Article for the “bio/mol/text” competition: Despite the rapid development of medicine, tuberculosis is in no hurry to lose its position, remaining not only relevant and deadly, but also a difficult to diagnose disease. But timely diagnosis is an opportunity to reduce the number of patients with active forms and influence the spread of infection! Traditionally, the Mantoux 2 TE test is used to diagnose tuberculosis. However, in recent years, alternative methods have appeared - Diaskintest and the IGRA (Interferon Gamma Release Assay) blood test. What kind of tests are these and are they able to completely replace the “old lady” Mantoux test, which recently turned 110 years old?
Competition "bio/mol/text"-2018
This work was published in the “Biopharmaceutics” category of the “bio/mol/text” competition 2018.
The nomination partner is medical.
The general sponsor of the competition is: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
The audience award was sponsored by the medical genetics center Genotek.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"
The problem of treatment and diagnosis of tuberculosis still remains extremely relevant. And it’s not just that Koch’s bacillus (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) develops amazing resistance to antibiotics: the situation is also complicated by the long incubation period of the disease. In fact, we are dealing with a pathogen whose carriers can be completely healthy for a long time! In addition, there are not only active forms of tuberculosis, but also latent carriage. And it is extremely difficult to predict whether it will go into an active form and when it will happen. However, not everything is so bad, because even latent carriage can be diagnosed and, if necessary, treated. The only question is that an accurate and effective method for diagnosing tuberculosis processes has not yet been developed. Therefore, for many years, scientists have been trying to develop an “ideal” test that would distinguish tuberculosis from post-vaccination immunity and latent carriage, would have a low cost and would not depend on the human factor.
However, a diagnosis is not yet a diagnosis, and the result of any test is not the ultimate truth. The diagnosis is still made based on several components:
- clinical picture;
- having contact with a tuberculosis patient;
- X-ray of the lungs, fluorography or computed tomography;
- results of diagnostic tests.
However, most of these methods diagnose tuberculosis after the fact - only screening tests help identify individuals at high risk of developing the disease or with an incipient process. And for more than 100 years, the main method of mass diagnosis of tuberculosis has been the Mantoux 2 TE tuberculin test (containing 2 tuberculin units). The test is controversial, with many false positive results, but it is the one that is used all over the world and there are no plans to abandon it yet.
T POTS TB - diagnosis of tuberculosis using the t-spot.tb method in St. Petersburg
T-SPOT.TB is an immunological method for diagnosing tuberculosis. The method is in many ways similar to the quantiferon test; it takes 3-4 days. To conduct it, you need the blood of the person being studied.
Attention! Testing for T-SPOT during quarantine measures will be carried out only on Wednesdays .
We also inform you that due to the “defect” of the T-SPOT.tb test systems, this analysis will become more difficult in the near future. As an alternative, we offer the Quantiferon test , which in all respects, including the cost of the study, is not inferior to T-SPOT. The method is based on the quantitative determination of interferon released by blood T cells in response to the introduction of the tuberculosis bacillus.
The name T-SPOT.TB stands for:
- the letter T stands for T-lymphocytes, blood cells, based on the response of which the study is carried out;
- The word SPOT is an English translation meaning "spot". As a result of a laboratory experiment, spots are formed in the well, each of which marks a T-lymphocyte;
- .TB is the international abbreviation for tuberculosis.
In Russia, the use of the T-SPOT technique was approved in 2012 by Federal Law - 2012/648.
This method of determining carriage of tuberculosis is very sensitive and informative; it allows one to exclude false-positive reactions to carriage of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in cases where most tests are erroneous or inaccurate. According to various estimates and in different regions of the world, the sensitivity of T-SPOT is estimated from 87 to 97%, the information content also reaches 97%. As you know, diagnosing tuberculosis in HIV-infected people is complicated, and T-SPOT in these cases is very informative and reliable. There are other cases in which the use of this test is preferable.
CASES OF PREFERRED USE OF T-SPOT
- in children vaccinated with BCG who have a false-positive Mantoux test. In this case, it is valuable to do this minimally invasive test before the chest x-ray.
