MRI is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing the condition of the human body. It is actively used in identifying congenital pathologies, neoplasms, and many types of difficult-to-detect diseases.
We have been professionally providing this type of diagnostics for many years, using expert equipment and the services of experienced doctors.
In this article, we have collected all the expert experience to answer important questions about the mechanism of MRI, indications and contraindications, decoding and other important aspects that may be of interest to patients.
How does MRI work?
The method is named after the type of technique used.
This is magnetic resonance imaging, which allows you to get a complete picture of the state of human tissue, see its blood vessels, congenital or acquired developmental anomalies, and neoplasms at an early stage.
The prevalence of this technique is associated with its main advantages. MRI is safe, does not create painful sensations for the patient, and is much more informative than radiography or ultrasound.
The technology is based on magnetic resonance. Like everything in the world, the human body is made of atoms.
Scientists are using the interesting property of various elements to create radio signals. To do this, they are first placed in a constant magnetic field, and then begin to be exposed to alternating ones.
Transmission of absorbed energy in the form of radio signals allows accurate readings of health status to be recorded. The tomograph is built in such a way as to not only capture recoil, but also significantly enhance it and create a clear image based on the information received and display it on the screen.
Due to the fact that hydrogen atoms predominate in the human body, the picture is clear - this element is one of the most susceptible to the magnetic resonance research method.
What to do if a biopsy confirms cancer?
If you had a biopsy and the oncology test confirmed cancer, take this not as a death sentence, but as a problem that can be solved. Of course, this will take a lot of time, effort and money, but most types of cancer can be successfully cured. Any cancer can be cured at an early stage, and some pathologies can even be cured at stages 3 or 4.
Here is the recommended sequence of your actions:
- Admit the problem. If you don’t recognize it, you will waste time deceiving yourself that the diagnosis is wrong, the cancer will go away on its own or can be cured with soda and propolis. Self-deception is fraught with progression of the disease and untimely treatment. In later stages, cancer is treated much harder, longer, more expensive, with a lot of moral and physical suffering. If you cannot cope with your psychological state on your own, ask for support from relatives or use the services of a psychologist.
- Specify the diagnosis. In addition to stating the fact of the presence of oncological pathology, diagnostics are also needed to clarify the stage of the disease. Contact a clinic that uses modern research methods: CT, MRI, PET and others. Sometimes invasive techniques such as laparoscopy or mediastinoscopy are required. Remember that machines only show the doctor the structure of your body, and do not make a diagnosis. It is important to contact a good specialist who will correctly interpret the data received, interpret the images, determine the stage of cancer and select adequate treatment.
- Get a second opinion. Don't be afraid to offend the doctor. Firstly, he is unlikely to be offended - a second opinion is normal practice. Secondly, your life and health are much more important than someone else's grievances or self-esteem. In the CIS countries, every third cancer diagnosis is made incorrectly. Consult with foreign specialists - you don’t even have to go abroad for this, you can get advice remotely.
- Get information about your illness. Avoid reading articles on the Internet - at best, they are unreliable information from people without medical education, at worst, they are “proven” recipes in the style of “how to cure cancer with cucumbers.” To get reliable information, read specialized literature or make a list of questions to ask your doctor at your next appointment.
- Consider different treatment options. For example, by default, if you have prostate cancer, your doctor will refer you for surgery. But for some patients, there are other treatment options, such as external beam radiation, brachytherapy or focused ultrasound. Another example: for breast cancer, you can partially remove the mammary gland and undergo a course of radiation therapy, or remove the breast completely without subsequent radiation.
- Check the possibility of innovative treatment. They are mainly available abroad. Some are more effective compared to standard approaches, others are less traumatic, others allow you to treat even advanced stages of cancer, etc. A few examples:
- In Germany, brain tumors are treated without craniotomy, destroying them with a targeted high-tech laser through a tiny hole with a diameter of 3.2 mm.
- New immunotherapy methods are being used for metastatic melanoma. In some patients, they allow complete regression of the tumor and all its metastases.
- For metastatic prostate cancer, a radiopharmaceutical is injected into a vein, which selectively accumulates only in cancer cells - it itself “finds” all metastases in the human body and destroys them, irradiating them with radiation from the inside.
- Follow the plan. Of course, clarifying the diagnosis, deciphering cancer and information about treatment is very important. But it’s even more important to start treatment as quickly as possible, before the disease progresses to the next stage. If the waiting list for radiotherapy in your country lasts for several months, go abroad so as not to waste time.
Features of the resulting image
The main advantage of images created using MRI is that they are obtained layer by layer. Just imagine that you are cutting some product into small slices with a very sharp knife. This makes it possible to get a detailed, clear image of everything that is inside.
The design of the device uses special gradient coils. Modern methods help create magnetic resonance on a specific selected layer. Doctors can move between layers.
The result is a tomogram. It can be called a map of the organ - many small sections, each of which is made in three directions. Thanks to this, even the smallest changes at an early stage of development will not be hidden from the physician’s gaze.
What types of tomographs are there?
Many patients are familiar with only one type of tomograph - a closed one, resembling a capsule. In fact, there are more types of devices. We will try to answer the question of what types of MRI there are and how they differ from each other.
