Ultrasound diagnostics have been used for many years to identify various pathologies in organs and systems of the body, confirm the fact of pregnancy, determine the state of fetal development, etc. Many people undergo diagnostic procedures dozens of times throughout their lives, but they are still concerned about the same things the same questions about how often ultrasound can be done and how harmful it can be. In fact, regular examinations of certain organs increase the chances of successful recovery if the disease is detected at an early stage. In turn, ultrasound prices directly depend on which part of the body is being diagnosed.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Is ultrasound harmful?
- Is ultrasound harmful during pregnancy?
- Is ultrasound harmful in early pregnancy?
- Is ultrasound harmful to the fetus?
- Is ultrasound harmful for pregnant women?
- Is ultrasound harmful for infants?
- Frequency of ultrasound
- Is ultrasound of the brain harmful?
- Is breast ultrasound harmful?
- Is kidney ultrasound harmful?
- Is 3D ultrasound harmful?
- Is it harmful to have an abdominal ultrasound?
- Is it harmful to have a pelvic ultrasound?
- Video
Harm of ultrasound: true or false?
The uterus is a sensitive organ and reacts sharply to ultrasound, as a result of which it may become toned during the procedure. According to some scientists, too frequent use of ultrasound during pregnancy can cause various types of neoplasms. In the early stages of pregnancy, the harm of ultrasound is much higher due to the formation of internal organs in the fetus. Any interference in this process can adversely affect the child's development. At 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, it is better to refrain from ultrasound and wait until the first screening. All experienced specialists know about this, so they do not prescribe such examinations again. Here we note that this information is relevant only if ultrasound is performed excessively often in Kaluga.
Researchers tried to find out which organs are most affected by ultrasound and came to the conclusion that the brain is the most vulnerable. Scientists have identified a connection between the frequency of fetal ultrasound and the number of left-handed children born. In their opinion, such children may have problems mastering writing skills at school. A study was conducted in America that showed that frequent vaginal ultrasounds lead to the birth of children with autism.
It’s worth making a note here: you shouldn’t be afraid to undergo an ultrasound, as this is necessary to monitor the normal development of the fetus. The main thing is that you are under the supervision of an experienced specialist who will regulate the frequency.
Introduction
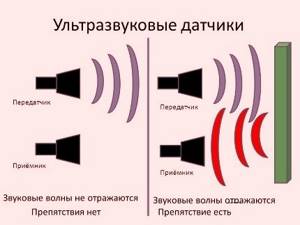
Ultrasound is special elastic sound waves, common in nature, with the help of which fish, dolphins, and bats communicate, but humans do not perceive them as sound.
Since the 30s of the last century, researchers began to look for the possibility of using these waves for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The ultrasound procedure is quite simple. The device's sensor, which acts as an emitter of ultrasonic waves with a frequency of 16 Hz to 20 kHz, concentrates them into a narrow beam and directs them to the area under study. Waves pass freely through soft tissues and air, but when they encounter denser objects, they are reflected from them. These reflected waves are captured by the same sensor and transmitted to the control panel.
|
Due to the fact that the underlying tissues absorb and reflect waves differently, the amount of ultrasound energy that reaches the organ under study will be less than that originally supplied by the sensor. Special programs convert the reflected waves into an image of the organ on the monitor.
Is ultrasound harmful?
|
| Ultrasound is an integral part of the diagnostic and treatment work of medical institutions |
Since the introduction of ultrasound into medical practice, the issue of ultrasound safety has not ceased to be discussed and debated among supporters and opponents of the method. Studies of the effect of ultrasound on the cells of a living organism were carried out in many countries of the world in scientific laboratories on animals, in experimental studies in vitro (in test tubes), experience of clinical use in humans was accumulated and processed.
Almost 90 years of practical experience with ultrasound has convinced the vast majority of physicians of the absolute safety of the method. But when it comes to screening pregnant women, fetuses, newborns and older children, concerns remain, most of which are based on unconfirmed myths.
Myth No. 1.
Ultrasound destroys human DNA. This opinion was based on the work of P.P. Garyaev, where he expressed concern about the delayed destructive effect of ultrasound waves on the human genome. After additional research, the world community refuted this opinion, and ultrasound began to be widely and safely used to examine the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy.
|
| Ultrasound of the fetus at 12 weeks of pregnancy |
Myth No. 2.
The frequency of ultrasonic waves of 20 Hz during ultrasound leads to dangerous resonant vibrations in cells, which can stimulate the growth of malignant tumors. This claim has been refuted by many scientists working in the field of oncology, who called this myth far-fetched.
Myth No. 3
. Ultrasound leads to the appearance of thermal and mechanical destructive effects on cells. This opinion was also refuted, because The low wave power of 500 MW/cm² and the large beam width cannot cause significant heating or any damaging effects for living tissue.
Myth No. 4
. Frequent ultrasounds are harmful, it destroys tissue. In fact, most ultrasound machines operate in a pulsed mode, reducing the time the ultrasound affects the human body. Ultrasound is simply vibrations, the effect of which is not cumulative. If ultrasound destroyed tissue, it would be noticeable primarily on the skin, but the integrity of the skin is not disrupted by the action of waves.
Myth No. 5.
Frequent ultrasounds of the pregnant woman and fetus are the cause of autism in children, because the coordinating work of the cerebral cortex is disrupted. The assumption was made on the basis of studies on mice; it has not yet been possible to prove this connection in humans.
The only statistically proven feature that was revealed as a result of numerous studies of pregnant women undergoing ultrasound scans was that the majority of boys born to them were left-handed. No other abnormalities in their development were found.
Thus, ultrasound does not have any negative effect on either brain cells or the functions of any other organs if the study is carried out in compliance with safety rules on a well-tuned apparatus by a qualified specialist.
The influence of ultrasound on the human body
Today, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is one of the most accessible and highly informative research methods in medical practice; it is performed on everyone - from infants to the most elderly people. There is even a fashionable trend among expectant parents: to confirm the contract made by another specialist, find out the sex of the unborn child, and take a photo as a souvenir. Unfortunately, many people forget that an ultrasound is still a special medical study, and not a video recording for memory. Why do you need an ultrasound?
As with any study, there are certain indications for ultrasound in obstetrics.
Firstly
, to confirm the fact of pregnancy, establish the location of the fetus (in the uterus or in the abdominal cavity), determine the number of fetuses, determine the age and sex of the fetus and the correctness of its development, recognize fetal anomalies and its death. An image of the fertilized egg can be obtained as early as 5-6 weeks of pregnancy. Image of the embryo - at 7-8 weeks. From about the 10th week of pregnancy, slow fetal movements are recorded. In the period from the 24th to the 34th week, the sex of the fetus can be determined.
Secondly
, to study the position, size and condition of the placenta - the main connecting link through which blood is exchanged between mother and fetus.