- in persons with allergic and autoimmune diseases;
- in medical workers, people who travel a lot, military personnel, pregnant women;
- for prisoners or those arriving from places of detention;
- in patients with drug addiction;
- in persons in contact with tuberculosis patients;
- in patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, such as glucosteroid or radiation therapy, treatment with replacement of renal function;
- in the presence of chronic diseases accompanied by decreased or depleted immunity, such as diabetes mellitus, the already mentioned HIV, or pneumoconiosis;
- if extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis are suspected.
Attention! BCG vaccination does not affect the results of the T-SPOT test.
It is important to remember that T-SPOT is a method of quantitatively diagnosing the presence of tuberculosis in the body, but does not make it possible to distinguish the active form of tuberculosis from the latent one.
T-SPOT FOR HIV. ADDITIONAL DIAGNOSTIC CAPABILITIES
This test in HIV carriers is of particular importance in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. The immunodeficiency virus infects precisely those cells that are used for diagnosis in any of the IGRA tests, which include T-SPOT, i.e. CD4 cells. Research has revealed that even in the later stages of HIV development, when the number of CD4 lymphocytes no longer exceeds one hundred per mm3, the detection of tuberculosis using T-SPOT remains very high.
EXPERIENCE OF OTHER COUNTRIES
T-SPOT was developed at Oxford University and Europe was the first to adopt it; in 2004, it was officially included in the standards for diagnosing tuberculosis in the European Union. The USA and Canada included T-POTS in official diagnostics in 2005, South Korea in 2006, Taiwan in 2009, People's Republic of China in 2010, Russian Federation and Japan in 2012.
DIFFERENCES OF T-SPOT FROM PCR STUDY
PCR is a DNA test, and since it is sputum that is examined, PCR excludes the possibility of identifying extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis. It turns out that T-SPOT is a universal method for diagnosing tuberculosis, and sputum PCR is specific. This is probably why T-SPOT, along with the quantiferon test, is called the “Gold Standard” in the diagnosis of tuberculosis throughout the civilized world.
Mantoux test
The Mantoux 2 TE test is a specific skin test based on tuberculin. Tuberculin is a mixture of various antigens obtained from inactivated Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its metabolic products (proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids - about 200 items in total [1], [2]). The preparation for the Mantoux test also contains phenol as a preservative, Tween-80 stabilizer, salts of phosphate buffer solution and sodium chloride.
The meaning of this test is that the human body infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis will respond to the introduction of its particles by producing T-lymphocytes [3]. If a person is healthy, such a reaction will not occur. However, there is one thing: the antigens that make up tuberculin are characteristic not only of Koch’s bacillus, but also of other strains of mycobacteria, including M. bovis - the basis for the BCG vaccination. Therefore, the Mantoux test does not “distinguish” well between those vaccinated with this vaccine and those actually sick with tuberculosis.
Three types of tuberculin are used in the world (Fig. 1): the Danish drug PPD (purified protein derivative) RT 23 , the American PPD-S and the Russian one - PPD-L . They differ in the types of mycobacteria from which they were obtained: in the production of Danish and American drugs, only M. tuberculosis is used, and in the production of Russian drugs, a mixture of M. tuberculosis and M. bovis (mycobacterium that causes tuberculosis in cattle; based on this strain The BCG vaccine was developed. The difference in the composition of tuberculin determines different limits for a positive result: 15 mm for children vaccinated with BCG, and no more than 10 mm for unvaccinated children under 5 years of age for the Danish drug, no more than 10 mm for the American and 5 mm for the Russian [4].
Figure 1. Tuberculin preparations
Nationwide shortage of tuberculin skin test antigens
Diagnosis using the Mantoux test is carried out as follows: a small amount of tuberculin is injected under the skin just above the wrist and after 72 hours the reaction is assessed, which is considered positive if a swelling (papule) more than 5 mm in diameter appears at the injection site.
