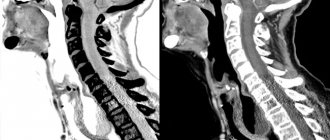
Computed tomography is a study of human internal organs using x-rays. The human body is illuminated layer by layer with X-rays from different sides. The resulting images are processed by a computer, which makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of the areas under study. This happens within a very short period of time, and the amount of information received by the doctor is quite large.
Due to the fact that when performing a CT scan a person receives a certain dose of training, patients naturally have questions about how safe the test is and how often it can be performed without harm to health. In some cases, CT is performed using a contrast agent, which can also be unsafe, because the contrast can cause an allergic reaction. In this regard, it is necessary to talk in detail about the maximum permissible radiation dose, the contrast used in CT, and contraindications to the procedure.
What is radiation exposure and its indicators on CT?
Today there is a standard for the maximum permissible dose of radiation that a person can receive within one year without harm to health. According to WHO recommendations, the maximum permissible dose of radiation exposure to the human body should not exceed 150 mSv per year.
A person receives a dose of X-ray radiation during many studies - fluorography, dental photography at the dentist, during mammography of the mammary glands. The total radiation dose that a person receives during these studies, as a rule, does not exceed 15 mSv.
When performing a CT scan of the brain, the dose is 1-2 mSv; diagnostics of large parts of the body, such as, for example, CT scans of the abdominal cavity or pelvis, is also insignificant - about 6-11 mSv. From this it follows that the study can be carried out several times a year without any harm to health.
Indications and contraindications
The key indication for computed tomography in oncology is suspicion of cancer of various localizations or assessment of dynamics during treatment. It can be:
- bronchopulmonary system;
- thyroid gland and area of the trachea, larynx;
- brain and spinal cord;
- formations in the pelvis;
- lesions of the skeleton and joints;
- chest formation;
- abdominal pathology;
- damage to blood vessels and lymph nodes;
- neoplasms of subcutaneous tissue or skin.
In addition, CT scanning according to compulsory medical insurance in St. Petersburg is necessary for planning surgical treatment, radiation therapy, assessing the ongoing treatment and correcting patient management tactics.
CT is contraindicated:
- during pregnancy;
- in children under 6 years of age;
- with a weight of more than 120 kg.
Additional contraindications for contrast studies:
- kidney failure;
- allergy to contrast and iodine preparations;
- general serious condition;
- decompensation of diabetes mellitus;
- hyperthyroidism (due to iodine overload).
Is there any harm from having a CT scan with contrast?
To perform a bolus-enhanced CT scan, a special radiopaque contrast agent is used, which is injected intravenously using a special pump. The contrast contains iodine-based drugs. It is this substance that can cause an allergic reaction in patients, therefore, if the patient is allergic to iodine or seafood, and also has a history of liver or gallbladder disease, serious cardiovascular pathologies or renal failure before the study, you need to inform the radiologist about this or refuse diagnosis with contrast.
In some cases, when the study is vital for the patient, but he has an increased sensitivity to iodine, an antihistamine is administered before the CT scan with contrast to eliminate the risk of developing an allergic reaction.
Even practically healthy people may also experience side effects during the procedure - nausea, slight vomiting, allergic skin reaction, loss of taste and smell. These disorders occur in only 1-5% of patients and usually go away on their own. Cases of more serious violations in the health status of patients are rare.
What will a CT scan of internal organs show?
The radiologist is faced with the task of identifying pathological changes and determining the nature of the disease
The patient often comes to a CT scan with a doctor’s referral, where, based on previously performed studies (ultrasound, colonoscopy, radiography, etc.), a preliminary diagnosis is indicated and the area of interest is indicated. Depending on the expected pathology, the radiologist uses various scanning modes and sets the optimal slice thickness.
CT scan of internal organs shows:
- inflammation and complications - abscesses, fistulas;
- stones in the kidneys, prostate (ultrasound is more suitable for identifying gallstones);
- tumor processes;
- developmental anomalies;
- traumatic injuries, etc.
The photographs show:
- internal organs: parenchymal - liver, kidneys, spleen, prostate - and hollow - trachea, esophagus, intestines, ureters, bladder;
- The lymph nodes;
- neurovascular bundles;
- osteoarticular structures.
