they fight parasites, and also take an active part in allergic reactions.
There are also few basophils in the blood. They travel to tissues where they become mast cells. When they are activated, they release histamine, which causes allergy symptoms (itching, burning, redness).
What is the research used for?
- To assess the body's ability to resist infection.
- To determine the severity of allergies, as well as the presence of parasites in the body.
- To identify the adverse effects of certain medications.
- To assess the immune response to viral infections.
- For differential diagnosis of leukemia and to assess the effectiveness of their treatment.
- To monitor the effects of chemotherapy on the body.
When is the study scheduled?
- Together with a general blood test during routine medical examinations and preparation for surgery.
- In case of an infectious disease (or suspicion of it).
- If there is a suspicion of inflammation, an allergic disease or parasite infection.
- When prescribing certain medications.
- For leukemia.
- When monitoring various diseases.
What do the results mean?
The leukocyte formula is usually interpreted depending on the total number of leukocytes. If it deviates from the norm, then focusing on the percentage of cells in the leukocyte formula can lead to erroneous conclusions. In these situations, the assessment is made based on the absolute number of each type of cell (in a liter - 1012 / l - or microliter - 109 / l). An increase or decrease in the number of any cell population is referred to as “neutrophilia” and “neutropenia”, “lymphocytosis” and “lymphopenia”, “monocytosis” and “monocytopenia”, etc.
Reference values
Leukocytes
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 6 - 17.5 *10^9/l |
| 1-2 years | 6 - 17 *10^9/l |
| 2-4 years | 5.5 - 15.5 *10^9/l |
| 4-6 years | 5 - 14.5 *10^9/l |
| 6-10 years | 4.5 - 13.5 *10^9/l |
| 10-16 years | 4.5 - 13 *10^9/l |
| More than 16 years | 4 - 10 *10^9/l |
Neutrophils
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 1.5 - 8.5 *10^9/l |
| 1-2 years | 1.5 - 8.5 *10^9/l |
| 2-4 years | 1.5 - 8.5 *10^9/l |
| 4-6 years | 1.5 - 8 *10^9/l |
| 6-8 years | 1.5 - 8 *10^9/l |
| 8-10 years | 1.8 - 8 *10^9/l |
| 10-16 years | 1.8 - 8 *10^9/l |
| More than 16 years | 1.8 - 7.7 *10^9/l |
Neutrophils, %
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 16 — 45 % |
| 1-2 years | 28 — 48 % |
| 2-4 years | 32 — 55 % |
| 4-6 years | 32 — 58 % |
| 6-8 years | 38 — 60 % |
| 8-10 years | 41 — 60 % |
| 10-16 years | 43 — 60 % |
| More than 16 years | 47 — 72 % |
Most often, the level of neutrophils is elevated during acute bacterial and fungal infections. Sometimes, in response to infection, the production of neutrophils increases so significantly that immature forms of neutrophils enter the bloodstream, and the number of band neutrophils increases. This is called a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left and indicates the activity of the bone marrow response to infection. There is also a shift in the leukocyte formula to the right, when the number of band forms decreases and the number of segmented forms increases. This happens with megaloblastic anemia, liver and kidney diseases.
Other causes of increased neutrophil levels:
- systemic inflammatory diseases, pancreatitis, myocardial infarction, burns (as a reaction to tissue damage),
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow.
The number of neutrophils may decrease with:
- massive bacterial infections and sepsis, in cases where the bone marrow does not have time to reproduce enough neutrophils,
- viral infections (flu, measles, hepatitis B),
- aplastic anemia (a condition in which bone marrow function is inhibited), B12-deficiency anemia,
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow and metastases of other tumors to the bone marrow.