Depending on its size, the degree of reaction is distinguished from negative (0–1 mm) to pronounced, or hyperergic (17 mm or more in children and adolescents, 21 mm or more in adults) [5]. And here the difficulties begin, because those vaccinated with BCG have a positive Mantoux reaction [6]! Moreover, the larger the post-vaccination scar, the higher the sensitivity to tuberculin [7]. Therefore, in BCG vaccinated people, not only the diameter of the papule is assessed, but also the size of the post-vaccination scar (Table 1). Table 1. Ratio of papule and scar size after BCG vaccination. [8]
| Time elapsed since BCG vaccination | Scar size after BCG | Vaccinated immunity (mm) | Unclear reason | Suspicion of infection |
| 1 year | 6–10 mm | 5–15 mm | 16 mm | More than 17 mm |
| 2–5 mm | 5–11 mm | 12–15 mm | More than 16 mm | |
| 0 mm | 2–4 mm | 5–11 mm | More than 12 mm | |
| 2 years | Regardless of size | Reduction in the size of the papule or its previous size | Increase in size by 2–5 mm from the previous positive result | The reaction changes to positive or the papule increases by more than 5 mm |
| 3–5 years | Regardless of size | 5–8 mm or reduction in papule size | Increase in size by 2–5 mm over the past year or no tendency to decrease | Change to a positive (5 mm) reaction or increase in papule by 6 mm; 12 mm for the first test; change from the previous size by 2–4 mm or a size of 12 mm |
| 6–7 years | Regardless of size | 0–4 mm | 5 mm | 6 mm or more |
| 7–9 years | If the child was revaccinated with BCG at the age of 7, the Mantoux test becomes positive again and the norms are repeated. | 0–4 mm | 5 mm | 6 mm or more |
| Adults | Negative reaction, redness of any diameter; papule up to 4 mm | More than 5 mm |
Of course, the method of assessing the result is quite subjective. But most importantly, the papule must be measured correctly, recording only the size of the convex part and ignoring the redness around it (Fig. 2).
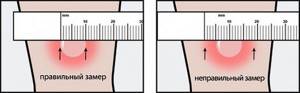
Figure 2. Correct and incorrect estimates of papule diameter
“Should I worry if the size of the mantu is 10 mm”
However, this is not the main disadvantage of the Mantoux test: the problem is that with its help it is difficult to distinguish post-vaccination immunity from the disease, and the cost of an error is an “unnecessary” course of antibiotics. Therefore, most often the result is only the first step, only a suspicion of tuberculosis. Interestingly, in severe cases of the disease, due to an inadequate T-cell response, there is usually no reaction to tuberculin [6], however, this phase of the disease is already clearly visible both in the clinical picture and on the radiograph.
Another difficulty with the diagnostic capabilities of the Mantoux test is that they depend on the lower limit of a positive result: the lower the limit, the more false positive reactions will be observed. For example, in Russia the threshold value is a papule of 5 mm. This leads to overdiagnosis—a large number of recorded reactions, but ultimately to a low percentage of actually detected cases of infection [4].
In general, it is not surprising that recently the informativeness of the tuberculin test has been constantly questioned. Moreover, it can cause allergic reactions not related to tuberculosis, so more and more healthy, but allergy-prone children are forced to go to a tuberculosis clinic in the hope of finding out the reason for the positive reaction. Finally, many factors can influence the test result: recent infections, chronic diseases, medications, changes in hormonal levels, or immunity to non-tuberculous mycobacteria [7].
If we talk about the advantages of the Mantoux test, then in addition to low cost, they will be the ability to detect tuberculosis in the early stages of development (except for persons with immunosuppression and young children under two years of age [7]) and a higher diagnostic value in those unvaccinated with BCG compared to vaccinated ( from 50% and below versus 65.4% [6], [9]).
Myths about the Mantoux test
- Tuberculin is harmful to health because inactivated mycobacteria cause allergies and “load the immune system . There is a small grain of truth here: as a drug, tuberculin can cause allergic reactions not associated with infection, but there can be no talk of any “load”, if only because antibodies are not produced against it.
- The Mantoux 2 TE test is toxic because the drug contains phenol . In the tuberculin test, phenol is a preservative that inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi [5]. Moreover, its amount is so small (0.00025 g) that it cannot have any effect on health. Phenol is a metabolic product of bacteria that inhabit our intestines, so it is formed in the tissues of the body, enters the blood and is excreted in the urine. Approximately 0.1–0.15 g of phenol is excreted daily, which is many times greater than the amount contained in the preparation for the Mantoux test.