Which examination is safer for patients: CT or MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most informative diagnostic methods that uses electromagnetic radiation. This study allows for a qualitative examination of organs that have a high percentage of fluid content, but which are located in the shell of the bone skeleton - the brain and bone marrow, intervertebral discs, and pelvic organs.
Computed tomography provides more information about the condition of bone tissue, therefore it is used to examine the musculoskeletal system. In addition, CT is used to examine the chest organs. When examining the organs of the urinary system or digestive tract, both studies are equally informative.
In terms of the duration of the procedure, CT takes much less time, so in emergency cases this research method is used.
Computed tomography of organs with contrast
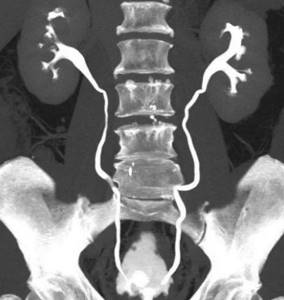
CT scan of the urinary system with enhancement
Contrast is not always required; administration of the drug is necessary when:
- primary tumor assessment - affected and normal tissues look different, which is important for determining the stage of the oncological process;
- suspected cancer recurrence after treatment - contrast helps clarify the nature of changes in the lymph nodes, differentiates fibrous degeneration after surgery and continued growth;
- the initial stage of the disease, when the changes are minor;
- conducting a comprehensive urological examination - CT scan of the urinary tract shows the function of each kidney individually, obstacles to the outflow of urine at any level, pathological refluxes, cysts, etc.
- clarifying the severity of the inflammatory process, diagnosing complications;
- identifying changes in blood vessels - CT angiography demonstrates the condition of arteries and veins, thrombus formation, occlusion, atherosclerotic processes, aneurysms, malformations, etc.
- contraindications for endoscopic diagnostics - CT scan of the intestine with double contrast provides the doctor with comprehensive information about the state of the digestive tract, etc.
Ways to introduce the amplifier:
- Intravenous, the most commonly used, iodine-based dye is injected into the antecubital vessel using an automatic injector.
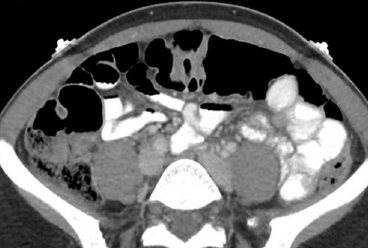
Visualization of internal organs on CT with contrast - when taking the solution orally
- Oral, used to diagnose diseases of the small intestine. More informative images are obtained with double contrast. A diluted iodine-based preparation is used as an enhancer. Oral contrast agents are suitable for patients with little intraperitoneal fat.
- Transrectal. Depending on the indications, an amplifier may be injected into the rectum before the study. This type of contrast is performed in a hospital setting to diagnose complications - suture dehiscence after surgery, the formation of a fistula tract. The photographs show pelvic abscesses located between the intestinal loops.
CT without contrast is performed to assess the location and density of stones in a patient with urolithiasis, to diagnose lung pathologies (except tumors).
In less than 10% of cases, side effects develop after intravenous administration of a dye with an iodine-containing base:
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- bronchospasm;
- generalized allergy such as Quincke's edema;
- deterioration of kidney function;
- lactic acidosis (while taking metformin).
Preparing for CT

Native computed tomography can be performed at the time of treatment. Preparation is necessary for a planned examination of the abdominal/retroperitoneal or pelvic organs with contrast. A few days before the diagnostic procedure, it is necessary to switch to a special diet, avoiding foods and drinks that cause bloating and increased peristalsis.
Excluded from the menu:
- fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs;
- marinades, smoked meats, spices, sauces;
- baking from yeast dough;
- milk and derivatives;
- fatty meat, poultry;
- confectionery;
- nuts, seeds;
- kvass, jelly, alcohol, strong coffee, tea, lemonade, sparkling water.
Depending on the area of interest and concomitant pathology, the attending physician may prescribe:
- cleansing the intestines with laxatives, enemas;
- taking antispasmodics, sorbents;
- enzymes, carminatives, etc.
