Ultrasound examination is the most common and cheapest method of additional instrumental research, which has received well-deserved positive reviews in terms of the speed and accessibility of the procedure.
Ultrasound allows not only to confirm the diagnosis, which is previously made on the basis of complaints, an objective examination, but also to prevent possible complications of the disease and recognize the chronic pathology of other organs in the human body, which occurs in a latent (hidden) form.
Ultrasound examinations are performed both routinely and urgently. Most gastroenterological, urological, surgical and cardiovascular diseases are not diagnosed definitively without ultrasound data.
Of course, there is no time to prepare for an urgent abdominal ultrasound, since only a few minutes are given to make a diagnosis. Often, the diagnosis of such acute conditions does not require such a thorough examination as a planned procedure and is carried out to exclude several dangerous pathologies:
- Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Renal and hepatic colic.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Acute appendicitis.
- Apoplexy of the ovary.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
With such a pathology of the above organs, lack of preparation for the ultrasound procedure does not affect the removal or confirmation of the diagnosis.
When undergoing ultrasound diagnostics, other characteristics of the condition of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space are routinely assessed:
- Possible increase in organ size.
- Violation of the structure of the organ.
- Blockage of the ducts or vessels of an organ by a foreign body or blood clot.
- Anomalies in the structure of the abdominal organs.
- Oncological lesions and neoplasms in the abdominal cavity.
In order for an ultrasound of any organ of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space to be as informative as possible, it is necessary to carefully prepare for it. If you do not follow the recommendations for preparing for an ultrasound, you may receive incorrect study results, which will be due to:
- Intestinal gas pollution. Excessive formation of gases in the intestinal lumen causes its expansion and change in shape. Therefore, during ultrasound, the shadow of the intestines can block the necessary parts of the organ being examined and give false results.
- Some pelvic organs can be visualized using ultrasound only when the bladder is as full as possible. If the bladder is empty during the procedure, the information content of the method will be equal to zero.
- A full stomach may interfere with examination of the upper (epigastric) abdomen. The wave-like movements that the stomach performs when grinding and wetting food with gastric juice interfere with the study of the pancreas, liver and gall bladder.
Taking into account the above facts, it must be said that proper preparation for an ultrasound is the key to a high-quality and reliable result of the study.
How to prepare for an abdominal ultrasound?
This study is prescribed to evaluate the work of:
- Pancreas
- Liver
- Spleens
- Gallbladder
- Kidney
- Ureters
Preliminary diagnoses that require ultrasound data:
- Food poisoning
- Gastritis
- Chronic and acute cholecystitis
- Cholelithiasis
- Chronic and acute pancreatitis
- Chronic and acute hepatitis of various etiologies
In these pathologies, combinations of inflammatory processes are often found. Since most organs of the epigastric region of the abdomen give a similar clinical picture of the disease, ultrasound is necessary to confirm the preliminary diagnosis and prevent possible complications that occur with inappropriate treatment.
To prepare for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space, it is necessary to exclude gas-forming foods (cabbage, potatoes, apples) from the diet. If you have a tendency to constipation, try to eat foods that stimulate digestion (oatmeal, kefir). If necessary, you can take a mild herbal laxative to cleanse the intestines of feces as much as possible. 5-6 hours before the test, you must stop eating any food to ensure your stomach is empty.
What does an ultrasound show?
Sonography is used in medicine both for diagnosing various diseases and for visual monitoring of complex surgical interventions.
The scope of application of ultrasound includes the study of:
- abdominal organs;
- thyroid gland;
- heart (echocardiography);
- vessels (carotid arteries or veins of the legs);
- mammary glands;
- uterus, ovaries (including during pregnancy);
- joints, such as the hip.
There are two types of ultrasound: diagnostic and therapeutic. Diagnostic ultrasound creates images using high-frequency sound waves generated by a transducer (probe). But for better visualization, the ultrasound head can also be inserted into the body through the gastrointestinal tract, vagina or blood vessels.
Therapeutic ultrasound also works with sound waves, but does not generate images. It is used to move and apply pressure to tissue, heat it, dissolve blood clots, or administer medications. Standard ultrasound has no harmful effects.
Abdomen
It is used both for diagnosing diseases and for monitoring the course of pathological processes in the body. Used to evaluate the condition of various organs, such as the liver, kidneys and spleen. The doctor determines the structure, size and location of the bladder, gallbladder and pancreas.
Limited assessment of bowel health is possible. It is also possible to detect free fluid in the abdominal cavity, such as inflammatory effusion or blood.
Thyroid
It is possible to determine the structure, size and focal formations. Scanning allows you to identify problems at the initial stages of progression, which makes it possible to begin treatment in a timely manner - before complications develop. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is the most accessible and informative research method that can be performed as many times as necessary without harm to the patient’s health.
