A dental x-ray is a detailed image of the teeth, bones and soft tissues around them, allowing us to identify various dental and oral problems. X-rays can show cavities, hidden dental structures (such as wisdom teeth), bone loss and other abnormalities that cannot be detected during a visual examination and a routine dental consultation. Dental X-rays are usually performed annually. It is also actively used for follow-up monitoring of teeth after treatment. X-rays may be prescribed more often if your doctor monitors the development of a dental problem directly during treatment.
Types of dental x-rays
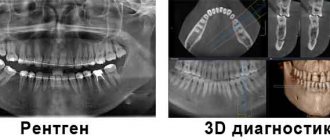
Today, there are four main types of dental x-rays according to their intended purpose:
- Bite X-ray – an image of the upper and lower rows of teeth in a closed state. This type of x-ray helps identify malocclusions, subsidence of bones, interdental caries, and the presence of hidden cavities. Also allows visualization of bone loss due to severe gum disease or dental infection.
- A peripheral x-ray of a tooth depicts the entire tooth, its surface and internal parts, that is, it is an image from the crown of the tooth to the part of the bone that supports it. These x-rays are used to identify dental problems below the gum or jaw line, such as affected teeth, abscesses, cysts, tumors, and bone changes associated with certain diseases.
- An occlusal photograph is aimed at identifying the condition of the roots of the teeth and the dental floor. It is actively used for jaw fractures, cleft palate symptoms, abscesses and suspected presence of hidden/not yet erupted teeth (including wisdom teeth). Occlusal x-rays can also be used to detect foreign objects.
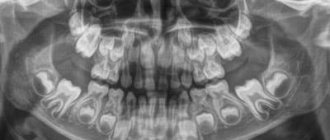
- Panoramic x-ray of teeth. Allows you to obtain a detailed image of the jaws, teeth, nasal cavity and jaw joints. This type of x-ray does not allow visualization of cavities. This type of x-ray is effective in diagnosing tooth fractures, various bone pathologies, cysts and neoplasms. Actively used before orthodontic treatment.
Why are x-rays prescribed in dentistry?
Not in all cases, a specialist can visually see the full picture of the disease, as well as check the quality and integrity of the filling. In such cases, x-rays come to the rescue. This type of research makes it possible to study the nature of the pathology and begin treatment measures in a timely manner. Often this makes it possible to relieve the patient from toothache later, which occurs in the absence of appropriate treatment. In addition, x-rays in dentistry are sometimes prescribed for preventive purposes, to identify possible pathologies that are not visually visible to the dentist.
In the image, the dentist can see the root canal, the filling and assess the quality of its placement, identify caries that can develop in hard-to-reach places and determine its depth, monitor endodontic measures (canal filling), and assess the condition of the tissues surrounding the tooth in case of periodontitis. X-rays are also prescribed for prosthetics and dental implantation, and when they are removed. The decision on the need to conduct this type of study is made by the attending dentist.
X-rays in dentistry allow you to see teeth that have not yet erupted and diagnose jaw fractures and malocclusions.
It is difficult to overestimate the need for x-rays in dentistry, because only thanks to this study it is possible to identify some pathologies and begin treatment on time.
Types of X-rays in dentistry
There are several types of x-rays in dentistry:
- Intraoral (dental) examination - used in cases where you need to see one or more teeth. To do this, a special film or sensor is placed in the patient’s oral cavity;
- Panoramic examination - the entire maxillofacial area is visible in the image; it is prescribed, if necessary, to study the jaw completely;
- Computed tomography - consists of taking several pictures in different planes, and also allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image. Today, this type of research is the most modern and informative.
What can an x-ray reveal?
Thus, using dental x-rays, the dentist can determine:
- inflammatory processes inside the tooth that are invisible during normal examination;
- presence, size and location of neoplasms (eg, cysts) or foreign bodies;
- quality of dental canal filling;
- the degree of development of caries and the presence of deep, hidden carious areas;
- the presence of an abscess or other purulent-inflammatory processes;
- cracks in teeth;
- abnormalities in bone development;
- the presence of hidden, unerupted teeth (for example, wisdom teeth).