Lymphocytes
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 2 - 11 *10^9/l |
| 1 - 2 years | 3 - 9.5 *10^9/l |
| 24 years | 2 - 8.0 *10^9/l |
| 4 – 6 years | 1.5 - 7 *10^9/l |
| 6 - 8 years | 1.5 - 6.8 *10^9/l |
| 8 – 10 years | 1.5 - 6.5 *10^9/l |
| 10 – 16 years | 1.2 - 5.2 *10^9/l |
| More than 16 years | 1 - 4.8 *10^9/l |
Lymphocytes, %
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 45 — 75 % |
| 1-2 years | 37 — 60 % |
| 2-4 years | 33 — 55 % |
| 4-6 years | 33 — 50 % |
| 6-8 years | 30 — 50 % |
| 8-10 years | 30 — 46 % |
| 10-16 years | 30 — 45 % |
| More than 16 years | 19 — 37 % |
Causes of elevated lymphocyte levels:
- infectious mononucleosis and other viral infections (cytomegalovirus, rubella, chicken pox, toxoplasmosis),
- some bacterial infections (tuberculosis, whooping cough),
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) and lymph nodes (non-Hodgkin lymphoma).
Reasons for decreased lymphocyte levels:
- acute bacterial infections,
- flu,
- aplastic anemia,
- taking prednisolone,
- AIDS,
- systemic lupus erythematosus,
- some congenital diseases of newborns (DiGeorge syndrome).
Monocytes
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 0.05 - 1.1 *10^9/l |
| 1 - 2 years | 0.05 - 0.6 *10^9/l |
| 24 years | 0.05 - 0.5 *10^9/l |
| 4 – 16 years | 0.05 - 0.4 *10^9/l |
| More than 16 years | 0.05 - 0.82 *10^9/l |
Monocytes, %
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 4 — 10 % |
| 1 - 2 years | 3 — 10 % |
| More than 2 years | 3 — 12 % |
Reasons for increased monocyte levels:
- acute bacterial infections,
- tuberculosis,
- subacute bacterial endocarditis,
- syphilis,
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow and lymph nodes,
- cancer of the stomach, breast, ovaries,
- connective tissue diseases,
- sarcoidosis
Reasons for decreased monocyte levels:
- aplastic anemia,
- treatment with prednisone.
Eosinophils
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 0.05 - 0.4 *10^9/l |
| 1-6 years | 0.02 - 0.3 *10^9/l |
| More than 6 years | 0.02 - 0.5 *10^9/l |
Eosinophils, %
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 1 — 6 % |
| 1 - 2 years | 1 — 7 % |
| 24 years | 1 — 6 % |
| More than 4 years | 1 — 5 % |
The most common causes of elevated eosinophil levels are:
- allergic diseases (bronchial asthma, hay fever, food allergies, eczema),
- infection by parasitic worms,
- allergic reaction to medications (antibiotics, allopurinol, heparin, propranolol, etc.).
More rare reasons for their increase:
- Lefler syndrome,
- hypereosinophilic syndrome,
- systemic connective tissue diseases,
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow and lymph nodes.
The number of eosinophils may decrease with:
- acute bacterial infections,
- Cushing's syndrome,
- Goodpasture's syndrome
- taking prednisolone.
Basophils: 0 - 0.08 *10^9/l.
Basophils,%: 0 - 1.2%.
An increase in the content of basophils is rare: with cancer of the bone marrow and lymph nodes, polycythemia vera, and allergic diseases.
The number of basophils may decrease during the acute phase of infection, hyperthyroidism, or long-term therapy with corticosteroids (prednisolone).
Also recommended
- Complete blood count (without leukocyte formula and ESR)
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Who orders the study?
General practitioner, therapist, pediatrician, surgeon, infectious disease specialist, hematologist, gynecologist, urologist.
Blood sugar test
A blood sugar test determines the level of glucose in a person’s blood, the amount of which affects the well-being and functioning of all internal organs. Conducting such a study is indicated for people suffering from diabetes, as well as those who are at risk for this serious disease. Preparation for analysis is a set of simple activities:
Sign up for blood tests
Make an appointment
Basic blood diagnostic methods
Without a blood test, it is difficult to make a diagnosis for almost any disease. This is the most accessible and fastest diagnostic method. Modern laboratories equipped with advanced equipment produce research results by the evening of the same day on which the biological materials were submitted. You can sign up for a blood test in Moscow through the city doctor portal.
What types of blood tests are there?
With any ailment - mild or serious, the blood reflects this condition. The main indicators of the main body fluid change, making it possible to identify the disease and develop a treatment algorithm. After reviewing the results of the blood test, the attending physician will prescribe a number of additional tests.
