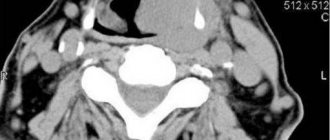
| X-ray of the pelvis at the German Family Clinic : consultation with a doctor, interpretation of images after the study. Make an appointment for an x-ray by phone. With the acquisition of the ability to walk upright, a person reduced the effect of radiation from solar irradiation several times, but increased the chances of diseases of the spine, pelvic organs, flat feet, hypertension and many others. The pelvis and the organs that it contains experience significant stress due to the vertical position, and fractures of the pelvic bones (4-7% of the total number of fractures according to statistics) are classified as severe injuries. |
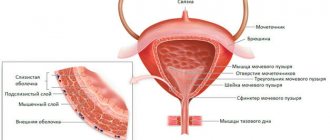
The pelvis is the part of the skeleton located at the base of the spine and consists of the ischium, ilium and pubis. It provides attachment of the lower limbs to the body, serving as a support and container for vital organs. The two pelvic bones are connected to each other and to the sacrum; form a bony ring of the pelvis, which is divided into the upper section (large pelvis) and the lower section (small pelvis). The male and female pelvis differ in shape: a woman’s is cylindrical, a man’s is cone-shaped.
In what cases may a pelvic x-ray be required?
Most often, x-rays of the pelvis and its organs can be prescribed by specialists in the following main cases:
- traumatologist: to assess the condition of the pelvic bones, if there are suspected fractures, joint dislocations
- gynecologist: to determine the causes of infertility, various pathologies of the reproductive organs;
- oncologist: for localization of foci of tumor growth and areas of metastasis;
- orthopedic traumatologist or rheumatologist: for clinical signs of osteoporosis, inflammatory processes
In case of suspected fractures of the pelvic bones, an x-ray is prescribed - the most accessible and informative method of diagnosis. Indications for prescription may be:
- complaints of severe pain in the pelvic area, hematoma and swelling;
- deformation of the natural shape of the pelvis;
- visually detectable change in the normal length of one limb in comparison with the other;
- urinary incontinence (may indicate a sacral fracture);
- signs of traumatic shock: pale skin, low blood pressure, extrasystole, cold sweat.
X-ray of the pelvic bones and organs that it contains is not a preventive procedure and is prescribed only for appropriate clinical indications by doctors.
How to sign up for the procedure
The doctors of the NEARMEDIC clinic are highly qualified, regularly take courses and confirm their certificates. Information about our specialists is freely available in the “Doctors” section.
NEARMEDIC clinics perform routine and emergency x-rays for fractures and injuries. The patient is referred for the planned procedure by a general practitioner or specialized specialist. If you have a referral from another clinic, you can conduct the test with us and get help from a NEARMEDIC specialist or pick up the test to show your doctor. To register, use the form on the website, call one of our branches or contact center.
Contrast X-ray of the pelvic organs - effective diagnosis of female infertility
Part of a woman's reproductive system is the fallopian tubes. These are the corridors along which the egg moves into the uterus. Scars, adhesions, and constrictions can become obstacles to the egg, and then conception may not occur. In order to examine the characteristics of the fallopian tubes, hysterosalpingography (HSG) is prescribed. This is the most informative method in this case, which helps not only to understand the patency of the fallopian tubes, but also to identify tumor nodes, polyps, and detect structural anomalies.
The GSK method is based on tracking the movement of a saline solution (contrast agent) through the fallopian tubes. In this case, water-soluble preparations are used that transmit X-rays due to iodine compounds in their composition. The procedure lasts about 30 minutes, and during this time 2 or 3 x-rays are taken.
Interpretation of the radiograph
Patients at the NEARMEDIC clinic receive an x-ray 20 minutes after the examination. The x-ray technician prepares a protocol that describes all the abnormalities he finds, but the final analysis and diagnosis remain with the specialized doctor.
When analyzing the finished image, the following indicators are important:
- Wiberg angles (about 30 is normal), neck-shaft angle (115-140 is normal), inclination of the entrance to the acetabulum (indicator 31-42 is acceptable);
- the width of the symphysis and the changes that have occurred in it;
- width of the sacroiliac joint;
- debris rotation;
- width of the joint space in the hip joint;
- deformation of the femoral heads;
- number and location of fragments during a fracture;
- displacement of bones, fragments along the length/width;
After identifying an injury or pathology, the doctor decides on the need for additional diagnostics; in this case, a computed tomography scan is prescribed for a more detailed study and clarification of the diagnosis. The advantage of CT over pelvic x-ray is that it monitors small tears and changes (up to 5 mm). CT results are useful for surgical planning.
