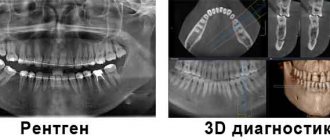
How is SCT research carried out?
The x-ray technician positions the patient in a special way, depending on the examination being performed. Next, the gantry (the device on which the tube and receiving sensors are installed) begins to rotate around the scanned area and makes slices of the area under study with certain parameters of power and tube passage step. When scanning the chest and abdominal organs, you will need to hold your breath several times, which the x-ray technician will warn you about. The scanning procedure lasts 2-4 minutes.
Why is a CT scan performed?
Medscan centers perform CT scanning, which allows you to visualize internal organs, bone structures, blood vessels, and analyze their condition in different projections and modes. All this is necessary for:
- identifying tumors, assessing their prevalence and the effectiveness of antitumor treatment
- diagnosis of vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis or vasculitis
- visualization of inflammatory changes, such as sinusitis
- clarification of the nature and differential diagnosis of various lung diseases, including viral pneumonia
- diagnosis of acute conditions such as strokes, thrombosis and thromboembolism, intestinal obstruction
- monitoring the results of surgical treatment (diagnosis of complications, for example, inflammatory changes in the abdominal cavity or foreign bodies after abdominal surgery)
- carrying out invasive manipulations (biopsy followed by histological examination) for diagnostic purposes under CT control
What can SKT do?
Computed tomography is simply irreplaceable in diagnosing the conditions of any bone structures, the condition of the lungs, and mediastinum in humans. SCT is also widely used in the study of abdominal organs (liver, spleen, gallbladder, pancreas), adrenal glands, kidneys, and pelvic organs. With the help of CT, it became possible to accurately detect any stones (for example, in the gall bladder, kidneys) and calcifications (for example, those changes that accompany tuberculosis, sclerosis).
Spiral computed tomography is leading in the diagnosis of complex bone injuries , multiple injuries (for example, road accidents) of bones and internal organs, in the diagnosis of complex or multiple injuries of the skull and acute injuries and hemorrhages of the brain.
SCT is also widely used by ENT doctors for a detailed assessment of the condition of the paranasal sinuses, auditory canals and temporal bones, since no other diagnostic method can compare with the accuracy and “depth” of computed tomography.
In studies of the spine using SCT, it is possible to determine the smallest damage in the bone structure, pathological calcifications in the ligamentous apparatus; to diagnose the condition of the intervertebral discs, it is best to use MRI.
The advisability of prescribing SCT in each individual case should be determined by the attending physician, who will subsequently interpret the results obtained from CT taking into account the entire picture and characteristics of the patient.
Abdominal CT
Abdominal CT scan with contrast
In cases where it is important for a specialist to examine certain structures of the abdominal cavity in more detail, CT diagnostics using bolus contrast may be required. Before the study begins, a contrast agent is injected into the patient's bloodstream. This is a safe substance that:
- does not cause side effects;
- well tolerated by humans;
- is independently excreted from the body.
An abdominal CT scan with contrast is performed if tumor formation is suspected. The substance perfectly illuminates such neoplasms, allowing doctors to detect them even in the early stages of development. The study helps specialists:
- study blood flow;
- assess the condition of blood vessels;
- detect pathological narrowings.
Computed tomography with contrast allows doctors to examine the condition of the walls of pathological capsules, for example, cysts. Thanks to this substance, specialists can study the excretory function of the kidneys and identify obstructions in the ureters. However, the price for an abdominal CT scan with contrast is higher than for a conventional computed tomography scan.
Features of the study
MSCT of the abdominal organs
What organs are examined when performing a CT scan of the abdominal cavity.
This diagnostic procedure allows you to study the condition, localization and size of pathological changes in the following organs:
- liver;
- gallbladder;
- kidneys and adrenal glands;
- adrenal glands;
- stomach and pancreas;
- spleen;
- vessels and lymph nodes.
Specialists have the opportunity to conduct diagnostics in three projections, this will help in a comprehensive study of the shape, size, structure, and condition of the abdominal organs. A CT scan will show the location of organs, minute changes and pathologies. The hollow organs, such as the stomach and intestines, are the most difficult to diagnose with computed tomography; they are often studied in conjunction with an additional study using fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS).
