A urine test is one of the simplest and most painless ways to determine a person’s health status.
Like a clinical blood test, a general urine test is often done for preventive purposes, for example, during medical examination, examination before entering the institute, when an infection is detected, before operations. But sometimes a urine test becomes important for diagnostic purposes. For example, it is carried out to monitor the progression of kidney disease or diabetes.
Despite the active development of medicine, urine analysis has not lost its importance and is prescribed for any visit to a doctor - urologist, gynecologist, endocrinologist. Therefore, it will be useful for everyone to familiarize themselves with the rules for passing this analysis and its results.
COST OF APPOINTMENT WITH A UROLOGIST (MEN, WOMEN)—RUB 1,000. CONSULTATION ON THE RESULTS OF AN ULTRASOUND OR ANALYSIS - 500 rubles. COST OF URINE ANALYSIS FROM 200 RUB.
CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
Indications for urine analysis
The content of the article
Urine is a product of the excretory system, including excess fluid, salts, proteins, sugars, blood cells and epithelium (integumentary tissues), etc. The human body gets rid of urine to maintain the balance of chemical compounds, salts and water. When health problems arise, the composition of urine begins to change. Various microorganisms appear in it, indicating the appearance of a urinary tract infection. All these deviations are revealed by urine analysis.
The doctor issues a referral for a urine test for various reasons: he wants to examine the genitourinary system for inflammation and infections, determine whether there is blood and sugar in the urine, and clarify the composition and concentration of salts. Referral to OAM should not be a cause for concern. This is a common procedure that is recommended for children and adults to undergo annually. The patient is also sent for a urine test if:
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- inflammation of the liver and gallbladder;
- metabolic disorders;
- diseases of the male reproductive system;
- sexual infections;
- toxicosis of pregnant women;
- hepatitis;
- diabetes;
- intoxication of the body with poisons and drugs;
- problems with the kidneys or bladder.
If the doctor, based on a number of signs, suspects the presence of pathologies and abnormalities, then a urine test helps confirm or refute his guesses. After treatment, the doctor prescribes a repeat test, which will show how effective it was.
Daily urine volume in children from 1 year to 7 years
After a child turns one year old, his body is already adapted to the environment.
The number of urinations is already 10–12.
Urine volume is from 500 to 600 ml.
The child's body still continues to grow rapidly.
But the pace is already significantly lower than that of an infant.
When a child reaches three years old, the number of urinations decreases to 7–9 per day.
This frequency will continue until the child reaches 7 years of age.
The only difference is the volume.
From 3 to 5 years, the daily volume of urine is from 600 to 700 ml.
After 5 and up to 7 years it increases to 650 - 1000 ml.
How to properly prepare for tests
Everyone has had to undergo a urine test , more than once, but the doctor is not always able to convey to the person information about the rules of preparation for this procedure in an accessible and competent way. Compliance with the recommendations affects the accuracy of the result obtained. Even the slightest ingress of foreign substances into the sample for analysis makes it impossible to obtain accurate data.
Proper preparation for the test includes several recommendations
- On the day before donating urine, you should avoid foods that contain dyes and cause color changes: beets, carrots, carbonated water.
- If medication treatment cannot be interrupted, be sure to notify your doctor. He will advise you to complete the course and then take the test. If the urine test is urgent, it is possible to interrupt treatment on the eve of the test.
- Avoid eating salty foods, dietary diuretics and multivitamins. They are able to change the properties and concentration of urine.
- If a urine test is scheduled a few days after a ureteroscopy or cystoscopy, it would be better to reschedule it. There is also no need to collect urine during menstruation. This will make the research result biased.
- On the day before the analysis, it is not advisable to visit a sauna or bathhouse, then a lot of fluid is released from the human body and the urine becomes more concentrated.
Please note some rules that must be taken into account when collecting morning urine:
- You need to collect urine in the morning; do not store urine that was collected a day ago or at night.
- Use a special disposable container, and for newborns you can buy a urine bag at the pharmacy.
- There is no need to remove the urine of a child or a bedridden patient from a diaper or diaper by squeezing it. Fabric fibers caught in it will distort the results of the study.
- Before collecting urine, be sure to perform genital hygiene.
