When the expectant mother feels the movements of the fetus, it is wonderful: the pregnant woman knows that the baby is doing well. But it is impossible to assess the possible onset of intrauterine suffering in a child based on motor activity.
In order to detect and prevent problems in time, it is necessary to use ultrasound research methods (CTG, ultrasound and Doppler). Fetal cardiotocography (CTG) is a simple and accessible method for assessing a baby’s heartbeat, with which you can notice the initial signs of oxygen deficiency.
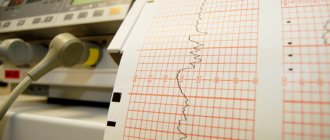
In addition, it is possible to identify changes in the muscle tone of a woman’s uterus, which can cause premature birth. CTG is a technique for recording uterine tone and heart rate on special calibration paper. That is, there are 2 graphs; some devices can record the child’s physical activity:
- heartbeats recorded by ultrasound
- uterine tone determined by a strain gauge
Is cardiotocography harmful to the fetus?
This is an absolutely safe procedure for both the fetus and the woman, does not cause discomfort and can be performed according to indications even daily (in case of fetal hypoxia), to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and make a decision on emergency delivery.
What the study shows
KTG allows you to monitor the condition of the fetal heart. It is important to understand that for a baby, “squeezing” through the birth canal during childbirth is not a pleasant journey, but a tedious job. During labor, the baby is exposed to certain dangers that can be recognized by observing its heart rate. A fetal heart rate that is too low may indicate, for example, hypoxia, and a rapid heart rate may be a signal of intrauterine infection.
Why is the assessment carried out?
The best period for carrying out the procedure is considered to be 30–32 obstetric weeks - this is due to the change in cycles of active movement of the child and calmness. Eg:
- active movements of the baby provoke the dominance of signals from the sympathetic system, which contributes to the acceleration of the heart rate;
- During sleep, impulses transmitted by the vagus nerve predominate, and the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle slows down.
These processes contribute to the formation of the so-called principle of antagonist unity - the main mechanism of the myocardial reflex. Its essence lies in the fact that the activity of the fetal heart muscle depends on its motor activity and ri. It is these factors that are taken into account to adequately assess the heart rate of the unborn baby and its intrauterine state.
With the help of one ultrasound examination, it is impossible to determine with high accuracy whether the child is receiving sufficient oxygen in the body, how he tolerates uterine contractions, and whether he can safely pass through the birth canal.
CTG is prescribed if:
- the expectant mother has a negative group Rh factor - in this case, the newborn baby may develop hemolytic disease;
- a pregnant woman has a history of chronic diseases, miscarriages or premature births, disorders of the functional activity of the endocrine glands;
- complications during pregnancy - severe toxicosis, elevated body temperature, post-term or multiple gestation;
- various anomalies of placenta formation and fetal development, previously identified by ultrasound;
- deviations in the baby's movements;
- a pregnant woman has alcohol, nicotine or drug addiction;
- complications after suffering from influenza or viral infection.
If the expectant mother is not worried about anything, a cardiotocographic study is performed once, and if deviations are detected, the procedure is repeated.
How long does a CTG take?
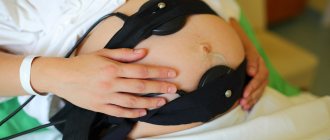
CTG is the most commonly used method for recording fetal heart rate. This is a non-invasive test and is not associated with pain or discomfort for the patient. The woman lies on her back, and doctors put two belts with electronic sensors on her stomach.
One of the sensors is an ultrasonic transducer that records the fetal heartbeat. The second sensor measures the strength and duration of uterine contractions. Both sensors are connected to a monitor on which these indicators are displayed in the current time and their dynamics are recorded. As a rule, CTG lasts half an hour; in some cases, the diagnostic procedure can be extended to an hour.
How is fetal CTG performed?
No special preparation is required to conduct CTG after thirty weeks. It is recommended to do the study during periods of greatest fetal activity, from nine in the morning to two in the afternoon, and from seven in the evening to midnight. It is not advisable to perform CTG on an empty stomach, as well as on a full stomach or immediately after the administration of glucose. The optimal time is an hour or an hour and a half after eating.
There are two different types of CTG during pregnancy - direct and indirect. Direct cardiotocography is rarely performed and only during childbirth when the integrity of the fetal bladder is damaged. It is done using a special spiral-shaped needle-shaped sensor, which is inserted into the presenting part of the fetus. Uterine tone is measured using a catheter that is inserted into the uterine cavity. Indirect fetal CTG is done through the anterior abdominal wall. Two sensors are used - one is attached in the place of best audibility of the heartbeat (the doctor determines it with a stethoscope before the examination), the other - in the right corner of the fundus of the uterus.
CTG is performed with the woman sitting or on her right side. It is not recommended to lay a pregnant woman on her back, as this may compress the main blood vessels and the CTG reading will be incorrect. The average procedure time is 40 minutes. If the fetus has a normal rhythm, CTG can be reduced to 15-20 minutes. During childbirth, the duration of the study should be at least twenty minutes, or five contractions.