Open
The main feature is the location of the magnets. They are installed at the top and bottom. When a person lies down on the examination table, there is nothing on his sides - the classic capsule in the form of a tunnel is missing.
This device has several important advantages:
- Even patients with claustrophobia tolerate the examination well - many do not feel the fear of confined spaces in this position.
- Screening children becomes much easier. Parents can be nearby - this reduces psychological stress. It is also important that a minimum of noise is created during operation.
- Fewer contraindications. This especially applies to foreign metal objects in the body, such as artificial joints and many others.
- Research costs less. For many patients this becomes a decisive factor.
The choice of an open-type tomograph is also supported by the availability for checking the condition of many patients with large body weight. In some cases, people with psychiatric illnesses are also allowed to be tested.
The device also has a number of disadvantages. Since it only produces up to 1 Tesla, testing takes longer than other instruments. Power also affects the quality of the images - they are less detailed compared to other examination tools.
If you need to find small tumors in the body, this remedy will not work.
To mitigate the shortcomings of a tomograph, it must be used to perform the right tasks. If a physician can use images with a low level of detail, such a tomograph will do the job well. In this case, large formations in the image will be clearly visible.
When the test does not require complete placement in a chamber, this type of examination is also better suited than others.
Closed
The most familiar device for most patients. It looks like a capsule. The patient is placed on a special couch, which is placed inside, where the examination is carried out. This creates a magnetic field that completely surrounds the human body.
The widespread use of such a device is due to its high power - for many types of equipment it is three times higher than the readings of open analogues. The power range is from 1.5 to 3 Tesla.
Other benefits include:
- Doctors receive an accurate and high-quality image. Thanks to increased detail, it is possible to distinguish even very small tumors.
- The speed of examination increases significantly compared to other MRI testing methods.
The disadvantages include more contraindications than other methods. So, if a pacemaker, artificial joint or metal implants are implanted into a person’s body, problems may arise.
Due to the design features of the device, problems may arise when testing children and people with a fear of confined spaces. They cannot calm down inside, and to check the body they need immobility. Patients with a large body weight may not fit in the tunnel.
It is also worth considering that the device is quite noisy. When a person is inside it, it can cause discomfort for some. Otherwise, the examination is still painless, simple and quick.
Vertical
Closed and open varieties assume that a person assumes a horizontal position. But vertical options can also be found in equipping medical centers.
This category of devices belongs to open tomographs. The person stands in the indicated place and finds himself between two magnets. The technique retains all the positive and negative aspects of examination on a standard open tomograph.
The main indication for conducting such a study is the need to create a natural weight load. Without it, it is impossible to track some types of spinal problems.
Another indication for such an examination is possible problems with the spinal cord.
It is in a vertical position, when the spine is loaded, that severe scoliosis, hernias, and vertebral displacements can be clearly seen on the device.
The unique features of testing on a vertical open tomograph include increased information content for certain types of examination.
In case of back problems, this figure increases by 40%. The more information doctors have, the higher the likelihood that treatment will go faster and more successfully.
Clarifying codes for oncological diagnoses
Sometimes when diagnosing cancer, the transcript includes optional TNM characters:
L – reflects damage to the lymphatic vessels. Next to it is the number 1 or 0. It means, respectively, the presence or absence of tumor invasion into the lymphatic vessels.
V – venous invasion. This indicator can have three numerical designations. V2 is when tumor invasion into the veins can be seen with the naked eye, V1 – tumor tissue is detected only by microscopy, V0 – absence of venous invasion.
Pn – perineural invasion. Indicates that a tumor has invaded the tissue surrounding a nerve. Can have values 0 or 1 (no invasion or presence of invasion).
Classification for sentinel lymph nodes
The sentinel lymph node is the first on the path of lymph outflow from the tumor. Its determination is very important for some types of cancer, as it often avoids removal of all regional lymph nodes.
A biopsy is performed to identify the sentinel lymph node. To understand which nodes are sentinel, the doctor injects a radioactive drug around the perimeter of the tumor, which is then detected by a gamma scanner. The node in which the radioactive substance has accumulated is the sentinel node. There is not necessarily one - there are often 2 or 3 such nodes.
The doctor removes the sentinel lymph nodes. They are examined in the laboratory, after which the diagnosis of cancer is expanded - new designations appear in it:
- pN0(sn) – no metastases;
- pN1(sn) – there are metastases.
If there are no cancer cells in the sentinel lymph node, this means that they are also absent in other nodes. Accordingly, there is no need to delete them. The desire of doctors to avoid the removal of unnecessary interventions on the lymphatic collector is due to the fact that lymph node dissection sometimes causes complications, such as lymphedema (lymphoedema).
Degree of differentiation
Cancer can grow from different cells. They can be primitive (lowly differentiated) or developed (highly differentiated). Primitive tumors are more dangerous - they grow faster and recur more often.
In some diseases (for example, prostate cancer), the degree of malignancy of the tumor affects the stage and treatment strategy. Histopathological differentiation is indicated by the letter "G" with a numerical value adjacent:
- G1 – highly differentiated tumor (favorable histological type).
- G2 – medium degree of differentiation.
- G3 – low degree of differentiation.
- G4 – undifferentiated tumor.
Breast, endometrial and liver cancer also have their own classifications, reflecting the aggressiveness of the oncological process.