Is preparation necessary?
The reliability of the study is influenced by a number of factors, namely what a person eats, drinks, overexertion, stress, taking food supplements and medications. Proper preparation reduces the risk of obtaining a distorted result:
- The day before the test, it is necessary to exclude from the diet those foods that change the color of urine. These are brightly colored vegetables and fruits, smoked foods, marinades and sweets.
- Completely exclude alcoholic beverages, vitamin complexes, dietary supplements, coffee, and strong tea from your diet.
- When taking medications, you must tell your doctor about this.
- It is important to reduce physical activity and eliminate stressful situations.
- Immediately before the test, it is necessary to carry out hygienic procedures for the genitals.
Unreliable results can be obtained when giving urine during menstruation, an infectious disease, increased body temperature, as well as high blood pressure. After cystoscopy, analysis is recommended to be carried out 7 days later.
Methods for collecting urine for general analysis
Urine for general analysis
It is collected in a clean jar in the morning immediately after sleep. Before collection, you need to wash your genitals with soap. Next, urine collection occurs. Tests are not prescribed during menstruation.
The most common option involves collecting an average portion of urine in a container. The first portion goes down the toilet, then the container is replaced. In this case, urination is not interrupted. In the second case, you need to collect all the morning urine in a clean container. Then the required amount is poured into the container. This method is much more informative and allows you to obtain objective data on the condition of the genitourinary system.
The results of the study are recorded on a special form indicating the patient’s personal data. With this document you can go to the doctor for a diagnosis.
How to collect urine for analysis depending on its type
- Urine according to Nechiporenko
is collected in the same way as for general analysis. The average portion is 100-150 ml. In the laboratory, the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes and other elements is counted. - For urine analysis according to Zemnitsky
, urine is collected every three hours in a separate jar, the first container is filled at 6.00. All containers are taken to the laboratory, because in this study, the change in urine density during the day is determined and its total excretion is calculated. - A three-glass test
is prescribed when you need to find out the localization of inflammation in the genitourinary tract. To do this, collect all the morning urine, dividing it into three portions. An increased number of leukocytes in all jars indicates inflammation of the kidneys or bladder, in the first - urethritis, in the first and third - a combination of urethritis and prostatitis.
Please note: urine is sent to the laboratory within two hours after the end of collection.
General research
This study involves collecting a morning portion of excreted fluid. In this case, the entire material must be placed in the jar. Normally, a person secretes from 100 to 200 milliliters of fluid in the morning.
For diagnostics, 80-130 milliliters will be enough. If your container is significantly smaller than the allocated volume, then it is worth collecting the urine in a separate container and then pouring the required part.

Decoding urine analysis: norms for adults and children
During this examination, the specific gravity, pH of urine (urine), its color and transparency are measured. During a microscopic examination of the sediment, the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes is determined, and the presence of sand, protein and sugar is detected.
Only the attending physician who has information about the patient’s health status can decipher the result obtained. The normal values for adults and children are slightly different.
Urine test norm for adults
| Criterion to be assessed | Norm |
| Color | Straw yellow, light yellow transparent |
| Transparency | Full |
| pH | Neutral |
| Density (specific gravity) | 1,018-1,025 |
| Osmolarity | 600-800 mmol/l |
| Glucose | No |
| Acetone | No |
| Protein | No |
| Red blood cells | No |
| Ketone bodies | No |
| Leukocytes | For women: 0-5 in the field of view, for men: 0-3 |
Normal urine test for a child
| Criterion to be assessed | Norm |
| Smell | Unsharp |
| Color | From light yellow to dark yellow |
| Transparency | Full |
| Specific gravity | 1,010-1,025 |
| pH | 5-7 |
| Glucose | Up to 1 mmol/l |
| Protein | Up to 0.14 g/l |
| Ketone bodies | 0-0.5 mmol/l |
| Bilirubin | Up to 8.5 µmol/l |
| Bacteria | No |
| Hemoglobin | No |
| Bacteria (nitrite test) | No |
| Urobilinogen | Up to 35 µmol/l |
| Leukocytes | 0-5 in sight |
| Red blood cells | 0-2 in sight |
| Cylinders | No |
| Epithelial cells | 0-5 in sight |
| Yeast mushrooms | No |
| Parasites | No |
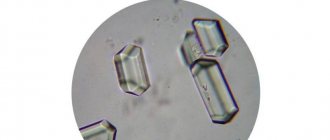
| Crystals | Are visualized |
Volume of daily urine in infants
The metabolism of children is completely different from that of adults.
