Ask your question to our specialist by phone or write to us! to get a consultation
During the first study, it is determined where the fetus is located, thus excluding the ectopic location of the ovum. Already from the first study, the fetal heartbeat can be determined.
The first screening study determines the thickness of the collar zone. An increase in the size of the collar zone is a reason for genetic consultation, as it is a marker of congenital malformations of the fetus.
In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, ultrasound examinations may reveal signs of fetal infection, including changes in the structure of the brain.
In the third trimester, the structures of the fetal lungs are assessed; this is necessary to determine the degree of maturity of the lungs if premature birth is suspected or necessary. The structure of the lungs is also studied to exclude intrauterine pneumonia.
All internal organs of the fetus (heart, intestines, liver, etc.) are carefully studied. During the examination, especially during the second trimester of pregnancy, the facial structures of the fetus can be examined to diagnose malformations such as cleft palate and cleft lip. It is also possible to diagnose the pathology of tooth formation.
Most expectant parents are interested in the question of whether Down syndrome can be detected using ultrasound. I would like to note that it is very difficult to make this diagnosis based on ultrasound data.
In most cases, an ultrasound examination performed after 12 weeks can determine the sex of the baby.
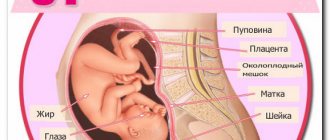
Placenta
The placenta is finally formed by 16 weeks of pregnancy. Before this period, they talk about the chorion - the predecessor of the placenta. The chorion is the outer shell of the embryo, which performs protective and nutritional functions. During an ultrasound examination, the placenta is attached - on which wall of the uterus the chorion or placenta is located, how far the placenta is from the internal os of the cervix - the place of exit from the uterine cavity. In the third trimester of pregnancy, the distance from the placenta to the internal os of the cervix should be more than 6 cm, otherwise they speak of low placental attachment, and if the placenta covers the internal os, placenta previa. This condition is fraught with complications - bleeding during childbirth. Low attachment of the placenta is also noted during ultrasound examinations performed in the first and second trimesters, but until the third trimester the placenta can migrate, that is, rise up the wall of the uterus.
During ultrasound examinations, the structure of the placenta is also assessed. There are four degrees of its maturity. Each degree corresponds to certain stages of pregnancy: the 2nd degree of maturity should last up to 32 weeks, the 3rd degree - up to 36 weeks. If the placenta changes structure ahead of schedule, they speak of premature aging of the placenta. This condition may be associated with impaired blood flow in the placenta caused by gestosis (a complication of pregnancy, manifested by increased blood pressure, the appearance of protein in the urine, edema), anemia (decreased hemoglobin amount), or may be an individual feature of the body of a given pregnant woman. Premature aging of the placenta is a reason for conducting Doppler ultrasound and cardiac monitoring studies.
During an ultrasound examination, the thickness of the placenta is determined. Normally, up to 36 weeks of pregnancy, the thickness of the placenta is equal to the gestational age +/- 2 mm. From 36-37 weeks, the thickness of the placenta ranges from 26 to 45 mm, depending on individual characteristics.
According to an ultrasound examination, it is possible to confirm the assumption of placental abruption, the cause of which is bloody discharge from the genital tract at any stage of pregnancy. Areas of detachment are visible on the screen.
Doppler measurements and the purposes of its implementation
Doppler ultrasound is a type of ultrasound and is performed to assess the blood circulation of the fetus and its blood supply to the mother's uterine and umbilical vessels. Violation of this connection provokes hypoxia in the child and the development of gestosis in the woman - late toxicosis, which has a negative impact on the functioning of internal organs and is the cause of maternal mortality.
Degrees of deviations in intrauterine circulation:
- First degree. It is divided into 2 types: A and B. In the first case, a violation of the uteroplacental blood flow is diagnosed, in the second - a violation of the fetal-placental blood flow. This deterioration is most often temporary, so the doctor will order an additional examination after a few weeks to assess the dynamics.
- Second degree. The disruption affects both bloodstreams, causing the fetus to constantly experience hypoxia. In this case, hospitalization of the patient and regular monitoring of changes in intrauterine circulation are required.
- Third degree. A critical circulatory disorder, most often associated with premature abruption or aging of the placenta. Requires immediate delivery.
Ultrasound is a mandatory procedure at the 32nd week of pregnancy, allowing you to assess the condition of the fetus and the readiness of the expectant mother for childbirth. If fetal hypoxia is suspected, the doctor prescribes Doppler ultrasound to study intrauterine circulation. Based on the results of these procedures, a decision is made on the need for hospitalization and the method of delivery.
Uterus
During an ultrasound examination, the size of the uterus is measured, the walls of the uterus are examined for the presence or absence of myomatous nodes, and for increased tone of the muscle wall. The thickness of the uterine walls is also measured.
