Endoscopic examination of the lower digestive tract
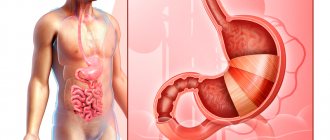
Sigmoidoscopy is a type of endoscopic examination that allows you to study in detail the lower (final) part of the digestive tract, as well as take tissue for biopsy, remove a foreign body and other manipulations.
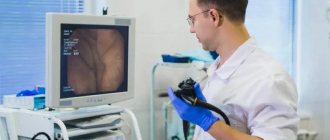
This endoscopy method is performed by introducing a device into the rectal cavity - a sigmoidoscope, with the help of which the image is transmitted to the monitor screen. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis after preliminary preparation, including bowel cleansing.
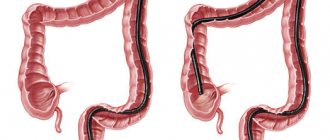
Unlike colonoscopy, this examination concerns a small area of the colon (rectum and part of the sigmoid colon - only up to 25 cm), so it does not take much time, is carried out without anesthesia and is easily tolerated by patients.
Performing rectoscopy at the Clinic of High Medical Technologies named after. N. I. Pirogova
The length of the colon is approximately 1-1.5 meters. During sigmoidoscopy, the first 25-30 cm are examined, the procedure takes little time and therefore RRS is usually performed without anesthesia. Some patients tolerate the examination easily, some experience discomfort or pain, it depends on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Before the procedure, the patient is given special disposable clothing for the lower half of the body, the patient lies down on a couch or examination table. During sigmoidoscopy, a person takes a special position as directed by the doctor. The choice of position is determined by the specialist based on anatomical features, research objectives and patient comfort.
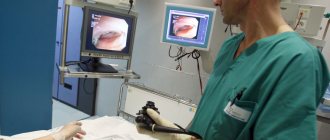
Before inserting the rectoscope, the doctor performs a digital examination to straighten the rectum in the area of insertion. Next, air is supplied into the anus to expand the lumen of the intestine, and a rectoscope is inserted, the tip of which is generously lubricated with Vaseline. When the device is inserted, the doctor makes gentle rotary movements (rotations) and continues to supply air, opening the intestine further. At this time, the camera from the tip of the rectoscope transmits the image to the monitor.
At the end of sigmoidoscopy, the air pumped into it remains in the intestine for some time. Therefore, increased gas formation during the day after the examination is a variant of the norm.
Indications
For an accurate diagnosis
The sigmoidoscopy procedure is widely used by doctors for primary diagnosis, that is, to determine the diagnosis of a patient who first contacts a proctologist with specific complaints.
A coloproctologist, gastroenterologist or therapist may recommend undergoing endoscopy of the lower digestive tract if you have the following complaints:
- blood, mucus or pus in the stool;
- pain, sensation of a foreign body in the anus;
- changes in the shape of feces (ribbon-shaped feces);
- persistent constipation followed by diarrhea.
Indications for the procedure of sigmoidoscopy of the intestines may appear during a consultative examination of a patient who has applied for an anal fissure or hemorrhoids. Such a study is necessary to exclude a tumor, inflammatory process, foreign body or other pathology.
For clinical observation and screening examinations
Sigmoidoscopy refers to studies that are not associated with radiation exposure to the body, and therefore can be performed as often as desired. At the same time, endoscopy provides maximum information about pathology when it comes to diseases of the mucous membrane.
Therefore, endoscopic examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon is widely used for preventive purposes - for clinical observation and screening examinations.
Preventive endoscopy of the rectum diagnoses cancer at the earliest stage of development, when the patient does not make any complaints, and the surgeon cannot palpate the tumor during a digital examination.
Dispensary monitoring of already diagnosed diseases using endoscopic methods makes it possible to prevent complications of the disease.
