If a gynecologist has diagnosed you with an ovarian cyst, do not be alarmed: as a rule, these formations are benign and do not pose a danger; surgery is not required. Often they do not need to be treated at all and disappear on their own within a few months. It is enough to periodically visit a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound examination.
- What types of ovarian cysts are there?
- When is laparoscopy performed?
- When is laparoscopy not performed?
- Benefits of laparoscopy
- Preparation
- How is laparoscopy performed?
- Postoperative period
- Complications
- Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
Sometimes ovarian cysts still have to be removed. Operations can be performed without an incision, through several punctures in the abdominal wall - laparoscopically. Euroonco employs expert-level gynecological surgeons who have extensive experience in performing such interventions. Come for a consultation with our specialist: he will tell you whether surgery is necessary in your case, and prescribe an examination that will help distinguish a benign neoplasm from a malignant one.
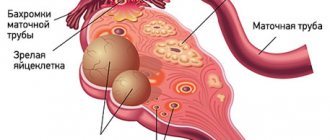
A cyst is not a specific disease. This term refers to any pathological cavity with fluid. The reasons for its formation are different. According to statistics, ovarian cysts are diagnosed in every tenth woman. They most often occur during puberty and menopause. Some girls have them from birth.
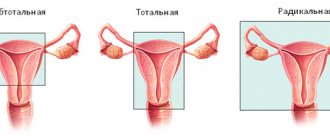
What types of ovarian cysts are there?
All ovarian cysts are divided into two large groups: functional , which occur in most cases, and pathological , which doctors have to deal with much less frequently.
Functional cysts are the result of disturbances during the menstrual cycle. Usually they do not cause complications and disappear on their own. They come in three types:
- Follicular . follicle matures in a woman’s ovaries . Normally, it should open and release the oocyte. If this does not happen and the follicle continues to grow, it turns into a cyst.
- Corpus luteum cysts . After the follicle releases the egg, it turns into a special gland - the corpus luteum . It produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum atrophies. And if fluid accumulates in it, it turns into a cyst.
- Theca-luteal cysts often develop as a side effect of infertility treatment with hormonal drugs.
Pathological ovarian cysts are not associated with the menstrual cycle. They are always characterized by the appearance of “wrong” cells that should not be present normally. The most common types of pathological cysts:
- Endometrioid . This is a form of endometriosis, a condition in which endometrial tissue (the lining of the uterus) gets into unusual places and grows there. In the ovaries, it can form cavities with fluid. They often appear as “chocolate” cysts filled with dark blood.
- Dermoid cysts , or teratomas , are a special type of benign tumors made from embryonic cells. There may be different tissues inside them, for example, skin, hair, nails. Dermoid cysts become malignant very rarely.
- Cystadenomas are benign neoplasms of epithelial cells. Usually they are filled with contents of a mucous or watery nature.
For more information about malignant cysts, please visit the ovarian cancer page on our website.
Dangerous repetition
Repeated operations require special attention, the difficulty of which lies in the fact that the surgeon starting work does not fully know the severity of the scar process left in a small patient after the previous intervention. After all, any healing in the body occurs through the formation of scar tissue. However, the degree of scarring may vary. Therefore, the most difficult stage of such an operation is the isolation of the organ, since it is quite problematic to excise the surrounding scars, since they often include important tissues, for example, vessels that feed the organs. Therefore, few surgeons, even in the world, decide to perform repeated laparoscopic operations, which are difficult not only technically, but also physically and psycho-emotionally. However, when it comes to urology, the risk of losing a kidney with repeated open surgery is higher than with repeated laparoscopic surgery. That’s why doctors still resort to these complex methods. And they often achieve excellent results.
When is laparoscopy performed?
If the ovarian cyst is small, does not cause symptoms and does not look cancerous, it can be left alone. No surgery needed. The gynecologist will prescribe periodic examinations and control ultrasounds. Moreover, postmenopausal women will have to do this more often, because they have a higher risk of malignant tumors.
Are there effective medications?