Third
, this is measuring the pelvis and assessing the condition of the birth canal (in particular, eliminating obstacles to the birth act, for example, pelvic deformities, ovarian cysts and others).
Fourth
, determination of the hormonal status of a pregnant woman. Of all the listed tasks, perhaps the most important is to identify malformations of the cardiovascular and nervous systems of the fetus in the early stages, more precisely, up to 20 weeks, when it is possible to terminate the pregnancy.
It is impossible to underestimate the ultrasound method. Thanks to the examination, the birth of children with severe facial defects: clefts of the hard and soft palate is practically excluded
children with poly- and syndactyly (extra fingers and fusion)
children with atresia (fusion) of the esophagus and intestines. This is not a complete list of pathologies available for ultrasound testing.
Currently, in developed countries, ultrasound screening programs are carried out for all pregnant women at 10-15 weeks, 18-24 weeks, and 32-34 weeks.
What is ultrasound?
The ultrasonic transmitter emits high frequency sound waves of 3.5 MHz, which are not perceptible to the human ear. These waves hit the object, are reflected from it and enter the receiving device (receiver), which interprets them in the form of a picture on the monitor screen. Reflecting from the child, the waves allow you to see his skeleton and internal organs. Various examinations of a pregnant woman are performed using ultrasound: ultrasound, Dopple cardiography, echography. The difference is what exactly the doctor examines (fetus, placenta, fetal heartbeat) and what kind of wave beam (scattered or directed) is used for this. For example, when determining the fetal heartbeat and studying blood flow in the placenta, a stronger and more directed beam of ultrasonic waves is used than during general scanning, but the beam is not directed to the fetal head, and the research time is calculated in a couple of minutes.
What determines the nature of the effect of ultrasound on the patient’s body? It depends on the intensity, exposure time, and sensitivity of living tissue. Ultrasonic energy can have a negative effect if its intensity exceeds 10 W/cm. The resulting disturbances are primarily associated with tissue heating, to which may be added
cavitation (formation of gas bubbles in a liquid). It is believed that with the diagnostic use of ultrasound energy with an intensity of 0.05-0.25 W/cm, tissue heating is practically absent. But whether cavitation occurs in this case is unknown.
However, doctors who work on ultrasound machines during the working day note the occurrence of tingling in their fingers. Therefore, there is currently no clear point of view regarding ultrasound: most doctors believe that this is a harmless procedure and can be performed many times without any damage to the health of the mother and baby.
But at the same time, alternative opinions are increasingly appearing: for example, in the USA, the National Institute of Health has not approved mandatory ultrasound for all pregnant women. In Japan, ultrasound examinations are performed for pregnant women only after a serious justification for the need for this examination. Why do countries with a high level of medical care, where there is enough ultrasound equipment and specialists proficient in the technique, still limit the use of this method? Western experts justify such tactics by the existence of an unrecognized risk.
Although it is stated that a person does not perceive the sound of the frequency used, the fact that children in the womb react extremely violently to this examination, responding to it with intense movement, has not yet been explained. Let the risk be purely theoretical. But if there is no benefit from the research, even the theoretical risk cannot be justified. In this case, data are used as arguments that ultrasound has an adverse effect on chromosomes, in particular, it can lead to mutations in the fetus, delayed growth of the embryo in animal experiments, and changes at the microscopic level found in studies on tissue samples.
In addition, one of the facts that alarmed the public was a strange pattern. It turned out that mothers who underwent this procedure several times had babies that weighed slightly less than the babies of mothers who had an ultrasound done only once - at 18 weeks. As a result, scientists decided to observe almost three thousand children for eight years. It turned out that babies who were repeatedly exposed to ultrasound caught up with the weight of their peers by their first birthday. In addition, no developmental abnormalities were identified in these children. Study leader John Newnham emphasized that today's machines reduce the procedure time and provide better images. And for mothers who still doubt the safety of ultrasound, the professor promises to continue monitoring their children and publish new data in a few years.
How necessary is an ultrasound?
The use of ultrasound examination during pregnancy should above all be reasonable. Neither the curiosity of the parents nor the convenience of the doctor can be an argument. Undoubtedly, ultrasound has greatly facilitated the work of obstetricians and reduced the number of unpleasant “surprises.” However, as a result of overuse of this method, obstetricians have become overly reliant on it. It is not necessary to listen to the fetal heartbeat using an ultrasound; there is a fetoscope for this, which is harmless to the child. To determine the presentation and position of the fetus in the uterus, you also do not need an ultrasound; this requires the hands of a competent obstetrician.
Weighty
The reasons for performing an ultrasound scan are: • predisposition to hereditary diseases
• birth in a family of children with developmental anomalies
• the effect of radiation or chemical agents on a pregnant woman
• transmission of serious diseases and viral infections leading to developmental defects, chronic maternal diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, phenylketonuria and others
• suspicion of placenta previa or premature placental abruption
• pregnancy problems such as hydatidiform mole, ectopic pregnancy, non-developing pregnancy, fetal development retardation.
In these cases, the frequency and duration of the examination is dictated by the need to preserve the health of the mother and child, so it is difficult to find an alternative research method comparable to ultrasound.
ultrasound in Astana
Similar articles
- 07/24/2014 Cystitis
- 05/22/2014 Abortion
- 08/02/2014 Folliculometry (ovulation monitoring)
- 05/19/2014 Transrectal ultrasound (truzi): ultrasound of the prostate gland or ultrasound of the prostate
- 05/26/2014 Ultrasound of the gallbladder
- 08/02/2014 Is it harmful to do an ultrasound?
- 06/15/2018 Ultrasound of the liver
- 05/19/2014 Ultrasound of cerebral vessels
Is ultrasound harmful during pregnancy?
| First ultrasound screening of a pregnant woman |
Even at the current level of development of medicine, not all the secrets of the processes of conception, gestation and birth of a child are known to us. The study continues continuously, including with the help of ultrasound, which accompanies pregnant women throughout the entire 9 months. Future parents are looking forward to meeting their baby for the first time, albeit virtually. This expectation is often mixed with fears and concerns about the health of the unborn child, which makes some parents sometimes refuse to conduct screening studies using ultrasound.
Is ultrasound harmful in early pregnancy?
In accordance with the regulatory documents of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, the first screening ultrasound of pregnant women is carried out at 12 weeks. Despite the proven absence of a negative effect of ultrasonic waves on the body of the pregnant woman and the fetus, obstetricians and neonatologists try not to prescribe unnecessary examinations without clinical need, perhaps playing it safe and fearing for the future of the child.
However, it is necessary to conduct a preventive study in the first trimester to determine
:
- condition of the placenta and uterus,
- Is the embryo developing normally and how many are there in the uterus?
- is there a threat of miscarriage?
|
| Two fertilized eggs in the uterus |
Of all the existing diagnostic methods, only ultrasound can be used during this period. The reason for conducting an unscheduled ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy (5-10 weeks) may be
:
- threat of miscarriage, increased uterine tone,
- suspicion of a “frozen” pregnancy,
- pronounced gestosis,
- acute or exacerbation of chronic diseases of the pelvic organs,
- serious abnormalities of fetal development that can lead to disability (Down syndrome, heart disease).
