TRUS (transrectal ultrasound) is an ultrasound examination of the prostate through the rectum. It is also possible to examine the prostate through the abdominal wall, but this method is significantly inferior due to its low information content, which is why TRUS is considered the standard for high-quality urological examination.
What is the prostate gland and why is it examined even if there are no symptoms of disease?
The prostate gland is a small, glandular and fibromuscular organ that covers the initial part of the male urethra. The secretion of the prostate gland is responsible for liquefying the ejaculate, activating the movement of sperm, and having an antimicrobial, buffering and enzymatic effect.
It is this organ that is most susceptible to pathological processes, which is associated with its close location to the urinary tract - the main channel through which pathogens of sexual diseases enter. Another reason for violations is the dependence of the activity of this organ on the regularity and quality of a man’s sexual life, and on his age.
Unfortunately, problems with the prostate do not manifest themselves at first; noticeable symptoms arise only when the process has progressed far in its development. Therefore, andrologists insist on annual preventive examinations of the prostate gland. A man should undergo regular ultrasound examinations starting at age 40. At this age, prostate pathologies appear in every third man, and after 50 years - in every second.
When is a prostate ultrasound prescribed?
An ultrasound may be prescribed if, during a rectal (digital) examination, the doctor finds that the prostate is hardened or enlarged. The study is necessary if there are signs of kidney failure: renal colic, dryness and discoloration of the skin, weakness and weight loss due to frequent urination, nausea and vomiting.
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound if a man has complaints:
- the appearance of blood in urine or semen;
- difficulty, pain when urinating, frequent visits to the toilet, feeling of incomplete emptying, increased frequency of urination at night;
- pain and discomfort in the scrotum, perineum, bladder or anus;
- strange discharge from the urethra;
- problems in the sexual sphere.
An ultrasound is prescribed if the doctor suspects that a man may develop cancer of the gland. The procedure is performed before and after prostate surgery. At the age of over 40-50 years (depending on medical history), doctors recommend including such an ultrasound in the annual preventive examination (screening).
When is TRUS prescribed without fail?
TRUS is prescribed by a urologist, andrologist or oncologist in the following cases:
- if cancer is suspected (after a digital rectal examination or transabdominal examination);
- in case of deviations in the results of blood or urine tests;
- for the purpose of clarification and monitoring during cryotherapy, brachytherapy, ultrasound ablation, drainage of abscesses, prostate cysts or cellular spaces of the pelvis;
- to monitor the extent of cancer during treatment or before other interventions. If a relapse is suspected after treatment;
- for male infertility , erectile dysfunction;
- for pain in the pelvis;
- any type of prostatitis.
The study is not prescribed in cases of exacerbation of hemorrhoids and in inflammatory processes of the rectum until the inflammation is relieved.
How do you know if this procedure is right for you?
We invite you to take a short test: answer the questions below:
- You are a man?
- Are you over 40 years old?
- Do you experience unpleasant sensations (discomfort, burning, pain, stinging) during urination?
- Have you been unable to have a child for a long time?
- Has anyone in your family or family had prostate cancer?
If you answered yes to at least one of these questions, you are at risk. Call and sign up for the TRUS procedure, the cost of which our consultants will tell you.
What does TRUS show?
TRUS is a highly effective method that allows you to study:
- prostate gland (shape, structure) . A complete description of the contours is possible, which in an unchanged state should be smooth and clearly displayed;
- size, volume of the prostate . Normal length is 25-40 millimeters, width and thickness are 23-43 millimeters. Volume – from 200 to 280 mm³. Exceeding these parameters is a pathology;
- seminal tubercle , which is located in the structure of the prostate, has a triangular shape and a size of no more than 3 millimeters.
Also, at the same time, the doctor examines nearby organs: the rectum, bladder and vas deferens.
The essence of the proposed study
The transrectal method of ultrasound is based on the same principle as classical ultrasound - a sensor inserted intraintestinal with ultrasonic waves allows you to create echo waves of various lengths, which indicates all sorts of pathologies of the body. From the calculated difference between the reflection length and the length of the ultrasonic wave itself, one can infer the shape, structure or density of the human organ in question. The received data is immediately reflected on the monitor screen of a computer connected to the ultrasound machine, which allows all emerging signals to be assessed in real time.