Reliability of diagnosis
C-factor is an indicator reflecting the accuracy of the diagnosis. The larger the number next to it, the more reliable the diagnosis:
- C5 – maximum level, determined only upon opening.
- C4 is the most accurate lifetime diagnosis that doctors receive after surgery to remove the tumor and study the resected tissue.
- C3 – data from a trial operation (for example, diagnostic laparoscopy or mediastinoscopy), washings, biopsy of the primary tumor and lymph nodes.
- C2 – data obtained during a special examination (CT, MRI, scintigraphy, biopsy, etc.).
- C1 – stage is established based on general diagnostic methods (clinical examination of the patient, radiography, endoscopic examination).
Treatment effectiveness
The R value is the residual tumor. It reflects the quality of the treatment performed. The lower the R value, the better the prognosis.
Doctors strive to remove the tumor in an R0 volume. This figure means that the cancer was completely removed and there is no residual tumor. R1 means that the remains of the tumor are determined microscopically, and with R2 the residual tumor can be seen with the naked eye.
Some treatments have separate efficacy designations. For example, for tumors that have spread throughout the abdominal cavity (such as ovarian or intestinal cancer), cytoreductive surgery is performed. The goal of treatment is to remove as many tumor lesions as possible. The results are indicated by CC (Completeness of Cytoreduction) symbols:
- CC0 – cancer foci are not visually detectable;
- CC1 – no foci of tumor process larger than 2.5 mm in diameter;
- CC2 – there are no areas of cancer spread more than 2.5 cm in diameter;
- CC3 – tumor areas remaining with a maximum length greater than 2.5 cm.
Power as the main parameter that differentiates tomographs
The difference between closed and open MRI is power. The higher it is, the clearer the image can be obtained using such a device.
The unit of power for the device is Tesla (T). When you undergo an examination with the most powerful machines, you can expect to receive truly detailed images, as well as a reduction in the duration of the process.
The table below shows the features of different device options.
| Type of tomograph | Power | Peculiarities |
| Low-floor | 0.1 – 0.5 Tesla. | Typically, such tomographs belong to the open category. They are used when the patient has noticeable pathologies or large tumors that can be seen even on pictures with little detail. There are a minimum of contraindications to the examination; it can be performed for people with large body weight and waist size, and children. This is also a good option if you suffer from claustrophobia. But you should prepare for the fact that the examination will take quite a long time - at least 40 minutes. |
| Mid-field | 0.5-0.9 T | They help reduce the examination time - a standard session takes from 20 to 30 minutes. The quality of diagnostics and detail will also be higher. |
| High-floor | 1-1.5 T | They are most often found in medical centers. The standard time to check a patient's condition is 15 to 20 minutes. Comprehensive examinations and contrast-enhanced testing may take longer. This power helps to get the most complete picture of the state of a person’s internal organs and identify many problems at an early stage. It should be borne in mind that all such types of equipment are classified as closed. Testing in them has a greater number of contraindications, and for people with claustrophobia and children it can be very uncomfortable. The use of such a device helps to obtain sections up to 1 mm thick. This indicates a very high accuracy of readings. |
| Ultra-high-field | Up to 3 Tesla | Such devices can very rarely be found in medical centers. The reason is that they are very powerful and expensive. The survey becomes simply unprofitable. High-field models help to obtain sufficient results for making a diagnosis. The main advantage is speeding up the process. The examination usually takes no more than 10 minutes. The cut is very accurate and the image quality is high. |
International clinical classification TNM
TNM is an international classification applicable to most malignant tumors (not just cancer). Its development began in the 40s of the last century, but since then the system has undergone significant changes. The seventh, and so far the latest, edition of the TNM system was published in 2009.
The decoding of the diagnosis of cancer and other oncological diseases according to the TNM system includes:
- forecast;
- therapeutic tactics;
- surveillance and control;
- assessment of treatment effectiveness.
The TNM system is accepted in most countries of the world. If you are diagnosed in Russia, Kazakhstan or Ukraine, then they will be able to read it in Germany, Israel or Singapore. This is a convenient tool for exchanging data between doctors around the world.
How do doctors designate cancer using the TNM system?
TNM is based on three criteria:
- T – reflects the characteristics of the primary tumor (most often size, but not only);
- N – metastases (mainly in regional lymph nodes, but not only);
- M – distant metastases.
The easiest way to diagnose oncology is to decipher M - if there is a 0 next to this letter, then there are no distant metastases, and if there is a 1, there are some. Sometimes there are letters of the Latin alphabet nearby, which determine the number or localization of foci of distant metastasis. For most diseases, M1 allows you to immediately diagnose stage 4, while with M0 it is stage 3 or lower.
Often the doctor indicates the location of metastases:
With the other two letters everything is more complicated. Each disease has its own designation. T can have a number from 1 to 4 next to it, and N has a different number of qualifying numbers, but no more than three. Regardless of the location and type of cancer, one pattern in deciphering an oncological diagnosis remains unchanged: the larger the numerical value next to any letter, the more severe the disease.
Let's take colon cancer as an example. Characteristics of the primary tumor:
- Tx – characteristics unknown;
- Тis – cancer in situ – the earliest stage, which does not even invade the epithelium of the mucous membrane;
- T1 – spread of the tumor to the submucosal layer;
- T2 – invasion into the muscular layer of the intestinal wall;
- T3 – spread beyond the intestinal wall, into fatty tissue, but not into other organs;
- T4 – tumor growth into nearby organs and structures.
