Cardiotocography during pregnancy is done to determine the state of the child’s cardiovascular system, his heart rate, physical activity, as well as the frequency of uterine contractions and the baby’s reaction to them.
To decipher the results in obstetric practice, the Fisher scoring system is widely used, which optimally shows the picture of the condition of the fetus in the womb. As a result of decoding, you can get a maximum of 10 points. The lower this result, the more alarming the situation. If the transcript of the CTG recording shows a figure from 8 to 10, then this is the desired norm and the pregnant woman can safely count on a favorable course of labor.
If the CTG results are 7 points, this indicates the initial stage of oxygen starvation of the fetus. Such indicators do not require emergency measures, but the pregnant woman should be under special supervision before delivery. If the result is less than 4 points, then they resort to active stimulation of labor or the child is removed during surgery.
When is CTG performed?
CTG can be performed during pregnancy from 28-30 weeks, but the most informative study becomes after 32 weeks. If the mother and fetus are in normal condition, examinations in the third trimester are recommended to be done approximately once every ten days. When there are indications, it is done more often, once every 5-7 days, and if necessary, daily. Indications for unscheduled CTG are as follows:
- Mother's Rh negative
- History of miscarriage, miscarriage, stillbirth
- Decreased child activity according to the mother
- Fetal pathologies identified by ultrasound (developmental delay, placental blood flow disturbances, umbilical cord and fetal abnormalities, decreased number of movements, changes in amniotic fluid)
- Gestosis of the last trimester
- Placenta previa or malpresentation of the fetus
- Multiple births, oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios
- Post-term pregnancy
- Extragenital pathologies in women (diabetes mellitus and other endocrine diseases, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, anemia, infectious diseases with fever).
Scheduled CTG is performed closer to 32-34 weeks; unscheduled CTG for special indications can be done earlier, as early as 28 weeks, with subsequent regular repetitions. Since the technique is safe, the examination can be repeated almost daily; it will not harm either the mother or the child.
Purpose of the event
Expecting a baby is a time full of excitement, so many expectant mothers are wary of any diagnostic procedure. Do not worry if the doctor has prescribed cardiotocography - this is a standard test that is performed twice during pregnancy (from 32 weeks), as well as during childbirth (as prescribed by the doctor). CTG helps to identify:
- intrauterine infections;
- hypoxia;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- rapid maturation of the placenta;
- abnormalities of the cardiovascular system.
If abnormalities are suddenly discovered during the examination, a repeat procedure may be performed. CTG is absolutely safe for a child and has no contraindications.
How is fetal CTG performed?
No special preparation is required to conduct CTG after thirty weeks. It is recommended to do the study during periods of greatest fetal activity, from nine in the morning to two in the afternoon, and from seven in the evening to midnight. It is not advisable to perform CTG on an empty stomach, as well as on a full stomach or immediately after the administration of glucose. The optimal time is an hour or an hour and a half after eating.
There are two different types of CTG during pregnancy - direct and indirect. Direct cardiotocography is rarely performed and only during childbirth when the integrity of the fetal bladder is damaged. It is done using a special spiral-shaped needle-shaped sensor, which is inserted into the presenting part of the fetus. Uterine tone is measured using a catheter that is inserted into the uterine cavity. Indirect fetal CTG is done through the anterior abdominal wall. Two sensors are used - one is attached in the place of best audibility of the heartbeat (the doctor determines it with a stethoscope before the examination), the other - in the right corner of the fundus of the uterus.
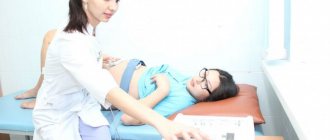
CTG is performed with the woman sitting or on her right side. It is not recommended to lay a pregnant woman on her back, as this may compress the main blood vessels and the CTG reading will be incorrect. The average procedure time is 40 minutes. If the fetus has a normal rhythm, CTG can be reduced to 15-20 minutes. During childbirth, the duration of the study should be at least twenty minutes, or five contractions.
The first ten minutes measure the basic rhythm, such a fetal CTG is called non-stress. It is supplemented by recording fetal movements (using a sensor or according to the pregnant woman). Then they move on to functional tests or stress CTG. The following tests are used to study the baby's heartbeat in the womb:
- Oxytocin test
- Mammary test
- Acoustic test
- Fetal palpation
- Reflex tests
The oxytocin test is carried out mainly before childbirth and in a hospital setting. With the help of oxytocin, contractions are provoked in a woman and CTG of the fetus is performed with increased contractions of the uterus; examination is rarely performed. The mammary test is essentially similar to the oxytocin test, but safer. The pregnant woman stimulates the nipples with her fingers, which causes increased uterine contractions. The test is contraindicated in case of increased tone and threat of premature birth. During an acoustic test, CTG records changes in the fetal heartbeat when exposed to a sound stimulus. During palpation of the fetus, its presenting part is slightly displaced. Reflex tests are rarely done. Functional tests that change the parameters of placental blood flow and the atropine test are no longer used.