In some cases, hormonal contraceptives may be helpful. They help prevent the formation of new cysts in the ovaries, but do not affect the growth of existing ones. If a woman is bothered by pain, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). But this is only symptomatic treatment. The only way to get rid of the formation is surgery.
If the cyst is “problematic,” then the doctor will definitely say that it needs to be removed. Indications for surgery:
- Large size of formation. In most cases, ovarian cysts have a diameter of 1–3 cm. Very rarely they reach 15–30 cm.
- Presence of symptoms: abdominal pain, pelvic pain, bloating, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, heavy periods, vaginal bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle. A large cyst can compress the intestines and bladder. This leads to problems with stool and urination.
- Suspicion of a malignant nature of the cyst - the risks are increased in postmenopausal women.
- Continued growth over 2–3 menstrual cycles.
- Pathological ovarian cyst.
What happens if the cyst is not removed?
If the doctor said that the cyst needs to be removed, then delaying the operation is primarily dangerous for postmenopausal women. They, as we have already mentioned, have a higher risk that the formation may turn out to be malignant. And with cancer, time is critical. The later treatment is started, the lower the chances that it will be successful and that remission will be achieved. The prognosis worsens and survival rate decreases.
At the Euroonko clinic you can receive treatment for ovarian cancer according to modern standards. Our doctors perform operations of any complexity; we have access to all the latest generation antitumor drugs registered in Russia. We work according to modern European, American, Israeli treatment protocols. For ovarian cancer complicated by peritoneal carcinomatosis, we use an innovative technique - hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
With benign ovarian cysts, serious complications can also occur, although they are rare. Large cysts may rupture. In this case, severe bleeding develops into the abdominal cavity, and severe abdominal pain occurs.
As the cyst grows, the risk of ovarian torsion increases. Due to compression of the blood vessels, it stops receiving blood supply, severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting occur. The result may be necrosis (death) of the ovary, and it will have to be removed urgently.
If you experience symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or a fever of more than 38 degrees, you should immediately seek medical help.
Preparation
Ovarian cysts are usually detected during an ultrasound examination. In order to better assess the size, location and internal structure of the neoplasm, the condition of the ovary, they usually resort to not only transabdominal (through the abdominal wall), but also transvaginal (using a special sensor inserted into the vagina) ultrasound.
In rare cases, usually when a malignant nature of the formation is suspected, computed tomography and diagnostic laparoscopy are prescribed. of cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) in the blood testifies in favor of cancer . But this analysis is unreliable, since a positive result can be obtained for uterine fibroids, endometriosis and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
Based on the examination results, the doctor advises the woman and explains which treatment tactics will be optimal in her case. If laparoscopic surgery is indicated, a date for hospitalization is set. You need to undergo a preoperative examination. It usually includes the following diagnostic methods:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood test for hormone levels.
- Tests for infections.
- Cervical smears - cytological, flora.
- Blood clotting study.
- Determination of blood group AB0, Rh factor.
- Electrocardiography.
- X-ray of the lungs.
Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts is performed under general anesthesia - endotracheal anesthesia. The woman is hospitalized in the hospital the day before surgery. You can’t eat anything for 8 hours before surgery, and you can’t drink anything in the morning. Some time before anesthesia, premedication : the woman is given drugs that help her relax and calm down.
Rehabilitation treatment after gynecological operations
Negative factors can negatively affect the course of both the early and late postoperative period. They often significantly reduce the effectiveness of surgical intervention and make it difficult for women to adapt to work activities and difficult living conditions. Therefore, surgery should not be the final stage in the treatment of gynecological diseases .
For a complete recovery, the patient needs special restorative therapy, which in modern conditions is a mandatory final component of any surgical intervention on the pelvic organs.
It should be aimed at preventing postoperative complications, preventing relapses of the disease and eliminating disorders caused by the main pathological process.