The first ten minutes measure the basic rhythm, such a fetal CTG is called non-stress. It is supplemented by recording fetal movements (using a sensor or according to the pregnant woman). Then they move on to functional tests or stress CTG. The following tests are used to study the baby's heartbeat in the womb:
- Oxytocin test
- Mammary test
- Acoustic test
- Fetal palpation
- Reflex tests
The oxytocin test is carried out mainly before childbirth and in a hospital setting. With the help of oxytocin, contractions are provoked in a woman and CTG of the fetus is performed with increased contractions of the uterus; examination is rarely performed. The mammary test is essentially similar to the oxytocin test, but safer. The pregnant woman stimulates the nipples with her fingers, which causes increased uterine contractions. The test is contraindicated in case of increased tone and threat of premature birth. During an acoustic test, CTG records changes in the fetal heartbeat when exposed to a sound stimulus. During palpation of the fetus, its presenting part is slightly displaced. Reflex tests are rarely done. Functional tests that change the parameters of placental blood flow and the atropine test are no longer used.
CTG during pregnancy can be performed using different equipment. Previously, most clinics used devices that recorded heartbeats and uterine contractions on paper; the doctor did the decoding himself. This required high qualifications and experience of a specialist. Nowadays, equipment with computer decoding is increasingly used, this allows one to obtain more reliable results. There are also opportunities to conduct CTG weekly online. Special sensors are attached to the skin of the abdomen, the signal is transmitted via a smartphone to a computer monitor, where the doctor is able to monitor changes in the fetal cardiac activity.
Decoding the results
The child's heart rate should be 120-160 beats per minute.
- If the fetal heart rate is below 110 bpm (bradycardia), doctors may suspect progressive fetal hypoxia.
- If the heart rate is more than 160 beats, the fetus has tachycardia (which can be caused by an intrauterine infection).
Such data allows specialists to quickly respond to alarm signals.
It is important to understand that an abnormal fetal CTG is not always an indicator of a problem! A result within the normal range is always a good sign, but if there are any warning signs, the specialist must take other factors into account. Sometimes increased or decreased indicators of fetal cardiac activity can even be caused by the mother’s uncomfortable position during the examination or her excessive anxiety.
When is CTG performed?
CTG can be performed during pregnancy from 28-30 weeks, but the most informative study becomes after 32 weeks. If the mother and fetus are in normal condition, examinations in the third trimester are recommended to be done approximately once every ten days. When there are indications, it is done more often, once every 5-7 days, and if necessary, daily. Indications for unscheduled CTG are as follows:
- Mother's Rh negative
- History of miscarriage, miscarriage, stillbirth
- Decreased child activity according to the mother
- Fetal pathologies identified by ultrasound (developmental delay, placental blood flow disturbances, umbilical cord and fetal abnormalities, decreased number of movements, changes in amniotic fluid)
- Gestosis of the last trimester
- Placenta previa or malpresentation of the fetus
- Multiple births, oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios
- Post-term pregnancy
- Extragenital pathologies in women (diabetes mellitus and other endocrine diseases, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, anemia, infectious diseases with fever).
Scheduled CTG is performed closer to 32-34 weeks; unscheduled CTG for special indications can be done earlier, as early as 28 weeks, with subsequent regular repetitions. Since the technique is safe, the examination can be repeated almost daily; it will not harm either the mother or the child.
Features of CTG at 34 weeks of pregnancy
The purpose of diagnostics during this period is to identify changes in the functional state of the fetus - the appearance of anemia, hypoxia, fetoplacental insufficiency, oligohydramnios. If the result obtained shows their presence, this will allow the doctor to timely carry out the necessary treatment and preventive measures and choose the appropriate time and method of delivery.
A pregnant woman does not need to prepare specifically for this test. 10 hours before the diagnosis, it is forbidden to take sedatives and antispasmodics - they may affect the results of the examination. The expectant mother must be healthy - the presence of a viral infection may cause suspicion of fetal hypoxia.
CTG 9 points during pregnancy
The only condition during the procedure is a relaxed state and a comfortable position. Before starting it, you should empty your bladder; it is recommended to eat food 2 hours before.
The woman can take a semi-sitting or lying position on the couch on any side of the body. Special sensors are placed on the abdomen - one in the place where the baby’s heartbeat is most frequently felt, and the other, which records the tone of the uterus, is fixed in the area of its right corner.
If during the study the fetus is in the resting phase, the doctor allows the woman a small snack of sweet food (a piece of chocolate is enough) - this will activate the child. In order to obtain the most reliable data on the condition of the fetus, monitoring of its cardiac activity is carried out for at least 30 minutes. This duration is due to the frequent change of phases of wakefulness and rest.
Deciphering CTG at 34 weeks is important for assessing the well-being and health status of the baby - the average frequency of contractions of the heart muscle and the height of their deviations, uterine activity, acceleration and deceleration of heart rate are studied
There are no contraindications for cardiotocography - this procedure does not harm the mother’s health and is completely safe for the baby. The examination is absolutely painless, and in some ways even pleasant - the mother can hear her baby’s heartbeat for a whole half hour.