X-ray with contrast
When increased image clarity is needed, a non-absorbable X-ray contrast agent is first injected into the tissue. X-ray contrast agents are either X-ray positive or X-ray negative. X-ray positive ones will contain iodine or barium, X-ray negative ones will contain air, carbon dioxide or nitrogen. Depending on the area and purpose of the study, X-ray contrast agents are administered separately or in combination. Comprehensive introduction for maximum radiographic clarity - milk contrast technique.
Features of the appointment of dental x-rays
If you are a new patient, you will likely undergo dental x-rays so that the new dentist can get a clear picture of your dental health. This is especially important if you do not have x-rays from your previous dentist. Children may need dental x-rays more often than adults because their dentists need to monitor the growth and development of their teeth. This is important because it can help the dentist determine whether baby teeth need to be removed to prevent complications, such as adult teeth growing behind baby teeth.
Prices for dental x-rays in St. Petersburg
How much does it cost to get a dental x-ray in St. Petersburg? The question of the price of dental x-rays in St. Petersburg is of interest to many people planning to undergo dental treatment. Let us note that the cost of this type of diagnostics is quite affordable and accessible to a wide range of patients.
The exact price of an image will depend on its type, the equipment on which it will be taken, and the pricing policy of the clinic where you will contact for the service. If you need a regular sighting shot, then its cost in St. Petersburg will fluctuate between 400-500 rubles (for 1 tooth).
Digital photographs and panoramic photographs of the jaws will have a higher cost. But the inflated price for diagnostics and performing x-rays in 3D format will be fully justified by the high accuracy of the images. If you need to take a panoramic photo of the jaws before dental treatment, its cost in St. Petersburg will start at 2,000 rubles.
To find out the exact cost of dental x-rays in St. Petersburg, you need to visit a consultation with a dentist, who will determine the problem and tell you exactly what kind of picture you will need to take before starting treatment.
Risks of Dental X-Rays
Dental X-rays involve radiation, however, the radiation levels are so low that it is considered safe for both children and adults. If your dentist uses digital X-rays instead of film X-rays, the risks from radiation exposure will be even lower.
Also, before the x-ray, the specialist will provide you with a protective apron to put on your chest, abdomen and pelvic area to prevent unnecessary radiation exposure to vital organs. In case of thyroid disease, a special thyroid collar may be used. Children and women of childbearing age may also wear it along with a lead bib.
Pregnancy is a contraindication for radiography. Women who are pregnant or think they may be pregnant should avoid all types of X-rays. Tell your dentist if you think you are pregnant because radiation exposure is not considered safe for the developing fetus.
Stages of implementation of commissioning of X-ray equipment
To ensure that the equipment meets sanitary requirements, the administration of the medical institution must carry out a set of measures. Among them are the following:
- Obtain a license to handle sources of ionizing radiation.
- Obtain a sanitary and epidemiological certificate for the same activity, as well as for the X-ray machine.
- Have a certified copy of the state registration of the device.
- Obtain a sanitary and epidemiological report for an x-ray office or a dental office with an x-ray.
- Have operational documentation for the device and a registration certificate for the cabinet.
- Draw up a protocol for dosimetric measurements in individual areas - workplaces, adjacent and adjacent territories.
- Draw up protocols for studying the parameters of the device and testing protective equipment (individual and mobile).
- Provide certificates for checking grounding and ventilation efficiency, if available.
- Obtain a conclusion from the medical commission that Group A personnel undergo preliminary and periodic medical examinations.
- Provide an order on the admission of employees to work and on the appointment of a person responsible for radiation safety.
- Organize a control program to ensure radiation safety at the enterprise.
- Check that Category A employees have documents confirming that they have been trained in the rules of operating the machines.
- Keep a log of training and instructions on radiation safety, etc.
