When should you get an MRI for headaches?
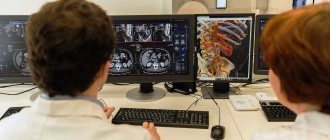
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is one of the modern and very informative types of diagnostics, which allows you to look inside a person’s head without causing any harm to him. If you are bothered by frequent headaches, this is a good reason to undergo an MRI. Tomography can show what is causing this problem. You should especially take headaches seriously if you begin to experience the following symptoms:
- A severe, sudden headache should make you suspicious. It may be a symptom of an aneurysm and hemorrhage.
- Progressive worsening of headaches, despite adequate treatment, may indicate the development of a brain tumor.
- If a headache is accompanied by difficulty speaking, double vision, or the person’s facial features have changed, or there is weakness in the arms or legs, an urgent need to contact a neurologist. This most likely indicates a pre-stroke condition. You can't hesitate here.
- If the headache becomes more intense when changing posture, when coughing, or during physical activity, these are all alarm bells for the possible development of a neoplasm.
- When pain first appears in a child under 5 years of age, it may be a sign of a growing head tumor.
- If for the first time a headache appears in a person for no apparent reason after 50 years, then this is a reason to suspect vascular pathologies.
To prevent brain diseases, doctors recommend doing an MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels at least once every 5 years and checking that everything is “in order with your brain.”
Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
In what cases is MRI of the brain prescribed?
A neurologist can give such a prescription if there are certain grounds for it, although today many medical centers are ready to provide the service without a referral. The following symptoms may be a reason to prescribe magnetic resonance imaging:
- Frequent headaches;
- Fainting conditions;
- Convulsive syndrome;
- A sharp drop in vision;
- Memory loss or deterioration;
- Lack of concentration;
- Speech problems;
- Impaired sensitivity;
- Poor coordination of movements.
The above symptoms can cause the following diseases or conditions:
- Received injury to the craniocerebral region;
- Acute osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- Previous heart attack and stroke;
- The presence of inflammation in the structure of the meninges;
- Developmental anomalies;
- Alzheimer's, multiple sclerosis;
- Tumors of various etiologies and so on.
The list of diseases that can be detected by MRI is wide; in order to make a reliable diagnosis, competent interpretation is extremely important.
What pathologies can a headache indicate?
Very often headaches accompany diseases such as:
- Acute sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses. Here, pain in the head occurs due to inflammatory phenomena occurring in the immediate vicinity of the brain. In this situation, the ENT specialist will provide a referral for an MRI of the sinuses.
- Middle ear infections. The ear is separated from the brain by a 3 mm thin plate of bone. Inflammation of the middle ear can easily spread to the meninges and even lead to death. With this pathology, the otolaryngologist will definitely refer the patient for an MRI of the ear and brain.
- Glaucoma. This eye disease is always accompanied by increased intraocular pressure and headache, mainly in the temporal region.
- Aneurysm of cerebral vessels. An immediate, very strong, almost unbearable headache may be a symptom of aneurysm dissection. And, if left untreated, this can lead to cerebral hemorrhage and death of the patient.
- Meningitis is a bacterial or viral inflammation of the meninges. If you have a headache, and the pain goes down to the neck and behind the shoulder blades, all this may indicate a possible infectious process.
- Brain tumor. Headache with this disease usually worsens with coughing and changes in body position.
Previous Next
How is the procedure performed?
In the case of recurrent headaches, an MRI examination procedure is prescribed to differentiate from complex organic brain lesions characterized by a structure similar to migraine. Such periodic pain cannot be removed by using analgesic drugs. Patients often and uncontrollably drink painkillers, which further aggravates the already difficult condition.
When carrying out a procedure using a tomograph, a neurologist adheres to a certain algorithm: scanning the brain, vascular bed and cervical system. If necessary, information is added to the overall result after angiography of the neck vessels. This is done for a general assessment of blood flow. On the resulting images, migraine is displayed in the form of numerous ischemic foci and modified blood flows. Before the onset of an attack of headaches, the blood vessels of the brain dilate significantly, and then their sharp spasm is visible.
Note!
In case of frequent headaches, it is not recommended to take painkillers unrestrainedly; it is better to immediately consult a neurologist.
Headaches after MRI examination
Although this diagnostic procedure is considered the most modern and safe, after it is carried out, some patients complain of increased and more frequent headaches. Attacks may be accompanied by nausea, dizziness, and general weakening of the body. Pain occurs in the area of the crown or back of the head. According to neurologists, this negative point is associated with an increased sensitivity threshold of patients who suffer from headaches. This effect is exclusively temporary. According to statistics, the intensification and frequency of pain disappears a few days after the MRI examination. At the same time, pain sensations of this spectrum can be easily removed with analgesics. Doctors claim that they are afraid of carrying out this diagnostic procedure; they should not.