Echocardiography
Typically, an echo examination of the heart is performed like any other ultrasound, that is, using a sensor that the doctor moves over the surface of the patient’s body. When diagnosing the heart, transesophageal (TEE - transesophageal) echocardiography can be performed. The doctor pushes a special probe through the esophagus to the entrance to the stomach. The heart is in close proximity and can therefore be examined better.
Doppler ultrasound
A comprehensive study aimed at determining the anatomical structure, nature, speed of blood flow and condition of the vascular walls (tension, elasticity). Allows you to identify damage to vascular structures, congenital anomalies and pathological tortuosity. Visualizes atherosclerotic changes, blood flow disorders, aneurysms and occlusions, as well as inflammatory processes and thrombophlebitis.
Ultrasound of female breast
A painless examination is the “gold standard” for the prevention of breast diseases. Allows you to examine all areas of glandular tissue, much more informative than with radiography and mammography. Using breast sonography, it is possible to identify various pathological changes: cysts and tumors, as well as assess the condition of the lymph nodes.
Gynecological ultrasound
Sonography of the pelvic organs is prescribed to evaluate ongoing therapy in gynecology or to identify pathological changes in the uterus, appendages, etc. Gynecological ultrasound reveals the fact of pregnancy, fetal development abnormalities and pathological disorders in the reproductive health of a woman.
Sonography of joints
Aimed at studying the condition of soft tissues and bone structures to identify pathological foci and prescribe effective therapy. Ultrasound of joints is performed for congenital anomalies, after injuries and to diagnose degenerative or inflammatory diseases. The diagnostic procedure does not replace radiography of the joint, since it does not allow assessing the displacement, the presence of fragments and the nature of the fracture.
How to properly prepare for a kidney ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the retroperitoneal organs, which include the kidneys, is prescribed to exclude pathological conditions that are caused by:
- Anomaly of the location, structure and functioning of the kidneys.
- Presence of kidney stones.
- The presence of sand in the kidneys.
- Blockage of the outlet of the kidney pelvis with a stone.
- Hydronephrosis of the kidney.
This study is prescribed for the following clinical symptoms:
- Urinary retention.
- Painful urination.
- Darkening of urine.
- Blood in urine.
- Pain in the lumbar region.
If an ultrasound is not performed in these cases, this can lead to an erroneous diagnosis and kidney failure, which can increase the risk of death.
In order to properly prepare for a kidney ultrasound, you do not need to do anything. Since this organ is located in the retroperitoneal space and is visible with ultrasonic waves in a lateral lying position.
Types of ultrasound of the pelvic organs
Depending on the gender of the patient and the area through which the examination is carried out, ultrasound can be:
- 1. Transabdominal. The sensor is moved over the abdomen, while the patient assumes a lying position. During the process, the doctor may ask you to change position, hold your breath, and perform other simple actions.
- 2. Transvaginal. How is a pelvic ultrasound done in this case? The sensor is inserted into the vagina.
- 3. Transrectal. The patient lies on the couch on his side. The sensor is inserted through the rectum. This technique is relevant when performing pelvic ultrasound in men to diagnose the prostate.
Regardless of how the test is performed, it will not cause pain. Some people may experience mild discomfort, but the procedure takes minimal time. If a pathology is visible on the screen, the specialist takes an image, which must then be provided to the attending physician.
How to properly prepare for an ultrasound scan of the adrenal glands?
Ultrasound of the adrenal glands is done in rare cases. More often, this procedure is carried out to determine a possible neoplasm of this organ or to determine an anomaly in its structure.
Ultrasound of the adrenal glands can show the size, condition of the parenchyma and the correct shape of the organ, which is very important for making many endocrinological diagnoses. Failure to do this procedure may lead to an inaccurate diagnosis, which will undoubtedly lead to incorrect treatment.
In order to properly prepare for an ultrasound scan of the adrenal glands, you do not need to do anything, since this paired organ is located at the top of the poles of the kidneys and is visible with ultrasound waves in the same way as the kidneys.
Explanation: norm and pathology in women
Only a qualified doctor can decipher the results of a pelvic ultrasound.
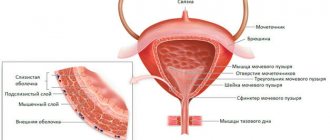
When examining the bladder, its walls should be uniform and the same thickness, about 2-4 mm. There should be no stones in the bladder cavity. If urolithiasis is suspected, ultrasound can detect dark areas with regular and clear boundaries. If there is thickening of the bladder wall, this may indicate a neoplasm, tuberculous inflammation or hematoma.