- The Mantoux test is done only in third world countries. This is not true: the tuberculin test is done all over the world, including the USA, Canada, Germany, Denmark and the Netherlands. However, due to the low incidence in these countries, tuberculin testing is usually carried out only in risk groups.
"Diaskintest"
Science, however, does not stand still, and alternatives to the Mantoux test exist. The only question is how alternative they are. After decoding the genome of M. tuberculosis in 1998, it became possible to develop completely new tests: the domestic skin test “Diaskintest” and IGRA blood tests. However, Diaskintest is the one that most claims to be a substitute test for the Mantoux test.
Compared to the tuberculin test, Diaskintest is a big step forward. And all because it does not contain hundreds of antigens, but only the recombinant protein CFP10-ESAT6 in a standard dilution, which does not react either to the vaccine strain of M. bovis or to most non-pathogenic mycobacteria - it is mainly sensitive only to Koch’s bacillus . In other words, only this protein can be used to diagnose an infection, which indicates the presence or absence of cellular immunity to M. tuberculosis. Diaskintest is administered intradermally and the result is checked after 72 hours.
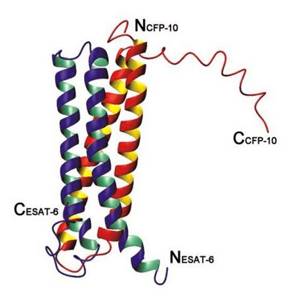
Figure 3. ESAT-6 and CFP-10 antigens
"Tuberculosis: the causative agent"
In the M. tuberculosis genome, the ESAT-6 and CFP-10 proteins are encoded in the RD1 region. They are expressed during the reproduction of mycobacteria and are associated with its virulence; therefore, the immune response to these proteins reflects the activity of the infectious process [10]. As part of Diaskintest, they are presented in the form of a recombinant protein from two related antigens ESAT6 and CFP10 (Fig. 3), synthesized by a genetically modified bacterial culture Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)/pCFP-ESAT [6]. Using a similar technology, another drug was obtained - Danish C-Tb , but it has a different ratio of ESAT-6 and CFP-10, and it is less sensitive compared to the Russian development [4].
Due to the fact that Diaskintest does not contain a cocktail of polysaccharides, lipids and proteins, but only a synthetic antigen plus excipients (phenol, sodium chloride, Tween-80), it is more highly specific than the preparation for the Mantoux test. That is, with its use, fewer false-positive results are recorded, as well as allergic reactions of a non-infectious nature [2].
As for assessing the activity of the tuberculosis process, in this “Diaskintest” is head and shoulders above its competitors, because a gradation of positive results has been developed for it (Table 2).
That is, the more pathogen in the body, the larger the size of the papule. This means that in the majority of tuberculosis patients the reaction to this test is more pronounced than in latent carriers (the only thing is that here again there is a subjective assessment of the result). Let's add to this the fact that Diaskintest allows us to identify carriers with a high risk of developing tuberculosis and reduce the amount of unnecessary therapy [11], as well as reducing the severity of the reaction to it in patients receiving a course of antibiotics [4], and we will get a very valuable competitive advantage over tuberculin test. Table 2. Assessment of response to Diaskintest. Compiled based on information from the instructions.
| Reaction | Size of hyperemia and papules |
| Negative | No papule and/or hyperemia, “prickly reaction” up to 2 mm |
| Doubtful | The presence of hyperemia in the absence of a papule |
| Positive: | Papule of any size: |
| - mild positive reaction | Up to 5 mm |
| - moderate reaction | 5–9 mm |
| - pronounced reaction | 10–14 mm |
| - hyperergic reaction | 15 mm or more, as well as with vesicular-necrotic changes and (or) lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, regardless of the size of the infiltrate |
However, Diaskintest also has disadvantages:
- It is not sensitive to M. bovis and, therefore, cannot diagnose the tuberculous process caused by this type of mycobacterium. Of course, the number of such cases is small, but it still reduces the effectiveness of the test.