For diagnostic and therapeutic procedures
Another advantage of the sigmoidoscopy procedure is the ability to combine endoscopic examination with diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
An endoscopic examination can be combined with a biopsy - tissue sampling from a suspicious tumor for cytological examination, which is the main diagnostic procedure when diagnosing a malignant tumor.
During sigmoidoscopy, the doctor can perform a number of microsurgical treatment procedures - cauterize a bleeding vessel, remove a foreign body, remove a polyp (benign neoplasm) of the rectum.
It must be said that the vast majority of polyps are dangerous in relation to malignant degeneration, therefore, after removal, doctors recommend regular preventive examinations (every 3-5 years).
Side effects
There are no restrictions regarding diet or lifestyle after the procedure. For several hours, the patient may feel slight discomfort in the anus associated with spasm and muscle strain. In addition, episodes of flatulence due to air entering the intestines are possible. Such side effects go away on their own after some time.
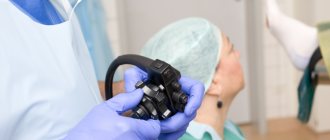
Sigmoidoscope
A cylindrical diagnostic device, which is inserted into the rectum during an endoscopic examination, is called a sigmoidoscope.
The lower part of the digestive tract has no bends. Therefore, for its endoscopic examination, both soft plastic and hard metal sigmoidoscopes are used.
Each sigmoidoscope is equipped with a set of additional devices of a fixed (illuminator) and removable nature. Replacing each other, removable elements allow you to perform additional tasks.
The standard package of the sigmoidoscope includes:
- air supply device;
- optical system, including an eyepiece and a light guide harness;
- forceps;
- biopsy channel;
- obturator
During the examination, the LED fiber of the sigmoidoscope transmits the image to the monitor screen, so that all manipulations are carried out under visual control.
After the study, a record is saved, which is of particular importance for dispensary patients, since it allows you to track the dynamics of the development of the disease.
Features of the procedure
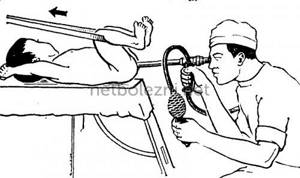
During sigmoidoscopy, the patient is in a supine position and bends his knees. To simplify the procedure, the patient is advised to lie on his side and press his legs to his stomach. At this stage of the procedure, sedation is already used, so there is no discomfort.
The attending physician examines the anus and uses palpation to determine the affected area. The rectum is examined with fingers and additional instruments, if necessary. During palpation, the patient breathes through the mouth. Gradually, a sigmoidoscope or rectoscope is introduced into the patient's anus. The length of the device is up to thirty centimeters.
This diagnostic device is classified as an endoscope. The tubular device has a diameter of about two centimeters, so it easily fits into the anus. A rectoscope allows you to visually examine the condition of the mucous membranes. Before starting the procedure, the device is lubricated with petroleum jelly. When passing a sigmoidoscope in the anus, the patient feels the urge to defecate. There is no need to restrain the urge. You should push, after which the passage of the device inside the intestine will be easier. After the device reaches the affected area, a certain amount of air is pumped through the tube.
At this point, the lower intestine begins to straighten, and the medical professional carefully examines the mucous membrane. Air is introduced through the anus, as a result of which the patient may feel discomfort. Flatulence and mild pain in the lower abdomen appear. Unpleasant sensations disappear after removing the device from the anus. Sometimes it will be necessary to cleanse the surface of the mucous membranes from feces.
If there is an excessive amount of feces, you will need to use a special device that eliminates liquid feces or mucous discharge. These manipulations do not cause discomfort to the patient. To remove tissue samples for histological analysis, a healthcare professional inserts biopsy forceps or a specially adapted brush. In order to eliminate polyps and growths, the doctor uses loops for electrocoagulation.
Often, during sigmoidoscopy, a biopsy of the anal canal is performed. This procedure is performed exclusively under local anesthesia to eliminate pain and discomfort. After completion of the procedure, the proctoscope is removed from the anus. The attending physician is required to measure pulse and blood pressure before, during and after the procedure. Thus, the work of the cardiac system is monitored and possible changes are recorded. After the procedure, air leaves the intestines. These sensations are present in most cases and are considered normal.