Transrectal ultrasound also allows for a biopsy, that is, taking affected areas of tissue of various organs for analysis, if such a need arises during the procedure. In this case, a needle is inserted into the area of the prostate gland, with the help of which microscopic samples of the necessary biomaterial are removed. According to doctors, it is impossible to damage organs during transrectal ultrasound, so in this regard the procedure is absolutely safe.
Preparing for the examination
After being referred for an examination, the doctor tells the patient about the procedure, benefits and possible complications.
Preparing for TRUS involves having a bowel movement. On the day of the examination or the day before, you must use a cleansing enema. It is also recommended to exclude foods that cause increased gas formation. The day before the procedure, avoid carbonated drinks, dairy products, cabbage, apples, pears and grapes. You can create a menu of cereals, lean meat or fish, and vegetables. Don't forget about personal hygiene.
As for the enema, it is not at all necessary to use “grandmother’s methods” and introduce a large amount of water into the intestines. Pharmacies sell special rectal suppositories called microenemas. Such microenemas, provided you follow a diet, are enough to completely prepare the intestines.
Another important point is psychological preparation. All exciting moments should be discussed with a doctor, because fear can cause additional spasm of the anal sphincter. This will interfere with the examination and time will be wasted.
Before the study, you need to relax and take a deep breath while inserting the sensor. If there are indications (increased suspiciousness, pain in the prostate area), the doctor can use a gel with lidocaine - this facilitates the insertion of the sensor and relieves pain.
Sign up for a prostate ultrasound
Clinic specialists Dr. AkNer offer their assistance in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate diseases. The doctor will be able to prescribe the necessary examinations for you and will tell you exactly what is better – TRUS or MRI of the prostate. Your case may require a different diagnosis. You can make an appointment with a urologist or, if you have a referral, go straight to an ultrasound. With our modern equipment, you will get clear results that will help you understand the cause of the problem. Still have questions? Ask them in the form on the website or by phone +7 (495) 098-03-03.
Urologist, andrologist Akopyan Nerses Grigorievich.
Back to list of articles
How is TRUS of the prostate performed?
Before the procedure, you must drink 3 glasses of water (no later than 30 minutes before the examination), and do not urinate until the examination is completed. A full bladder prevents the organ from leaving and increases the contrast of the prostate.
The patient lies on his left side, bends his legs and brings them closer to his stomach. You need to relax as much as possible and breathe deeply. The sensor is inserted while exhaling. The rectal sensor is protected with a rubber cap (or a special condom), then inserted to a depth of 5-6 cm into the rectum.
The procedure takes several minutes. The doctor carefully examines the organs and makes a conclusion. However, if the purpose of the study is the bladder, then TRUS takes place in two stages:
- examination with a full bladder;
- examination of the pelvic organs after emptying the bladder, measurement of urine residues.
It is worth noting that the amount of liquid you need to drink before the study increases to 1.5 liters.
If during the examination the doctor identifies suspicious areas, then a biopsy is performed using a special needle - taking a piece of tissue to check for malignancy.
In men over 40 years of age, the risk of pathologies of the genitourinary system increases. Therefore, for the purpose of prevention, in addition to an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, you need to regularly take blood tests for biochemistry and tumor markers. These tests detect inflammation and early oncological processes that are not visible on TRUS.
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)
Ultrasound doctor of the highest category Pedanenko Alexander Yurievich.
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)
TRUS is one of the most effective and safe methods for assessing prostate health. Based on TRUS data, the doctor will be able to give you the correct diagnosis and select suitable drugs for the treatment of prostate adenoma, drugs for the treatment of prostatitis or other diseases of the male reproductive organs.
In what cases is TRUS prescribed?