- According to studies, Diaskintest has a fairly high sensitivity in detecting tuberculosis infection both in children - 90-96.7%, and in adults - 78-81.5% [2]. However, there remain approximately 10–20% of cases that it misses.
- Diaskintest can be negative in tuberculosis patients with severe impairments of the immune system due to severe disease, as well as in HIV-infected patients (in this case, the sensitivity of the test depends on the level of CD4+ T-lymphocytes [2]).
What you need to know about skin testing?
- The preparation for the Mantoux 2 TE test and Diaskintest are markers of tuberculosis allergy, that is, they are “allergens”. Tuberculosis allergy is associated with an immune response to M. tuberculosis, which makes the body sensitive (sensitized) to even small amounts of mycobacterium. Using skin tests containing an irritating factor (inactivated particles of Koch's bacillus), this process can be recorded. Infectious allergy is a delayed reaction, so the test result is not assessed immediately, but after 72 hours.
- The skin reaction to these tests is a marker of a T-dependent immune response, which involves CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and associated proinflammatory cytokines, IFNγ, TNF, etc. Therefore, skin tests are also sensitive to latent carriage, when the amount of mycobacteria is extremely small [4], [6].
- As can be seen from tables 1 and 2, the results of skin tests are observed over time, if necessary, comparing the values of previous years. Therefore, there is no point in doing a tuberculosis diagnosis, as they say “for show”: only for a medical card for kindergarten or school - it must be done annually (or at least once every two years).
- In the interpretation of the results of skin tests, there is the concept of a turn - a sharp increase in the diameter of the papule by six or more millimeters compared to the previous test. In addition, the transition of a negative reaction to a positive one, not related to BCG vaccination, is considered a turn. A Mantoux test does not always mean infection (it can also be of an allergic nature), however, to clarify the situation, an additional examination and consultation with a phthisiatrician is usually prescribed.
What to choose: Mantoux test or Diaskintest?
If we compare the diagnostic effectiveness of tests, then “Diaskintest” gives a significant head start to the tuberculin test. Nevertheless, among phthisiatricians there are adherents of both the Mantoux test and Diaskintest. However, comparative studies do not speak in favor of tests with tuberculin - after all, a reaction to them does not mean illness or infection with mycobacteria. Plus, mass BCG vaccination sharply reduces their diagnostic abilities [6].
An example is a domestic study that compared the results of skin tests [6].
It turned out that in adolescents who lived in close contact with patients with an open form of tuberculosis (bacterial excretors), positive reactions to the administration of tuberculin were observed in 77.9% of cases, while the disease was detected only in 4.9%. At the same time, positive reactions to Diaskintest were noted in only 5.6%, of which tuberculosis was detected in 62.5% of cases [6]. According to Russian scientists, the effectiveness of Diaskintest in detecting active tuberculosis can exceed the effectiveness of the Mantoux 2 TE test by 40 times (Table 3) [11]! Table 3. Comparison of the results of Diaskintest and the Mantoux test in different situations. [9]
| Mantoux test result | Diaskintest result | |
| Fine: | ||
| in those unvaccinated with BCG | Negative | Negative |
| in those vaccinated with BCG | Weakly positive or positive without hyperergy | Negative |
| If infected: | ||
| in those unvaccinated with BCG | Positive | Weak or positive depending on the activity of the process* |
| in those vaccinated with BCG | Strongly positive | Weak or positive depending on the activity of the process* |
| * The situation (10–20% of cases) when the Diaskintest result is false negative is not taken into account. | ||
Difference from Mantoux?
The main difference between Diaskintest and the classic Mantoux is the accuracy of the data. When performing Mantoux, the accuracy of the result ranges from 50 to 70%. Tests have shown that the intradermal test is 90% accurate.
In addition, each test has a different composition, which contains different active ingredients. In Mantoux, the main active element is tuberculin, contained in tuberculosis bacteria. However, this protein is present not only in tuberculosis, but also in microorganisms similar to the disease. Diaskintest contains as its main element a protein that is found only in this disease. Therefore, the reaction to the tests is different. With a positive Mantoux test, there is a high risk of the presence of bacteria that are not the causative agents of tuberculosis.