Please note that tumor size is not taken into account in this classification at all. This is due to the fact that they do not affect either the prognosis or treatment tactics. For example, a T1 tumor may be larger than a T3 tumor if it grows into the intestinal lumen rather than extending deep into the intestinal wall.
Within each T variant, subtypes are possible. For example, the Kikuchi classification of early stage colon cancer involves dividing tumors into the following groups:
- T1sm1 – the tumor has grown into the submucosal layer by a third;
- T1sm2 – tumor germination by two thirds;
- Т1sm3 – complete infiltration of the submucosal layer of the intestine.
Next to the T and the number indicating the characteristics of the tumor, there may also be a letter of the Latin alphabet. For example:
- T4a – the neoplasm has spread beyond the intestine into the visceral peritoneum;
- T4b – spread to other neighboring organs.
N for any disease with the number 0 means absence of lymph nodes. Nx means no evidence of metastasis. Otherwise, the values are specific for different diseases. For example, N indicators for bowel cancer:
- N1a – 1 metastasis in the lymph node;
- N1b – 2-3 metastases in the nearest lymph nodes;
- N1c – metastases in the intestinal mesentery in the absence of them in the lymph nodes;
- N2a – damage to 4-6 lymph nodes;
- N2b – damage to 7 or more lymph nodes located near the tumor.
Thus, there are no universal values for T or N. For each disease, the oncology diagnosis codes will be completely different. The stages are also formed in different ways - not only based on the size of the tumor and the number of affected lymph nodes, but sometimes also taking into account the histological type of the tumor, the presence of hormone receptors or mutations in genes. That is why deciphering an oncological diagnosis by code is not an easy task, requiring consultation with a specialized specialist.
Correspondence between clinical cancer stages and TNM data
TNM is the basis for determining cancer staging. But for many diseases, the stage is determined not only by this classification; other factors are also taken into account.
The corresponding TNM stage for each disease is different. As an example, I show the stages of bowel cancer in the table below.
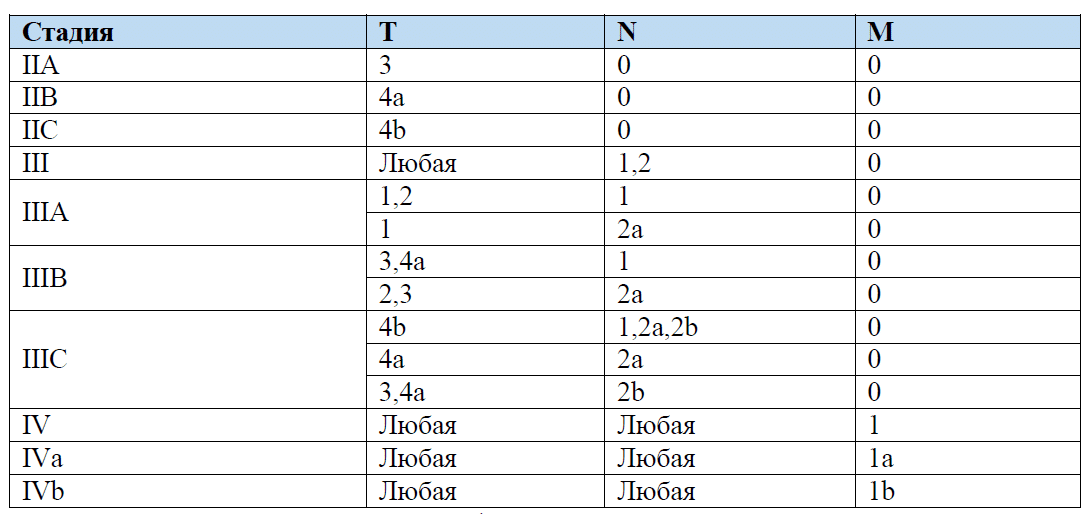
To detail the stage, oncologists can use subcategories:
- m – multiple primary tumor;
- y – stage of the oncological process after treatment;
- r – stage of recurrent tumor;
- a – the stage of cancer is indicated according to autopsy data (usually used in patients in whom cancer was not diagnosed during life or its stage was not determined).
The listed designations do not affect the stage of cancer.
TNM can be preceded by the letter "c" or "r". It reflects the method of diagnosis: cTNM – clinical assessment of the extent of the tumor process, pTNM – pathohistological assessment.
What can you see from MRI results?
Many patients are interested in the question of what an MRI shows. To date, this method is the most informative. With its help, you can examine the entire body, internal organs, tissues, and vascular system. At the same time, not only the current state is shown, but also the structure and its minor changes, which is also very important for patients.
Unlike most alternative diagnostic tools, this one helps doctors obtain not only static, but also dynamic images. This is the only way to check foci of brain activity, check the state of blood flow in organs, and the movement of cerebrospinal fluid.
When examining the cardiovascular system and identifying its pathologies, diagnostics also shows good results - it is possible to check parameters such as the degree of perfusion, myocardial contractility and other important parameters.
There are also serious opportunities for testing tissues - from cartilage and blood vessels to ligaments, muscles, gray matter, and nerves.