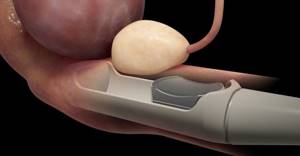
If you suspect prostate adenoma. Transrectal examination allows you to determine the volume of the prostate gland, as well as identify the true cause of urination disorders (compression or stricture of the urethra, pathology of the bladder, etc.). Depending on how enlarged the prostate is, the doctor determines the stage of the adenoma and also selects the appropriate treatment tactics (drug therapy, microwave or radiofrequency therapy, transurethral resection of prostate tissue, etc.).
If prostate cancer is suspected. TRUS allows you to detect the presence and determine the size of malignant neoplasms within the prostate gland. Ultrasound examination of the prostate through the anus is used for early diagnosis of cancer. In this case, the presence of a malignant tumor can be definitively confirmed or refuted only after a biopsy of the prostate gland and histological examination of its tissues. In this case, the material is also collected transrectally.
For other diseases of the reproductive system. Transrectal examination is used to diagnose the cause of male infertility, including in patients with azoospermia. TRUS is also used to detect abscesses and cystic formations in the prostate gland.
How is the TRUS procedure performed?
Before the procedure, you will be asked to remove your pants and underwear, lie on your side and bend your knees. Your doctor will then place a protective cover over the ultrasound probe, lubricate it, and gently insert it into your rectum. The device emits high frequency ultrasonic waves. Depending on the force of their impact on the tissues of internal organs and biological fluids, more or less intense vibrations of the reflected sound wave are observed. These changes are reproduced in real time on the monitor. During the research process, reflected sound waves are recorded. The discomfort of TRUS is similar to that of digital rectal examination or prostate massage. The procedure will take about 15 minutes.
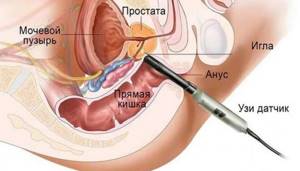
How to prepare for TRUS.
Since the transducer is placed in the rectum to perform TRUS, the intestines must be cleansed the day before the procedure. This allows you to avoid distortion of the study results and unpleasant sensations during the insertion of the sensor. In most cases, defecation in the morning on the day of TRUS is sufficient to cleanse the intestines. If you have difficulty with bowel movements, it is recommended to do a cleansing enema the night before or in the morning (several hours before the test). Wear comfortable trousers that do not restrict movement and can be easily unbuttoned, as before TRUS you will need to remove clothing from the area being examined. The andrologist may also ask you not to take blood thinning medications, such as aspirin, for a few days before the ultrasound. You can get more detailed recommendations on preparing for TRUS from your doctor.
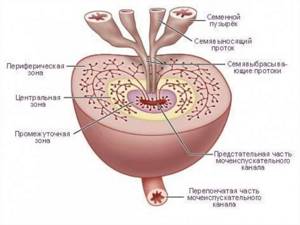
Sonographic anatomy.
On average, 70% of the normal prostate gland consists of glandular elements, and the remaining 30% is made up of fibromuscular stroma. The glandular tissue of the prostate usually consists of internal glands, which include the transition zone and periureteric glandular tissue, and external glands, which occupy the peripheral and central zones. TRUS can usually distinguish the transition zone, which is located anteriorly as a hypoechoic area, from the peripheral zone, which is echogenic and uniform in echotexture compared to the rest of the gland. The central zone, on the other hand, is barely different from the peripheral zone in healthy adult men. The transition zone is the site of hyperplastic changes, constitutes a large proportion of prostate tissue in older men, and may additionally be the site of prostate cancer development in approximately 20%. It should be noted that 1% to 5% of prostate cancer is located in the central zone. The peripheral zone, being also the main site of development of chronic prostatitis, leads to approximately 70% of prostate cancer. Cancerous lesions in the transition zone, on the other hand, are unlikely to be distinguished from nodules in benign prostatic hyperplasia on TRUS.