The length of the cervix normally during pregnancy should be 4-4.5 cm. Shortening of the cervix - in a primigravida up to 3 cm, and in a multigravida - up to 2 cm, the opening of the uterine pharynx allows a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, in which the cervix begins to open already at 16-18 weeks, unable to hold the developing pregnancy.
With a transvaginal examination, it is possible to establish the gestational age starting from 2-3 weeks, calculating the expected date of birth, fetal biometry, and assessing: weight and size of the fetus, presentation, appearance and position, starting from 12-14 weeks it is possible to determine the sex of the fetus (if the position is favorable for research). A study of the organs and systems of the fetus is carried out for the purpose of early diagnosis of developmental defects, the amount of amniotic fluid, the position and degree of maturity of the placenta is also assessed, and its pathology can be identified. Ultrasound can also reveal:
- umbilical cord pathology,
- multiple pregnancy,
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency,
- presence (absence) of pathology in the postpartum period.
The first screening (11 - 14 weeks, optimally 12-13 weeks) is done to determine the characteristics and presence of a fertilized egg. When it is found, cardiac activity, movements and the degree of its development are analyzed (whether it corresponds to the timing of pregnancy). During the first screening, the following may be detected: non-developing and ectopic pregnancy, problems with the chorion, inadequate development of the embryo (signs of Down syndrome, anencephaly, neck hygroma). Ultrasound also detects abnormal conditions of the uterus. Therefore, early fetal ultrasound is extremely useful for identifying pathologies at the initial stage.
The second screening is carried out at 18 - 21 weeks (optimally 20 - 21 weeks). At this stage, all the insides of the embryo, in terms of development, are very close to the final state and it is possible to assess whether they are developing correctly. Of course, ultrasound cannot detect all anomalies, but the vast majority can still be detected. If a pathology is found, then a prognosis is given for its development during the remaining weeks of pregnancy. The second screening is necessarily complemented by fetal Dopplerography and assessment of uterine blood flow, for the detection and timely treatment of chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
The third screening is carried out at 30 - 34 weeks (optimally 32 - 33 weeks). The main goal is to assess the internal structure of the fetus to identify the development of malnutrition and its delayed somatic development. If intrauterine malnutrition of the embryo is not detected, this can cause psychosomatic and intellectual delay in the development of the child after birth. At the moment, diagnosis allows for timely treatment and elimination of possible complications. During this screening, Dopplerography of the uterine arteries and fetus is also mandatory, and the placental blood flow is analyzed.
Ultrasound during pregnancy (non-screening periods) - the study is performed in addition to screening studies (does not replace screening studies) if indicated, or at the request of the patient. It is carried out at any stage of pregnancy.
Ultrasound during pregnancy is a study of the condition of the fetus using special ultrasound equipment. On the screen of the ultrasound machine, the specialist sees how your baby is located in the uterus, how much its development corresponds to the period of pregnancy, and judges the state of health of the unborn child using special indicators. Modern ultrasound during pregnancy allows you not only to see your baby, but even to photograph it as a souvenir.
Ultrasound diagnostics is highly informative in assessing the development of the fetus and is harmless to the mother and child. Intrauterine development of the fetus is a dynamic process, therefore ultrasounds during pregnancy are carried out at a time that provides maximum information about the anatomy of the fetus. During pregnancy, 3 mandatory ultrasound examinations are performed. In the early stages (up to 12 weeks), ultrasound diagnostics are carried out according to the following indications:
- diagnosis of the fact of pregnancy in case of infertility, spontaneous miscarriages in the anamnesis;
- clarification of the deadline;
- presence of signs of a threat of miscarriage (pain, bleeding);
- space-occupying formations of the uterus and ovaries.
The first screening test is carried out at 12-14 weeks. During these periods, the correspondence of the size of the fetus to the gestational age is assessed, and signs of chromosomal pathology in the fetus are identified. Ultrasound during pregnancy allows you to study the anatomy of the fetus: the structure of the brain, the presence of a stomach, and a bladder. The fetal heart rate is assessed. The localization of the chorion, the structural features of the uterus and the presence of ovarian pathology are determined.
Ultrasound diagnostics in the first trimester plays an important role in the early diagnosis of congenital pathology, identifying signs of chromosomal abnormalities (expansion of TVP), in identifying the pathological course of pregnancy and its timely correction. If there is an enlarged nuchal translucency in the fetus, pregnant women are referred to a geneticist for a comprehensive examination and additional diagnostic methods.
The second screening examination is carried out at 22-24 weeks. The main purpose of ultrasound diagnostics is to identify fetal malformations and signs of chromosomal pathology; the development of all organs and systems of the fetus is assessed. In addition, fetal growth, the amount of amniotic fluid and the condition of the placenta are assessed. During this period, the sex of the fetus is determined.