The patient leaves the medical facility after the effect of the sedatives wears off, pulse and blood pressure levels normalize, and general condition improves. On average, the duration of a diagnostic study is fifteen minutes. Recovery after the procedure takes a maximum of forty minutes, after which the patient goes home.
What the study will show
Endoscopy is an examination of the mucous membrane of the digestive tube. Doctors receive information about the condition of other layers of the intestinal wall indirectly from changes in the pattern of the mucous membrane, abnormal bends, etc.
Sigmoidoscopy of the intestine will provide the maximum amount of information about the following diseases of the lower intestinal tube:
- inflammatory reactions;
- benign neoplasms;
- oncology;
- enlarged hemorrhoids;
- foreign bodies in the intestinal lumen;
- injuries;
- congenital anomalies.
During a sigmoidoscopy examination, the doctor will examine all parts of the rectum (anal canal (4 cm), the following ampullary extension (8-10 cm) and the supramullary part (2-4 cm)), as well as the adjacent part of the sigmoid colon (10-15 cm).
If there is a need to examine the upper parts of the large intestine, then a colonoscopy is prescribed, but if it is advisable to limit the diagnosis to the study of the anal canal, an anoscopy is prescribed.
Sigmoidoscopy in children and pregnant women
Pregnancy is not considered a contraindication to sigmoidoscopy, but it significantly complicates its implementation. As a rule, small-diameter instruments are used to examine pregnant women, which reduce the likelihood of injury.
Cerebral edema is a complex pathological condition that occurs as a result of infection, injury, or excessive stress. The phenomenon often occurs against the background of coma, which in turn complicates the situation and does not allow one to accurately predict the situation and requires long-term treatment. Read more in the article: “cerebral edema: causes and consequences.”
In childhood, the procedure is carried out if there are appropriate indications - suspicion of congenital gastrointestinal defects, hemorrhoids, rectal prolapse, anal bleeding. In this case, in addition to physical training, the child’s psychological attitude plays an important role. For infants and preschool-age children, sigmoidoscopy is usually performed under general anesthesia.
Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications to endoscopy. The exception is pathologies that do not technically allow this absolutely safe study to be carried out (mechanical obstruction of the rectum).
Doctors advise postponing the examination if the patient is in serious condition:
- acute infectious diseases;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases of the pelvic organs;
- decompensated cardiovascular, renal or liver failure;
- condition after a heart attack, stroke, etc.
Difficulties with sigmoidoscopy of the intestines can arise in mentally ill people. In such cases, the issue is resolved individually (examination under anesthesia or replacement with another type of diagnosis).
Who should not undergo the procedure?
Before referring a patient for rectoscopy, the attending physician (therapist, oncologist, proctologist) must find out whether there are contraindications, and, if necessary, refer the person to an appointment with medical colleagues in other areas, or to undergo clarifying tests.

Contraindications for use:
- presence of bleeding from the rectum;
- acute anal fissure;
- general serious condition, for example, if the patient is connected to life support devices;
- narrowing of the diameter of the intestinal lumen;
- acute inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity, peritonitis;
- pulmonary and heart failure;
- acute paraproctitis: purulent inflammation of the tissues around the rectum;
- some mental disorders.
In such cases, endoscopic examination should be postponed until the end of the course of conservative therapy aimed at improving the patient's condition.
Preparing for the study
Preparation for sigmoidoscopy involves cleansing the intestines of gases and feces. To prevent increased gas formation, three days before the procedure you should avoid peas, pearl barley, cabbage, beans, fresh vegetables and fruits, juices, sparkling water, kvass, alcohol, rye bread and other foods that provoke flatulence.
The day before the procedure, they switch to a slag-free diet (low-fat dietary meat (chicken, turkey), fermented milk products, eggs). Dinner on the eve of the event should be light and early (no later than 12 hours before the examination).