Before CT, a 4-6 hour fast is required. A light snack 20 minutes before the test can eliminate nausea, drooling, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Important points
Before diagnosis you should:
- take a blood test for creatinine (the result is valid for 10 days);
- In consultation with your endocrinologist, stop taking metformin for 72 hours; an alternative treatment regimen is possible;
- For women during lactation, make a supply of several servings of breast milk and dispose of the excess.
What to take with you:
- passport;
- compulsory medical insurance/voluntary medical insurance policy (if it means payment for diagnostics through the health insurance fund);
- extracts from the medical history;
- doctor/consultation referral;
- results of previous studies.
Ways to protect patients during CT scanning
To reduce the radiation exposure to the patient, the following protection methods are used during the procedure.
- Reducing the procedure time. To do this, the study is carried out in only one projection, the radiation intensity and the number of tomography phases are reduced.
- Use of bismuth screens. These devices also allow you to reduce the radiation dose.
- Increasing the distance between the patient's body and the X-ray tube. To protect areas of the body that are not being examined, lead-filled protective aprons or vests are used.
Computed tomography in many cases is the only diagnostic method that provides the doctor with a complete amount of information about the state of the organs and systems of the body, especially in establishing an accurate diagnosis or analyzing the condition of a patient in critical condition. And if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the study will be absolutely safe for the patient.
At the medical office, you can perform a computed tomography scan of any organ or system of the body at any convenient time, as well as receive detailed consultation from a specialist based on the results of the examination. The study is carried out using modern expert-level diagnostic equipment, which allows obtaining high-quality images of the areas under study. You can make an appointment for a CT scan by phone.
Features of CT
During a CT scan, an X-ray beam passes through the patient’s body in a circle, due to which layer-by-layer transverse sections are formed at different angles. The device creates images based on the varying ability of tissues to transmit the X-ray beam. The computer tomography program processes numerous scans of tissue sections, ultimately creating a three-dimensional model.
For greater clarity in the examination of blood vessels and hollow organs, contrast is used with safe drugs that are excreted by the kidneys.
CT scan at SM-Clinic
To make an appointment for a CT scan at the oncology center and clarify the price, please call. The study is carried out using a Siemens Somatom Emotion 16 multispiral device (a 32-slice device is installed in the clinic on Vyborg highway). Due to the multi-row detector array, it allows you to make sections quickly and with high quality images. The installation has 3 functions to reduce radiation exposure, an effective climate control system in the area where the patient is located and is equipped with powerful data processing programs.
Benefits of the study:
- due to the built-in SOMATOM Emotion algorithm, you can select an individual scanning zone;
- radiation dose dosing capabilities;
- The FAST Spine function allows you to perform a CT scan (without contrast) in 3 minutes.
How is a CT scan done?
“Is it scary to climb inside the apparatus, what if I have claustrophobia?” There is a stereotype that you will be “stuffed into a narrow pipe, where it will be scary and dark.” This is wrong. During the procedure, the patient lies down on a special table that fits into a portal - inside a large ring. It doesn't look like a pipe, but rather like a donut. The portals of modern tomographs have a wide open area to provide greater physical and psychological comfort. You are not lying in a closed space - not the whole body is inside the ring, but only the part being examined. At this moment, medical workers are monitoring the process from the next room and communicating with you through a speakerphone.
The computed tomography procedure on previous generations of computed tomographs lasts 5-40 minutes, depending on the area being examined. With a new generation of tomographs, such as the SOMATOM go.Up from Siemens, a CT scan of, for example, the sinuses is scanned in just 10 seconds. The only unpleasant thing can be the need to lie still all this time, and during a CT scan of the lungs, also at the doctor’s command, to hold your breath. Therefore, for people with increased excitability or claustrophobia, the doctor may prescribe a sedative before the examination. The time it takes to prepare results with transcripts depends on the density of the examination schedule, but not more than a few hours.
When conducting an MRI examination, the following is unacceptable:
- the patient has implants that are activated by electronic, magnetic or mechanical means (an ear implant, for example)
- presence of a pacemaker
- presence of a metal foreign body in the orbit
- the presence of metal clips on the arteries of the brain
- the presence of built-in insulin pumps and built-in nerve stimulators
- intracranial aneurysms clipped with ferromagnetic material (hemostatic clips)
- hematopoietic anemia (with contrast)