The third screening study is carried out at 32-34 weeks. The anatomy of all organs and systems is assessed to identify possible anomalies, the position of the fetus and placenta, the amount of amniotic fluid, signs of delayed fetal development and fetoplacental insufficiency are determined.
Doppler is an assessment of blood flow in the uterine vessels and fetal vessels (umbilical cord artery). The main indications for Doppler testing are: diseases of the pregnant woman (hypertension, kidney pathology, vascular diseases), fetal growth retardation, changes in the amount of amniotic fluid, gestosis in the pregnant woman, signs of premature ripening of the placenta.
Three-dimensional echography (3D ultrasound) - obtaining a three-dimensional image of the fetus in real time. Used as an additional method when performing ultrasound during pregnancy during screening periods. The safety of the method has been tested many times by scientists around the world. Ultrasound diagnostics is recognized as a safe and reliable method of fetal imaging; the intensity and power of the ultrasound wave remains the same - the same as with conventional ultrasound diagnostics.
Three-dimensional echography has advantages in identifying malformations of the face and limbs. Three-dimensional echography allows you to more clearly see the unborn child: how it is positioned, how it moves, what emotions it experiences. From 26-28 weeks of pregnancy, using three-dimensional imaging in real time, we become eyewitnesses of all behavioral reactions of the fetus. You can clearly see lip movements, tongue protruding, chewing movements, and wide opening of the mouth. During an ultrasound during pregnancy, parents can see their child's first smile, and a photograph of the unborn child can be taken. With the help of ultrasound diagnostics, you can look into that area that is hidden from people’s eyes; this provides emotional support for the development of pregnancy. When undergoing a three-dimensional ultrasound during pregnancy, it is necessary to take into account that the examination time may be slightly longer than with a standard two-dimensional one. The quality of the resulting image when using three-dimensional ultrasound diagnostics depends on the position of the fetal body, the location of its limbs, the umbilical cord and the placenta. Difficulties in obtaining volumetric images may be due to a small amount of amniotic fluid, even in cases where their relatively small amount is not yet pathological (oligohydramnios). Significant problems in the quality of the picture usually arise if the pregnant woman is overweight or if she has scars on the anterior abdominal wall after abdominal surgery. The success of three-dimensional ultrasound during pregnancy (obtaining high-quality images of the fetus) often depends on motor activity - the more active the fetus, the greater the chance of seeing more interesting pictures of intrauterine life.
The third ultrasound during pregnancy is done almost before birth at 32-34 weeks. The doctor examines the baby’s organs again to rule out the possibility of pathologies and provide timely treatment if they are detected. At each ultrasound, the condition and maturity of the placenta is assessed. The results of an ultrasound examination also provide data on the amount of amniotic fluid.
During an ultrasound, the thickness of the walls of the uterus is determined. If the parameters do not coincide with the norm, then this indicates increased tone of the uterus. And if symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen or lower back are added to the increased tone, there may be a threat of miscarriage.
Fetal development
At this stage, the baby weighs on average 1.7 kg with a height of 42.4 cm. Usually he is already head down, but breech presentation of the fetus at 32 weeks is not a death sentence. There is still plenty of space and time for a coup. You can help this happen by swimming or doing some simple exercise. Lie on your back for 10-20 minutes with your hips raised. You can place a pillow under your buttocks. Breathe calmly, trying to lengthen your exhalation. In most cases, by 38 weeks the baby will be in the correct position in the womb.
Fetal movement at 32 weeks of pregnancy
The child’s nervous system is quite developed, and you probably already feel that a cycle of activity and rest has been established. For an hour he can actively move and push, and then suddenly calm down. Many pregnant women complain that the baby's waking hours coincide with their sleep. There is nothing surprising. Your rhythmic movements, for example, while walking, simply rock the baby. When you suddenly go to rest, the baby wakes up. Many newborns continue this habit in the first months of their life and sleep exclusively while moving.
Is ultrasound harmful during pregnancy?
At the moment, ultrasound is one of the safest research methods in medicine and in obstetrics in particular. However, ultrasound is a relatively new method of diagnosing pregnancy and monitoring pregnancy (it has been widely used for about 40 years). The negative effect of ultrasound on the fetus has not yet been sufficiently studied; there is no long-term statistical observation base.
Doctors recommend three scheduled ultrasound examinations during a normal pregnancy. It makes sense to do additional ultrasounds only if the doctor suspects any pregnancy complications.
Remember! Ultrasound should not be abused on one’s own initiative, for example, in order to see how the child is developing there. Leave your entertaining experiments for other occasions! The purpose of ultrasound is to preserve the health of the mother and the birth of a healthy child. All other reasons are not worth risking the proper development of the unborn child.