But there are situations when the need for ultrasound arises very early
, even in the first week of pregnancy:
- with an unfavorable genetic history of the parents,
- if intrauterine infection of the fetus is suspected,
- after an infection by the mother and treatment with antibiotics,
- if you suspect an ectopic pregnancy,
- with IVF.
|
| 2 weeks pregnant |
Nowhere in the world is ultrasound routinely prescribed before 10-12 weeks of pregnancy, unless there is a threat to the life of the mother or fetus - this is the WHO recommendation. It is not recommended for pregnant women to do this at their own request, just to confirm the fact of fertilization or the duration of pregnancy.
Is ultrasound harmful to the fetus?
| Fetal ultrasound |
The only criterion for a normal pregnancy is a healthy fetus that develops in accordance with the prescribed deadlines and does not have any pathological abnormalities. And this is carefully monitored by obstetricians, gynecologists, neonatologists, and ultrasound diagnostic specialists during routine ultrasound screenings.
- Objectives of the 1st study at 12-13 weeks
:- confirm that the embryo is attached to the uterine cavity, i.e. exclude ectopic pregnancy, hydatidiform mole;
- clarify the number of embryos and their viability;
- determine the exact duration of pregnancy;
- determine the size of the fetal sac;
- study the fetal heartbeat;
- determine developmental anomalies: pathology of skeletal development, absence of the brain, the presence of spina bifida.
- Objectives of the 2nd ultrasound at 18-22 weeks
:- study the condition of the umbilical cord and placenta, determine its presentation;
- study the location of internal organs and body parts of the fetus;
- determine the length of the bones;
- identify congenital malformations and deformities of the fetus;
- determine the sex of the fetus.
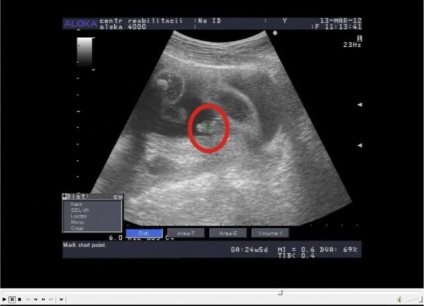
Determining the gender of the child (boy) - Objectives of the 3rd ultrasound at 32-34 weeks
:- determine the weight and size of the fetus;
- assess placental blood flow;
- compare the size of the fetal head with the size of the mother’s birth canal;
- determine the position of the fetus in the uterus;
An important point is the study of the circulatory system using Doppler ultrasound, when it is possible to trace the movement of blood in the heart and vessels of the fetus, in the umbilical cord and in the vessels of the mother’s placenta. This is necessary for the timely detection of heart defects, vascular abnormalities and possible problems with the placenta.
The need for an ultrasound scan of the fetus is justified, aimed at the normal completion of pregnancy. Ultrasound waves do not pose any danger to the development of a child: they do not change the structure of DNA, do not violate the integrity of tissues and organs, and do not disrupt brain activity. The role of ultrasound in maintaining the health of the fetus is only positive.
The benefits of ultrasound
The need for it remains obvious, and paid ultrasound services are in steady demand in Kaluga. It is usually prescribed to women 3 times throughout pregnancy to identify pathologies:
- 11-14 weeks of pregnancy. During this period, the risk of developing defects, such as Down syndrome, increases. At this stage, the ultrasound specialist will determine the number of fetuses in the uterus and set the exact date of pregnancy.
- 18-22 weeks of pregnancy: the doctor clarifies the general condition of the child and determines its gender.
- 30-32 weeks of pregnancy: the presentation of the baby and its level of development are determined.
Nowadays, 3D and 4D ultrasounds are most often performed. On the screen you can watch the baby's actions and get the baby's first photo.
If a pregnant woman does not want to have an ultrasound, she has the right to refuse. These studies are desirable (to eliminate possible risks), but not mandatory. However, the minimum recommended number of ultrasound examinations is recommended to be done in order to get a complete picture of the course of pregnancy.
Additional ultrasounds are not prescribed if the woman is feeling well. But there are cases when ultrasound examinations are required beyond the norm. For example, if it is vital for the fetus or the mother has a number of chronic diseases. An ectopic pregnancy is detected using ultrasound. An abortion performed according to medical indications can save the life of a pregnant woman. However, you need to remember that the frequency of ultrasound is determined by the gynecologist. In addition, with us you can undergo all types of similar studies for different organs, and, for example, for ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head, the price is one of the most affordable in the region.
Both harm and benefit from ultrasound exist. To give birth to a healthy baby, you need to treat this study with caution and follow the clear instructions of your doctor.
Add a comment Cancel reply
Privacy Policy Site Map Website Promotion – Digital Agency Dial
Photo
Is ultrasound harmful for pregnant women?
|
| Ultrasound screening for pregnant women is necessary for normal pregnancy |
When sending pregnant women for an ultrasound, doctors adhere to the order and timing
, established by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 1, 2012.
- At 11-14 weeks of pregnancy, the woman’s pelvic organs are examined and the location of the embryo and the condition of the placenta are determined.
- At 18-21 weeks of pregnancy, an expert-level fetal ultrasound is performed, the main purpose of which is to identify intrauterine malformations and deformities of the fetus.
- At 30-34 weeks of pregnancy, readiness for childbirth is determined, and the timing and method of delivery are planned.
In the normal course of pregnancy, this is sufficient for the timely detection of conditions threatening the woman or fetus. A particularly important stage is ultrasound in the second trimester, when the question of the possibility of continuing the pregnancy or the need for termination for medical reasons is decided if anomalies or malformations of the fetus are detected.
|
| Malformation of the fetal eyeballs (cyclopia) |
The approved ultrasound standards are determined by the desire to minimize the influence of external factors on a woman and child, even such as harmless ultrasound. An exception to the rule is situations in which additional, unscheduled ultrasound examinations are indispensable
:
- if you suspect an ectopic pregnancy,
- it is necessary to exclude or confirm the development of multiple pregnancy,
- if you suspect a miscarriage, etc.
Unscheduled ultrasound is required during IVF to dynamically monitor the condition of the embryos.
Thus, there can be many reasons for performing an ultrasound during pregnancy, but all of them must be justified, aimed only at the main thing - the successful completion of pregnancy. You should not do this for your own pleasure - take a fashionable 3D photo of the baby, document the fact of pregnancy, or find out the sex of the child as early as possible. Undoubtedly, ultrasound is a safe procedure, but unnecessary interventions are unlikely to benefit the baby.