FAQ
Is a biopsy always performed to make a diagnosis?
A biopsy is used in most cases, but not always. Sometimes it is too dangerous, and in some situations it makes no sense. Examples of diseases for which a biopsy is not necessary:
- Skin cancer. A biopsy increases the risk of tumor metastasis, so it is not done. The tumor is excised and then examined.
- Kidney cancer. A biopsy is not required because the type of tumor (benign or malignant) can be determined using medical imaging techniques. The material is examined after the kidney has been removed. But if surgery is not performed, then a biopsy is necessary.
- Brain tumors. Any primary tumor of the central nervous system, except lymphoma, can be diagnosed without a biopsy using MRI. The material is examined after surgical removal.
Is it possible to cure cancer without surgery?
Most types of cancer are completely curable only with surgery. But there are exceptions to this rule. Some tumors can be destroyed by laser, radiation, or focused ultrasound. These are mainly non-aggressive neoplasms of the initial stages.
Is it possible to cure cancer if there are metastases in the lymph nodes?
Cancer can be cured, but other procedures will be required in addition to surgery to remove the primary tumor. Usually the doctor performs a lymph node dissection - removing the lymph nodes affected by the tumor along with the surrounding tissue. Surgery is often followed by a course of radiation and chemotherapy.
Is it possible to cure cancer if distant metastases appear?
In most cases, the appearance of distant metastatic foci indicates that the disease cannot be cured completely. In such situations, systemic treatment methods come to the fore, which simultaneously suppress the primary tumor and distant metastatic foci, regardless of their location. Doctors use chemotherapy, hormonal, targeted, and immune therapy.
There are exceptions to this rule. Sometimes there are only 1 or 2 distant metastases. Then the doctor can remove the site of metastasis or destroy it with radiation.
Does it make sense to undergo diagnostics abroad?
Abroad, the examination may cost more, but it is more accurate. Accordingly, to answer this question, you need to decide what is more important to you: money or health.
In Germany, more advanced equipment is used to diagnose tumors. Excellent doctors work here, and their activities are better controlled. There is no negligence in German clinics - you can be sure that no one will confuse your tests in the laboratory.
Cancer staging in Germany will be accurate, so doctors will be able to choose the best treatment - on the one hand, sufficient to cure the disease, on the other, as gentle and safe as possible.
How long does it take to be examined abroad?
It all depends on the methods used. Most programs last 2-3 days. The results of most instrumental studies can be obtained immediately, the results of analyzes can be obtained the next day. But some tests take a long time. After a tumor biopsy, you have to wait a week, and sometimes more, for an answer from the laboratory.
What diseases can be detected using this method?
Since the list of diseases depending on the patient is very extensive. In the table below you can see detailed information.
| Systems and organs | Detectable diseases |
| Brain | It is with the help of MRI that doctors successfully determine the signs of ischemic stroke. This is done early, which allows action to be taken. Thanks to the possibility of examining pregnant women, it is possible to determine the presence of pathologies of brain development in the child. In the early stages of development, magnetic resonance reveals both malignant and benign tumors, aneurysms, encephalitis, and multiple sclerosis. In some cases, it is even possible to establish the cause of mental disorders. An examination for epilepsy is also prescribed - it helps to understand where the focus is located. |
| Spine | Using MRI, you can check the spine, both in a calm and loaded state. In the first case, standard horizontal scanners are used, in the second - vertical ones. The technique helps to check the condition of the bone marrow, vertebrae, nerves, adjacent tissues, and intervertebral discs. MRI detects protrusions and hernias, inflammation of the spinal cord, compression fractures. A complete picture of neoplasms and the metastases they produce is given. |
| Bones and joints | Magnetic resonance allows you to check whether a person has injuries, where foci of degenerative and inflammatory lesions are located. It is an effective method for monitoring femoral head necrosis, dislocations, traumatic joint injuries, and a variety of other problems. |
| Large vessels and heart | MRI as a diagnostic approach is excellent in early detection of problems leading to heart attack and stroke. It shows aneurysms, tumors, areas affected by necrosis or ischemia. You can check the pulmonary and coronary arteries, the myocardium, and identify pericarditis, myocarditis and epicarditis. |
| Other organs | The examination can be carried out on almost all internal organs. This is how diseases of the pelvic and abdominal organs, lymph nodes, adrenal glands, liver, kidneys and spleen are checked. |
Indications for MRI examination
The procedure is always prescribed by a doctor. He should check the medical history, listen to the patient's current complaints and evaluate the treatment history.
Based on this, a decision will be made whether it is worth booking an MRI or whether any alternative means can be used.
There are several reasons to use this type of diagnostic test:
- Suspicion of various types of injuries, damage to bones, ligaments and soft tissues.
- Problems with the pelvic organs - frequent urination, foreign inclusions in the urine, menstruation problems and much more.
- Suspicions of problems in fetal development, the likelihood of hereditary pathologies.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system, manifesting themselves in arrhythmia, tachycardia, shortness of breath and other symptoms. If there are signs of impaired blood flow in the internal organs, it is also worth signing up for a test using magnetic resonance.
- Diseases of the endocrine system - from incorrect functioning of the thyroid gland to the appearance of neoplasms with different localizations. They can manifest themselves in increased fatigue, hormonal instability and other symptoms.