What is the difference between CT and MRI
This is one of the most common questions radiologists hear. CT computed tomography and MRI magnetic resonance imaging are diagnostic methods. They have both similar features and big differences.
They are similar in the similarity of the equipment on which the research is carried out. Tomographs differ externally only in the diameter of the inner part of the tomograph ring in which the patient table is located. A CT scanner has a much wider ring and no tunnel, unlike an MRI scanner, which makes the procedure as comfortable as possible for people suffering from claustrophobia.
And the main difference between the procedures is a completely different method of obtaining information:
- diagnostics uses x-rays,
- MRI – magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses.
The appropriate method for each patient and clinical case is determined by the attending physician, taking into account the goals and characteristics of the area or pathology that require diagnosis.
Preparing for diagnosis
Preparing for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity
It is important to remember that computed tomography of the abdominal cavity requires special preparation from the patient. In order for the scan results to be as accurate as possible, the patient must:
- Do not eat 8 hours before the test. It is very important to arrive for the procedure on an empty stomach.
- 2 days before the procedure, avoid products that increase gas formation.
- Perform a cleansing enema the day before the CT scan and immediately before going to the clinic.
Before the scan begins, the patient will be asked to remove all metal objects, jewelry, clothing with zippers and studs, and piercings. If this is not done, the results of an abdominal CT scan may be unreliable. Metal objects can create interference that will lead to distortion in the pictures. Therefore, it is very important for the patient to listen to the doctor’s requirements.
It is important to remain completely still during the examination. If for some reason the patient is unable to fulfill this condition, his body is fixed using special fasteners. In our clinic you can undergo an abdominal CT scan at any convenient time. Just make an appointment by phone or fill out the online form on the website.
Computed tomography technique
The procedure itself is non-invasive and completely painless and does not require mechanical influences. The patient lies down on a special mobile couch of a device that slowly moves into a tomograph ring in which the beams are located. The X-ray tube rotates 360° in a circle, scanning the organs of the study area layer by layer and sending sections to a computer, which, using algorithms, combines them into a three-dimensional, detailed image.
During the diagnosis, the patient is alone in the office, the doctors are nearby, in a special room from where they monitor the progress of the procedure and give recommendations via a specially installed speakerphone.
Indications for prescribing CT scan of the abdominal cavity
Diagnostics helps in rational planning of operations on internal organs and clarifying controversial diagnoses made on the basis of other types of diagnostics, physical examination or laboratory tests.
Some reasons why an abdominal CT scan may be ordered:
- abdominal pain of unknown nature;
- inflammatory, cystic, benign and malignant tumors and metastases;
- formation in the abdomen detected by palpation;
- stones in the gall bladder, liver, spleen and kidneys;
- sudden unexplained weight loss
- suspicion of intestinal obstruction;
- injuries and analysis of their consequences, the presence of a foreign body in the body;
- in preparation for surgical interventions;
- monitoring the progress of treatment, the effectiveness of radiation and chemotherapy.
Contraindications
Computed tomography has no absolute contraindications; the technique is considered safe and can be used repeatedly. But since the essence of the method is the use of X-rays, although a very small proportion of radiation is still present. Therefore, there are categories of patients, pregnant women and children under 14 years of age, for whom there is a recommendation to replace CT with another diagnostic method.
The decision to perform an abdominal CT scan is made by the attending physician, always taking into account all the features of the clinical case.
Diagnostics will be impossible if the body weight exceeds 200 kg, since this is the maximum technical capabilities of the device.
Particular attention should be paid to the procedure of CT scanning of the abdominal cavity with contrast. Not every patient can undergo an abdominal CT scan with contrast. The method is contraindicated in pregnancy and children under 14 years of age, as well as in patients with an allergy to iodine, since this substance is the basis of the contrast. Experts note a number of relative contraindications. These include:
- chronic kidney disease;
- diabetes;
- thyroid diseases;
- severe heart diseases;
- bronchial asthma.