The most commonly prescribed types of blood tests are:
- clinical or general;
- biochemical;
- immunological;
- analysis for hormonal group.
Clinical (general) blood test
Blood is taken from a vein or from a finger according to the doctor’s decision. Such a study reveals the slightest deviations in the body’s activity; it will tell about inflammatory processes. During the analysis, the following is determined:
- number of leukocytes (white blood cells). Many pathological conditions are diagnosed by changes in the leukocyte formula;
- erythrocytes (red blood cells) and the amount of hemoglobin;
- hematocrit - the ratio of formed elements to volume;
- platelet count . This indicator indicates the state of the coagulation system;
- number of eosinophils . It makes it possible to determine the degree of allergization of the body, as well as identify some infections.
Blood chemistry
Blood biochemistry is a popular and most informative type of research. It makes it possible to determine the following indicators in the subject:
- glucose level . An important factor in making a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, as well as identifying other diseases associated with carbohydrate metabolism problems;
- triglycerides . A high rate indicates obesity or, on the contrary, starvation, anemia, large blood loss, poisoning, alcoholism, endocrine disorders;
- cholesterol _ The component is included in the composition of cell membranes and controls their permeability. If cholesterol is in excess, this indicates atherosclerosis, the risk of stroke and heart attack. A deficiency of the component is possible in some genetic disorders. During the study, lipoproteins - cholesterol transport complexes - are also determined;
- squirrels _ These are albumins, the level of which increases during inflammation, globulins, their amount increases with iron deficiency. Detection of immunoglobulins reports allergies. C-reactive protein indicates acute inflammation. Blood clotting proteins are also determined during the study. The detection of certain proteins or a violation of their ratio indicates a number of diseases;
- plasma enzymes . These are aminotransferases, the activity of which increases sharply in diseases of the liver and heart. Creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase report the stage of myocardial infarction;
- residual nitrogen . An increase in this indicator is observed with dehydration, tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, pneumonia, kidney disease, cirrhosis of the liver;
- pigments . The main one is bilirubin. Based on its content, liver diseases are diagnosed;
- sodium _ The content of the element decreases with dehydration, insufficient dietary intake, intense sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, taking diuretics, renal failure;
- potassium _ Deficiency of the element is recorded with dehydration, metabolic disorders, long-term use of diuretics, and kidney disease. Excess potassium is observed in burns and serious injuries;
- acid-base state . This indicator reveals acidosis or alkalosis;
- phosphates, calcium . Abnormal content of these elements indicates many diseases - kidney failure, rickets, impaired absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract.
Immunological blood test
Blood is drawn from a vein. The study makes it possible to diagnose HIV, sexually transmitted diseases, various types of hepatitis, rubella, toxoplasmosis, and measles. This analysis is used in establishing oncological diagnoses and in allergological studies.
IMPORTANT! Antibodies, immunoglobulins, specific proteins, which are found in the membranes of lymphocytes, tissue fluid and blood serum, neutralize foreign viruses, bacteria and toxins.
For immunological studies:
- determine the Rh factor;
- analyze specific immune responses;
- detect C-reactive protein;
- carry out serological tests.
Hormonal blood tests
Research in the hormonal field identifies problems in the endocrine system. Based on blood taken from a vein, the amount of hormones of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland and sex hormones.
Before taking any blood test, preparation is necessary, otherwise distorted results may be obtained. To do this, you should familiarize yourself with the rules for preparing for research.
The norms of blood parameters differ depending on the gender and age of the subject. In women, they even depend on the menstrual cycle. It is necessary to carefully study the obtained data and save it. The main thing is that only the attending physician can make a diagnosis based on test results.
As an advertisement
The most relevant in the category: Interesting
More interesting in the genre: News
Blood test for hormones
A blood test for hormones is prescribed by a specialist to determine the condition and correct functioning of many systems of the patient’s body. Hormones are biological active substances that regulate all important biochemical processes - growth, reproduction, metabolism and others. Changes in hormonal balance indicate pathological processes leading to the appearance of various diseases. As a rule, hormonal studies are recommended for suspected malfunctions of the internal secretion organs and associated abnormalities. The most common:
Blood test for hormones
taken in the morning, on an empty stomach. On the eve of the procedure, it is prohibited to drink alcoholic beverages or smoke. Eating should be stopped 8 hours before biomaterial collection. Taking hormonal medications must be stopped 7 days in advance, after consulting with a specialist. Women are advised to remember that hormonal levels change depending on the menstrual cycle. The most favorable days for taking hormonal tests are considered to be from 5 to 7 days from the first day of menstruation.
