The most informative method of examining the fetus and the expectant mother during pregnancy is ultrasound. Planned ultrasound examinations are prescribed at 11–13, 18–22 and 30–34 weeks. With each ultrasound, the main attention is paid to the fetometry of the fetus. What is meant by this concept? What are the standards for fetometry indicators at different stages of pregnancy?
Why is BPR determined?
Biparietal size is measured to determine the degree of development of the fetal nervous system. The indicator helps to assess the possibility of passage of the fetal head through the birth canal. It is necessary to establish their ratio. In cases where the BPD exceeds the required size, it makes sense to perform a caesarean section. The indicator is determined by the internal or external boundaries of the skull.
Method of implementation
It is recommended to perform an ultrasound examination of the biliary tract in the second or early third trimester of pregnancy. Sizing is determined transabdominally. In cases where this type of examination is difficult, the examination is performed transvaginally.
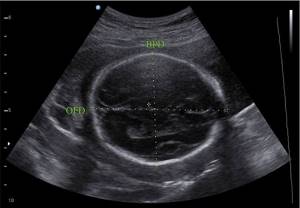
Ultrasound of BPR: normal values
Biparietal size indicators will change depending on the age of the fetus. At 12 weeks, the BPR is 21 mm. For 13 weeks – 24 mm. At 16 weeks the size increases to 34 mm. 24 weeks corresponds to a BPR value of 61 mm. At 32 weeks, 82 mm is considered normal. The size increases to 84 mm at 38 weeks. At 40 weeks, 96 mm is determined.
This size should be determined by an experienced ultrasound doctor. There are deviations from normal values up and down. Similar changes occur in various conditions. It is important to diagnose changes in time for timely adoption of therapeutic measures.
Some conditions characterized by changes in the biparietal size of the head require termination of pregnancy for medical reasons due to the threat to the life of the fetus and mother.
All women without exception during pregnancy must undergo an ultrasound procedure as directed by a gynecologist. After completing the study, the patient receives a ready-made protocol with all the results that comprehensively characterize the child’s development. It describes many indices that indicate the possibility of development or the appearance of deviations. What it is? The most important point of the examination is considered to be fetal fetal fetal development by week on ultrasound or biparietal head size. It is he who most accurately speaks about the baby’s age (especially from 12 to 28 weeks).
What is this criterion?
The term “BPR of a child’s head” refers to the segment from the outer to the inner contour of the parietal bones. It is carried out over the thalamus. In this case, the specialist must be very careful during the examination, because the slightest inaccuracy leads to the results being significantly distorted and the gestational age being determined incorrectly. At different times throughout pregnancy, the norm of fetal BPD changes by week, as described in a special table. When figuring out what it is, you need to remember that, for example, at twelve weeks this figure will be 21 mm, at thirteen weeks it will increase to 24 mm, at sixteen to 34, and so on.
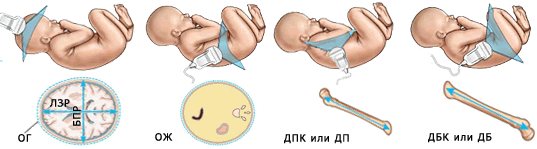
Ultrasound examination parameters of the fetus
What do the parameters of the fetal BPR and LZR tell about?
When figuring out what a study like BPR is, you will have to remember that the biparietal size of the fetal head is never assessed in isolation from another parameter - LZR on ultrasound. So what is it? This is the fronto-occipital size, measured during pregnancy together with the BDP and representing the segment between the frontal and occipital bones. The values of these indicators change in direct proportion to the age of the unborn child.
If the results obtained correspond to the established “norm,” this means that the baby’s development is proceeding normally, without deviations, that such development does not cause concern, and the BPD correlates with normal data. If the values do not correspond to the expected ones, you need to figure it out, taking into account several important factors.
How is the procedure for measuring fetal parameters carried out?