Before a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity is performed, doctors ask the patient to take a biochemical blood test. It helps identify kidney failure. If this illness is confirmed, then the patient is denied the test.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
Advantages of abdominal CT
The advantages of abdominal CT include the following characteristics:
- painless and non-invasive;
- highly accurate results and detailed images;
- virtual reconstruction of the studied areas, organs, tissues;
- CT can be performed on patients who have pins, plates, or pacemakers;
- short diagnostic time.
The disadvantages include:
- radiation exposure;
- the presence of few contraindications.
Research results
After the examination, the patient receives the tomography results in the form of an image, recorded on a disk or flash card. With the help of which the attending physician will be able to examine the examined area from different angles, detect the smallest changes and pathologies, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe timely and effective treatment. Plus description and interpretation of computed tomography if necessary.
Book an abdominal CT scan
Our institutions are equipped with modern and high-precision diagnostic equipment. This allows the clinic’s specialists to carry out highly accurate comprehensive examinations of patients with various pathologies.
You can find out what the price of an abdominal CT scan is at the Open Clinic on the website or by calling the phone number provided. We regularly hold promotions and offer pleasant discounts on diagnostic tests.
In our clinic you can undergo an abdominal CT scan at any convenient time. Just make an appointment by phone or fill out the online form on the website.
What does SKT “dislike”?
First of all, these are movements . Any movements during scanning of the study area distort the resulting images, of course, reducing their information content for the doctor. If in a series of images obtained, even just 1-2 scans are distorted by motion artifacts, then subsequent 3D reconstructions will already have defects and their information content for the doctor, of course, will be reduced.
Secondly, metal. Metal is to X-rays what a mountain is to the sun—it leaves a “shadow.” A large amount of metal in the examination area can significantly distort the resulting images. But if the metal is located in any place other than the area being examined, it cannot in any way affect the quality of the scans.
What do you need to have with you for SCT?
Before the study, you must give your existing medical documentation to the x-ray technician or radiologist (a referral from the attending physician, which indicates the preliminary diagnosis, study area, clinical task, specific comments), data from previous studies (which directly relate to the reason for prescribing SCT to you) and other medical documentation, after analyzing which the radiologist will be able to formulate the most accurate diagnostic conclusion on SCT, taking into account the data of your medical. cards and recommendations of the attending physician. If you do not provide medical documentation in full, then the radiologist will evaluate only the directly obtained SCT scans, without taking into account previous injuries and diseases, any possible consequences that they could entail, and without taking into account possible concomitant pathologies.
Remember, there is no absolute and universal method of medical diagnosis: MRI will never replace SCT, SCT will never replace ultrasound, ultrasound will never replace radiography. All these methods complement each other and sometimes, data from previous studies have the decisive word in the correct interpretation of the resulting picture by a radiologist during computed tomography.
Make an appointment
Make an appointment by calling:
+38 (044) 393 0933
+38 (067) 230 2432
+38 (050) 332 3339
How is the CT scan procedure performed at Medscan in Moscow?
Before the examination, the x-ray technician carefully interviews the patient, collects an anamnesis of life and illness (information about previous diseases). Sometimes, before a contrast study, results of a test of renal excretory function (creatinine test) may be needed. If the patient has data from previous studies (CT, MRI, PET-CT, etc.), then their images are imported into the information system, and scans of extracts and analyzes are attached to the medical history.
The patient lies down on the tomograph table and the first “marking” low-dose scan (topogram) is taken, on which the rest of the study is marked; the table moves back and forth, and the patient may be asked to hold their breath through a speaker.
If a contrast study is required, after the topogram an injector (a special automatic syringe with a contrast agent and saline solution) is connected to the intravenous catheter.
Next, one or more CT scans are performed, and between them, a contrast agent is injected intravenously into the patient using an injector at high speed; The table moves forward or backward with each scan and instructions to hold your breath may be heard again. The patient can hear the tube and detector rotating inside the gantry, but the noise level is low and does not cause discomfort. The patient does not experience any sensations from the operation of the X-ray tube.
The x-ray technician controls the examination from the next room, which has a special window through which he can see the patient; The speaker and microphone built into the tomograph allow the laboratory assistant and the patient to be constantly in touch.
The entire CT procedure lasts from 3 minutes if the study is non-contrast, to 20 minutes if contrast is required.
The contrast agent is safe for the body and is excreted by the kidneys within 12 hours.