All patients need restorative treatment - with adhesions in the pelvis and abdominal cavity after previous abdominal operations, with diseases of the cardiovascular, urinary and endocrine systems, disorders of fat metabolism, foci of chronic infection, the large volume and traumatic nature of this operation, as well as after surgical interventions on the internal genital organs (there is a high probability of the formation of extensive adhesions in the area of the right appendages of the uterus) and the appendix in children and adolescents.
The patient should receive the first information about the expediency, objectives and essence of restorative therapy even before the operation and then before each new appointment with a mandatory assessment (in positive tones, but without obvious lies) of the results of previous interventions. The clinical objectives of reconstructive treatment are largely determined by the extent of the operation and the woman’s age.
Types of operations and their features
Recovery after surgery depends on a number of objective factors:
- whether the operation was emergency or planned;
- the woman’s general health status before surgery;
- volume and complexity of surgical intervention. The complexity of the operation determines its duration, and, therefore, the time spent under anesthesia;
- whether the operation was laparoscopic or laparatomy or whether the perineal and vaginal approach was used;
- what type of anesthesia was used: endotracheal or epidural anesthesia.
In laparoscopy, the operation is performed with small, delicate instruments inserted into the abdominal cavity through several small holes in the abdomen. A camera is inserted into one of them, which displays the image on a large screen. The doctors' hands move from the outside to operate instruments inside the abdomen.
This approach can significantly reduce tissue trauma, blood loss during surgery, and the risk of adhesions.
The holes in the abdomen heal quickly and become invisible after 2-3 months. And no one, looking at you in a bikini, will guess that you have undergone surgery.
Laparotomy is an operation through an incision in the abdomen, which in modern medicine is carried out along the pubic hair line.
The laparotomy approach is used for operations that require the removal of a significant part of the organs and in emergency situations that involve the presence of a large amount of blood in the abdomen. For example, a ruptured tube during an ectopic pregnancy.
Gynecological operations that are performed “from below” are operations for prolapse of the pelvic organs or plastic surgery of the perineum when its muscles diverge.
In the last 10 years, gynecological cosmetology has been added here - creating intimate beauty at the request of the patient.
Recovery is easiest after removal of small benign ovarian tumors. The most common of them are simple serous cystadenomas, endometrioid cysts and teratomas. The operation is performed laparoscopically and takes 30–40 minutes. This also includes gynecological cosmetology.
The next day the patient will be home. If you follow the surgeon's recommendations, recovery in this case occurs quickly.
It is much more difficult to recover after removal of the uterus and its appendages, including, possibly, the ovaries. And there may be different options for events.
Recovery after complex gynecological operations
First. "I can no longer have children"
This applies to isolated cases. Modern gynecological surgery is aimed at organ-preserving operations. And he fights with all his might for the possibility of motherhood for women. And even if a major operation is necessary, patients of reproductive age have the opportunity to preserve eggs, cryoembryos, use donor eggs, and surrogacy.
Second. “What if I go into premature menopause?”
If the ovaries are preserved during surgery, then all the physiological changes of the menstrual cycle are preserved, only menstruation is absent. Removing the uterus does not bring menopause closer. It occurs in accordance with the biology of the body.
I would recommend that patients ask the surgeon in detail after the operation, how intact are the ovaries? If necessary, hormonal levels can be checked 2–3 months after surgery.
If it begins to change for the worse, or if the ovaries were removed during surgery, it makes sense to discuss the transition to hormone replacement therapy with your gynecologist. Fortunately, modern pharmacology now provides a large number of fairly effective and safe hormonal drugs.
Third. “What about sex after?”
Very often, women are worried about sex life after major surgery. I will answer from my extensive experience of communicating with patients after major gynecological operations. Libido does not decrease. Moreover, the disappearance of symptoms associated with gynecological diseases, such as intermenstrual bleeding, and the disappearance of fear of pregnancy makes sexual life brighter and richer.
No man will ever feel your “internal anatomy” during sex. A partner’s doubts about his feelings in sex can only begin if a woman describes to him in detail the operation she went through.