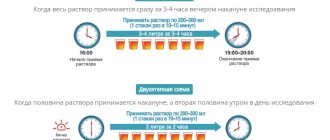
Immediately before the study in the evening and/or morning, the intestines are cleansed with an enema (to clean water) or with a laxative such as Fortrans, which is taken according to the instructions included with the drug.
How does the procedure work?
Before an endoscopic examination of the lower intestine, you will need to undress from the waist down and remove your underwear. If the device is equipped with a metal sigmoidoscope, the examination is carried out in the knee-elbow position. When using a soft plastic device, the procedure is performed in a lying position on your side with your knees pulled up to your chest.
Immediately before the procedure, the doctor conducts a digital examination to assess the tone of the sphincter, ensure the patency of the anal canal, and identify swelling, soreness or other pathological symptoms.
After a digital examination, the doctor carefully inserts a sigmoidoscope lubricated with medical petroleum jelly, pumps air, straightening the folds of the mucous membrane, then conducts an examination, and performs diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations according to indications.
The entire procedure takes 10-40 minutes, depending on the structural features of the patient’s intestines, the complexity of diagnosis, and the need for additional manipulations.
How is sigmoidoscopy performed?
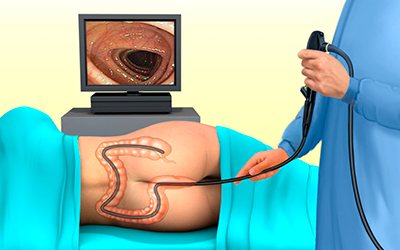
Many people are interested in how sigmoidoscopy is performed. First, a digital rectal examination is performed. Only after this the doctor begins to examine the intestines. The procedure for RRS is as follows:
- The sigmoidoscope treated with Vaseline is carefully inserted into the intestine 5-7 centimeters.
- After reaching the desired depth, a device is installed for visual inspection of the walls.
- In the area where the rectum passes into the sigmoid colon, air is pumped to straighten the intestinal folds.
- If necessary, a biopsy or cauterization of vessels and polyps is performed.
The duration of the procedure is 5-10 minutes.
Rules of conduct after the examination
Endoscopic examination does not require hospitalization of the patient. After the procedure, the doctor will suggest you rest for a few minutes on the couch, then you can go home.
Since the procedure is accompanied by the injection of gases into the intestines, their free passage is possible throughout the day. This is fine.
When washing the intestines with Fortrans or an enema, beneficial bacteria are “washed out,” and the procedure itself can have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane. Therefore, for 5-7 days after the procedure you need to adhere to a diet (fermented milk products, dietary meat, eggs).
After a week, if there are no other indications, you can abandon the restrictions.
Patient reviews about the procedure
We analyzed reviews of intestinal sigmoidoscopy. It can be concluded that the vast majority of patients who underwent the procedure characterize the study as unpleasant, but painless.
Many reviews record the impression that waiting for the procedure brings more unpleasant worries than the examination itself. In some patients, the bowel cleansing procedure caused discomfort. To avoid such sensations, it is better to use laxatives like Fortrans instead of microenemas, which can cause irritation of the mucous membrane.
There are relatively few complaints of pain during sigmoidoscopy examination of the intestine. Patients complain of pain and discomfort during the entry of air into the intestine, as well as during the examination procedure.
What diseases can sigmoidoscopy diagnose?
Sigmoidoscopy is performed to diagnose a variety of proctological and gastroenterological pathologies. The procedure helps medical professionals determine the presence of malignant and benign tumors in the intestines. The presence of polyps, growths, hemorrhoidal cones, inflammatory and infectious processes is detected.
Sigmoidoscopy is also used to diagnose:
- pathological processes of the sigmoid and rectum, for example sigmoiditis and proctitis;
- diverticulum or protrusion of the intestinal wall;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- hemorrhoids at any stage;
- violation of the integrity of the intestinal mucosa;
The study is often carried out to eliminate problems of the gastrointestinal tract.