What to discuss with your doctor
- If you cannot cope with increased anxiety during this period of pregnancy on your own, consult a perinatal psychologist. He will help you analyze and accept your emotions and, if necessary, prescribe therapy. You can find such a specialist in many maternity hospitals and antenatal clinics. Admission here is free.
- If your stomach often pulls, the pain is probably associated with stretching of the tissues of the growing uterus, as well as with the gradual divergence of the pelvic bones. However, expert supervision will not hurt. Find out how to distinguish physiological discomfort from pathological uterine tone or other pathologies.
3D ultrasound during pregnancy
Let’s make a reservation right away: in the vast majority of cases, three scheduled 2D ultrasounds are sufficient to diagnose and monitor a pregnancy.
3D and 4D ultrasound - three-dimensional and four-dimensional ultrasound examinations are prescribed for medical reasons extremely rarely and are mainly the whim of the baby’s future parents. Of course, all parents want to see their baby before birth and capture ultrasound data in photos and videos, but this issue must be approached not only from the point of view of curiosity. “3D ultrasound” as a diagnostic method can only be used for special indications as prescribed by a doctor and is not recommended for standard examination during pregnancy, and even more so for obtaining images of the fetus without medical indications (for the sake of curiosity).
Remember! Any examination during pregnancy is necessary to ensure the normal course of pregnancy, without any complications. In this sense, additional irradiation of the fetus during 3D ultrasound is undesirable.
The best prevention of edema is the right lifestyle
Swelling at 32 weeks of pregnancy occurs quite often. If the swelling is minor and goes away on its own, there is nothing to worry about. But if more than 3 days have passed, and your blood pressure has risen or you have noticeably gained weight, immediately consult a doctor to rule out preeclampsia, a life-threatening condition for the baby.
To prevent swelling, it is important to eat right. Reduce your intake of fats, salt and sugar, which contribute to fluid stagnation in the body. But remember to eat at least 5 servings of fruits and vegetables a day. Monitor your weight gain week by week: This is another effective tool for preventing swelling.
Don't forget about physical activity. Even a five-minute walk in the park will help prevent swelling. And don’t be afraid to drink more fluid, no matter how paradoxical it may sound. By preventing dehydration, you eliminate excess salt and the need to store water.
Conclusion
Ultrasound diagnostics is an integral part of modern obstetrics and gynecology. Ultrasound during pregnancy has good reviews from both doctors and parents. Thanks to her, it became possible to prevent very serious and life-threatening diseases for the child and mother. And this is not some local data - this is information from all over the world and it’s hard to imagine how many parents and their children this method has helped.
However, it is worth understanding that you cannot limit yourself to ultrasound alone. It is also worth using other diagnostic methods, both instrumental and laboratory. Also, you cannot do without consulting a doctor, since without a correct assessment, the cost of this study is too low.
Fetometry results – a verdict or a hint for action?
It should be noted that the intrauterine development of a child is individual and somewhat undulating. Therefore, only an obstetrician-gynecologist in charge of pregnancy can make a reliable interpretation of the ultrasound results. Of course, the data obtained from each examination correlates with the parameters in the table above. However, they are not called average for nothing. A factor such as genetic predisposition also plays an important role in the development of a child.
For example, if the parents are short in stature, there is some discrepancy between all the actual parameters of the baby, i.e. their decrease in what is considered normal is quite expected. But if the difference turns out to be only 1-2 parameters and it is significant or the parameters differ from the norm - behind/ahead - by more than 2 weeks or 2 lines in the table, this will become a reason to find out the reasons for this phenomenon and prescribe additional diagnostics .
It is thanks to fetometry that a gynecologist, together with a geneticist, can diagnose such serious diseases as hydrocephalus (a disorder of brain development), malnutrition (discrepancy between the weight of the fetus and its length, caused by nutritional deficiency), intrauterine growth retardation, etc. at an early stage of the baby’s development.
In such cases, the development of an individual pregnancy management program, which necessarily includes emergency therapeutic measures and adjustments to the pregnant woman’s lifestyle, almost always gives positive results, and a healthy baby is born.
So, fetometry is a great way to get to know your baby before his birth and make sure that his development, as well as the course of the entire pregnancy, proceeds without complications.
CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Average fetometric indicators at 32 weeks of gestation:
- weight – 1800-1950 g;
- height – 42-43 cm;
- head circumference – 283-325 mm;
- abdominal circumference – 258-314 mm;
- biparietal head size – 78-89 mm;
- humerus length – 52-60 mm;
- length of the femur – 56-66 mm.
Don’t worry if there is a slight deviation - it all depends on heredity; miniature parents may well have a healthy child with a little less height and weight. It’s also the other way around - if both parents have impressive dimensions, a slightly larger baby is the norm for them.