So, the patient, to obtain the results of the fetal developmental function, comes weekly to an ordinary ultrasound room, where the usual ultrasound examination is always carried out. This time everything goes exactly the same: the pregnant woman’s belly is smeared with a special gel to better advance the device’s sensor and the fetus is examined through the abdominal wall. In principle, the study can be carried out in another way: through the vagina. In this case, a condom must be put on the sensor.

During the examination, the attending physician or ultrasound specialist measures all indicators of diameter, circumference, length that interest him and compares the data obtained with established tables, which give the norm based on each week of development.
Standard figures BPR, LZR
What is the resulting value? Special tables always show the average normal values for the BPD (biparietal size) of the fetus, obtained by ultrasound during pregnancy, as well as all possible changes and deviations. Moreover, all values are given in so-called percentiles (the average figure, lower and upper limits of normal values are indicated).
Therefore, when studying the plate, you need to find the fiftieth percentile and assume that all other numbers mean the limits of the norm. For example, in the twelfth week of development, the norm for the BPR value is 21 mm, but the permissible deviations are in the corridor from 18 to 24 mm. That is, parents should not worry if the baby’s value is 19 or 22 mm. Perhaps this is due only to individual developmental characteristics. The table shows all the data on BPR and LZR of the fetus:
| Gestational age (by week) | BPR size (in mm) | ||
| 10 | 50 | 95 | |
| 11 | 13 | 17 | 21 |
| 12 | 18 | 21 | 24 |
| 13 | 20 | 24 | 28 |
| 14 | 23 | 27 | 31 |
| 15 | – | 31 | – |
| 16 | 31 | 34 | 37 |
| 17 | 34 | 38 | 42 |
| 18 | 37 | 42 | 47 |
| 19 | 41 | 45 | 49 |
| 20 | 43 | 48 | 53 |
| 21 | 46 | 51 | 56 |
| 22 | 48 | 54 | 60 |
| 23 | 52 | 58 | 64 |
| 24 | 55 | 61 | 67 |
| 25 | 58 | 64 | 70 |
| 26 | 61 | 67 | 73 |
| 27 | 64 | 70 | 76 |
| 28 | 67 | 73 | 79 |
| 29 | 70 | 76 | 82 |
| 30 | 71 | 78 | 85 |
| 31 | 73 | 80 | 87 |
| 32 | 75 | 82 | 89 |
| 33 | 77 | 84 | 91 |
| 34 | 79 | 86 | 93 |
| 35 | 81 | 88 | 95 |
| 36 | 83 | 90 | 97 |
| 37 | 85 | 92 | 98 |
| 38 | 86 | 94 | 100 |
| 39 | 88 | 95 | 102 |
| 40 | 89 | 96 | 103 |
| Gestational age (by week) | LZR (in mm) |
| 10 | |
| 11 | – |
| 12 | – |
| 13 | – |
| 14 | – |
| 15 | – |
| 16 | 41 |
| 17 | 46 |
| 18 | 49 |
| 19 | 53 |
| 20 | 56 |
| 21 | 60 |
| 22 | 64 |
| 23 | 67 |
| 24 | 71 |
| 25 | 73 |
| 26 | 77 |
| 27 | 80 |
| 28 | 83 |
| 29 | 86 |
| 30 | 89 |
| 31 | 93 |
| 32 | 95 |
| 33 | 98 |
| 34 | 101 |
| 35 | 103 |
| 36 | 104 |
| 37 | 106 |
| 38 | 108 |
| 39 | 109 |
| 40 | 110 |
Why is this research so important?
So, why is it so important to conduct such an examination and find out the parameters described above, what is it? The fact is that ultrasound gives results of BDP, but with other meanings it makes it possible to identify delays and deviations in the child’s development, for example, hydrocephalus or a large fetus.
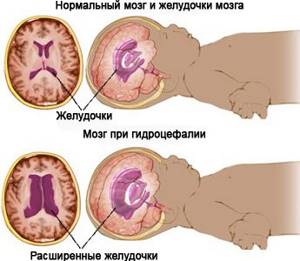
fetal hydrocephalus
But you cannot rely on the data obtained in isolation from other data: it is necessary to measure the whole child. If the whole body (chest, tummy, head) increases at the same pace, then the doctor expects a large fetus. But if only LZR and BPR increase, then the specialist will diagnose hydrocephalus, a disease caused by intrauterine infection.