And this is only part of the indications for use. The technique is also actively used in pediatrics.
Unlike X-rays, this method helps to give more accurate readings about the condition of a growing organism without radiation harmful to the body.
Examples of deciphering cancer stages
Stomach cancer T2N1M0. Corresponds to stage IIA. The tumor has grown into the muscle layer of the stomach. 1 or 2 lymph nodes are affected. There are no distant metastases.
Skin cancer pT3N1M0. Corresponds to stage III. Before RT means that the stage is established based on a pathomorphological examination - skin cancer is not diagnosed in any other way. The tumor is larger than 2 cm in greatest dimension, but has not yet grown into nearby structures (bones, muscles, etc.). There is no more than 1 metastasis per lymph node, and it has a diameter of less than 3 cm in its greatest dimension.
Lung cancer T2bN1M0. Corresponds to stage IIB. The code encodes the following: tumor size is from 5 to 7 cm (T2b), ipsilateral peribronchial or pulmonary lymph nodes of the lung root are affected.
Liver cancer T4N1M0. Corresponds to stage IVA. As we can see, even the fourth stage of cancer occurs without distant metastases (M0). It is diagnosed if the tumor grows into nearby organs (except the gallbladder) or penetrates through the visceral peritoneum. N is only 1 or 0 for liver cancer (there are metastases or not). In our example they are (N1), but if they were not, the stage would still be classified as fourth.
Kidney cancer T1aN1M0. Corresponds to stage IV. The tumor is less than 4 cm in size and does not even extend beyond the kidney. But if there is metastasis in at least one lymph node (N1), then the fourth stage is established.
Cervical cancer T2a1N0M0. Corresponds to stage IIA1. To determine the stage of cervical cancer, the characteristics of the tumor are most important. There can be so many options that after T there are not enough numbers and letters - after the letters there are again numbers (T2a1). But the presence or absence of foci of regional metastasis does not affect anything. The appearance of distant metastases is a sufficient basis for establishing stage 4, but it can also be diagnosed without them - if the tumor has grown into the bladder or rectum.
Medullary thyroid cancer T1aN1aM0. Each type of tumor has its own classification. In this case we are dealing with stage III. The size of the tumor is small - less than 1 cm in diameter, and the cancer does not extend beyond the thyroid gland. But metastases appeared in the pretracheal and paratracheal, or prelaryngeal lymph nodes, and this is an unfavorable prognostic sign.
As you can see, the TNM classification of different oncological diseases differs significantly. In addition, macroscopic characteristics of the primary tumor and the presence of lymph nodes are not always the only staging criteria. Sometimes the doctor must additionally take into account the molecular biological or histological type of the tumor, which affects its growth rate and susceptibility to various types of treatment.
Main purposes of MRI
There are several purposes that MRI testing serves. Among them the main ones are the following:
- It is necessary to clarify where the pathology is located, how intensively it spreads, and what danger it poses. This allows you to choose an effective further treatment method.
- Check whether there are neoplasms of a benign or malignant type in the human body. At the same time, all problems can be identified at an early start - a proven contrast enhancement system works for this.
- Monitoring the success of treatment or rehabilitation period. MRI is often performed after injuries, treatment of oncology and other pathologies of the body.
- Analysis of the presence of problems in the body. These may include bleeding, foci of inflammation, necrosis, the current state of cysts and other types of neoplasms in the patient’s body.
Among the goals is the need to find foci of ischemic brain damage.
Main contraindications to undergoing the procedure
There are relative and absolute contraindications to MRI. This method is one of the most universal and suitable for most patients.
Absolute contraindications
These include those cases when a person cannot undergo such a procedure at all. Among them:
- Foreign devices in the human body. These include pacemakers, cardioverter-defibrillators, and insulin pumps. The magnetic field may prevent them from working correctly.
- Metal objects implanted on purpose or accidentally entered into the body. These are implants, special designs, such as Ilizarov apparatuses, prostheses, artificial joints.
- Personal intolerance to drugs administered during the process. These include components of contrast enhancement agents.
Also, the use of a contrast agent will be contraindicated if the patient suffers from renal and liver failure or allergies. Contrast-enhanced MRI is not recommended during pregnancy and lactation.
Relative contraindications
They say that for some time a person will not be able to undergo an MRI procedure or that special consultation is required from the doctor who makes the final decision.
These include:
- Fear of confined spaces. It is no coincidence that the question of how not to be afraid of closed-type MRI is popular online. If it is performed, the patient is placed in a tunnel with a device - many may experience psychological discomfort.
- Pregnancy in the first trimester. Although the magnetic field is safe, it is best not to risk exposing the fetus to it.
- Poor condition of the patient. This includes various types of heart and kidney failure, as well as other diseases in which it is very important for the doctor to monitor the patient’s condition.
- Inability to remain still. It can develop in different cases, including when a person has severe psychological illnesses, nervous tics and other problems. As a last resort, for such patients it is possible to use anesthesia.
- Discrepancy between the size of a person’s body and the parameters of tomographs. In most models, the tunnel width is 60 cm.
- Severe spinal deformities. During the examination, the person will have to lie on his back and remain completely still.
- Metal parts in the patient's body. In some cases, this includes filling large spaces on the skin with a tattoo containing a high percentage of metallic ink.
