Currently, the main methods of radiation diagnostics are radiography, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which only at first glance are very similar in principle of operation. Many of our patients have a question: “What is the difference between CT and MRI, and what are their differences from radiography?”
All of the above methods allow you to quickly and painlessly visualize organs and tissues of the area under study. However, there are a number of significant differences that may be decisive when choosing one or another research method. We will look at them in detail so that our patients have complete information and can evaluate the benefits of each of them.
CT or X-ray examination
CT is a fairly new and improved method of x-ray examination. It is quite difficult to answer exactly which is safer, X-ray or CT. Both methods are based on the passage of ionizing radiation through the human body. The dose received depends on many factors: from the irradiated area to the technical characteristics of the device. Today, research facilities are being modernized, their harm is being minimized. Therefore, it is impossible to say unequivocally what is more harmful, x-rays or computed tomography. But in general, x-ray is a safer method than CT, although less informative.
Difference between CT and X-ray
The usual x-ray method is line scanning. The image is created by passing a beam of rays once through the area of interest. Pictures are taken only in one plane. CT makes it possible to make layer-by-layer sections of the examined area. Images are created in different planes.
Limitations for CT and X-ray
Limitations to both studies are:
- cardiac diseases;
- diabetes;
- severe pathologies of the liver or kidneys;
- tuberculosis;
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- hypersensitivity to iodine.
If there is a chance to diagnose in a more gentle way (by doing an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging), it is better to exclude CT and X-rays.
CT scan
This is a more modern version of radiography, which has retained its key features: the basis for obtaining an image is x-ray radiation, which, passing through the patient’s tissues, is absorbed and attenuated in different ways (based on their density). However, an important difference is that computed tomography is a set of layer-by-layer X-ray images of a certain slice thickness, from which a volumetric projection is built, and not a plane, as in an X-ray. This (as well as the high image quality) is one of the main advantages of computed tomography over the traditional x-ray research method.
Despite the safer and more efficient operation of modern devices, frequent computed tomography is still not recommended due to the possible impact of X-ray radiation on the body. However, computed tomography is the leading method for diagnosing diseases of the chest and lungs, adrenal glands and the musculoskeletal system.
Advantages and disadvantages of both methods
Which is better, X-ray or CT?
Conventional X-ray:
- More accessible. The equipment, as a rule, is available in all medical institutions.
- Cheaper. The price for examinations is low: from 300 to 1500 rubles.
- Safer. The radiation dose is 0.2-09 mSv, it is possible to repeat the study in a few days.
X-rays clearly show bone and other tissues, but not their structure.
CT allows:
- see the organ separately, from several angles;
- more accurately determine the size and depth of the pathological focus;
- reduce the effect of the overlap of other organs, reducing the procedure time.
The images show structures whose densities differ by only 0.1%.
Disadvantages of CT compared to radiography:
- higher cost, averaging 3-6 thousand rubles. • higher radiation dose with CT (3-10 mSv) than with X-ray.
When is CT used and when is X-ray used?
X-ray is used in diagnosis:
- various injuries and degenerative changes in bone tissue;
- diseases of the bronchi and lungs;
- oncological neoplasms;
- gastrointestinal problems;
- dental and ENT diseases.
If radiography does not provide the necessary information, CT comes to the rescue. It is mainly prescribed when it is necessary to examine:
- complex areas (brain, inner ear, teeth);
- gastrointestinal tract, bladder, bronchi, lungs;
- tumors and metastases.
CT allows you to simultaneously assess the condition of bones, soft tissues and blood vessels with an accuracy of 97-98%.
Dangers of CT and X-rays
When undergoing the procedure, the danger is ionizing radiation, which can:
- temporarily change the composition of the blood;
- degenerate tissue molecules;
- change protein structure;
- disrupt the process of cell functioning;
- cause cataracts and various neoplasms.
Although the study uses low-energy radiation and time intervals are kept to a minimum, it is important to follow all safety precautions prescribed by the instructions.
Radiography
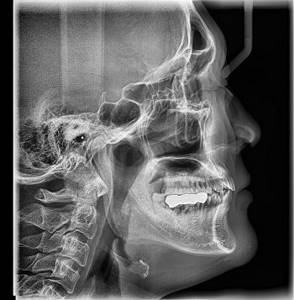
The principle of operation of the X-ray machine is that X-rays, passing through the different-density environment of the area under study, are attenuated in different ways: denser bone tissue absorbs X-ray radiation to a large extent, less dense subcutaneous fat weakens it to a small extent, and air, contained in the paranasal sinuses or lungs, does not retain at all. These unevenly attenuated beams of X-rays, falling on the photosensitive layer of the film, form an X-ray image - an image that displays all the structures of the area under study, layering them on top of each other. In this case, the resulting image allows you to determine the shape, size and structure of the area under study, identify or suspect structural disorders, and the study in two or more projections allows you to determine the localization of the identified changes. Most often, radiography is used to study bones, lungs, kidneys, and intestines.