Preparation for pelvic x-ray diagnostics
Preparing for a pelvic x-ray involves eliminating from the diet two days before the procedure any foods that cause gas formation in the intestines. It is recommended to take an enema the night before the procedure. An x-ray of the pelvic organs is performed on an empty stomach, and one hour before the procedure you should not drink liquid, and immediately before the x-ray you should empty your bladder. In the X-ray room, you will need to remove all metal objects and free the area of the body being examined from clothing. Before performing HSG, you cannot have sex with a partner from the moment of the onset of menstruation until the X-ray diagnosis itself.
Who should not have a CT scan of the pelvic bones?
Contraindications to CT
The examination is prohibited for pregnant patients, regardless of the period (X-ray exposure harms the fetus), and for patients in unstable physical condition. The procedure is not recommended for children under five years of age. The design features of the devices do not allow diagnosis of patients with a body weight above 150 kg, or a chest or abdominal circumference of more than 150 cm.
When planning tomography with image clarity intensifier, it is important to exclude iodine intolerance or allergies to radiocontrast medications, since the risk of anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema is high. Contraindications to such a procedure are severe renal and liver failure (a person’s health will deteriorate due to problems with metabolization and removal of contrast agents from the body), hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, and children under 12 years of age.
Contraindications for the procedure
Before ordering an X-ray of the pelvis, the doctor will make sure that there is no possibility of pregnancy in the woman. Pregnancy is clearly a contraindication for the X-ray procedure, which should be replaced with an ultrasound diagnostic method. In addition, hysterosalpingography is contraindicated in cases of inflammation of the uterus and its appendages, severe forms of cardiovascular diseases, infectious and bacterial diseases of the vagina. The doctor must also exclude the possibility of an allergic reaction in a woman to iodine-containing drugs. After HCT, it is recommended to use contraception for a month to prevent pregnancy. X-rays are prescribed for children under 15 years of age when it is impossible to use an alternative diagnostic method.
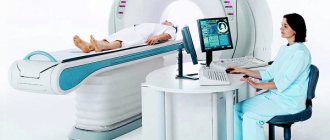
Computed tomography technique
Before starting the diagnosis, the patient talks with a radiologist. The specialist is interested in such aspects as a preliminary diagnosis, whether there have been surgical operations in the past, the results of previous examinations, whether there are any metal structures in the body, etc. Then the patient takes off things that could distort the image and lies down on the mobile table of the device. The doctor adjusts the settings, places the patient in the ring-shaped chamber of the CT scanner, and monitors the scan on a computer monitor in an adjacent room. The procedure lasts from 5 to 15 minutes. During this time, the subject must lie still.
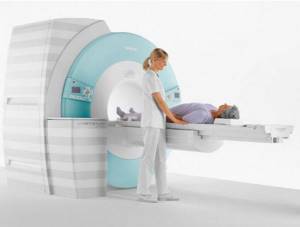
Native diagnosis is usually not accompanied by discomfort. Mild malaise, dizziness, and nausea sometimes appear after the administration of contrast, but these phenomena pass rather quickly. Computed tomography, as a rule, does not cause complications, and after the procedure you can return to your usual activities.
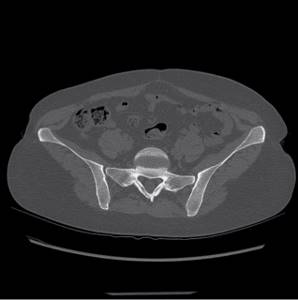
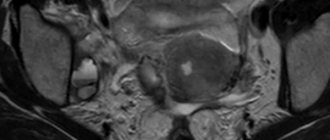
Fibrous dysplasia of the pelvic bones on CT
Fibrous dysplasia is a tumor-like disease characterized by impaired skeletal development with partial replacement of bone structures by connective fibers. Because the new tissue is not strong enough, fractures occur repeatedly in the affected area. Most often, one or both iliac bones are involved in the pathological process, very rarely – the ischium and pubis.
The disease is caused by disorders of intrauterine development and mainly occurs in children and adolescents. The peculiarity of fibrous dysplasia of the pelvic bones is the absence of symptoms at the initial stage. In the early stages, it is accidentally discovered during an examination for another reason.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture and the results of an X-ray, CT or MSCT of the hip joint: the images show an increase in the volume of the pelvic bones without disturbing their contours and foci of darkening resembling ground glass.
Are x-rays of the pelvis and pelvic organs harmful to the body?
Very often, doctors are asked how harmful pelvic x-rays are for the body. Of particular concern to women and men is the appointment of an X-ray of the pelvic organs, because organs performing reproductive functions are concentrated there - it is believed that X-rays carry a mutagenic danger. There is an opinion that the most weakened vulnerable organ can suffer from radiation first of all. Therefore, a contraindication to X-ray diagnostics is a state of severe illness or bleeding. A healthy body with good immunity will quickly recover after additional radiation exposure. The younger the patient, the greater the impact X-ray radiation will have on the body. But, if this is unavoidable, for example, in the case of injury to the pelvic bones, then the parents’ task is to minimize the radiation exposure from the procedure. Fortunately, the development of technology has made this possible.