In some cases, problems may arise after various types of surgical intervention, for example, after removal of the gallbladder, puncture biopsy, sectoral resection and many other problems.
If you have any relative contraindications, you will need to further consult with your doctor. In some cases, the procedure can be postponed, in others it can be replaced with another diagnosis.
Sometimes the solution is to use alternative methods, for example, a vertical tomograph instead of a horizontal one.
If you still have foreign metallic inclusions in your body, you will need to provide documents confirming its complete safety or admissibility of use in magnetic resonance therapy.
How are the stages of cancer designated: clinical classification
Most cancers have stages. They are different for each disease. Usually there are four stages. For some types of cancer, stage 0 is also used - the earliest stage, when the tumor does not even extend beyond the mucous membrane or epithelium.
An approximate description of the stages that you can use as a guide when deciphering oncology:
I (1) – initial stage of cancer with a small tumor size and no metastases.
II (2) – a large primary tumor or the presence of single metastatic foci in nearby lymph nodes.
III (3) – many foci of regional metastasis, tumor growth into nearby organs and tissues.
IV (4) – the appearance of distant metastases, regardless of their location and quantity.
For most diseases, the stage is indicated not only by a number, but also by a nearby Latin letter. For example, stage IIIB. For some cancer pathologies, there may be another number next to the letter.
It is impossible to determine the prognosis by stage alone. For example, with small cell lung cancer at stage 2, the disease can no longer be cured - such patients are not even operated on. At the same time, breast cancer even at stage 3 can be completely cured. There are cancers in which the survival rate at the third stage is higher than at the second.
Thus, the stage of cancer gives you a guide and allows you to understand how advanced the cancer process is. For example, if you have the first stage, then it is definitely curable, but if you have the fourth stage, in most cases complete victory over cancer is impossible. At stages 2-3, the prognosis can be different - it is very different for different diseases.
What is the Latin word for the diagnosis of cancer?
The Latin word for cancer is "cancer". The term refers only to epithelial tumors. But popularly, any tumor is called cancer if it is malignant. For example, leukemia is a blood cancer, glioblastoma is a brain cancer, and osteosarcoma is a bone cancer.
Here's what a person with cancer might see in their medical record:
- cancer;
- abbreviated versions of the word cancer – Ca, Cr;
- carcinoma or a similar word (for example, adenocarcinoma).
Sometimes doctors write tumor or Tr, which means “tumor.” She needs to understand that not every tumor is malignant. Moreover, what the doctor saw on an ultrasound or x-ray is not always a tumor. Many other lesions, such as a cyst, scar, or area of post-radiation necrosis, look the same.
How to do an MRI for children
The issue of the admissibility of MRI for children is always very acute. Many parents fear that after such an intervention the baby will have any problems.
It is important to understand that the use of magnetic resonance is a safe and informative technology that does not produce harmful radiation.
There are several problems that can arise and they are all psychological. Let's look at how to overcome them.
How to make a child remain calm and still during the examination?
One of the most difficult requirements during such diagnostics is maintaining stillness. So one session inside a closed-type tomograph lasts 20-30 minutes.
Movement in this case may cause noise in the pictures.
There are several recommendations that will help parents prepare their children for an MRI examination. These include:
- For children under one year of age, you need to carefully choose the time for the procedure. It is best to wait until the baby starts to fall asleep - the visit to the session should be selected taking into account the current regime. To prevent the child from being frightened by noise, only open-type tomographs can be used.
- When the child's age ranges from one to three years, it is practiced to use special medications to help sleep. In this case, special sensors are used to help monitor sleep.
- Children aged 3 to 5 years are already more conscious and can be told about the importance of the procedure. For example, boys are often interested in the futuristic appearance of closed devices. You can tell them that this is part of the cosmonaut training program and it is very important to take it responsibly, listen to doctors and not be afraid.
The main thing is not to worry yourself, because children strongly feel their parents’ anxiety. Remember that the process is safe.
Is it possible to undergo an MRI procedure under a medical insurance policy?
In Russia, you can undergo an MRI under two types of health insurance policies.
These include:
- Compulsory medical insurance. This is a compulsory health insurance policy, the procedures for which are paid by the organizers.
- VHI. A voluntary health insurance policy can be paid for either by the person himself or by the company that employs him. In this case, the composition of services may be different.
Let's look at the features of MRI for each type of policy
MRI according to compulsory medical insurance
For the owner of a state insurance policy, it is possible to undergo an MRI for free. In this case, the examination can only be carried out if the medical institutions included in the system have magnetic tomographs available.
The procedure itself will be as follows:
- Consult a specialist based on your symptoms. In this case, the doctor will give you an official referral, which must be signed by the head of such institution.
- Get detailed information about whether it is possible to go with such a referral under compulsory medical insurance to a specific clinic.
- Sign up for an examination. Please note that, in accordance with regulations, the waiting period for your turn cannot be more than 30 days. There are also cases when the waiting process can be reduced to 14 days. This is permissible in cases where there is a suspicion of cancer or the patient’s condition is rapidly deteriorating.
- Come for examination. You must have with you not only a referral, but also a compulsory medical insurance policy and SNILS. Please note that when the procedure is performed on children, they must be accompanied by an adult. You must have your birth certificate with you.
