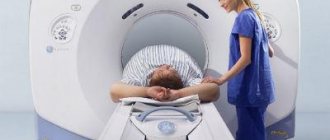
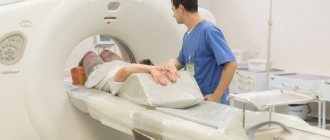
Computed tomography with contrast
CT with contrast involves examining the patient's body using minimal doses of X-ray radiation. This type of diagnostic method also involves introducing a contrast agent into the human body before the procedure. This is necessary in order to significantly increase the contrast between healthy and diseased tissues, identify even the slightest signs of the disease and make a diagnosis in the early stages.
Why do you need a CT scan with contrast?
CT scan using contrast can identify healthy and pathological tissues of the body, therefore it is often prescribed for suspected cancer. This is explained by the fact that pathological tissues are supplied with blood much better than healthy ones, so the iodine contained in the contrast accumulates in them, making it possible to find out the size, location and confirm the presence of a tumor.
The blood vessels through which the contrast agent moves are often also examined and any abnormalities identified. It also often happens that contrast-enhanced computed tomography is prescribed to examine the abdominal organs, since this can significantly improve the clarity of the resulting image. All areas that accumulate contrast are highlighted in white in the images, which makes it possible to detect even small tumors.
Advantages of implantable port systems

- Such a system is installed only once, thereby eliminating the risk of injury to the veins that occurs with repeated insertions of venous catheters. Frequent puncture can lead to the development of phlebitis or thrombophlebitis.
- Since port systems are very compact, the patient can lead a normal life without depriving himself of his usual joys, hobbies and communication with family. It is enough to tell the doctor about what sports or outdoor activities you are interested in, and the doctor will choose the optimal place to install the system.
- Direct access to the port system, and accordingly to the vein, is easier, faster and painless than when installing an IV, i.e. This method increases patient comfort during treatment.
What contrasts are used for CT
As a rule, various iodine-containing preparations are used to increase the contrast of the resulting image. All of them are divided into two groups - fat-soluble and water-soluble. Medicines of the first group are very viscous, so their use is limited. They are administered only locally, for example, into the peritoneal cavity to identify fistulas, etc. If we are talking about computed tomography with bolus contrast (the drug is administered into a vein with a special injector) or about the drug being administered orally, water-soluble contrast is used. The toxicity of such drugs is several times lower, and they also quickly enter the blood vessels.
How is contrast agent administered?
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography involves several ways to administer a contrast agent. The method chosen will depend on what exactly needs to be inspected. Contrast can be injected orally, into a vein, rectally, into an organ, or even into the lesion itself. It is worth taking a closer look at the most common methods.
Oral route
This method is most often used when examining the gastrointestinal tract; in this case, the patient must drink the drug according to the recommendations specified in the instructions. The medications are quickly absorbed, significantly increasing the clarity of the image of the mucous membranes of the stomach and allowing you to see polyps or narrowings. Often combined with intravenous contrast.
Intravenous administration
CT using intravenous contrast involves several types of injection of a substance into the body. Namely:
- Before the procedure, a nurse will inject the drug into the patient’s vein;
- first, a regular CT scan is performed, then the computer tomograph is stopped, contrast is injected into the patient’s vein, and the procedure continues with a contrast agent;
- the substance is administered as a bolus using a special syringe or a dropper if you need to administer the drug slowly.
Computed tomography with intravenous contrast is most often performed.
Into the lumen of the cavity
In such a situation, fat-soluble substances are used to determine the presence of diverticula, fistulas and other abnormal formations. Sometimes when examining hollow organs (for example, the bladder, colon), contrast is injected into them before the procedure begins. The harm of CT with contrast will be slightly higher, since fat-soluble compounds are more toxic than water-soluble ones. But, nevertheless, problems with removing the substance from the body do not arise if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed.
Computed tomography - Contrast enhancement
- one of the “gold standards” all over the world when examining patients with oncological, surgical and many other diseases.
Advantages of intravenous contrast:
Improves differentiation of organs, tissues, blood vessels.
Allows you to identify lesions that are not visualized on ultrasound.
NB! CT scan of parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys, etc.) without contrast enhancement may be less informative than ultrasound!
Allows you to evaluate not only the localization of the process, but also its prevalence, relationship to surrounding organs (invasion, compression).
Makes it possible to evaluate the vascular bed using a non-invasive method (CT angiography).
Studies without intravenous contrast are only suitable for structures with naturally high contrast (bone, stone detection, lung parenchyma) and for the detection of hematomas. Almost all other types of soft tissue CT examinations benefit from the use of intravenous contrast enhancement. New methods of computed tomography in Donetsk are based on the analysis of various phases of perfusion after contrast.
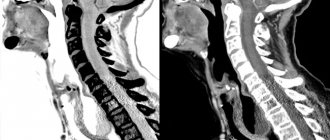
CT scan of the abdominal organs . Multiple metastases in the liver.
Without IV contrast.
With IV contrast.
Brain metastasis
Without IV contrast.
With IV contrast.
What substances are used for intravenous contrast.
Modern intravenous contrast agents usually contain iodine. There are ionic (Urografin, Triombrast, Trazograph, etc.) and non-ionic (Tomohexol, Omnipak, Ultravist, etc.) contrast agents. Initially, ionic iodine-containing contrast agents were developed, but their intravenous administration is fraught with a large number of complications and currently they are most often used for contrasting the gastrointestinal tract, since they are absolutely not absorbed in the stomach and intestines and are released unchanged naturally.