Reasons for the shift
The following factors are identified that lead to a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left:
- infectious diseases of various origins, including systemic infections (mumps, salmonellosis, meningococcus);
- pus production;
- inflammatory pathologies of infectious, autoimmune and other origins;
- condition after surgical interventions and mechanical damage;
- death of part or all of an organ (burn, heart attack, stroke);
- intoxication with ethanol, salts of heavy metals, toxic substances;
- malignant neoplasms.
If a large number of immune cells are present in the blood, its rejuvenation occurs. This may indicate malignant pathologies. For example, leukemia, spread of metastases.
A shift of the leukocyte formula to the left is considered normal in the following conditions:
- recovery of the body after illness or surgery;
- heavy physical activity;
- bearing a fetus.
Patients are identified who constantly have a slight shift in their leukocyte count to the left. These include only a small percentage of people from all over the planet. At the same time, there is no pathology in their body.
It is impossible to determine the cause of the condition by neutrophilia alone. It is necessary to combine this symptom with other signs to suggest a diagnosis. Neutrophilia develops in different ranges, mild, moderate and severe. The latter is considered the most unfavorable, developing in conditions that pose a threat to human life and health.
Immunological blood test and allergological studies
Immunological blood tests and allergological tests help assess the state of a person’s immune system, the presence of antibodies in his blood, and also determine the allergological status. This research method is recommended for use in cases where the patient is concerned about:
Blood is taken for examination from a vein in the morning, on an empty stomach. It is recommended to stop eating 12 hours before the procedure, and one day to exclude fatty and spicy foods, as well as alcohol, from the menu. Women should not get tested during their period. If the patient is prescribed special medications, then the doctor should be warned about this.
Blood test for PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
A PCR (polymerase chain reaction) blood test allows you to correctly diagnose any viral or bacterial infection at an early stage of the disease. Typically, this laboratory test is prescribed for serious pathological conditions:
You can undergo a similar study to determine the likelihood of infection after accidental unprotected sexual contact.
and during pregnancy in order to prevent diseases that can cause abnormalities in the development of the fetus. Preparation for a PCR blood test depends on the type of pathogen and the nature of the suspected disease. General recommendations are to exclude spicy and fatty foods and alcohol from the menu the day before the procedure. Blood is drawn from a vein in the morning, on an empty stomach. However, it is believed that the accuracy of the results does not depend on whether the patient had breakfast before the test or not.
Sign up for blood tests
Make an appointment
What do granulocytes say?
Part of the leukocytes are granulocytes, which get their name due to the presence of granules. There are three types of cells: neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. The types of granulocytes differ from each other due to the color of the granules and the structure of the nucleus.
The granules store immune substances that are important for protecting the body. Thanks to them, cells participate in inflammatory processes. The job of granulocytes is to absorb proteins and chemicals. Granulocytes also digest them.
The cells mature in the bone marrow, where the resulting quantity is stored for another 3-4 days. Mature cells enter the blood, where they circulate for 6 hours. After the end of the cycle, granulocytes enter the tissues, where they perform their functions.
The largest number of leukocytes are neutrophils, of which there are always about 1010 in the blood. If a bacterial infection enters the body, neutrophilia begins - an increased amount of neutrophils in the blood. The number of cells that appear depends on the number of harmful bacteria.
The duration of stay of neutrophils in the body is only 4 days, which is why still immature cells (band cells, metamyelocytes, and others) enter the body. This phenomenon is called a “shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.” With neutropenia (reduced number of neutrocytes), the body is less protected from infections.
About 5% of leukocytes are eosinophils, the number of which depends on adrenal hormones. In the morning there are the largest number of them. They are stored in the layer under the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. A quantity above the norm indicates that the following processes are occurring in the body:
- Infestation with parasites;
- Allergy;
- Autoimmune processes.