Is ultrasound harmful for infants?
| Ultrasound of a newborn is a safe and necessary procedure |
Why do you need to do preventive ultrasounds for a healthy newborn child, because during pregnancy there were 3 planned ultrasounds during which the development of the fetus was monitored? Is such frequent exposure to ultrasound harmful to the baby? Pediatricians around the world answer this question from concerned parents: “There is no harm from ultrasound. There will be nothing but benefit from these examinations.” Too many problems in children develop gradually, without clinical manifestations. Of course, during the mother’s pregnancy, the child’s development process was under the constant supervision of doctors. But the likelihood of promptly identifying pathology is much higher when the child is already born, and not through the amniotic fluid and the mother’s abdominal wall.
Therefore, the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, in order to timely detect deviations from normal development, has established a mandatory comprehensive ultrasound at the age of 1 month and, on a recommendation basis, for indications up to 1 year.
Ultrasound of the brain for newborns (neurosonography) – mandatory examination at the age of 1 month
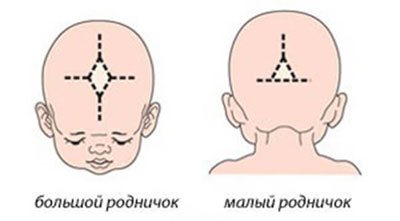
The brain is an organ on whose health the physical and mental development of a child depends. The bones of the baby’s skull gradually heal; at birth, there remain places devoid of bone tissue - these are the fontanelles (anterior, anterolateral and posterolateral).
|
Ultrasound of the brain is often performed through the anterior fontanelle; a gel is simply applied to this area and the information is read using a sensor. The procedure takes no more than 10 minutes. To do this, you can choose a time when the child is sleeping, but even if he moves, this will not interfere with the examination.
During this time, the doctor receives very valuable information about the presence or absence of cysts, tumors, fluid,
|
| Neurosonography for a newborn |
Neurosonography is indicated
:
- premature babies, moreover, repeatedly, for dynamic control,
- born as a result of cesarean section, prolonged or rapid labor, or with signs of hypoxia
- if the child weighs less than 2.7 kg at birth,
- in the presence of neurological symptoms (impaired hearing, vision, frequent regurgitation, convulsions),
- in the presence of external anomalies and other developmental defects,
- if a birth injury is suspected.
Since the fontanelles on the back of the head close by 3 months, and the central one by 1 year, it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the brain before these dates. In the future, you will have to resort to MRI, and, most likely, using anesthesia, i.e. the procedure will no longer be as safe for the baby compared to a harmless ultrasound. Therefore, if it was not possible to conduct neurosonography during the first comprehensive ultrasound at 1 month, it is recommended to do it at 2-3 months.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in children
The study is carried out at 1 year through the abdominal wall, i.e. transabdominal. The baby's internal organs are checked: liver, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, ureters, bladder. Of the congenital pathologies in newborns, the most common are pyloric stenosis or pylorospasm (obstruction of the esophagus) and diseases of the urinary organs (in 5% of cases - dilatation of the renal pelvis). Often, as the child grows, everything returns to normal without additional interventions, but in such cases dynamic ultrasound control is required.
|
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs of the baby |
Ultrasound of the hip joint
This study is recommended to be carried out on all children at the age of 1 month without fail to exclude hip dysplasia. This pathology occurs in 1-3% of newborns, more often in girls, and is associated with a congenital disorder of the joint formation process, which causes dislocation or subluxation of the joint, often leading to disability. Timely diagnosis of this pathology increases the chance of effective correction. And in this case, the use of an ultrasound method that is safe for the baby has an undeniable advantage over x-ray examination.
|
| Ultrasound of the hip joint in a newborn |
Ultrasound of the heart
In many regions of the Russian Federation, this study is included in a comprehensive ultrasound examination at the age of 1 month. This is done for the purpose of timely diagnosis of heart defects, which require constant monitoring, and sometimes immediate surgery.
The approved calendar for ultrasound screening of newborns is advisory in nature, and parents may refuse to have their baby examined, taking into account the myths about the non-existent negative impact of ultrasound. But before doing this, it is necessary to understand how many invisible congenital and acquired pathologies can be identified and treated in a timely manner in order to provide the baby with a full life.
Frequency of ultrasound
|
| Ultrasound is a safe procedure for the patient, so the frequency of its appointment depends on clinical indications |
The frequency of ultrasound is determined only by clinical necessity, because the harmlessness of the procedure is beyond doubt. The study is equally often used in women during pregnancy and lactation, during the intrauterine period of the fetus and immediately after the birth of the baby, in children at any age, in adult men and women.
When prescribing ultrasound, obstetricians-gynecologists and pediatricians adhere to
current orders of the Ministry of Health and regulations aimed at the judicious use of ultrasound in pregnant women and babies. There are the concepts of “mandatory screening ultrasound” and “ultrasound according to indications”:
- For pregnant women
Mandatory screening examination includes ultrasound:- at 12-13 weeks,
- at 20-22 weeks,
- at 33-33 weeks.
- at other times - according to indications.
- For newborns
:- comprehensive ultrasound at 1 month of age, including ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography) and ultrasound of the hip joint
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - at 1 year.
- other ultrasounds - according to indications.
For adults, for preventive purposes, ultrasounds are performed during medical examinations and routine medical examinations. Cancer screening is of particular importance
:
- for women, ultrasound of the mammary glands: at the age of 20-30 years – once every 3 years, 30-50 years – once a year, over 50 years – 2 times a year;
- for men over 40 years old, ultrasound of the prostate gland – once a year.
In the process of treating chronic diseases, in the postoperative period, ultrasound is performed as often as required by dynamic monitoring until the process stabilizes. There are no contraindications to ultrasound. The study can only be complicated by damage to the skin (burn, scar, cut, ulcer) in the study area.
Areas where ultrasound is used
Gynecology (obstetrics)
Used to examine the pelvic organs and monitor the course of pregnancy and fetal development. A pelvic examination can be prescribed for both women and men. The only difference can be considered only the type of research being carried out, since in women it can be carried out not only abdominally (through the abdominal cavity) and rectally (through the rectum), but also transvaginally (through the vagina).
Transabdominal ultrasound
Preparing for this type of study involves eliminating from the diet foods and drinks that cause gas formation, which can distort the data. In addition, in most cases, it is recommended to carry out the manipulation with a full bladder. To do this, the patient is recommended to drink 1.5 liters of still water 2 hours before the procedure.
Transrectal examination
Before the study, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines. For these purposes, both medications (laxatives, microenemas) and ordinary cleansing enemas with water can be used. It is recommended to carry out cleaning no later than 6-8 hours before the examination. In cases where a biopsy is necessary, the patient may be advised to take antibiotics.
Transvaginal examination
This type of research usually does not require any special preparation. It is desirable to eliminate intestinal gas pollution and empty the bladder. Ultrasound of fetal development and pregnancy is performed three times:
- At 9-14 weeks;
- At 20-24 weeks;
- At 30-34 weeks.
If necessary, the monitoring doctor may prescribe additional studies.