Children in the first month of life receive fluid from their mother's milk during breastfeeding.
Or dosed from a bottle - with artificial feeding.
As you gain body weight, the required amount of food increases.
Accordingly, the water load increases.
Up to six months, children tend to urinate frequently up to 20–25 times a day.
The daily volume of urine at this age ranges from 250 to 450 ml.
After 6 months, the child’s rate of weight gain decreases.
At the same time, the amount of food he receives is still growing.
But during this period of time, the baby gets acquainted with new food - complementary foods.
Taken together, the restructuring of the body leads to a decrease in the number of urinations per day to 15–16.
In this case, the daily volume of urine remains between 300 and 500 ml.
Evaluation of urine test indicators
Urinalysis involves the assessment of physicochemical, biochemical properties and microscopy of urinary sediment.
Physicochemical characteristics
Such properties are considered to be the color and smell of urine, its quantity, chemical reaction and specific gravity. The color of urine is determined by the presence of dyes in it. At the same time, by changing the shade, you can determine the presence of pathologies and diseases of the internal organs of a person.
Normally, urine is clear, but if turbidity is observed, this is a sign of excess salts, mucus, bacteria, fatty particles or epithelial cells in the urine.
A characteristic odor can be felt after long-term storage of liquid in a closed container, especially at high temperatures. It is also possible to diagnose certain diseases by smell.
The chemical reaction of urine is affected by the patient's diet. A slightly acidic or neutral reaction is considered normal. A sign of kidney problems is a markedly acidic pH level. A deviation from the norm also indicates heart failure, gastrointestinal diseases, infectious diseases, or simply pregnancy.
An alkaline reaction appears with vomiting, pathologies of the endocrine system, use of diuretics, kidney diseases, heart and lung diseases.
The density or specific gravity of urine is determined taking into account the amount of compounds such as pigments, glucose, proteins, blood elements and bacteria, and is normally 1.001-1.040 g/l.
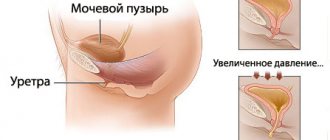
The amount of urine is determined by the amount of liquid drunk per day and varies between 1-2 liters. The only disease in which the patient can excrete more than 8 liters. urine per day - diabetes mellitus. In other cases, frequent urination, especially at night, is a clear sign of kidney pathologies, cystitis, prostatitis, prolapse (prolapse) of the genitourinary system, which is often found in women, or mental disorders.
Biochemical indicators
These data are very important in the process of diagnosing diseases. They give an idea of the content of proteins, ketone bodies, glucose, acetone, bile pigments and other compounds in the urine.
A healthy person does not have protein in their urine. Its presence is called proteinuria. The reasons for this phenomenon may be different:
- Extrarenal: protein from the urinary tract enters the urine.
- Renal: protein penetrates from the blood plasma under the influence of stress, cold or overwork, as well as during kidney inflammation.
Normally, glucose is also practically absent and is not detected by standard research methods (biochemistry, OAM): its concentration does not exceed 0.06 - 0.083 mmol/l. If it is detected, this indicates excessive consumption of carbohydrates (physical glycosuria). Glucosuria of the pathological type is often caused by pathologies of the adrenal glands, diabetes mellitus or dysfunction of the pituitary gland.
Glucose is also normally absent. If it is detected, this indicates excessive consumption of carbohydrates (physical glycosuria). Glucosuria of the pathological type is often caused by pathologies of the adrenal glands, diabetes mellitus or dysfunction of the pituitary gland.
The presence of ketone bodies (acetone, beta-hydroxybutyric acid, acetoacetic acid) in the urine should alert you. This is a symptom of diabetes, inflammation of the liver and kidneys. In diabetes mellitus, the presence of ketone bodies is especially dangerous; the condition can lead to coma.