For intravenous contrast, nonionic contrast agents are now used all over the world, in which iodine is bound by covalent bonds, which significantly reduces the risk of complications. According to world statistics, the frequency of complications with intravenous administration of non-ionic contrast agents is 1 in 10,000 cases, i.e. 0.01%. As a rule, this happens in people with a tendency to allergic reactions. Therefore, if you are prone to allergies and you are going to undergo a CT scan with IV contrast, you MUST inform our administrator or nurse about this.
How does contrast work and what does the patient feel during this time?
To perform intravenous contrast , before the test, the nurse will place an intravenous catheter in your cubital vein. Directly during the scan, a non-ionic contrast agent will be injected through this catheter. It is not administered manually, but using a special device - an injector, which does this with specified parameters (volume of substance, injection rate). These parameters are of great importance in observing certain phases of contrast, which gives a huge advantage in the subsequent diagnosis. The volume of contrast agent administered varies depending on the person’s body weight and the objectives of the study (from 50 to 150 ml).
Injector
During administration, you will feel a warmth spreading throughout your body, which will quickly pass. It is extremely rare to experience urticaria (a reddish allergic rash on the skin), which quickly goes away with the administration of antihistamines. If you feel any discomfort, tell your nurse right away.
Already in the fifth minute, almost 90% of the contrast agent administered to you ends up in the urine. The rest is excreted within 24 hours.
Plain water or a diluted solution of ionic contrast agent can be used to contrast the gastrointestinal tract. The volume that you will have to drink can range from 1 liter to 1.5-2 liters. The solution has a slightly bitter taste. It does not cause any unpleasant sensations. Occasionally, slight looseness of stool may be observed. This is due to the fact that the solution has a high density and causes an influx of fluid into the intestinal lumen, but it is absolutely not absorbed in the intestine and leaves unchanged naturally. This effect is similar to that which occurs if you drink a saturated saline solution.
Indications for intravenous contrast
The range of indications for intravenous contrast is quite wide. Let's mention only the most important ones:
If there is any suspicion of oncological or surgical pathology, or if this pathology is established and its prevalence needs to be determined, intravenous contrast is ALWAYS performed - this is the GOLD STANDARD all over the world.
A CT examination of the abdominal organs, retroperitoneal space, and pelvic cavity, with rare exceptions (trauma, search for stones in the urinary system), is done without IV contrast.
Contraindications for intravenous contrast
An absolute contraindication to intravenous contrast is a history of intolerance to nonionic radiocontrast agents, i.e. if they have already been administered to you and you have had a serious reaction to them. You MUST inform your nurse about this fact before the test. All other contraindications described in the literature (serious condition of the patient, cardiac, renal failure, hyperthyroidism, etc.)
RELATIVE, since if there is an acute question about the life and health of the patient and it is not possible to make a correct diagnosis by other means, then with appropriate preliminary preparation, IV contrast can and should be performed
And the most important thing! The question of the need to use contrast (intravenous or any other) is decided by a radiologist!!! And only him!!!
Abroad, if a patient refuses contrast enhancement without good reason, he may be denied the study. Since the feasibility and diagnostic value of such a study will be low.
Find out
how much CT diagnostics costs in Donetsk
How is tomography with contrast performed?
If you do not know how to prepare for a CT scan with contrast, it is worth checking with your doctor before the procedure, as recommendations depend on what exactly needs to be examined. The procedure itself is quite standard: after the contrast is administered, the patient is placed on the tomograph table, then the diagnosis begins.
CT perfusion
This procedure is non-invasive. This type of tomography is performed only using contrast and involves examining the blood vessels of the selected organ - liver, brain
, kidneys, etc. The advantage of the procedure is that it will be possible to examine all the structures of the organ at the capillary level.
Angiography
To find out what the contrast-enhanced CT procedure shows, you need to first become familiar with its main difference from other types of tomography. This research method involves surgical intervention in the body. Such diagnostics allows you to assess the condition of the blood vessels and determine how normal their lumens are. Through a puncture, which is usually made by the arteries of the groin area, a special catheter is inserted, allowing one to gradually reach the organ being examined and obtain all the necessary information.
Installation and operation of the port system
The port system is installed subcutaneously under local anesthesia. This operation lasts about 20-30 minutes. The port can be used for its intended purpose after the first minutes after implantation is completed.
A catheter connected to a port is inserted into one of the central veins. Then the nurse pierces the port membrane with a special needle, the infusion system is connected to the needle, and that’s it. The process of administering the medicine begins.
Whether this treatment will take place in one stage or in courses that are separated by time intervals does not matter. The port system will not disturb the patient in any way.
Who is contraindicated for contrast agents?
There are many contraindications to CT with contrast. Contrast cannot be used if:
- allergies to iodine or seafood;
- pregnancy at any stage, even small;
- diabetes mellitus;
- renal or heart failure;
- thyroid diseases;
- myeloma disease.
Breastfeeding mothers will have to wean their baby off the breast for two days after the procedure, as some contrast may pass into the milk. It is also worth knowing that the CT procedure as such becomes impossible in the case of a large patient’s weight - the devices are not designed for a weight of more than 150-200 kg. The tomography procedure is not prescribed unless absolutely necessary for patients under 14 years of age, as well as for patients with an unstable mental state or suffering from claustrophobia. In some cases, light medicated sleep can be used.