If after a few days the pain continues to bother the patient, then it is necessary to consult a doctor. In addition to medication, it is recommended to consume less fluid, and also eliminate the possibility of physical or mental stress. An MRI examination cannot cause any harm to the patient’s health, since it is the most modern, safe and non-invasive diagnostic method.
Will a head MRI show the causes of headaches?
An MRI of the head can reveal anatomical causes of headaches. Tomographic images will clearly show:
- neoplasms of benign and malignant nature;
- degree of tumor spread and metastasis;
- neurological lesions of the eyes, inner ear;
- signs of inflammatory processes in the sinuses;
- vascular pathologies;
- lesions of the membranes of the brain;
- conduction disturbance in nerve fibers (demyelination).
Using tomography data, a neurologist will be able to use exclusion to find the true cause of headaches and decide on treatment tactics.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Price by Discounts During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of cerebral vessels (MR angiography) | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of neck vessels (MR angiography of the neck) | 3500 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6800 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| Comprehensive MRI examination of brain and neck vessels | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MR arteriography | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
MRI of the cervical spine for headaches
The cause of the headache may lie in the neck. Cervicogenic headaches are associated with tension in the muscles of the head and neck. The cause of this tension may be displacement of the cervical vertebrae, impaired mobility, or manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis. Sometimes the pain is caused by a pinched occipital nerve. Typically, such a headache begins in the back of the head and spreads to the ear, eye or forehead. For cervical headaches, you can almost always feel the painful points where the nerve exits. To diagnose cervicogenic headaches, a comprehensive MRI examination of the neck and head is performed.
Is it necessary to do an MRI of the brain with contrast for headaches?
For headaches, you need to start your diagnostic journey with a basic, non-contrast MRI of the brain. If the initial MRI examination reveals tumor abnormalities, the patient will be offered a contrast agent. During diagnosis, a contrast agent is injected to enhance the signal in the area of possible anomaly. With contrast, you can reliably determine the structure, size, boundaries and zones of pathological processes in the brain. MRI with contrast will give the doctor the opportunity to see the extent of the spread of the tumor abnormality to the surrounding structures, reliably assess dynamic changes and see the number of foci.
Previous Next
Headache - what to do?
First of all, do not endure the pain, but consult a doctor: pain may turn out to be only a symptom of a dangerous disease occurring latently in the body. One of the most serious cases is cancer. If a specialist has sent you for an MRI of the head, do not delay the examination: the sooner you detect the pathology, the easier and faster its treatment will be. At the Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center, an MRI for headaches will be performed for you by experienced specialists with many years of experience using expert-class equipment.
Sign up for an MRI for headaches at the Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center near the Baumanskaya metro station (see map) by phone: 8 (495) 127-03-71 or leave a request on the website.
Baumanskaya metro station (see map) 8
leave a request on the website
What to choose: CT or MRI for headaches?
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are two ways of looking at the same problem differently.
MRI is a medical imaging technique, a way to look inside the human body without resorting to cuts or punctures. A study is carried out using a magnetic field. The magnetic field strength of the tomograph is many times higher than on Earth. Phones stop working near an MRI machine and bank cards become demagnetized. However, the magnetic field used is safe for humans. It makes it possible to look inside the human brain without X-rays and detect pathology at an early stage. CT differs from MRI in its operating principle based on X-ray radiation. A CT scanner is a modern version of an X-ray machine that can take a large number of scans from different angles and from them create a three-dimensional model of the area being examined. Magnetic resonance imaging is the dominant type of examination for head pathologies. Therefore, for headaches, it is best to start diagnostics with an MRI of the brain, rather than a CT scan, which is associated with radiation exposure to the body. Here, MRI of the brain will be the most informative and comprehensive type of diagnosis. However, there are situations when doctors will prefer to give a patient a CT scan of the brain. This happens in emergency cases. The main indication for a head CT scan will be traumatic brain injury. When doctors need to very quickly decide on surgical intervention, and they do not have 20-30 minutes for an MRI scan of the head, they will use computed tomography. If a patient is suspected of having a stroke, neurologists need to quickly differentiate whether the stroke is ischemic, associated with a blood clot, or hemorrhagic, which is caused by bleeding in the brain. Treatment for these two types of stroke is radically different. Therefore, if a person is admitted by ambulance, doctors will do a quick CT scan rather than an MRI if a stroke is suspected, and based on its results they will begin intensive therapy. Author: Varlaty Valentin Pavlovich
Neurologist, acupuncturist with 40 years of experience
Indications for vascular MRI
In addition to the above reasons, the doctor may prescribe magnetic resonance imaging if the following diseases are suspected:
- Vascular malformation, which is manifested by the formation of additional connections between arteries and veins, which leads to mixing of venous and arterial flow;
- Aneurysms are excessive expansion of the vascular wall, which can lead to rupture and subsequent hemorrhage;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Vasculitis, which is a consequence of rheumatism of various etiologies.
In addition, it is worth saying that a computed resonance imaging scan is an informative source of information before performing brain surgery.