Indications for prostate biopsy (prostate gland)
- Induration on digital rectal examination;
- Persistent increase in serum PSA (prostate-specific antigen).
- Prostate-specific antigen is a protein that is secreted exclusively by epithelial cells of the prostate. Conditions that can affect PSA levels include: prostate cancer (PCa), benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), chronic prostatitis, trauma, digital rectal examination, and taking 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. Therefore, for correct diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account all possible factors influencing changes in PSA levels.
PSA norms: 40-50 years - from 0 to 2.5 ng/ml, 50-60 years - up to 3.5 ng/ml, 60-70 years - up to 4.5 ng/ml, 70-80 years - up to 6.5 ng/ml. With a PSA level of 2.5–10.0 ng/ml, 75 percent of patients are diagnosed with benign prostate diseases; with a PSA level above 10 ng/ml, prostate cancer is most likely.
- Decrease in the ratio of total and free PSA, increase in PSA density (ratio of PSA to prostate volume);
- Increased level of PSA 3 in urine. This marker is the most specific. It is recommended for use in patients with persistently elevated PSA levels and a negative biopsy.
- Detection of suspicious lesions by transrectal ultrasound (TRUS), MRI.
What information does the examination of biopsy material provide?
The transcript is usually ready in 10 days.
In prostate cancer, the degree of development of tumor cells is revealed:
- If the value of the indicator is in the range of 2-4, then a low risk of tumor spread is diagnosed, because the cells differ slightly from normal;
- Values 5-7 correspond to an average risk of developing cancer;
- Values from 8 to 10 indicate a high degree of risk.
If a man's relatives have had prostate cancer, you should donate blood for PSA and consult a urologist every year, starting at the age of 45.
It is important to save the results of the examinations in order to observe changes in the PSA value, and if it increases, conduct additional studies.
Preparing for a prostate (prostate) biopsy
- discontinuation of antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants at least 3-5 days before the procedure to avoid the risk of bleeding;
- prescription of antibiotics (ciprofloxacin 500 mg 2 hours before the procedure and for 3 days after) to prevent infectious complications;
- cleansing enema;
- use of local anesthesia;
In the vast majority of cases, this procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, does not cause severe discomfort, takes only 20-30 minutes, after which, after 2-3 hours, the patient can go home on his own.
The diagnostic value of a prostate biopsy depends on two main factors: the correctness of tissue sampling by the urologist and the qualifications of the pathomorphologists who give the final conclusion.
Carrying out the procedure
There are several methods for carrying out the procedure:
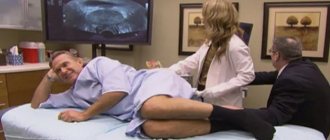
- Transrectal ultrasound biopsy. Half an hour before the procedure, the patient is given an enema. An anesthetic injection is first given to the intestinal area.
- The man lies on his side with his knees bent or sits in a special chair to provide the doctor with easy access. The progress of the procedure is monitored using transrectal ultrasound. The probe is inserted into the rectum. A special spring needle inside the probe takes from 6 to 14 tissue samples from different places in the prostate gland. The entire procedure takes approximately 30 minutes. For some time after it, the patient is under the supervision of a doctor.
- Transurethral prostate biopsy. It proceeds as follows: the patient lies on his back, spreading his legs and placing them on special stands. The tissue is taken using a special device - a cystoscope - a flexible probe with a light bulb and a video camera, at the end of which there is a cutting loop. The cystoscope is inserted into the opening in the penis and guided through the urethra to the prostate gland, where a biopsy sample is taken. It is performed under general, local or spinal anesthesia. The duration of the procedure is 30-45 minutes.
- Transperineal prostate biopsy (through the perineum). Biopsy in this way is performed less frequently than the previous ones. Local or general anesthesia is used.
The patient's position is on the back or side with the knees pulled up to the stomach. The doctor makes a small incision in the skin in the perineal area and inserts a thin needle through it, which, turning in the tissue of the gland, takes its samples. Tissue is needed from different parts of the organ, which is why the needle is inserted repeatedly. The prostate is then pressed to stop bleeding. The procedure takes 15-30 minutes. Sutures are usually not required. The patient spends about a day in a medical facility.
The cost of a prostate biopsy depends on the complexity, type of anesthesia and location of the procedure. For example, a transrectal biopsy will cost less than a transperineal biopsy. Prices in different cities of Russia can vary significantly.
How is a prostate biopsy performed?
Transrectal prostate biopsy
In modern clinics, prostate biopsy is performed under the control of a transrectal ultrasound sensor and using thin biopsy needles loaded into special guns. In accordance with modern standards, a 12-point biopsy is performed (at least 12 columns of tissue 15-20 mm long, that is, 12 “shots”).
The use of modern equipment and materials makes performing a biopsy as informative and painless as possible. Today, finger biopsy of the prostate is categorically unacceptable; mandatory ultrasound control is required. There are also perineal and transurethral techniques, but they are performed quite rarely, solely according to doctor’s indications.
A repeat biopsy is indicated if the results of the primary biopsy are negative and there are still indications for the study. Repeat biopsy detects prostate cancer in 20 percent of men in the absence of tumor in the initial histological examination. Done in 3-12 months.
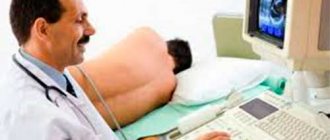
Ultrasound image of the prostate during a biopsy
During the manipulation, the specialist sees a 5-7 times enlarged image of a section of the prostate gland on the ultrasound machine screen. Through a special working channel in the rectal ultrasound sensor, precision “shots” are performed in the required areas of the prostate using a biopsy gun.
Scheme of transrectal prostate biopsy
Saturation biopsy.