Internal organs
This list includes almost all organs and systems of the body (abdominal cavity, urinary system, etc.). Preparation for the study usually does not require serious measures and is prescribed depending on the current situation. Most often, ultrasound diagnostics are required in cases where it is necessary to examine the kidneys, bladder, ureters, prostate gland, gallbladder and pancreas.
Cardiology
In this case, ultrasound covers not only the heart itself, but also most (the entire) circulatory system. During the study, the doctor gets an idea of the condition and functional characteristics of the patient’s circulatory system and heart.
Endocrinology
Most often, the thyroid and thymus glands, adrenal glands, as well as some other organs directly related to the endocrine system are subjected to ultrasound. Examination of the thyroid gland helps determine its size, structure and the presence of tumors. Diagnosis of the condition of this organ is prescribed not only in cases of suspected pathological processes, but also for preventive purposes. Ultrasound as a preventive measure is necessary for: - pregnant women; — persons employed in industries with hazardous working conditions; - patients forced to take hormone-containing drugs for a long time; - persons with heredity complicated by diseases of the endocrine system.
Ophthalmology
Necessary for visually determining the position of the eye lens and measuring its size.
Mammalogy
Ultrasound of the mammary glands is performed to determine the condition of the ducts and timely detection of tumors. Thus, ultrasound is indicated for women who have been diagnosed with mastopathy, have had trauma, or have had surgery. In addition to the above, ultrasound is necessary to examine the lymph nodes, muscles, joints and vessels of the extremities.
Is ultrasound of the brain harmful?
|
| Ultrasound of head vessels |
There are many methods for diagnosing pathological processes in the brain:
- x-ray,
- Ultrasound,
- CT,
- MRI,
- EEG.
Ultrasound of the brain is more often used to examine the fetus and newborns up to a maximum of one year old, because By this time, the formation of the bone tissue of the skull ends, and the fontanelles, through which the structures of the brain can be seen (neurosonography), are overgrown. The density of bone tissue does not allow ultrasound waves to pass inside, so other diagnostic methods are used in children over 1 year of age and in adults.
During the period of intrauterine development of the fetus and for infants, ultrasound is the most optimal method due to the harmlessness and safety of the method. This has been proven by special laboratory studies of the influence of ultrasound on the structure of DNA and the function of brain cells in laboratory animals and many years of clinical experience in pediatric use. Ultrasound is harmless to brain cells.
For children over 1 year of age and adults, examination of the brain using ultrasound is often carried out indirectly, through ultrasound of the vessels of the head or neck.
|
| Ultrasound of head vessels: vein aneurysm |
Despite the availability, lack of negative influences and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound, if a tumor is suspected, it is better to use the more accurate MRI method. For newborns, especially if hydrocephalus or damage to brain structures is suspected, the best option is neurosonography, i.e. Ultrasound.
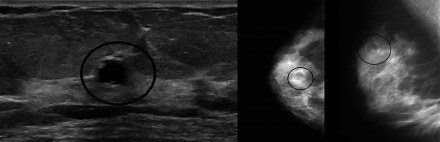
Is breast ultrasound harmful?
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands |
Today, every woman knows about breast cancer; this pathology is in first place among cancer problems in women. But knowledge alone is not enough; it is necessary to actively identify the very initial stages of any abnormalities in the condition of the mammary glands, because in 95% of cases the disease is asymptomatic. Pathological changes in the structure of the mammary glands can be identified using self-palpation, regular examination by a gynecologist and mammologist, ultrasound and mammography.
Ultrasound is the most accessible, reliable, safe and painless method. The procedure is simple, does not take much time (15-20 minutes), and the woman does not experience any discomfort. But the results surpass all far-fetched concerns and fears that are based on myths about the negative impact of ultrasonic waves on the mammary glands. All studies conducted with one goal - to identify the harm of ultrasound waves on the human body - could not reasonably prove a single fact of negative consequences from the use of ultrasound. At the same time, there are a huge number of proven facts of detecting breast cancer in the early stages using ultrasound, of which, with timely treatment, 98% of women retained not only their health, but also their lives.
Ultrasound can detect
, practically all diseases of the mammary glands, examine the condition of the lymph nodes, identify small tumors, even if they are located in the depths:
- cancer, carcinoma,
- diffuse cystic mastopathy,
- fibroadenoma, lipoma, papillomas,
- galactocele, other cysts,
- inflammatory and purulent diseases (mastitis, abscess),
- metastases in the lymph nodes.
Ultrasound waves passing through the mammary gland are reflected from the tissues in different ways. Dense structures (tumors) completely reflect the waves, so these places are displayed on the screen as light areas.
|
| Breast carcinoma on ultrasound |
At the border of glandular tissue and fluid, ultrasound is reflected from the dense walls of the cyst.
|
| Breast cyst |
No special preparation is required, but the study is best carried out on days 5-10 of the menstrual cycle; on these days, the woman’s hormonal background is stable and does not affect the structure of the glandular tissue. During menopause or while taking hormonal contraceptives, you can undergo an ultrasound at any time.
The safety of ultrasound allows the method to be used quite often if there is a clinical need for it. For preventive purposes, it is better to follow the developed recommendations.
:
- Women aged 20-30 years – once every 3 years,
- At the age of 30-50 years – once a year
- Over 50 years old – 2 times a year
You should not be afraid or ignore ultrasound of the mammary glands; this annual procedure should become the main guarantor of health and beauty for women.
Myth 1. Ultrasound negatively affects DNA.
This belief has taken root among people due to developments in USSR institutes before 1992, which were not brought to their logical conclusion. Against the background of past studies of ultrasound, there have been no published articles about the dangers of diagnosis and its negative impact on humans. In addition, in the work of P.P. Garyaev’s “Wave Genome” - she also made a significant contribution to the masses - and there was no evidence base at all, so the scientific community could not take his opinion seriously. As a result, the widespread use of ultrasound diagnostics in various fields of medicine began in 1995, helping many people to this day.
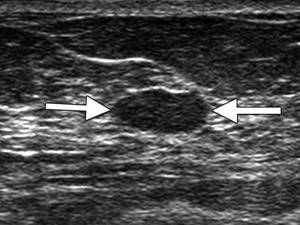
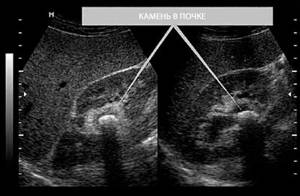
Is kidney ultrasound harmful?
|
| Kidney ultrasound |
According to WHO and the UN, kidney disease will become the No. 5 killer disease in the near future; already 10% of the world's population has kidney pathology. The main causes leading to end-stage renal failure are chronic inflammatory diseases, diabetic nephropathy and malignant neoplasms. Ultrasound of the kidneys allows you to promptly identify almost any kidney problems.
|
| Kidney stone (light spot on photo) |
Considering the proven safety of the method, the advantages of ultrasound
relate:
- harmlessness, non-invasiveness, painlessness,
- the ability to simultaneously examine soft, denser and parenchymal tissues, hollow formations containing air and fluid (cysts),
- availability, efficiency,
- the possibility of examining pregnant women and children on a planned and emergency basis.