Microscopy of urinary sediment
This method allows you to determine the presence of blood elements in the urine: leukocytes, erythrocytes, casts and epithelial cells.
The presence of red blood cells in the urine is called hematuria. Macrohematuria is a large number of red blood cells in the urine. Microhematuria - red blood cells are noted only in the field of view under a microscope.
The presence of red blood cells indicates pathologies such as kidney stones, injuries and malignant tumors, kidney infarctions, tuberculosis, and inflammatory processes in the urethra.
The number of red blood cells in the urine is determined by three samples (three-glass test):
- Blood in all three samples: kidney pathologies.
- Blood only in the third sample: inflammation or tumor.
Cylinders are cells that are similar in shape to renal tubules. OAM can detect hyaline and epithelial cell casts. Hyaline casts indicate chronic nephritis, and epithelial cellular casts indicate pathology of the renal tubules (for example, nephrosis).
Epithelial cells in urine can be flat (formed on the mucous membranes of the genital organs), transitional (lining the inner surface of the renal pelvis and bladder), renal (found in kidney infections and poisoning).
Leukocytes in the urine are contained in small quantities in the field of view. If the doctor detects a collection of leukocytes under a microscope, then the presence of pus in the urine can be suspected. This condition is typical for pyelonephritis, purulent pathologies of the genitourinary system. The cause of the accumulation of pus in the urine can be identified using the three-sample method, as in the determination of red blood cells.
How to collect
This question especially worries mothers, because at first glance such a process does not seem possible.
For example, parents of a baby who is already 3 or 4 months old, faced with the need to collect urine for preventive testing, are at a loss, because at this age the child goes to the toilet most of the time directly into the diaper.
Urination can be stimulated in several ways:
- Breastfeed your baby without a diaper. Many children pee while eating;
- Remove the diaper after a night's sleep. The baby may feel cold and pee;
- Bring your baby into the bathroom and turn on the water. Its noise is often a good stimulant;
- During the massage, lightly press on the lower abdomen.
If the newborn is on mixed feeding, he can be given water. The same applies to children who have reached the age of 5 months, when many mothers begin to give them baby water or juice drop by drop as their first complementary food.
Doctors strongly do not recommend resorting to such unhygienic collection methods as squeezing liquid out of a diaper or diaper.
In the first case, the liquid usually turns into a gel thanks to special substances, and in this form not every laboratory is ready to accept it for research. And tissue particles can get into the container from the diaper, which change the composition of the urine.
There are devices designed to make it easier for parents to collect urine from a baby of any age - at least 1, at least 6 months. This:
- A urinal is a small bag, made of plastic or any other material, with a hole, which is secured between the child’s legs using special Velcro. Parents can only wait for him to do his job;
- Plastic measuring cups with lids. They are suitable for older children.
Often mothers use cleanly washed baby food jars or plastic bags washed with soap. The last option cannot be called the most suitable, due to the fact that the composition of the liquid rarely remains unchanged in this case.
The main thing is to remember that any container you choose must be sterile.
At 8 months, many babies can already sit, and some even begin to take their first steps.
It is also well suited for a 9-month-old baby, when his first acquaintance with the potty may take place. Not all children immediately accept this device, and the mother’s hopes of collecting urine in it and then pouring it into a container disappear.
So, how much urine is needed for a general analysis of a baby?
As we already know, 10 ml is usually enough. The main requirement is that the liquid level reach 1 cm. However, a lot here depends on the laboratory employee. Some take smaller amounts, while for others 10 ml is not enough, and they send their parents home.
In order not to waste time, it is better to visit the laboratory at your clinic and find out the exact number.
The administration of the portal categorically does not recommend self-medication and advises consulting a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease. Our portal presents the best medical specialists with whom you can make an appointment online or by phone. You can choose the right doctor yourself or we will select one for you absolutely free
.
Also, only when you make an appointment through us, the price for a consultation will be lower than in the clinic itself.
This is our little gift for our visitors. Be healthy!

A urine test in a baby will help determine the condition of his body. From the third month you need to regularly monitor changes. One of the simplest and most informative tests is a urine test.