From the very beginning of its existence, this diagnostic method raised many questions among patients about the effects of X-ray radiation on the body. To date, experts have confirmed the harm of x-rays and its ability to influence the development of unwanted processes in the body. However, this method of radiation diagnosis continues to be in demand because it requires minimal costs.
Safety measures and possible complications during diagnostic radiology studies
The pathogenic effects of X-rays cannot be completely reduced, but they can be minimized. To this end, a number of measures are provided:
- Research should be carried out only as indicated and prescribed by a doctor;
- Two or more x-rays cannot be taken during the day;
- Parts of the body in the immediate vicinity of the test area should be carefully covered with aprons or lead covers.
If all precautions are taken, non-contrast X-ray examinations and MSCT do not cause complications.
If the test is performed using a contrast agent, reactions to the contrast may occur. The clinical picture of complications can vary from mild urticaria to severe conditions (anaphylactic shock, acute left ventricular failure, asthmatic condition).
If an X-ray contrast test is prescribed, the patient should immediately inform the doctor if he has any allergic reactions.
How else do these methods differ?
The methods also differ in information content and dose load (the amount of exposure to ionizing radiation on a person). “If we compare these indicators for X-ray and fluorography, a lot depends on the generation of the equipment and its condition. The general trend is that analog devices provide a higher radiation dose and less information content than digital ones. The dose loads of modern digital fluorographs and digital X-ray machines are comparable, and the information content of a standard study (in frontal and lateral projections) is also comparable,” says the radiologist.
According to the expert, CT is more informative than radiography, but it also has a higher dose load. “CT also provides new opportunities: it allows for examinations using contrast agents (a special substance that is injected into an organ, body cavity or bloodstream). CT with contrast is performed in cases where it is necessary to very clearly separate normal and pathological structures in the human body or to conduct functional studies. For example, if we look at the contractility of the heart muscle. The dose load with CT is greater than with radiography if we compare the study of the same organs. But modern developments in radiation diagnostics are aimed at reducing the maximum dose load. There is a low-dose CT scan of the lungs, which gives a dose load of less than one millisievert, while radiography of the abdominal organs in several projections can give more than one millisievert,” explains Kharlamov.
Unlike X-ray diagnostic methods, MRI does not have a dose load. The patient is placed in the device in a high-intensity magnetic field, where there is no ionizing radiation.
Article on the topic
IVF, MRI, “chemistry”. What kind of medical services seem to be paid?
Is it possible to perform radiography and CT at the same time?
The recommended interval between two x-ray examinations should be 1-2 months.
Exposure to radiation during subsequent radiological diagnostic procedures is high, but may not cause significant harm to the patient's health. A physician should not perform two radiological examinations without good reason. Sometimes, after an X-ray examination, it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis with a more reliable method, especially if an oncological process is suspected.
Magnetic resonance imaging
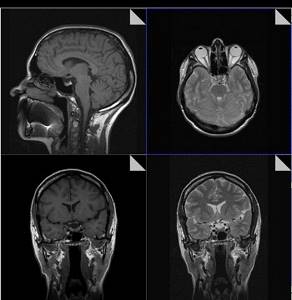
MRI is based on the phenomenon of magnetic resonance, which is based on the re-emission of radio waves interacting with hydrogen atoms contained in excess in the human body. These re-emitted electromagnetic waves are captured by the MRI sensor, amplified, and appear on the monitor screen in the form of digital images. This is a harmless and absolutely safe method of radiation diagnostics for human health, since the image is obtained without X-ray radiation, so MRI can be taken an unlimited number of times, at any interval.
A significant advantage of MR imaging over CT is that it is not contraindicated for pregnant women in the second and third trimester and is completely safe for children. In MRI, the area under study is scanned in three projections, which allows the radiologist to fully assess the condition of the tissues and organs of the area under study, and high image contrast and spatial resolution allow visualization of the gray and white matter of the brain, assessment of the condition of the bone marrow and soft tissues of various locations . In addition, the MRI method allows you to obtain images of the vessels of the brain and neck vessels without the introduction of a contrast agent.
Of course, like many other research methods, MRI has a number of contraindications. However, if you carefully read them, you will notice that they are mainly associated with the presence of metal-containing implants (devices that do not have magnetic properties are not a contraindication), as well as with severe claustrophobia. Thus, in most cases, MRI can be the most optimal and completely safe alternative to computed tomography and radiography.
Results - what to choose?
The capabilities of conventional X-rays are limited; they cannot replace CT. The question here is whether it is advisable to use tomography. You should not expose your body to unnecessary radiation exposure in order to find out the consequences of a domestic injury and diagnose the presence/absence of a fracture.
If the data obtained is insufficient or the patient’s condition seriously deteriorates, then tomography will be a priority, which will help identify hidden pathologies.
✓ On the project, you can sign up online for a CT scan of the sinuses, spine, heart and other anatomical areas at a convenient diagnostic center in Moscow.