The disadvantages of ultrasound
relate:
- subjectivity of interpretation of ultrasound results, dependence of diagnostic accuracy on the experience and qualifications of the doctor,
- insufficient quality of the resulting static images,
- inability to diagnose malignant neoplasms and conduct a study of the functional capacity of the kidneys.
If a kidney tumor is suspected, if it is not possible to use other diagnostic methods, the study is carried out using echo contrast agents (tiny gas bubbles dissolved in an aqueous solution, which are administered intravenously).
| Ultrasound of the kidneys with contrast (left) |
Gas bubbles dissolve in the blood within 10-15 minutes without consequences for the patient.
Kidney ultrasound is prescribed
:
- In acute inflammatory processes (glomerulonephritis), exacerbation of chronic kidney diseases (urolithiasis).
- In emergency cases - in case of renal colic, suspected “acute abdomen”, patients in severe physical condition, with abdominal injuries.
- Pregnant women, because While the fetal kidneys are not formed, the functional load on a woman’s kidneys increases, which increases the risk of developing diseases.
- To monitor the development of the kidneys in the fetus
, the examination is carried out during three mandatory ultrasounds of pregnant women: 10-12 weeks - an already formed pyelocaliceal system is visible on ultrasound, - 20-24 weeks – you can see the structure of the kidneys, determine the size and position of the kidneys,
- 30-32 weeks - the kidneys are fully formed and should function normally.
The frequency of use of ultrasound is not limited; the procedure can be repeated as many times as required according to clinical indications.
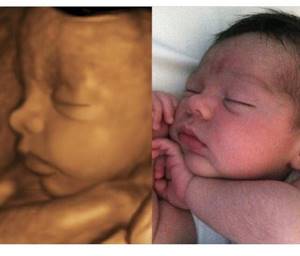
Is 3D ultrasound harmful?
|
| 3D photo of the fetus (left) and photo of the newborn (right) |
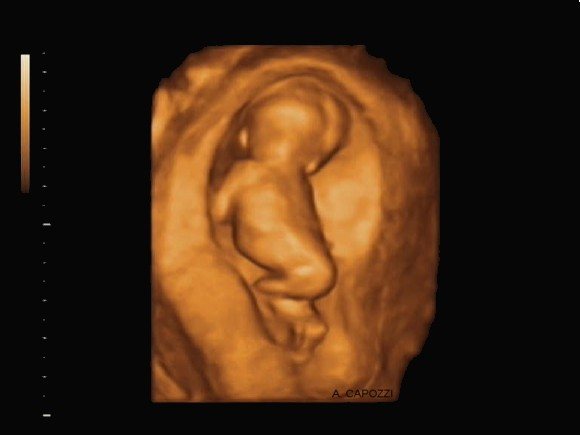
Since ultrasound has firmly strengthened its position as an indispensable diagnostic tool in obstetrics, both the technique itself and the devices are constantly being improved, new opportunities have emerged for obtaining information about the condition of the fetus and the course of pregnancy. One of the latest innovations is the technique of obtaining 3D images. In contrast to an image, a two-dimensional ultrasound produces a three-dimensional three-dimensional polychrome picture, which allows one to examine the details of the structure of the fetus: the face, the structure of the skull, and reliably determine the sex of the child. And if you add a fourth dimension to the three-dimensional image - time (4D), then you can trace the movement of arms and legs, facial expressions.
Parents usually like this when they can look at their child from all sides, see his face, sometimes his smile, and watch his movements.
But in addition to aesthetic pleasure, 3D images allow you to clearly see external intrauterine abnormalities in the development of the child
:
- facial defects (cleft lip),
Cleft palate (“cleft lip”) on a 3D image - change in the number of fingers on the limbs,
- spinal cord nonfusion,
- defect of the anterior abdominal wall,
- abnormal development of the genital organs.
All these changes can only be detected using 3D ultrasound, which is very important for planning treatment tactics.
Despite the fact that 3D ultrasound, like conventional ultrasound, does not have any direct harmful effects on the body of the fetus and mother, gynecologists do not recommend abusing this procedure, taking into account such arguments
:
- The 3D ultrasound procedure takes 45-50 minutes, while 15 minutes is enough for a conventional ultrasound, which theoretically does not exclude thermal effects on brain cells.
- Trying to get a clearer shot, doctors are forced to increase the power of the wave emitter, which increases the risk of negative influence.
- 3D ultrasound allows you to obtain information only about the external data of the baby, but does not provide any information about the condition of the internal organs.
- The cost of the study is significantly higher than the cost of conventional ultrasound, so the method is often recommended only for commercial reasons.
- There are several restrictions for three-dimensional ultrasound
: gestational age - the procedure is best performed no earlier than 24 weeks of pregnancy, - the position of the fetus in the uterine cavity in relation to the sensor; sometimes the fetus can only be seen from the back.
|
| Position of the fetus in the uterus |
Therefore, 3D ultrasound should rather be used only as an addition to conventional ultrasound. The FDA (Food and Drug Administration, USA) states that this type of diagnosis should be carried out only with a doctor's prescription and opposes the use of the technique for commercial purposes.
Doctors from the UK share the same opinion. The international medical community encourages all obstetricians to adhere to the principle of safe ultrasound examination - ALARA (As Little As Possible). In Russia there are no prohibitions on the use of 3D ultrasound; there are only ethical standards. There are commercial medical centers that specifically indicate in their advertisements that 3D examinations are performed only upon the direction of a doctor.
Any examination of pregnant women has only one goal - to promptly diagnose the development of pathology, monitor the course of pregnancy and fetal development. For this purpose, there are established deadlines for preventive mandatory ultrasound. Whether to perform an additional 3D ultrasound to get a photo of the baby is, of course, up to the parents to decide, but it is better to discuss this issue with a doctor.
Is ultrasound during pregnancy harmful? What about Wi-Fi? Alarming questions about radiation in medicine and everyday life
This message (material) was created and (or) distributed by a foreign media outlet performing the functions of a foreign agent, and (or) a Russian legal entity performing the functions of a foreign agent.
Sign the petition demanding the repeal of the law on foreign agents!
Photo: RooM the Agency / Alamy / Vida Press
It is customary to treat radiation of any kind in Russia (and in other countries) with caution. Ultrasound and Wi-Fi, microwave ovens and magnetic resonance imaging - all this seems somehow dangerous. We decided to explain why radiation from medical devices and other types of radiation are not so scary.
Why is everyone so worried about x-rays and ultrasounds?
All research methods in which a person is scanned in one way or another are considered very dangerous in our country, since it is all “radiation”. But in reality they are very different.
There is a computed tomography (CT) scan, during which a person is actually irradiated.