CTG in the third trimester of gestation is prescribed once every 7 days, but it can be performed even daily! This informative diagnostic technique allows you to identify the slightest threats to the life of the fetus. If deviations from normal values occur, additional examination and appropriate therapeutic and preventive measures are carried out.
What does a score of 9 mean?
The final data obtained during the study have great diagnostic value - they are necessary:
- to assess normal fetal development;
- identifying pathological processes in the cardiac, vascular and nervous systems;
- timely implementation of treatment and preventive measures to correct detected anomalies.
Practitioners recommend that expectant mothers undergo CTG 2 times - at the thirtieth obstetric week and after the 36th. Based on the results of two diagnostic studies, the doctor has a complete understanding of the child’s condition. A fetal condition score of 9 is considered normal. This examination result means that the unborn baby is developing and feels well, without deviations from the norm. There is no reason to worry about his health!
Indications for cardiotocography
In most cases, expectant mothers receive referrals for testing at the 32nd week of pregnancy. However, there are also devices that allow you to perform CTG from the 26th week. Indications for conducting a study in a antenatal clinic are the presence of the following risk factors for oxygen deficiency:
- a woman has a narrow pelvis;
- malposition;
- extragenital diseases in women (hypothyroidism, non-toxic and thyrotoxic goiter,
- arterial hypertension, congenital heart defects);
- multiple pregnancy;
- large fruit;
- polyhydramnios;
- recurrent miscarriage (miscarriages that occur 2 or more times in a row);
- uterine fibroids (benign tumor in the muscle layer of the organ);
- miscarriage of infectious origin;
- scar on the uterus;
- placental disorders;
- post-term pregnancy.
In a maternity hospital, indications for fetal CTG include delayed labor after rupture of the membranes, infections of the kidneys, bladder and genital tract, uterine rupture, childbirth complicated by a short umbilical cord, its prolapse or entanglement around the fetal neck. This list should also include premature placental abruption, antepartum hemorrhage with bleeding disorders, and primary (secondary) weakness of labor.
What does it mean to evaluate cardiotocography according to the Fisher system?
The results of the study are interpreted using the method of studying the final data on a ten-point scale and summing up the obtained parameters. Taking into account the total number of points, a qualified specialist who conducted a diagnostic examination assesses the condition of the unborn child and determines the presence of anomalies in its development. Let's take a closer look at the Fisher scale. The final CTG indicators are assessed in the range of 0–2 points.
Normal CTG readings
Basal rhythm indicators:
- less than 100 beats/min or more than 180 = 0;
- 101–121 and 159–179 =1;
- 119–160=2.
Rhythm amplitude:
- less than 3 beats/min = 0;
- 3-5 = 1;
- 6-24 = 2.
Change in heart rate over 60 seconds:
- less than 3 = 0;
- 3–5 = 1;
- more than 6 = 2.
An increase in fetal heart contractions in response to a contraction or clamping of the umbilical cord - acceleration:
- absence = 0;
- 1–4 = 1;
- more than 5 = 2.
Decrease in heart rate during uterine contraction or active movement - deleration:
- atypical = 0;
- lungs = 1;
- shallow = 2.
Diagnostic procedure technique
To perform CTG, a device with a specialized ultrasound sensor based on the Doppler effect is used. The device is fixed on the belly of a pregnant woman in the area where the baby’s heartbeat can be clearly heard.

To determine the attachment site for the cardiotocograph sensor, the obstetrician-gynecologist listens to the expectant mother’s abdomen with a special stethoscope.
A signal wave arrives from the ultrasound sensor to the fetal heart, which is transformed from the organ and returns to the sensor again. The information obtained during this process reflects the contractions of the child’s heart muscle in 60 seconds. CTG results can be recorded on tape using various methods - light, graphic and sound.
It is recommended to perform the diagnostic examination on an empty stomach. After eating food, the concentration of glucose in the blood of the expectant mother increases - this provokes an increase in the baby’s activity and its sensitivity to influences from the external environment.
On the eve of diagnosis, a pregnant woman should rest well and eat food 2–3 hours before the test. The child’s activity mode is also important - conducting CTG is pointless during the child’s sleep. It is necessary to find a comfortable position for the woman - she should not feel any discomfort. To improve the conductivity of electrical impulses, a special gel is applied to the sensor.
During pregnancy with complications, CTG is performed once a week. There are many variants of deviations from the norm; it is difficult to organize them into one system. There are cases in which diagnostic parameters are within the acceptable range, but their combination with other factors indicates a violation of the fetal condition.
Sometimes, during a normal pregnancy, a false CTG recording is possible, which indicates the presence of pathologies. This is observed when conducting diagnostics without using a gel for the sensor, as well as during the baby’s sleep, multiple pregnancy, or the expectant mother being obese.
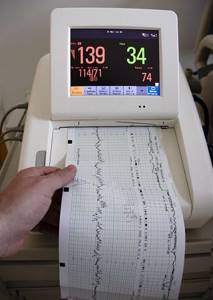
Today, the prenatal medical industry has modern devices that, using computer programs, automate the interpretation of cardiotocography results as much as possible.