RECOVERY AFTER GYNECOLOGICAL SURGERY
Any, even minimally invasive gynecological operation represents a serious intervention in a woman’s body. For a significant time after it, the body is in a state of severe stress. The task of doctors at this time is to promote the patient’s recovery, prevent the development of postoperative complications, and help return to normal physical and mental shape.
The methods of rehabilitation medicine cope perfectly with these tasks. As a rule, doctors usually divide the postoperative period into primary and secondary. If the primary period begins immediately after the patient leaves the operating room and takes place in the hospital of the medical institution where she had the operation, then it is better to undergo secondary rehabilitation in institutions specializing in non-drug rehabilitation therapy.
Natural remedies - healing mud and silt ( balneological treatment ), mineral waters, salts, herbal remedies, etc. gently but strongly affect the body, restoring it. Physiotherapy in several courses actively affects hormonal balance, has a wonderful antitoxic, antiseptic, relaxing and analgesic effect. Physiotherapy at a later date (1-2 months), due to its varied effects on the skin, activates the body’s resources and stimulates; and the unique positive effect of massage and reflexology lies in the activation of nerve endings through the skin, which increases blood circulation, “boosts” the immune system, and accelerates tissue regeneration.
Unlike drug treatments, most rehabilitation therapy methods are not only gentler and gentler, but also much more comfortable. Agree that physiotherapy and massage sessions are more pleasant than pills, painful injections and IVs. And if the choice is obvious, then you should not postpone the decision.
REHABILITATION AFTER OPERATIONS
No less difficult a task than the successful implementation of a surgical operation is the rehabilitation of the patient after surgery. During the initial rehabilitation period, the body of a patient who has undergone surgery is in a state of severe stress. Even after time, doctors claim that the secondary rehabilitation period is characterized by an increased risk of postoperative complications, greatly reduced immunity, and dysfunction of organs and systems due to their incomplete recovery.
Methods from the arsenal of rehabilitation medicine come to the rescue. Using non-drug remedies, mostly natural and time-tested. Most rehabilitation therapy techniques have been refined over centuries. Doctors help the patient’s body achieve complete regeneration, prevent the risk of complications, stabilize the physical and psychological state and increase resistance to diseases.
For example, hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches) is indispensable for restoring blood circulation and has an anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effect. Healing mineral waters and mud balance the body at the cellular level and demonstrate a wonderful cleansing and antitoxic effect. Many post-effects of operations can be treated with physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy, due to their diverse positive effects on the body.
Thousands of women have successfully undergone postoperative rehabilitation treatment in our clinic. Thanks to the complex, gentle and at the same time powerful effects of restorative medicine, the patient’s well-being and quality of life quickly improve, tissues are regenerated and functional defects caused by surgery are eliminated, the patient returns to a normal, fulfilling life. Rehabilitation medicine is a smart treatment choice without negative consequences.
Comments
No comments.
Add a comment
How is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopic intervention is performed through several punctures in the abdominal wall. Through one of them, in the navel area, a laparoscope - an instrument with a miniature video camera. It broadcasts an enlarged image onto the screen. For better visualization during surgery, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas.
Special laparoscopic instruments are inserted through additional punctures, and the cyst is removed with the help of them.
Depending on the specific situation, the scope of the operation varies:
- Often it is possible to remove only the cyst, preserving the ovary.
- In some cases, it is necessary to remove the entire ovary - to perform an oophorectomy (oophorectomy) - while the second ovary can be saved. This has to be done if a malignant tumor is suspected, or if the cyst is in an “inconvenient” location, when it is difficult to remove it separately.
- In rare cases, both ovaries may have to be removed. This operation is performed only in extreme cases, especially in women of reproductive age, since menopause occurs after removal of both sex glands. The levels of female sex hormones decrease, and this can lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, hot flashes, etc.
Don't hesitate to ask your doctor questions before surgery. Ask what is the likelihood that during the operation you will have to remove both ovaries, what negative consequences this threatens, and how to cope with them.