Preparatory stage
The preparation is not particularly difficult. The patient is simply required to adhere to a certain diet two days before the scheduled examination date. It involves avoiding foods that stimulate increased gas formation:
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- black bread;
- dairy products.
Because of them, the visualization of the structures of the pelvic area is reduced by an order of magnitude, which may cause the need for a repeat study, once again exposing the body to radiation. And, if the disease or pathology is at an early stage of development, then it is unlikely to be examined at all due to increased gas formation.
An exception to the preparation rule is for patients who are urgently admitted to the hospital department. The doctor makes a decision on the spot, in case of receiving a blurry and uninformative image, about the choice of further diagnostics.
If the examination is routine, you will need to stop eating twelve hours before the procedure. It doesn’t hurt to do a cleansing enema the day before to better prepare the area to be examined for visualization during the examination.
An alternative is to use special pharmaceutical products that are freely available. Their cleansing effect is identical.

Another important point of preparation will be to warn the doctor about whether the patient has built-in electronic mechanisms in the body. We are talking about built-in hearing aids, pacemakers and other similar devices that may fail during this study. Moreover, their location does not play a significant role.
But the presence of metal inserts, such as supporting pins, pins or staples after previous fractures, does not pose a serious threat, including in terms of the information content of the study. It is enough to simply warn the radiologist and the attending physician about this feature in advance.
Also, immediately before the examination, you will need to remove metal jewelry and other removable metal elements that can limit the information content or clarity of the resulting image.
Having figured out how to prepare, all that remains is not to forget about two important contraindications:
- pregnancy;
- childhood.
The first point applies to women at any stage of gestation. Despite the fact that for adults the device provides radiation exposure within the limits of the officially permissible dose, for the fetus it can become an impetus for the appearance of developmental anomalies. We are talking about disorders in mental or physical development. For pregnant women, they usually choose to study the condition of the pelvis using a more gentle examination format - ultrasound or MRI diagnostics, starting from the second trimester of pregnancy.
Almost the same applies to the situation with children under fifteen years of age. But here the contraindication is classified as relative. In practice, this means that if the benefits of the study predominate over the possible harm, X-rays are still indispensable.
To reduce radiation exposure to other parts of the body, special lead aprons are used. They are designed to protect the thyroid gland from excessive load, because it is this organ that is considered the most sensitive to the effects of radioactive radiation.
The standard radiation level for a pelvic examination ranges from 1.57-2.23 mSv. The exact indicator depends on the number of projections required to establish a diagnosis, as well as the release date of the device itself. The older it is, the more unnecessary radiation it will emit.
Advantages of X-ray diagnostics using digital equipment
The main advantage, of course, is the minimization of the resulting radiation. This effect is achieved due to a number of factors:
- no X-ray film or chemicals are used;
- the device limits the area under study as much as possible, and thus reduces the load on adjacent organs that do not require X-ray diagnostics;
- The procedure time required to obtain a high-quality image is reduced.
In addition, the advantage of the digital radiography method is the ability to obtain clear, informative images, eliminating the need to repeat the procedure due to poor image quality. With the digital image format, it is easier and more functional for specialists - thanks to special programs, it is possible to “glue”, for example, long tubular bones or parts of the spine. It is convenient to store digital images for both doctors and patients in an electronic archive or on any digital media.
The German clinic has X-ray diagnostic equipment that can be used even for infants, and experienced specialists with extensive experience in pediatrics will help make an accurate diagnosis.
Attention: the prices presented on the website are not a public offer. Please check the cost of services by calling +7 (812) 432 32 32.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Structural subdivision of Polikarpov Alley Polikarpov 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Structural subdivision of Zhukov Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Structural subdivision Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
We draw your attention to the schedule of technological breaks in the CT and X-ray rooms.
If you are looking for where you can quickly, efficiently and effectively do an X-ray examination of the pelvis, come to a multidisciplinary medical center in St. Petersburg. The center operates an emergency room equipped with a modern Italian X-ray diagnostic device Clinomat, which allows for complete diagnostics in the shortest possible time, studying images in various processing modes¸ which is especially important, given the specifics of the emergency room. Experienced and sensitive doctors at the Medical Center will carefully examine you, take an x-ray of the hip joint, identify the disease,, if necessary, refer you to a specialist and prescribe a course of treatment and recovery.
A person is designed in such a way that the hip joint is involved in the process of walking and sitting and plays an important role in the implementation of these functions. Injuries, pathologies and diseases of this joint can lead to serious consequences and even disability. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose the disease in the early stages and begin treatment in time. X-ray of the pelvis in this case will be the primary and most informative method of obtaining data on the condition of the upper thigh, ischium, pubic bone, and hard tissues of the pelvis.