After the examination with contrast, we monitor the patient’s well-being for 20 minutes, during which time we prepare a digital medium on which all obtained images are recorded. After a 20-minute wait, the intravenous catheter is removed from the patient and the procedure is completed.
Then a team of radiologists comes into action, analyzing hundreds and thousands of images obtained during each study. The doctor carefully examines all the sections obtained, compares them with previous studies and analyzes what he saw, taking into account the anamnesis, medical history and treatment performed. The result of image analysis is a protocol (conclusion), which describes the identified changes and draws conclusions about their nature. It is ready within a few hours, maximum within a day.
This is not an easy job, but our centers employ real professionals who love their job; Our radiologists constantly improve their qualifications by participating in consultations, seminars, webinars and conferences, reading modern foreign literature in their specialty.
Who deciphers the results and when they can be obtained.
The resulting SCT images must be examined by a radiologist (a doctor who specializes in CT, MRI, X-ray studies and has the appropriate certificate). It is necessary to “read” all the scans, study the provided medical information. documentation, compare it with the obtained CT image, describe the study, draw a diagnostic conclusion, shoot film with scans. On average it takes about 1-3 hours. At ACMD, we undertake to prepare the results for delivery by the end of the Clinic’s working day.
After the examination, you receive films with scans and a diagnostic report, which will be signed by a radiologist. Also, the diagnostic report may contain recommendations regarding your further actions (which doctor to contact with these results, what types of further examination are recommended, and so on).
Consultations and questions regarding your SCT study.
A radiologist is not a clinician (a doctor who treats you) and, as such, cannot provide any advice or recommendations regarding your treatment or diagnostic procedures.
To make objective comments on an SCT study, it is necessary to fully know the patient’s objective data, the picture of his previous studies, the characteristics of his current condition, anamnestic data, and much more.
You can ask all your questions to your attending physician or physician, whose consultation will be recommended to you by a radiologist.
If you still have any specific questions about computed tomography, you can ask them in the specialized MRI and SCT diagnostics section on our Forum.
Check out comprehensive body check packages with up to 30% discount
Contrast techniques for SCT.
When examining the abdominal organs, the patient will be asked to drink 500–1000 ml. drinking water with a contrast agent dissolved in it in order to “separate” the stomach and intestines from nearby organs and tissues, as well as to ensure that intestinal loops do not create additional “interference” for the radiologist during the study. This is the so-called oral contrast.
The same technique of intravenous administration of a contrast agent is very often used in order to “highlight” areas with pathological changes, to study the blood flow of tumor formations, or specifically to study blood vessels.
Types of CT
Globally, computed tomography options can be divided into non-contrast and contrast. The first does not require the introduction of a contrast agent into the body and is intended for visualization of radiopaque structures. The most common CT scans performed without contrast include:
- CT lungs
- CT scan of paranasal sinuses and teeth
- CT scan of bones
- CT scan of the spine
- CT scan of the brain for injuries (to exclude brain contusions, intracranial hematomas and skull fractures)
If the primary target of the study is soft tissue structures or vessels, it is necessary to intravenously administer a special contrast agent to the patient, which, as its name suggests, increases the contrast of soft tissue structures and vessels on CT images. Among the most common contrast CT studies are:
- Abdominal CT
- CT scan of the kidneys and urinary tract
- CT angiography of the brachiocephalic arteries
- CT angiography of the aorta
- CT coronary angiography
- CT scan of the chest for cancer
The price of a CT scan depends on the part of the body being examined and the need to use a contrast agent.
Is the SCT procedure painful and is it harmful? What are the contraindications? Where to get a CT scan in Kyiv?
The SCT examination is absolutely painless; the scanner itself does not directly touch your body.
The method is based on X-ray radiation. Naturally, during an SCT study, the patient is exposed to x-rays, therefore, when prescribing this study, the doctor must have fairly compelling reasons and take into account the negative impact of x-rays on the body.
An absolute contraindication for SCT is pregnancy and breastfeeding. Also, SCT is strongly not recommended for children without significant reasons. In other cases, you should consult your doctor.
a computed tomography (CT) scan in Kiev at the ACMD clinic, a 64-slice tomograph (the radiation level is reduced significantly!)