When the entire wall of the bladder thickens, cystitis and amyloidosis are diagnosed. Deviation from the norm may be due to blockage of the internal opening of the urethra with a stone or due to a neoplasm. In this case, you can find out the location, structure, size of the cervix and ovaries, and the condition of the fallopian tubes. A change in the condition of these organs leads to discharge, pain in the lower abdomen and other symptoms.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the spleen?
An ultrasound of the spleen is always performed when an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is prescribed. This organ is examined for the presence of pathological formations, changes in size, structural anomalies or injuries.
To properly prepare for an ultrasound scan of the spleen, it is necessary to exclude foods that contribute to gas formation in the colon from the diet for 2-3 days before the examination. These are the products:
- Apples.
- Raw cabbage.
- Potato.
If there is a need for an urgent ultrasound examination of the spleen, you can do an enema, which will cleanse the descending colon and provide visual access to the spleen.
If the above rules are not followed, the enlarged colon will overlap the shadow of the spleen, which will give inaccurate information and lead to an incorrect diagnosis.
Ultrasound in three dimensions
SonoAce Ultrasound Magazine
Contains current clinical information on ultrasonography and is aimed at ultrasound doctors, published since 1996.
Over the past decade abroad and in the last two years in our country, a new method of ultrasound diagnostics - three-dimensional ultrasound - has become increasingly popular among both patients and doctors. How does this study differ from the traditional, two-dimensional one?
The first ultrasound devices began to be developed in 1955, and at the moment it is difficult to imagine medicine without this diagnostic method. The safety of the method has been tested many times by scientists around the world. Ultrasound is recognized as a safe and reliable method of fetal imaging.
The first “three-dimensional” device appeared in 1989 in Austria. Unfortunately, the quality of the images was very poor, and it took up to 30 minutes to obtain one static 3D image. Naturally, the method has not found wide application in medicine. Only in 1996, thanks to a breakthrough in computer technology, a scanner with the ability to perform three-dimensional reconstruction in real time appeared. And from now on, the 3D ultrasound technique is increasingly used in medicine, especially in the field of obstetrics!
Devices for two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasound look identical in appearance and differ only in the presence of a special built-in module (a set of high-tech electronic boards) and special sensors. Understanding this is very important, since only new functions are added, while the scanning frequency (usually 3.5 MHz), intensity and power of the ultrasonic wave remain the same
- the same as with conventional ultrasound examination. That is, in a physical sense, three-dimensional ultrasound is no different from two-dimensional ultrasound, but in diagnostic terms it expands its capabilities.
A few words about the sensor the doctor uses to conduct a three-dimensional examination. Externally, it differs from the sensor you are used to only in that it is several times larger. This is due to the fact that inside its body there is a conventional two-dimensional sensor, which is constantly moving using a special mechanism. Multiple scans - two-dimensional images - are transferred from the sensor to a powerful computer located inside the scanner, where they are summarized using the aforementioned built-in module. The resulting three-dimensional (volumetric) image is displayed on the device screen.
To be fair, it must be said that modern two-dimensional ultrasound machines enable specialists to obtain the maximum amount of information necessary to determine the condition of the mother and child. Unfortunately, not every medical institution has a fleet of devices that meets modern diagnostic requirements. Considering that the two-dimensional ultrasound technique has been used and improved for several decades (since the 50s of the last century), it can be stated that specialists have clearly developed methods for standardizing the data obtained from ultrasound examination. So, each period corresponds to certain sizes of the head, limbs, internal organs of the fetus, including certain structures of the brain, heart and others. Three-dimensional examination data provides additional information, especially for the diagnosis of certain developmental defects: limbs, face, spinal column. Thus, suspicion of the presence of such defects can also be considered a medical indication for conducting a three-dimensional study.
3D ultrasound is a natural technical development of 2D ultrasound, not only adding precision to the examination, but also allowing the expectant mother to get to know the baby before birth. The most optimal option for ultrasound examination is a combination of both methods. In this case, the doctor first of all receives all the necessary information using a traditional study, supplements it with the help of three-dimensional vision and confirms his opinion about the well-being or unfavorability of the course of this pregnancy. Parents have the opportunity to see the baby not in the form of incomprehensible black and white “floating” lines and dots, but in the form of a three-dimensional image in real time, reminiscent of “old” video recording. If you use this “miracle of technology” for all 3-4 ultrasound examinations required during pregnancy, then by the time the baby is born, a whole video will have been shot about it. It is probably unnecessary to talk about how parents react to footage of such a film, both at the time of its creation, and when watching the videotape and remembering what the child was like when he was in his mother’s tummy. In this regard, it is also interesting that it will be easier for you to explain to your baby where he was when he was not there yet. And existing older children, having been in the ultrasound room, treat the upcoming appearance of a brother or sister with greater responsibility and understanding. 3D ultrasound combined with video recording is a beautiful and modern part of family documentation.