But how much urine from a baby needs to be collected for analysis, how to collect urine from a baby, what measures to take to conduct a correct analysis, how to decipher the results of the analysis.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
This procedure is considered as an additional method of examining urine in order to clarify the degree of leukocyturia (the number of leukocytes). Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko is prescribed when a general urine analysis reveals an excess of leukocytes and erythrocytes or laboratory technicians find cylinders in it.
For this analysis, an average portion of morning urine is used. A sufficient amount of liquid is 5 ml. The concentrate is obtained by centrifugation for 10 minutes. Then he is placed in Gorachev’s chamber, where the blood elements are counted. The resulting numbers are multiplied by 250 and a final number is obtained, by which a particular disease is determined:
- The number of leukocytes is more than 2000 in 1 ml of urine: prostatitis, inflammation of the bladder, kidney disease, pyelonephritis.
- The number of red blood cells is more than 1000 per ml: kidney infarction or glomerulonephritis (in the presence of a number of characteristic signs).
- Detection of casts: renal pathology.
As you can see, a urine test helps to detect various health problems in a timely manner.
Amount of child's urine for diagnosis
Unlike adult norms, the baby’s portion of fluid secreted may be significantly smaller. So, if a person needs to collect 100 milliliters for a general analysis, then 20-50 will be enough for the baby. Remember: the laboratory assistant cannot refuse you an analysis due to the fact that there is not enough material.
If the study needs to be carried out on a newborn, then the portion may be even smaller. Babies in the first month of life can urinate only 10 milliliters at a time. This amount of liquid will be quite enough for diagnosis. Only in some cases can a doctor prescribe collecting two different portions of material in one container.
How much does it cost to take a urine test?
The price of a urine test depends on the commercial direction of the clinic. In our laboratory you can donate urine at the lowest cost, while obtaining a high-quality, accurate result.
| Cost of analysis | price, rub. |
| General urine analysis with sediment microscopy | 325 |
| Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko | 275 |
| Sulkowicz test | 175 |
| Biochemical urine analysis | Price, rub |
| Rehberg test (endogenous creatinine clearance) | 415 |
| Total protein in urine | 240 |
| Calcium in daily urine | 285 |
| Albumin in urine (microalbuminuria) | 410 |
| Phosphorus in daily urine | 285 |
| Total amylase in daily urine | 280 |
| Uric acid in daily urine | 255 |
| Creatinine in daily urine | 255 |
| Magnesium in daily urine | 285 |
| Urea in daily urine | 255 |
| Potassium, sodium, chlorine in daily urine | 295 |
| Potassium in daily urine | 270 |
| Sodium in 24-hour urine | 270 |
| Chlorine in daily urine | 270 |
| C-peptide in daily urine | 635 |
| Glucose in urine | 205 |
Daily urine volume in children from 7 to 13 years
At the age of 7 years, the child’s body has slow metabolic processes.
Until the age of nine, the number of urinations will remain up to 7–8 per day.
After 9 years of age, on average, urine output occurs 6 to 7 times.
At this age, the child can already consciously control the level of thirst and fluid intake.
Changes also occur in the daily volume of urine.
For children from 7 to 11 years old it ranges from 800 to 1400 ml.
After 11 years, the volume increases slightly to 1000 - 1600 ml.
Next, the child’s body is already undergoing changes that are associated with hormonal changes during puberty.
Excretory and metabolic processes acquire characteristics similar to those of an adult.
Where to take a urine test in St. Petersburg
Private clinic Diana offers its patients to undergo any type of urine tests in our laboratory. We guarantee an accurate result that you won’t have to doubt. At the clinic you can consult a urologist and gynecologist and, if necessary, undergo additional examination.
CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Factors that distort the results
In order for a urine test to show objective data, it is necessary to eliminate factors that can distort it and complicate the correct diagnosis:
- stress suffered the day before;
- consumption of alcohol, heavy food, sweets;
- taking diuretics and other medications;
- in women - phases of the monthly cycle;
- intense physical activity shortly before the analysis.
The result of the study also depends on the time when the material was received. As a rule, urine is collected from the first urination after waking up. Urine must be sent to the laboratory immediately. Long-term storage can also distort the results of the study.