If you receive a positive result after Diaskintest, you can be completely sure of infection with tuberculosis, which means you can apply the correct treatment in a timely manner.
Thus, the method shows more accurate results in detecting a dangerous disease, applying treatment to avoid serious complications. examination practice shows that Diaskintest is effective at any, even the earliest stages of tuberculosis
Blood tests for tuberculosis: pros and cons
The discovery of M. tuberculosis-specific antigens allowed the development of laboratory tests for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. These are the well-known IGRAs (Interferon-Gamma Release Assays), which include T-SPOT®.TB and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tub (“Quantiferon”).
The technology for carrying them out is quite simple: venous blood is taken from the patient, mixed with the proteins ESAT-6, CFP-10 and TB 7.7, and then the reaction is observed. That is, the number of T-lymphocytes (T-SPOT®.TB) or gamma interferon (“Quantiferon”) [12].
Many unreasonably consider these tests to be the “gold standard” for diagnosing tuberculosis and its latent forms, although their results can only indirectly indicate active infection with mycobacteria or carriage - processes that IGRA analyzes do not distinguish [12]. And if we rely on the guidelines of the WHO, as well as the European Center for Disease Control and Prevention (ECDC), there are no “gold standards” in diagnosing latent forms of tuberculosis. Just as there is no adequate model of latent tuberculosis infection. Therefore, to assess the limits of the results of IGRA tests, it is necessary to use so-called “surrogates” - testimonies of people with confirmed active tuberculosis [12]. And this only complicates the situation, because patients with tuberculosis have reduced cellular immunity, and their indicators cannot serve as a basis for assessing the diagnosis of latent infection [6].
In addition, a negative IGRA blood test result does not guarantee the absence of the disease; They are also not immune to false results. For example, when testing with Quantiferon, false negative results are possible:
- in the early stages of infection;
- in immunodeficiency conditions;
- due to improper blood collection or transportation;
- due to errors during decoding of results.
I will add that IGRA tests require high-quality equipment, special reagents and qualified personnel, so their cost is quite high.
In addition, compared to skin tests, a significant disadvantage of these tests is the in vitro determination of only interferon-gamma production or T-cell activity. Therefore, in countries with high incidence (and Russia is undoubtedly one of them, with an indicator of more than 50 patients per 100,000 population [13]), IGRA analyzes do not have any additional advantages [12]. Moreover, their ability to diagnose the tuberculosis process ranges from 42–90% for different age groups, and they do not mark latent carriage [12]. In other words, for residents of our country, blood tests for tuberculosis are generally a waste of money, although in countries with low incidence (USA, Canada, Western Europe) they are more informative and are recommended to replace tuberculin tests for those vaccinated with BCG [14].
There are more than half a billion latent carriers of M. tuberculosis living in the world. Moreover, not every one of them ends up getting sick, because the proliferation of mycobacteria is restrained by the immune system. For example, out of 100 children infected with Koch bacillus, only one develops an active form of tuberculosis, so diagnostic tests are aimed not only at identifying latent carriers, but also at assessing the risk of developing the disease [15].
How else to test a child for tuberculosis without Mantoux, what tests to take
There are several other ways to check a child for tuberculosis without Mantoux:
- Radiography is a fairly informative research method, but is absolutely not suitable for young children. It negatively affects the child’s development process, therefore it is prescribed only in exceptional cases. X-ray shows existing lesions in the lungs, does not reveal other forms of the disease, and gives an almost instant result.
- Quanteferon test - has no contraindications, is completely safe, provokes a response of the immune system to tubinfection. A positive test result does not always confirm the presence of infection in the body, and a negative test result does not at all exclude active disease. Can be used to diagnose the latent form of tuberculosis and immediately after BCG placement. The reliability of the result is 99%, but there is also a high probability of receiving an erroneous answer.
- The Suslov test is a blood test suitable for diagnosis in children with a history of allergies and at a young age. The test is absolutely safe, but has low sensitivity to antibodies. It is considered rare, and a disease localized in the lungs is almost impossible to detect using this method.