When undergoing a three-dimensional ultrasound, it is necessary to take into account that the examination time may be slightly longer than with a standard two-dimensional one. The quality of the resulting image when using three-dimensional ultrasound depends on the position of the fetal body, the location of its limbs, the umbilical cord and the placenta. Difficulties in obtaining volumetric images may be due to a small amount of amniotic fluid, even in cases where their relatively small amount is not yet pathological (oligohydramnios). Significant problems in the quality of the picture usually arise if the pregnant woman is overweight or if she has scars on the anterior abdominal wall after abdominal surgery. The success of a three-dimensional study (obtaining high-quality images of the fetus) often depends on motor activity - the more active the fetus, the greater the chance of seeing more interesting pictures of intrauterine life. If the fetus is motionless and is located inconveniently for the researcher, then the doctor may suggest interrupting the examination for a while to wait for a suitable position of the child. During this time, it is advisable to drink some sweet drink (for example, sweet tea), which usually increases the motor activity of the fetus after 10-15 minutes.
The information obtained and the type of three-dimensional picture depends on the stage of pregnancy at which the examination is carried out. During pregnancy from 3 to 8 weeks, 3D images are not effective. From the 10th to the 16th week you can see the entire fetus, its posture, arms, legs, umbilical cord (without distinct small details). In some cases, during these periods it is possible to visualize the face of the unborn child, however, it should be understood that the face of the fetus during these periods bears little resemblance to the face of a person. The optimal pregnancy period for 3D ultrasound is from 15 to 30 weeks. At such a time frame, it is possible to obtain images of live facial expressions in the fetus. After 23–25 weeks, the fetus becomes so large that obtaining an image of it as a whole is no longer possible, so on the screen you can see the head and shoulders, arms, legs, and torso in turn. With upcoming repeat births, the gestational age at which 3D ultrasound can be successful increases to 34-38 weeks.
To summarize all of the above, three-dimensional ultrasound in obstetric practice has already taken its strong place next to two-dimensional research. Being a modern high-tech method, it improves the diagnosis of various anomalies and gives a new look at fetal malformations already identified by the usual method. And a visit to the doctor’s office with the whole family makes an invaluable psycho-emotional contribution to preparing for the arrival of a new person. If for some reason you do not have the opportunity to undergo all the ultrasound examinations necessary during pregnancy in combination with a three-dimensional technique, then do not miss this at least in the third trimester, when the baby will be almost the same as when you personally “met” in the delivery room.
SonoAce Ultrasound Magazine
Contains current clinical information on ultrasonography and is aimed at ultrasound doctors, published since 1996.
How to prepare for a prostate ultrasound?
For men over 45 years of age, prostate ultrasound should be a routine procedure once every 6 months. This rule may provide early detection of gland tumors and prevent its transformation into a malignant tumor. Prostate ultrasound should be done:
- When the intensity of urination and its pain changes.
- Pain in the bladder area.
- Urinary incontinence.
To properly prepare for a prostate ultrasound, you need to drink 1-2 glasses of plain still water 20-30 minutes before the examination. This will ensure a full bladder and good visualization of the prostate using ultrasound waves. If your bladder is not full enough, you need to drink more water.
The examination evaluates the size and structure of the gland parenchyma. Based on these data, a diagnosis of possible hyperplasia (enlargement) of the gland is made, and a prognosis is made about the man’s health and ability to urinate freely.
If the preparation recommendations are not followed, the result of the ultrasound examination will be zero and the diagnostician will be forced to send the patient for water and wait approximately 30-40 minutes, which will prolong the time of diagnosis and increase the risk of complications.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs: preparation and features of the procedure
Pelvic ultrasound is an informative examination of the patient using ultrasound.
Thanks to it, it is possible to determine the structure, shape, and dense tissue, which makes it possible to diagnose certain diseases, and based on the results, create an effective treatment regimen. Pelvic ultrasound in women and men is performed in our medical center using modern equipment and the experience of qualified doctors. Ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to determine the presence of pathological processes, and it has many strengths, including:
- 1. The price of pelvic ultrasound is within reasonable limits and is an affordable diagnostic technique.
- 2. Allows you to obtain accurate results about the condition of the pelvic organs.
- 3. During the procedure, the patient will not feel pain or excessive discomfort.
- 4. The results are displayed on the monitor and decrypted immediately. This is done by an ultrasound doctor or a specialist attending physician.
- 5. What does a pelvic ultrasound show? Demonstrates a complete picture of the condition of the examined organs and the localization of pathogenic foci.
- 6. The procedure will not take the patient much time - on average it takes 20-30 minutes.