If these and other requirements are met, the X-ray room or X-ray machine in the dental office will operate in accordance with the standards.
Preparation and carrying out the procedure
Dental X-rays do not require special preparation. The specialist will guide you through each step of the x-ray process. He may leave the room briefly during filming. You will be required to stand or sit still for short periods of time. Spacers (film holders), if used, will move and adjust in the mouth to produce correct images.
Once the images are ready—immediately in the case of digital x-rays—your dentist will check them and determine whether or not there are any abnormalities.
How to properly place an X-ray machine in a separate room
To place an X-ray machine in a separate room, a project is needed. It is developed by a design organization that has the appropriate license, then a sanitary and epidemiological conclusion is drawn up for the project. The equipment of the office must comply with the requirements of regulatory and technical documentation.
Suitable materials for flooring are linoleum, artificial or natural stone, ceramic tiles and other non-conductive substances. It is necessary to organize proper air exchange to maintain temperature and humidity in a given range, for which window fans, air conditioners or supply and exhaust ventilation are installed in the room.
Digital radiography
Today there is a new technique for dental radiography using digital technology. The new method eliminates the need to develop X-ray film in a dark room; instead, the X-rays are sent directly to a computer and can be viewed on screen, saved or printed. There are several advantages of using this technology:
- minimal radiation;
- saving time - the image is available on the screen a few seconds after shooting is completed;
- the ability to enlarge images multiple times compared to their actual size on the computer screen;
- the ability to send images by email (for example, to another specialist to get a second opinion, etc.);
- software installed on a computer can help dentists digitally compare current images with previous ones in the process of subtraction radiography. Using this technique, everything that is similar between two images is "subtracted" from them, leaving a clear, detailed image of only the part that is different. This helps dentists easily see subtle changes that might not be immediately noticeable.
Dental radiography is of fundamental importance for correct diagnosis. Thus, today radiography is an integral and extremely important part of professional dental care.
Radiation doses and safety –
A patient's radiation exposure is measured in either microsieverts (µSv) or millisieverts (mSv). The recommended radiation dose for the population received as a result of X-ray studies (according to the recommendations of SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03) should not be more than 1000 μSv per year (= 1 mSv per year).
Below we will give examples of different types of images in dentistry and the corresponding radiation exposure to the patient (data from the Ministry of Health of Russia dated July 22, 2011 and December 21, 2012)…
- Targeted images on a digital radiovisiograph – → lower jaw in adults – 2 μSv, → lower jaw in children under 15 years old – 1 μSv, → upper jaw in adults – 5 μSv, → upper jaw in children under 15 years old – 3 μSv.
- Sight shots using film – 10-15 µSv.
- Digital panoramic image – 55 µSv, but if the patient is less than 15 years old – 24 µSv.
- Digital teleroentgenogram – 7 µSv.
Conclusions: thus, targeted images using a radiovisiograph provide the lowest radiation dose compared to other types of x-ray examination in dentistry.
During one visit to the dentist, you can take 5-6 pictures on a digital radiovisiograph without risk to health, but no more than 100 such pictures during the year. A digital orthopantomogram (panoramic x-ray of the jaw) can be done 1-2 times a month, but no more than 10 times during the year. Panoramic films on film provide a greater radiation dose to the patient, and they can be taken less frequently than digital ones.
Mammography
Allows you to identify signs of the formation of atypical cells - microscopic accumulations of calcium salts - 1-2 years before the formation of breast cancer. If the diagnosis is confirmed at an early stage, the scope of surgery is minimal and the organ is preserved. According to the standards of domestic medicine, patients without complaints should undergo mammography annually upon reaching the age of 40. It is extremely important for everyone and especially women with a hereditary predisposition to adhere to this schedule.
Indications for unscheduled mammography:
- lumps and/or tenderness in the breast;
- discharge from the nipple.
The procedure is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding; up to 35 years of age is carried out as prescribed by a doctor.