- Diaskintest - based on the reaction of the skin to a specific tuberculosis protein, is considered a complete analogue of the Mantoux test, but as improved as possible. Doctors evaluate the result after 72 hours - they measure the diameter of the papule. The method is simple, accurate, but has a high probability of obtaining a false negative result.
- Ziehl-Neelsen technique - the patient donates saliva for testing. The analysis is complex and involves several chemical reactions. It is safe and can be performed in case of existing allergies and chronic internal pathologies. The result will be a simple recording of the presence of Koch's bacillus without a clear definition of the stage of the disease and localization.
We recommend reading about whether it is necessary to make Mantoux. From the article you will learn when and why Mantoux is made, whether it is necessary to use it for kindergartens and schools, when you don’t have to do a test. And here is more information about how to write a refusal from Mantoux.
The Mantoux test is not the only method for diagnosing tuberculosis; parents have the right to choose blood tests. Their results can be used for admission to school and kindergarten, in most cases they will be more reliable.
Blood tests vs skin tests: comparison of effectiveness
When assessing the effectiveness of tests for diagnosing tuberculosis, two parameters are most often taken into account: sensitivity and specificity. Sensitivity refers to the ability of a method to identify individuals with the disease or carriers at high risk of developing tuberculosis. Specificity is the ability of the test to correctly identify people who do not have tuberculosis (that is, this parameter characterizes the risk of erroneous false-positive results) [12].
According to studies, IGRA blood tests have a fairly high specificity, but problems with sensitivity (Table 4), so they cannot become the main tool in the diagnosis of tuberculosis, especially in countries with high incidence.
As for Diaskintest, if you believe domestic publications [4], [6], [10], [11], it has both high specificity and high sensitivity (Table 4). A miracle, not a test! However, high sensitivity does not equal absolute sensitivity, which is why “Diaskintest” also experiences “punctures” in the form of false results (most often they are observed in children under two years of age or in persons with concomitant severe diseases [11]). Table 4. Assessment of the sensitivity and specificity of IGRA blood tests in comparison with the Mantoux tuberculin test and Diaskintest in the diagnosis of active tuberculosis
| "Quantiferon" [12] | T-SPOT®.TB [12] | Mantoux test [12] | "Diaskintest" [2] | |
| General sensitivity | 80%* | 81%** | 65%*** | 93,3% |
| General specificity | 79% | 59% | 75% | 93,7% |
| * Overall sensitivity 81% (95% CI 78–84%) for patients with confirmed tuberculosis. ** Overall sensitivity 92% (95% CI 90–93%) for patients with confirmed tuberculosis. *** Overall sensitivity 68% (95% CI 63–72%) for patients with confirmed tuberculosis. CI - confidence interval, confidence interval. | ||||
In general, blood tests are unlikely to be able to completely replace the Mantoux 2 TE test (and especially the Diaskintest if we are talking about the Russian Federation).
But perhaps they can become one of the additional tools in the diagnosis of active tuberculosis infection? Yes, such a possibility exists, but there are caveats here too. For example, for patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis, HIV-infected people or children over five years of age, they can be considered as an additional method. However, at present there is a limited number of studies on these tests [12], so it is too early to draw far-reaching conclusions (Table 5). Table 5. Assessment of the specificity and sensitivity of IGRA blood tests, the Mantoux test and Diaskintest in children and adolescents in the diagnosis of tuberculosis
| Mantoux test [12] | "Quantiferon" [12] | T-SPOT®.TB [12] | "Diaskintest" | |
| Specificity | 89,4% | 85,8% | 84% | 86,3% [2] |
| Sensitivity | 65,4% | 79,9% | 42,2% | 90,5–96,7% [2] |
| 94,8 [11] |
Patient preparation rules
The main requirement for patient preparation is to exclude local procedures and the use of medications in the area of the planned collection of biomaterial 24 hours before collection (if this is possible due to the patient’s condition). Maybe:
During the working day of the ML department "DILA". A break of at least 6 hours after eating (fatty foods should be excluded).
You can add this study to your cart on this page
Which test should you choose?