Not all doctors decide to issue such a referral. Refusal can be expected when you do not have symptoms for an MRI and there are contraindications for examination.
But since the procedure is quite common and there are long queues for it, free treatment is often denied under the pretext of the availability of similar, less expensive diagnostic methods.
Attempts to replace MRI with X-rays or ultrasound can have negative consequences - incorrect diagnosis or significant delay in the process.
MRI according to VHI
A voluntary health insurance policy helps you undergo a free tomography examination if such an option is included in the insurance package and the clinic with which the insurance company has contracts has the necessary equipment.
When using this policy option, there are several basic steps:
- A specialized doctor writes a referral. It indicates which symptoms led to the appointment of an MRI.
- The patient contacts the insurance company with which he has a contract. You need to clarify whether an MRI procedure is included in your insurance package. It is also worth deciding on a clinic in advance and checking whether it provides services for your VHI.
- The insurance company itself contacts the medical center. You must obtain a letter of guarantee written specifically in your name.
- The patient is given an appointment date. At this time, you will need to come to the session and have a set of documents with you - a VHI policy, a referral from a doctor, a passport.
As you can see, you can conduct an examination using different means. The main thing is to get a referral in advance, choose a quality clinic and an experienced doctor who is well versed in diagnostics.
What are CT and MRI?
Behind the letter "T" in both abbreviations lies the word "tomography", which means "slice study" (Greek). In both cases, the organ is scanned layer by layer, and a three-dimensional image is displayed on the monitor. The patient lies down on a conveyor table that moves inside the scanning tunnel. With MRI, a person is placed in a chamber, while with CT, only the area of his body being examined. But this is only an apparent similarity; in fact, the methods have different mechanisms of action. CT is based on the effects of X-ray radiation. The organ is illuminated by rays directed perpendicular to the body. Tissues of different densities absorb radiation energy differently. Further, weakened by passing through tissue, the rays are captured by special devices and converted into signals of an electrical nature. A three-dimensional image of the organ appears on the monitor, along with the location of violations, if any. MRI uses powerful magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses. Magnetic fields can be constant or pulsating. A constant field causes a change in the position of hydrogen atoms in structures and tissues. The installation generates a radio frequency pulse perpendicular to the magnetic field, which causes hydrogen nuclei to generate signals that are collected in a scanner by a special receiver. The tomograph detects vibrations of cellular structures that have entered into resonance, and then builds three-dimensional images from them.
Features of the examination
The entire process of conducting an MRI can be divided into three main stages - preparation, actual execution and writing of the report. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Stage 1: Preparation
Before undergoing an MRI examination, you need to make sure of several aspects:
- Complete the documents. To undergo an MRI, you need to have a referral in hand. It will tell you what type of diagnosis you will need to get, as well as additional details, such as when contrast enhancement and other add-ons will need to be used.
- Make sure that the particular clinic provides services according to your type of policy. If the work is supposed to be carried out under voluntary health insurance, you will need to clarify whether the contract has been concluded with your insurance company. The same applies to compulsory medical insurance, because not all hospitals operate under such a policy.
- If you want to pay for the service from your budget, enter into an agreement with the clinic. This is a special agreement for the provision of paid medical services. An agreement on the protection of personal data is also concluded.
Usually, when searching for a suitable clinic, you should also immediately check with the doctor in what form the results will need to be provided. Thus, some only ask for a snapshot, while others require recording on a special medium.
The next step will be a meeting with a doctor. It is very important to determine whether you have contraindications for a certain type of examination.
Doctors pay great attention to preparation because it can affect the quality of the resulting image.
It is also worth paying attention to the correct selection of contrast that will be introduced into the circulatory system.
It is selected at the preparation stage; you need to make sure that there are no personal incompatibility, allergic reactions and other potential problems.
To undergo the procedure you will need to choose the right clothes. You should not be wearing chains, things with metal buttons, and much more.
Also, before the process, you will have to remove rings, bracelets, and watches.
Stage 2: conducting research
After preparation, the patient enters a room with an installed scanner. There he is placed on a special medical table.
The nurse talks about how the procedure will be performed, what you will feel inside the device, and what you should be prepared for.
It is important to understand that although the CT scanner is usually comfortable, many people may be concerned about the loud noise. The doctor will also tell you that you should not move during the process.
We advise you to remember that the process is completely safe. Although the doctors go into another room during the procedure, they monitor your condition - you don’t have to worry about anything.
If you are concerned that loud noise will disturb you during the procedure, you can wear earplugs or special headphones. They are issued at the medical center.
It is especially worth considering preparation for contrast-enhanced MRI. The patient is given an injection with a previously selected medical solution.
Remember that you will need to remain still so that the finished image does not appear distorted, making it difficult to read and make a diagnosis.
Stage 3: preparation of results
The standard package for transmitting results is photographs and a conclusion signed by a specialist.
Previously, doctors were given only ordinary images, but today the equipment helps record data on various media, including flash drives.
The images go not only to the patient, but also to the doctor. He studies the information received and prepares a conclusion. Preparation takes from 30 to 60 minutes. Sometimes the process can take longer – up to two days.
All patients receive information based on the results of the conclusion. Based on such a document, it will be possible to prescribe further treatment with the correct choice of drugs.