If the sizes of the BPR and LZR obtained on ultrasound are smaller than normal (and other parts of the body do not decrease), the doctor diagnoses microcephaly. In cases where the data obtained, together with the rest of the fetal size, is less than normal, developmental delay may be diagnosed.
If the problems are not too serious, the woman will be prescribed certain treatment that eliminates the causes of the pathology. It includes measures aimed at increasing utero-placental blood flow, oxygen supply, nutrients necessary for the child, and taking certain medications, including antibiotics.
If the study reveals a deviation from normal data:
In cases where the indicators obtained during the study do not correspond to normal limits, the doctor takes the following steps: he evaluates all other parameters of the unborn child. Perhaps the fetus is simply growing spasmodically, and after a few weeks all the values will straighten out and level out. If the deviations are significant, it’s time to sound the alarm and look for serious problems.
- An increased BPR value indicates tumors of the brain, as well as cranial bones, cerebral hernia or hydrocephalus. If the latter is diagnosed, the woman will simply undergo the necessary treatment, including taking antibiotics. In all other cases, the pregnancy will be terminated.
- A decent deviation in a smaller direction indicates underdevelopment of the brain, the absence of the cerebellum, and even the cerebral hemispheres. The pregnancy will also have to be terminated.
- A reduced value may also indicate a simple developmental delay. The woman will undergo the necessary treatment and keep the child.
Further diagnostics
During diagnostics, it is necessary to take into account a number of third-party factors.
- Reduced values may be due to hereditary characteristics if the mother and father are themselves short. The same applies to cases when all indicators fit into the norm except, for example, the length of the femurs. Perhaps the relatives have a similar structure, and the baby simply inherited this trait.
- The child grows in leaps and bounds. In a couple of weeks, all values will increase and may well correspond to “healthy” numbers.
The alarm should be raised if, not for the first time, the doctor notices that the results obtained are two lines behind or exceed the norm and do not meet the deadline.
If this happens, the woman is necessarily sent for CHT, Doppler ultrasound, and the dynamics of the development of the fetus is monitored. All delays and pathologies are diagnosed not only by an obstetrician-gynecologist, but also by a geneticist, so further examinations include a trip to this specialist.
Ultrasound for pregnant women
This is the only way to determine the baby’s hereditary predispositions, the causes of problems (these may include not only intrauterine infection, but also the age of one of the parents, various bad habits, the mother or father’s work in hazardous enterprises, chromosomal abnormalities and other factors).
Conclusion
Having received the survey data, you should not understand it yourself and be horrified in advance. The doctor conducting the examination only writes down all the results, and the obstetrician-gynecologist deciphers everything and tells the patients about the situation.
The examination procedure itself is completely painless and does not cause negative emotions in the woman; she calmly finds out what such a study gives her. The obtained result of fetal developmental fetal function on ultrasound gives the opportunity to learn about the condition of the child, the level of its development, the presence of pathologies and diseases long before birth.
Ultrasound of BDP: indicators are less than normal
Ultrasound of BDP: indicators are less than normal - what to do? If the biparietal size is too low, it is necessary to determine the reasons that caused these changes.
Such values indicate underdevelopment of the brain, possibly the absence of some parts of the brain, which requires resolving the issue of immediate termination of pregnancy for medical reasons. The following conditions lead to a decrease in the BPR indicator:
- Intoxication of the mother's body. Smoking and alcohol abuse lead to chronic intoxication. Bad habits that can cause deviations from the normal size of the fetal skull.
- Lack of rational and balanced nutrition. Lack of vitamins and important elements contributes to delayed intrauterine development of the child.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Infectious diseases. The presence of infection in the mother during pregnancy increases the risk of developing pathology in the child.