The incidence of PCa detected by repeat saturation biopsy (>20 cores) varies from 30 to 43 percent and depends on the number of tissue cores. In special cases, saturation biopsy can be performed transperineally. This makes it possible to diagnose prostate cancer in an additional 38 percent of cases. It should be noted that 10 percent of patients develop acute urinary retention after this study.
Contraindications
Prostate biopsy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- acute inflammation of prostate tissue;
- bleeding disorders (hemophilia, coagulopathy);
- recent abdominal-perineal rectal extirpation (removal of the rectum from the abdominal cavity and perineum);
- severe hemorrhoids;
- acute infectious diseases;
- significant anal stricture (narrowing of the anal canal);
- acute inflammation of the anal isthmus and rectal tissue;
- the patient's serious health condition;
- constant use of antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants.
After the biopsy
- Possible discomfort in the anorectal area;
- In 70 percent of cases, patients complain of the appearance of blood in the urine (hematuria) - disappears within 5 days, 35 percent - in semen (hemotospermia) - can be present for up to 2 months, 1 percent - rectal bleeding (disappears after 2-3 days) .
- Urinary retention occurs in 1-2 percent of cases and, as a rule, goes away on its own;
Recommendations
- It is recommended to spend the first day after the procedure at home
- Limit sports activities in the first two weeks, start heavy physical activity no earlier than after 1 month
- Having sex is allowed after 7-10 days
- Drink plenty of fluids for a week after the procedure (1.5-2.5 liters per day).
- For several weeks, eliminate alcohol, spicy food, coffee,
- Reduce your intake of fiber-rich foods to prevent constipation.
The importance of a prostate biopsy can hardly be overestimated - all further diagnostic and treatment tactics depend on its results. The use of modern equipment and materials makes performing a biopsy as informative and painless as possible.
The degree of pain of the procedure
During the test, the patient feels a slight prick and slight discomfort when the biopsy needle is inserted. When using the transrectal technique, pressure is felt during insertion of the ultrasound probe. The insertion of the needle may be accompanied by slight pain.
When the analysis is completed, the patient should not physically work for several hours.
The patient may feel slight pain in the pelvic area, there is often blood in the urine after the procedure, and the semen changes color. All changes usually take place within a month.
If the biopsy is taken transrectally, the rectum may bleed.
In cases where general anesthesia is used, the patient remains in the hospital for several hours after the end of the analysis, and the feeling of fatigue will be observed all day.
Both prostate adenoma and cancer often present with the following symptoms:
- Problems arising during urination (tension of the abdominal muscles may also be required);
- Increased urge to urinate, especially at night;
- Noticeable weakening of the urine stream, interruptions, drip leakage of urine;
- The feeling of fullness does not disappear even after emptying the bladder;
- Hematuria (significant blood in the urine). In 20% of cases this means the development of a malignant tumor (prostate cancer). But if hematuria is detected, the kidneys and bladder should always be examined as well.
Questions about the article
.Sergey Mikhalev
April 29, 2021 at 08:40
Hello. I am 35 years old. a couple of weeks ago, discomfort appeared when urinating. The TAM contained bacteria, leukocytes, hemoglobin, platelets and mucus. Prescribed antibiotics Manural as prescribed by the doctor, and everything went away. The discomfort and pain went away, and then they sent me for a PSA test. According to the results of the analysis, Psa total - 5.02, PSA total/psa free - 9.96, PSA Free - 0.5. Does this mean that I have cancer, and what procedures need to be completed to confirm or exclude this diagnosis?
Anton Evgenievich Rotov
April 29, 2021 at 05:38 pm
The increase in PSA in your case is most likely due to inflammation in the prostate - prostatitis. Just retake the test 2-3 weeks after the inflammation has subsided
Ruslan, 41 years old
December 14, 2021 at 04:26 pm
Hello, Doctor! Several years ago, 10 years ago, I was treated for chronic prostatitis. In 2021, I took PSA tests. Total PSA = 0.335 ng/ml, free PSA = 0.130 ng/ml, Free PSA/total PSA ratio = 38.81% I recently took PSA tests. Total PSA = 0.349 ng/ml, free PSA = 0.080 ng/ml, free PSA/total PSA ratio = 22.92%. The reference values of the laboratory service indicate that the norm is from 25% to 100%. Please tell me if there is any cause for concern? Thank you.
Anton Evgenievich Rotov
December 16, 2021 at 04:55 pm
Everything is fine, there is no reason to worry
Altats
September 4, 2021 at 09:55 pm
Hello!!! My father had an operation, but the dog’s level after the test shows 1.6. Is this result normal or what? He takes medications and hormones prescribed by his doctor regularly.
THIS is normal
Anton Evgenievich Rotov
September 4, 2021 at 10:08 pm
It depends on what kind of operation we are talking about. If we talk about radical prostatectomy, then this is too much. It is better to discuss this with an oncologist (if the diagnosis is oncological)
How do you prepare for the procedure?
All recommendations for preparing for a prostate biopsy are announced to the patient by a doctor at the Central Clinical Hospital. In some cases, at the preparatory stage, the patient needs to take antibiotics for prophylactic purposes.
The analysis is carried out by a urologist from the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, using high-tech diagnostic equipment.
During the procedure, the patient is dressed in special clothing. The area of skin where the puncture will be performed is treated with an antiseptic composition, and the adjacent areas are covered with sterile cloth. The actions are carried out under ultrasound control.
Before the procedure, the doctor needs to know:
- What is blood clotting?
- Does the patient suffer from allergies and to what products?
- Does the patient take medications regularly, and what kind.
Diagnosis through the rectum requires preliminary cleansing of the rectum - the patient is given an enema. You will need to take a sedative about an hour before the test. The procedure is performed with a dropper.