There is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which has nothing to do with radiation. MRI and ultrasound use non-ionizing radiation - these are low-energy waves that cannot damage DNA, but can, for example, heat tissue.
There is radiography - this method, like CT, is based on ionizing radiation, that is, one that can tear off electrons in atoms (thus creating ions) and provoke mutations in DNA. Ionizing radiation in high doses can increase the risk of developing cancer.
But it is impossible to say that CT and radiography have such an effect: scientists drew conclusions about the dangers of ionizing radiation mainly from the consequences of major disasters (for example, the explosion of the atomic bomb in Hiroshima and the Chernobyl accident). So we cannot speak with confidence about the dangers of CT and radiography: after all, the radiation doses in these cases are quite small. It is even possible that such methods do not harm health in any way - or they do, but not as much as is commonly thought.
Adding to this confusion is the fact that doctors often prescribe completely meaningless tests - a person can receive a significant dose of radiation in vain, and because of this he will not be allowed to undergo another, truly important study. For example, for lower back pain, some kind of radiation diagnostic methods are needed only in 5% of cases, and these situations are determined by “red flags”. In about 95% of patients, the cause of the pain is not that important because the treatment will still be the same. Nevertheless, in Russia, in case of muscle pain in the back, people are often sent for an MRI, and for migraine, for ultrasound of blood vessels, etc.
They took an x-ray and a month later they scheduled a CT scan. So it is possible?
Yes, if the potential benefit from this research is greater than the potential harm. This should be assessed by a doctor. The decision also depends on your age, gender, indications and on which tissues have already been irradiated (they have different susceptibility). Sometimes it is better to conduct another test, but diagnose a serious disease and save the person from big problems.
Computed tomograph at the Research Institute of Childhood Infections of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency
Photo: Pavel Karavashkin / Interpress / TASS
I'm currently undergoing radiation therapy. I'm not radioactive, I'm not dangerous to others?
If this is a type of radiation therapy where you are irradiated using a special machine, then no, you are not radioactive. There is simply no source of radiation in the body. After a CT scan and x-ray, you are also safe for others. But if it's brachytherapy (where radioactive elements are injected into the body to destroy a tumor), you actually become a source of radiation, although it is actually quite weak. But at first it is still better not to communicate with children and pregnant women: they are the most vulnerable to radiation.
Is ultrasound during pregnancy harmful?
No. Ultrasound is not ionizing radiation, which damages DNA, and the huge amount of data that we now have suggests that it does not have any negative effect on the woman or fetus. Still, it is better to do an ultrasound only in cases where your doctor has prescribed it for you. The same applies to magnetic resonance imaging: these are electromagnetic radio waves that are not ionizing radiation, and researchers have not found any harm from them. True, only those cases were studied when the magnetic field of the tomograph was not the greatest.
I'm pregnant and they told me to get an x-ray. Maybe it's better not to?
Depends on the circumstances. Sometimes the doctor may believe that x-rays will do more good than harm. Radiation exposure to the abdomen during this procedure can be reduced, for example, if the picture is taken from the back. X-rays of the head, neck, chest and extremities do not particularly harm the fetus, especially if a lead apron is used. CT scans of different parts of the body are also relatively harmless if the abdomen is covered. In addition, CT scans can be done at slightly lower quality to reduce radiation exposure.
An absorbed radiation dose of 0.05 Gy (5 rad) in a pregnant woman is not a cause for concern. And most studies do not go beyond these boundaries. During pregnancy up to 14 days, a dose of 0.1 Gy (10 rad) or more leads either to “resorption” of the embryo or has no effect on it. Over a longer period, such irradiation increases the risk that the fetus will develop with delays, the child will have congenital developmental defects, and limited intellectual capabilities. But irradiation after 20–25 weeks is relatively safe.
Should I have a mammogram? It can cause cancer itself.
If there is evidence for this, then it is necessary. During a mammogram (x-ray examination of the mammary glands), a woman receives a small dose of radiation, but with this method it is possible to catch breast cancer at an early stage, which is likely to save the woman's life. Therefore, now the recommendations are as follows: from the age of 50, you need to undergo mammography every two years. However, in women with BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations, annual mammography appears to increase the risk of developing breast cancer as they age. But we can’t talk about this with certainty yet.
I fly often. Could this be dangerous in terms of radiation?
Yes maybe. At altitude we are exposed to more cosmic ionizing radiation than on earth. People who fly frequently can be compared to crew members, and they are more likely to develop melanoma (aggressive skin cancer), breast cancer, and women are more likely to have miscarriages. The International Commission on Radiological Protection considers that the maximum permissible radiation dose for a number of professions is 20 mSv per year. In the European Union, the limit is stricter - 6 mSv per year. For comparison: a transatlantic flight is 0.08 mSv. The radiation dose from scanners at airports is approximately equal to what we receive while spending 3-9 minutes on the ground, so this load can be ignored.
Can I put my phone near my pillow?
There is no clear answer yet (there is not enough data), but, for example, the connection between mobile phones and cancer, which the media like to scare, seems to still not exist. Phones emit non-ionizing radiofrequency radiation, the effect of which on humans is not 100 percent studied. But for now, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there is no reason to give up cell phones.
Is Wi-Fi harmful?
No. This is radio frequency radiation, and it is much weaker from a router than from a mobile phone. However, there are people with so-called electromagnetic hypersensitivity (“Wifi allergy”): they experience a variety of symptoms when Wi-Fi is turned on - headache, muscle pain, fatigue, insomnia, rash, nausea and much more. But studies have shown that they feel sick even when nothing is actually turned on.
Can you cook in the microwave? This is not dangerous?
No, it's not dangerous. A microwave oven operates using electromagnetic radiation. These waves practically do not extend beyond the furnace due to good protection. Electromagnetic waves can cause burns, but for this to happen, the microwave door must be damaged or slightly open.
The editors would like to thank Sergei Morozov, Director of the Scientific and Practical Center for Medical Radiology of the Moscow Department of Health, for his assistance in preparing the material.
We don't give up because you are with us
"Medusa", I'm with you
Daria Sargsyan
Moscow
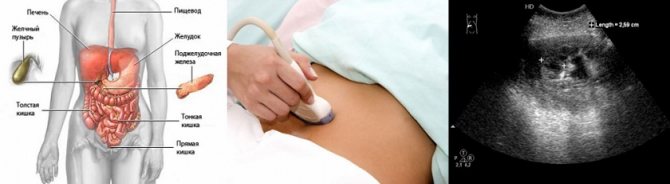
Is it harmful to have an abdominal ultrasound?
|
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs |
Almost all organs of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) are located in the abdominal cavity: intestines, stomach, liver, pancreas, gall bladder. In Russia, about 12,000–13,000 new cases of gastrointestinal diseases are registered annually per 100,000 population, which require careful diagnosis. For this purpose, the most accessible, inexpensive and highly informative ultrasound method is most often used as the primary research method.