Medical offers to sign up for diagnostics and tests. In our laboratory it is possible to take all types of tests in Tula. Tel. for recording.
The smallest number (less than 1%) are basophils. They play a role in the release of histamine during allergic reactions. It is these cells that are responsible for itching, redness, irritation and bronchial spasms.
Depending on the location of basophils in the body, the following reactions differ:
- Bronchial asthma;
- Rashes
- Hives;
- Quincke's edema (swelling of the larynx).
Blood test for hCG
A blood test for hCG is the most popular test among women today. This method allows you to quickly and accurately determine whether a patient is pregnant at the earliest stages.
HCG is a human chorionic gonadotropin hormone that is produced by the chorion of the embryo. The level of this hormone in the blood indicates the onset of pregnancy or its absence. You can take the test starting from the first day of missed menstruation, or 14 days after sexual intercourse. You should refrain from eating 3 hours before the procedure. Blood is drawn from a vein. The results of the analysis can be known within a few hours.
Blood test for parasites
A blood test for parasites is the most accurate diagnostic method, allowing you to prevent serious inflammation of internal organs caused by various types of parasites entering the body. Studies are prescribed for adults and children. The material is taken from a vein. Preparing for analysis:
Study for the presence of tumor markers
Testing for the presence of tumor markers is one of the methods that determines the likelihood of a tumor process developing in the body. Using this analysis, it is possible to detect oncological diseases in the early stages, as well as prevent their relapses. A study for the presence of tumor markers is prescribed by a specialist. Preparation for the procedure includes excluding spicy and fat-rich foods from the diet, smoking and alcohol 3 days before the analysis. The patient is prescribed rest and minimal physical activity. You should not take medications other than vital ones prescribed by your doctor. Blood is drawn from a vein in the morning.
Leukocytes - what are they?
Leukocytes are the body’s protective army. They make up a large group of white blood cells whose purpose is to rid the body of infections. Leukocytes take part in allergic, autoimmune and tumor processes. White cells are divided into types, which are responsible for their specific function.
A complete blood count shows the total number of cells. The leukocyte count is responsible for accurately identifying the cell types that cause an increase (leukocytosis) or decrease (leukopenia) in white cells in the blood. The formula can be found in an expanded form of a blood test. There are five types of cells, their number and relationship to each other.
The blood test is assessed using an automatic analyzer, which calculates the percentage of each type of the total number of cells. The device also calculates the white blood cell count per liter of blood.
Additionally, a visual assessment of the blood smear using a microscope may be required. A “manual” check of analyzes may be necessary in the following cases:
• Changes in the leukocyte formula; • There are altered or immature cells; • Signs of anemia are visible; • Reduced platelet count.
If the analysis is processed manually, only the percentage will be visible. Each type of assessment allows you to correctly diagnose diseases, understand their causes and prescribe the correct treatment.
Blood test for trace elements
A blood test for microelements allows you to most accurately determine the reserves of useful substances in the human body, identify disturbances in water-salt balance and various types of rheumatic conditions. Insufficient content of certain groups of vitamins and enzymes or their excess can cause the development of pathologies or deterioration of well-being. When testing blood for microelements, biomaterial is taken from a vein, exclusively in the morning and on an “empty” stomach. Before the procedure, eating and drinking alcohol is prohibited; it is recommended to limit physical activity 24 hours before. It is important to remember that a blood test for trace elements should be performed before starting a course of taking any medications or two weeks after stopping them.
Modern medicine offers a large selection of various blood tests that make it possible to identify various diseases even before the first clinical symptoms appear. With their help, the effectiveness of treatment and the correctness of selected medications for existing pathologies are assessed. For a correct diagnosis and accurate results, you need to know what blood tests exist, how and when they need to be taken.
Monocytes are killers in the body
Monocytes make up 10% of white blood cells and perform the main “destructive” function of the immune system. Also called tissue macrophages. They are formed in the bone marrow within 5 days and immediately go out to “hunt” without leaving a reserve. They quickly penetrate tissues and destroy foreign proteins. A large number of monocytes are found in the liver, spleen and lungs. They exist for about 60 days and process foreign proteins into antigens, which are subsequently dealt with by immune cells.