A decrease in all indicators of fetal development is possible. This further helps to establish developmental delay. There are three degrees
Other fetometry indicators and their meaning
In the 1st trimester of pregnancy it is impossible to measure many parameters that are determined in later stages of pregnancy. When assessing early fetal development, the following indicators are considered:
- Diameter of the fertilized egg. The greatest diagnostic value is before 12 weeks of pregnancy, when it is difficult to determine the size of the fetus. The membrane grows quickly, so using measurements you can find out the age of the embryo with an accuracy of several days. This characteristic allows you to determine how successfully the embryo develops. If there is no growth of the fertilized egg within 2-3 weeks, a frozen pregnancy is suspected.
- Coccyx-parietal size. This is the distance from the pelvic end of the embryo to the crown. The indicator allows us to identify how the embryo grows in the early stages, since during this period its full growth cannot be determined due to the underdevelopment of the limbs.
- The thickness of the nuchal translucency is an important indicator of the first screening of pregnant women. It indicates the size of the fold at the back of the neck. TVP makes it possible to identify child developmental defects caused by genetic abnormalities.
- The length of the nasal bone is also a mandatory parameter for the first screening. If the DN does not meet the norms, the child is suspected of having chromosomal abnormalities.
At the second and third screening, the studied indicators make it possible to identify malformations of the child that cannot be determined in the early stages, or to refute or confirm previously identified deviations. Starting from 15 weeks of pregnancy, the following parameters become important:
- Interhemispheric distance of the cerebellum. Indicates the dynamics of the formation of various parts of the brain. MRM is given special attention when identifying an increased risk of pathologies of the nervous system.
- Abdominal circumference. Allows you to track the formation of the child’s internal organs. OB is an important indicator in the diagnosis of intrauterine growth restriction.
- Weight. Indicates the dynamics of fetal development, allows one to suspect a developmental delay, evaluate the functioning of the placenta, and clarify the tactics of labor management.
- Length of the femur. This parameter helps to establish the gestational age if difficulties arise in identifying bipolar disorder. It may also indicate a risk of developing skeletal dysplasia.
- The lengths of the humerus and forearm bones are measured to track the rate at which the baby's skeleton is developing. They also allow you to calculate the approximate height of the child.
- Head circumference. OG is measured to assess the development of the brain and cranium. In late gestation, determining the fetal head circumference helps determine the preferred mode of delivery.
It should be borne in mind that fetal fetometry indicators are considered in aggregate. Deviation from the standards of one of them does not mean that the baby is behind in development. Only a specialist can give a correct assessment of the results. In many cases, a repeat ultrasound reveals that the indicators correspond to normal values.
Ultrasound of BDP: indicators are higher than normal
In the case when the value of the biparietal size exceeds the age norm, it is necessary to determine other indicators of the development of the fetal skull. These include abdominal circumference, thigh length, and shoulder length. A large fruit is defined when all of the above indicators are significantly exceeded. If indicators, except for BPD, are normal, then we can assume that the embryo is developing spasmodically. Over time, all other indicators will level out. Excessively elevated biparietal size values require immediate diagnosis. Tumor formations of the skull or brain, hydrocephalus, and brain hernias lead to similar values. Some of these diseases require immediate termination of pregnancy.
Prevention of changes in biparietal size
In order to minimize the risk of changes in ultrasound indicators of the size of the fetal head, it is necessary to prepare for pregnancy in advance. The following recommendations must be followed:
- Rejection of bad habits. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption will increase the chance of normal fetal development.
- Adhere to a balanced and rational diet. Dishes enriched with vitamins, micro and macroelements contribute to the proper formation of the child.
- Timely detection of chronic diseases. Pregnancy can aggravate many conditions. Given this, the expectant mother needs to pay attention to her health in advance.
- Vitamin therapy. This type of prevention applies to both mother and father. Healthy parents are able to conceive and bear a healthy child.
The above recommendations will help the correct formation of the unborn child. It is important to carry out ultrasound screening in a timely manner to monitor developmental abnormalities. Timely diagnosis will allow the doctor to take measures to eliminate the violations.