Since ultrasound does not use ionizing x-rays, the method is absolutely safe - this opinion was officially promulgated by the American medical community in 1980 and is accepted by all doctors today. Therefore, ultrasound is used as often as the situation requires and as established by clinical guidelines.
:
- for preventive purposes – once every 3 years,
- for chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - as needed (1-2 times a year),
- in the treatment of acute diseases - without restrictions.
Ultrasound generated by the ultrasound machine's sensor is reflected differently from organs depending on their density
.
- Parenchymal organs (liver, spleen, pancreas) have a dense structure consisting of cells, there are no cavities in them, so on the screen they look like homogeneous formations.
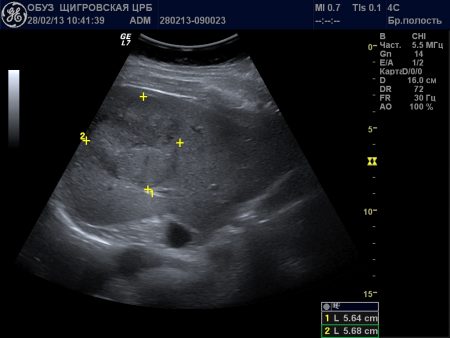
The liver is determined by ultrasound as a homogeneous formation - Hollow organs (stomach, gall bladder, intestines) are displayed by the contours of their walls, so ultrasound gives a greater picture of parietal pathology.
| Ultrasound clearly shows the walls of hollow organs (stomach) |
There are no contraindications to the use of ultrasound.
For a more in-depth diagnostic examination, the use of contrast enhancement is sometimes required - for this, echo contrast agents (a small amount of liquid with tiny gas bubbles dissolved in it) are injected intravenously; these substances are absolutely harmless to the patient.
|
| Ultrasound without contrast (left) and with contrast enhancement (right) |
During pregnancy, the abdominal organs gradually move upward and to the sides by the growing uterus, the woman’s usual diet changes, so the indications for ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
:
- stomach ache,
- signs of toxicosis (nausea, vomiting),
- pallor or yellowness of the skin,
- strange changes in blood tests.
In these cases, ultrasound is preferable to other diagnostic methods (CT, X-ray, MRI), because the absence of negative effects allows the method to be used at any period of pregnancy, emergency and planned. For the same reason, ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract is more often used in children; the first ultrasound for children, according to indications, is performed in the maternity hospital.
Ultrasound diagnostic method
It is very important for the doctor and the patient to correctly diagnose the disease and find the true causes of the disease in order to prescribe competent treatment. In our Private Practice clinic, we constantly have to use ultrasound, which today is one of the most modern, reliable and effective diagnostic methods. Ultrasound diagnostics has existed for several decades and during this period has shown only its best side. Let us immediately note that ultrasound should not be confused with an X-ray machine. Ultrasound, unlike x-rays, does not irradiate the body.
Ultrasound is a high-frequency sound wave that is absolutely safe for humans, just like any other sounds that surround us from birth. Only, unlike ordinary sound waves, ultrasound used in medicine has a higher frequency and is not audible to the human ear.
The method is based on the fact that human internal organs have different echo densities. The sound wave is sent by the sensor (echo signals) of the ultrasound machine, it is reflected from the organs to varying degrees and returns to the sensor. Ultrasound, reflected from body tissues, is converted into digital form and appears on the monitor screen in the form of dots (echo signals). By moving the sensor, the doctor constantly changes the image in order to examine the organ being examined from different angles. Thus, the doctor receives an image in real time and “sees” in detail what is happening in the patient’s body.
The event lasts on average 10–20 minutes. Ultrasound examination is performed using a certain frequency range (depending on the organ being examined), which allows you to obtain an image with the most complete information.
Is it harmful to have a pelvic ultrasound?
|
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs |
The pelvic organs include: kidneys, ureters, bladder, rectum, in women - the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, in men - the prostate gland and seminal vesicles.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women
Inflammatory diseases of the urinary organs and reproductive system in women are the most common problems in the outpatient healthcare system. Just as often the question arises about the need for diagnostic studies. The most accessible, informative, harmless and inexpensive method is ultrasound, which is prescribed
:
- if you experience pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding or vaginal discharge,
- if a malignant or benign tumor is suspected,
- for menstrual irregularities,
- in order to determine the cause of urinary obstruction, diagnosis of stones in the kidneys or ureters,
- to confirm pregnancy,
- in case of infertility,
- for dynamic monitoring after abortion.
The study lasts from 5 to 20 minutes, ultrasound examination in women is possible
:
- transabdominal - through the anterior abdominal wall,
- transvaginally - the sensor is installed in the vagina,
- transrectally - the sensor is located in the rectum,
Ultrasound waves do not have any negative effect on the pelvic organs, reproductive function, pregnancy or fetal development.
Examination of the pelvic organs in men
One of the most common problems in the pelvic area in men is prostate pathology, for the timely detection of which ultrasound is often used. For the purpose of early diagnosis of inflammatory or tumor diseases of the prostate gland, men over the age of 40 are recommended to undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs once a year.
|
| Ultrasound of the prostate in men |
In addition to preventive purposes, indications for performing pelvic ultrasound in men include:
:
- urinary disturbance (pain, discomfort),
- pain in the lower abdomen, scrotum, perineum,
- discharge from the urethra,
- infertility,
- violation of potency.
In men, ultrasound is performed in two ways
:
- transabdominal,
- transrectal - the most informative method, but is contraindicated in case of exacerbation of hemorrhoids.
There are no other contraindications or restrictions, complications or negative consequences when performing ultrasound of the pelvic organs in men.
Ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to accurately determine neoplasms, inflammatory processes in the prostate gland and kidneys, purulent diseases of the pelvic organs, and the presence of stones in the urinary organs.
Thus, ultrasound for diagnosing pathology of the abdominal organs can be successfully used in adults and children, because the procedure does not cause any negative consequences, is painless, and can be performed in medical institutions and at home, in an inpatient setting and in a clinic, in a city and in a rural outpatient clinic.
How often can research be done?
The number of ultrasound procedures required to make a correct diagnosis is determined by the attending physician. To do this, you can do ultrasound frequently without worrying about your health. This has long been proven by modern science:
- sound waves do not have a negative effect on the body;
- ultrasound does not accumulate in tissues;
- Unlike X-ray examinations, ultrasound diagnostics has no contraindications and, if necessary, is performed on pregnant women and children.
As part of an annual preventive examination, women are recommended to undergo a mandatory ultrasound of the mammary glands and pelvic organs. In the presence of chronic and other diseases, the frequency of diagnostic examinations is determined by the doctor.
Experienced medical professionals can assure their patients that ultrasound can be done frequently if it helps timely detection of pathological changes in the body and speedy recovery. In turn, ultra-modern equipment allows us to guarantee high accuracy and reliability of the results.