As they say, with all the wealth of choice, there are few alternatives. Unfortunately, when choosing a test, many are guided not by its diagnostic characteristics, but by its harmlessness to health, because phenol in skin tests scares many. And there is even a movement against the Mantoux test, whose support group periodically suggests replacing it with IGRA blood tests. But, as noted above, such fears have no basis. In addition, being a waste product of the body, phenol does not accumulate, but is excreted along with urine. Therefore, the main criteria are still the sensitivity and specificity of the tests.
At the moment, only Diaskintest demonstrates the best characteristics. However, despite this, the Mantoux 2 TE test continues to be used in mass diagnostics, and it completely satisfies phthisiatricians. After all, Diaskintest (as well as IGRA tests) does not respond to infection caused by M. bovis. In addition, it was introduced into mass diagnostics only 10 years ago, and this is too short a time to fully verify its diagnostic effectiveness and “write off” the tuberculin test as unnecessary.
As for IGRA blood tests, they are too expensive, do not surpass Diaskintest in sensitivity and do not distinguish between latent carriage. And in a world where there are more than 10 million tuberculosis patients and 1.7 billion carriers of mycobacteria [3], this is a significant drawback.
Literature
- Nesterova Y. (2017). “The 6 most popular tests for tuberculosis: the problem of choice.” MedAboutMe;
- Koretskaya N.M. (2013). Diaskintest: new opportunities in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. "Medicine in Kuzbass." 4, 3–8;
- A disease that refused to give up;
- Slogotskaya L.V., Bogorodskaya E.M., Levi D.T., Seltsovsky P.P. (2017). 10 years of skin test with recombinant tuberculosis allergen (Diaskintest) and 110 years of Mantoux tuberculin test - comparison of effectiveness. “BIOpreparations. Prevention, diagnosis, treatment." 17, 67–77;
- “On improving anti-tuberculosis measures in the Russian Federation.” (2003). Order No. 109 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation;
- Slogotskaya L.V. (2013). Tuberculin diagnostics and new tests to detect infection. "Medical Bulletin". 16, 14–15;
- Filinyuk O.V., Kolokolova O.V., Kabanets N.N. Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children and adolescents. Tomsk: Siberian State Medical University, 2013. - 174 p.;
- Methods for detecting tuberculosis in children (methodological manual). Moscow, 1990;
- Yakovleva G.P. (2017). DIASKINTEST vs MANTU. "Tuberculosis allergy";
- Slogotskaya L.V. (2014). Immunological tests with Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific proteins ESAT-6 AND CFP-10. "Tuberculosis and lung diseases." 1;
- Slogotskaya L.V., Senchikhina O.Yu., Nikitina G.V., Bogorodskaya E.M. (2015). The effectiveness of a skin test with recombinant tuberculosis allergen in detecting tuberculosis in children and adolescents of Moscow in 2013. “Pediatric Pharmacology.” 12, 99-103;
- ECDC guidance: Use of interferon-gamma release assays in support of TB diagnosis. Stockholm: ECDC, 2011. - 32 p.;
- Nechaeva O.B. (2016). Epidemic situation of tuberculosis in Russia. Central Research Institute of OIZ;
- Testing in BCG-vaccinated persons. (2016). CDC;
- Aksenova V.A. and Levy D.T. (2012). Tuberculosis in children and adolescents. “BIOpreparations. Prevention, diagnosis, treatment." 1, 22–27.
general characteristics
The causative agent of tuberculosis is Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease is characterized by a variety of forms, affects various organs and systems, and often occurs in a latent form, which complicates timely diagnosis and contributes to further spread. The PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method allows you to identify the genomic material of the pathogen in the examined biological material and establish a diagnosis. The choice of biomaterial to be tested must be made in accordance with clinical data. The test system detects not only the DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but also the so-called non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTMB, non-tuberculosis), which can cause mycobacteriosis and other lung diseases. Among them are M. kansasii, M. scrofulaceum, M. ulcerans, M. xenopi, M. malmoense, M. terrae, M. haemophilum, M. genavense, M. fortuitum, M. gordonae, M. simiae, M. mucogenicum, M. mageritense, M. smegmatis group, M. neoaurum-like, M. lentiflavum and others. Differentiation of non-tuberculous mycobacteria is not carried out by this test system.