Small access – big benefits
Once upon a time, doctors used the following phrase: “Big surgeon, big cut.” But this statement has long since lost its relevance. And all thanks to the introduction of so-called minimally invasive (that is, gentle) surgical methods. After all, such operations (as doctors say, with limited access) do not require large incisions, but are carried out through barely noticeable 3-4 punctures, which are made in the patient’s anterior abdominal wall. Through these holes, miniature manipulative instruments are inserted, which the surgeon uses to perform the operation. An optical device with a light source is inserted through another puncture. Modern optics are connected to a monitor screen, where a detailed and comprehensive image of the internal organ is displayed. You can view it in detail, and you can also use the image enlargement function. Naturally, an excellent overview of the surgical field is very convenient for the surgeon, which improves the quality of his work.
There are also benefits for the patient. Blood loss after laparoscopic operations is less, pain is lower, and the cosmetic result is better. Healing occurs faster, the rehabilitation period is simpler and shorter. And there are significantly fewer complications. Of course, at first glance, such operations represent a complete benefit for both the doctor and the patient. But is it really that simple?

Hovhannes Sarukhanyan: “Pediatric surgery and traumatology has something to be proud of” Read more
Complications
Laparoscopic operations are associated with a low risk of complications. As after any surgical intervention, in rare cases, infection and suppuration in the area of surgical sutures and bleeding are possible. If you are concerned about severe pain, vaginal bleeding, or increased body temperature, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Adhesions may occur after surgery. Very rarely, during surgery, damage to neighboring organs (intestines, bladder) is possible.
At the Euroonko clinic, operations are performed by experienced gynecological surgeons. Our operating room is equipped with modern equipment, multifunctional laparoscopic stands from leading manufacturers. This helps to minimize risks and perform the operation as safely as possible.
After removal, the cyst may recur, in the same ovary or on the other side. Only removal of both ovaries helps to completely eliminate relapse. But such an operation leads to menopause and undesirable consequences, so it is resorted to only in extreme cases.
From 5-6 days you can eat:
- pureed soups in weak meat broth or water;
- boiled fish;
- egg white omelet;
- 100 g of crackers, biscuits or dry white bread;
- liquid mashed porridge with water and half and half milk;
- unsweetened cottage cheese;
- from meat - beef, veal, chicken and rabbit;
- dairy products.
It is recommended to consume 1.5-2 liters of liquid in fractional portions. It is allowed to switch to a gentle diet from the eighth to tenth day - you should stick to it for at least one and a half months. Until three months it is forbidden to lift more than 5-7 kg. These simple rules allow you to easily endure the postoperative and recovery period without complications.
Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
You can get pregnant even with an ovarian cyst. Most often, they do not interfere with pregnancy, but they can make it difficult to conceive a child.
If during surgery only the cyst is removed or at least one ovary is left, the woman’s fertility is preserved. She may become pregnant in the future. Of course, you need to understand that reproductive function is affected not only by surgery. The ovarian reserve (the number of eggs in the ovaries - it constantly decreases with age) and concomitant diseases play a role.
Get a consultation with a doctor at the Euroonko clinic. Our doctor will tell you whether treatment is needed in your case, what type of surgery is indicated for you, and what is the likelihood that you will be able to conceive and carry a pregnancy in the future.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Jewelry work
The second important principle that is used today in pediatric laparoscopic surgery is the principle of minimal invasiveness. Doctors are confident that a small approach must be combined with minimally invasive (that is, gentle) surgery, then this justifies the essence of the method itself and guarantees the absence of postoperative injuries for the patient. Therefore, doctors performing laparoscopic operations on children try to work very carefully and literally with precision. This principle also implies the most gentle attitude when intervening to neighboring healthy organs and tissues. With an open operation, this is almost impossible to achieve, since the surgeon’s eyes cannot provide such a detailed image as a video camera can, showing the organ from all sides. In addition, manual manipulation is always more traumatic than working with thin instruments. In this regard, laparoscopic surgery provides great advantages.
Laser, plasma, TV... Which type of operation should you choose? More details