The most common indication for TRUS examination of the prostate is the diagnostic evaluation of suspected prostate cancer. Early detection of prostate cancer is closely associated with a reduction in mortality, since detection at an early stage of the disease is often the only chance for cure. Before the widespread introduction of diagnostic tools to detect disease at an early stage, such as digital rectal examination, TRUS and PSA testing, prostate cancer was often diagnosed at a late stage, resulting in patients dying in a shorter time. Although a serum total PSA (TPSA) level greater than 4 ng/mL may suggest the presence of prostate cancer, patients with BPH and inflammatory prostate disorders may also have elevated serum total PSA levels. The lack of specificity of serum total PSA for PCa screening inevitably led to further efforts to identify an ideal protocol that would combine PSA, TRUS, and digital rectal examination to improve specificity without compromising sensitivity.
BPH is a common disease among older men that involves nodular hyperplasia of fibrous, muscular, and glandular tissue within the periurethral glandular zone and transition zone. The main role of ultrasonography in the study of patients with BPH is to assess the size of the prostate gland and residual urine volume (RVR) before treatment. The technique can also be used to assess the transition zone, which is closely related to the severity of BPH. Transabdominal ultrasound may play a role in the follow-up of patients with BPH because it is effective in calculating the increase in TOM levels. Increasing TOM levels increases the risk of urinary retention. In addition, the upper urinary tract should also be examined for any changes.
The main TRUS changes in BPH are diffuse or nodular enlargement of the transition zone with a hypoechoic or heterogeneous appearance compared with the peripheral zone, protrusion of the prostate capsule, cystic changes and calcifications in adenomatous nodules, and compression of the peripheral zone by an enlarged transition zone. In addition, corresponding changes in the proximal urinary tract can be detected, such as: elevation of the base of the bladder, increased volume of space, formation of bladder trabeculae and hydroureteronephrosis, which are secondary to varying degrees of bladder outlet obstruction.
A surgical defect may be found in the central portion of the transition zone in patients with previous transurethral resection of the prostate for BPH, which should not be misinterpreted as a cystic lesion. Cysts secondary to degeneration of hyperplastic nodules associated with BPH are quite common in clinical practice. Most importantly, protrusion of an enlarged transition zone should not be confused with tumors that develop from the base of the bladder. Accurate differential diagnosis can be made by interrupting the contour of the prostate lesion using sagittal TRUS scanning.
The term "prostatitis" is used for a variety of prostate disorders that cause pain in the pelvic region and are mainly of non-bacterial etiology. Clinically, this pathology is classified as acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic aseptic prostatitis, chronic pelvic pain syndrome and asymptomatic prostatitis. The role of TRUS is limited in patients with acute prostatitis because the diagnosis is mainly based on the clinical picture. Patients with acute prostatitis usually complain of fever, pain, dysuria, urgency and pyuria, and even severe discomfort when inserting a probe into the rectum due to severe pain from the inflamed prostate gland. TRUS may show inflammatory changes such as a rounded, enlarged prostate with decreased echogenicity and diffuse hypervascularity on color or power Doppler. However, the main role of TRUS in acute prostatitis is to exclude abscess formation in patients who do not respond to treatment.
Where to make TRUS
Considering the fact that TRUS of the prostate is a complex laboratory test that involves intervention in the body, and interpretation of the results can only be carried out by qualified specialists, you can only seek help from an accredited medical center, which is.
When you first contact our clinic, our consultants will tell you how much TRUS costs, contraindications and limitations, and using the example of a doctor, you will learn about all the intricacies of the procedure, how to prepare for it and what the final price for TRUS of the prostate gland will be , taking into account all additional analyses.
TRUS protocol: interpretation of results, norm and recommendations
During the examination, the following indications are measured: longitudinal and cross sections of the prostate, mass, volume and specific gravity are calculated, the condition of the seminal vesicles, echogenicity, homogeneity, vascularization are analyzed. Any deviation from the norm is an important indicator that something is wrong with the body. The changes may not indicate the onset of the disease, but the doctor should definitely prescribe additional tests.
If the doctor has suspicions that the patient has cancer, and one of the purposes of TRUS is to confirm or refute these suspicions, we recommend performing a biopsy. To do this, under the control of a sensor, a specialist takes a small piece of tissue for analysis. After the examination is completed, he is sent to the laboratory. In this case, the price for TRUS of the prostate will be slightly higher.