An increase in monocytes in the blood, or monocytosis, indicates that there are chronic infections in the body. They can also talk about infections that are located in the cells themselves: viruses, chlamydia and mycoplasma.
Blood test cost
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 090001 | Total protein | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090002 | Albumen | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090003 | Protein fractions | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 345.00 rub. | 690.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090004 | Creatinine | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090005 | Urea | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090006 | Uric acid | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090007 | Total bilirubin (TB) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090008 | Direct bilirubin (DB) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090009 | Total cholesterol | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090010 | HDL cholesterol | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090011 | LDL cholesterol | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 345.00 rub. | 690.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090012 | Triglycerides | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090014 | Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, GPT) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090015 | Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, GOT) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090016 | Gamma glutamine transferase (GGT) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090017 | Alkaline phosphatase (ALCP) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090018 | Acid phosphatase* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 345.00 rub. | 690.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090019 | Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090020 | Alpha amylase | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 345.00 rub. | 690.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090021 | Creatine kinase | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090022 | Creatine kinase-MB* | blood (serum) | count | 5-6 hours**** | 1725.00 rub. | CITO only | |
| 090023 | LDH 1st fraction (a-HBDH) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090024 | Myoglobin | blood (serum) | count | 5-6 hours**** | 2345.00rub | CITO only | |
| 090025 | Lipase | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 345.00 rub. | 690.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090026 | Cholinesterase* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090027 | Iron | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090028 | Total iron binding capacity of serum (TIBC) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090029 | Vitamin B 12 (Cyanocobalamin)* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1035.00 rub. | 2070.00rub | 0 |
| 090030 | Folic acid* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1035.00 rub. | 2070.00rub | 0 |
| 090031 | Ferritin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 920.00 rub. | 1840.00rub | 0 |
| 090032 | Transferrin* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 690.00 rub. | 1380.00rub | 0 |
| 090033 | Calcium | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090034 | Phosphorus | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090035 | Magnesium | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090036 | Ca2+/Na+/K+/Cl- | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 690.00 rub. | 1380.00rub | 0 |
| 090037 | Glucose | blood with sodium fluoride | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090040 | Rheumatoid factor RF | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 575.00 rub. | 1150.00rub | 0 |
| 090041 | Antistreptolysin-0 Asl-0 | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 575.00 rub. | 1150.00rub | 0 |
| 090042 | Glycosylated hemoglobin (HB A1C) | blood with EDTA | count | 1-2 k.d. | 690.00 rub. | 1380.00rub | 0 |
| 090043 | Zinc | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 345.00 rub. | 690.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090044 | Fructosamine | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1380.00 rub. | 2760.00rub | |
| 090045 | Troponin I | blood (serum) | count | 5-6 hours**** | RUR 2530.00 | CITO only | |
| 090046 | Apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI) | blood (serum) | count | 3-5 k.d. | 690.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 090047 | Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) | blood (serum) | count | 3-5 k.d. | 690.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 090048 | Pancreatic amylase | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 460.00rub | 920.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090049 | Erythropoietin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1380.00 rub. | 2760.00rub | 0 |
| 090051 | Lactic acid (lactate)* | blood with sodium fluoride | count | 1 k.d. | 920.00 rub. | 1840.00rub | 0 |
| 090052 | Unsaturated iron binding capacity of serum (IBC) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 460.00 rub. | 920.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090053 | Haptoglobin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1380.00 rub. | 2760.00rub | 0 |
| 090054 | Ceruloplasmin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1035.00 rub. | 2070.00rub | 0 |
| 090055 | Alpha-2 macroglobulin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1035.00 rub. | 2070.00rub | 0 |
| 090057 | Lipoprotein(a) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 2300.00 rub. | 4600.00rub | 0 |
| 090059 | C-reactive protein (Highly sensitive method) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 805.00 rub. | 1610.00rub | 0 |
| 090061 | VLDL - cholesterol | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090068 | Ca2+ | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 460.00rub | 920.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090069 | Na+/K+/Cl- | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 460.00rub | 920.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090070 | Cystatin C | blood (serum) | count | 3-5 k.d. | 4600.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 090078 | Vitamin B12, active (holotranscobalamin) | blood (serum) | count | 1-2 k.d. | 2300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
All our services and prices
Sign up for blood tests
Make an appointment