CTG during pregnancy can be performed using different equipment. Previously, most clinics used devices that recorded heartbeats and uterine contractions on paper; the doctor did the decoding himself. This required high qualifications and experience of a specialist. Nowadays, equipment with computer decoding is increasingly used, this allows one to obtain more reliable results. There are also opportunities to conduct CTG weekly online. Special sensors are attached to the skin of the abdomen, the signal is transmitted via a smartphone to a computer monitor, where the doctor is able to monitor changes in the fetal cardiac activity.
Reasons for prescribing CTG
Clinic specialists prescribe fetal cardiotocography to all late-term pregnant women and women whose previous pregnancies had unfavorable outcomes. Our clinic specialists recommend regular CTG for pregnant women with high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease.
CTG devices allow you to monitor the condition of the fetus, both during pregnancy and during labor. Modern equipment for conducting cardiotocography allows you to make the right decision: continuation of pregnancy or its artificial termination, natural birth or cesarean section, etc.
Also, at the earliest stages, using CTG, it is possible to determine whether there are risks of hypoxia, anemia, and disturbances in the development of the fetal cardiovascular system.
CTG - transcript
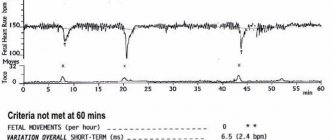
Fetal CTG indicators are heart rate, base heart rate and its variability, acceleration and deceleration. Accelerations are defined as an acceleration of the heart rate by 15 beats or more, for 15 seconds or longer. Decelerations - slowing down the heart rate by the same number of beats in a similar period of time. Normally, CTG decoding records the fetal heart rate at the level of 120-160 beats per minute, its variability is 5-25 beats. Decelerations should be absent or rare and shallow. There can be two or more accelerations for ten minutes.
CTG decoding is carried out according to a three-point system, the result is evaluated in numbers from zero to two. When measuring the basal rate, a score of zero is assigned if the fetal heart rate is below 100 beats per minute or above 180 beats. One point - with a heart rate of 100-120 or 160-180 beats. Two points - with a normal number of contractions, in the range of 120-160 per minute. If the amplitude of contractions is less than 3, 0 points are recorded, with an amplitude of 3-6 beats - 1 point, with a normal amplitude of 5-15 beats - 2 points. If accelerations are not detected, the CTG transcript is scored 0 points, with 1-4 accelerations (single or periodic) they are assigned 1 point, with 5 or more single accelerations of the rhythm they are given 2 points. The presence of late severe or atypical decelerations is scored 0 points, early severe and variable decelerations are scored 1 point, the absence of decelerations or mild variable decelerations is scored 2 points. Also, the weekly CTG scale includes an assessment of fetal movements. Their absence - 0 points, 1-3 movements - 2 points, 3 or more movements - 2 points.
CTG interpretation is considered normal if its total score is 9-12 points. In such a situation, only dynamic monitoring of the pregnant woman is carried out. When the score is 6-8, fetal hypoxia is diagnosed, without a threat to its life in the next 24 hours. Fetal CTG is repeated the next day. If the cardiotocogram is scored at 0-5 points, then there is a threat of intrauterine fetal death and urgent delivery is necessary.
What is CTG?
Fetal cardiotocography is a non-invasive method that allows you to objectively assess the condition of the unborn child, based on observations of changes in heart rate in response to fetal movements or uterine contractions. Monitoring the fetal cardiac activity allows for the most objective assessment of indicators.
Would you like to make an appointment?
Request a call back
Fill out the form to make an appointment
Cardiotocography (CTG) is the most accessible and safe method of monitoring the functional state of the fetus.
How is CTG (cardiotocography) performed during pregnancy? During the study, doctors use special devices - cardiotocographs, which are based on the Doppler effect. These fetal cardiac monitors record changes in intervals that occur between cycles of fetal cardiac activity, convert them into signals and provide information in the form of a graph. The presence of two sensors at once allows you to simultaneously assess the motor activity of the fetus and uterine contractions.
What is a cardiotocogram? This is a graph that represents 2 curves, one of which reflects the fetal heart rate (heart rate), and the other - fetal movements and uterine contractions (contractions).
What to do if the CTG interpretation is unsatisfactory
When the CTG interpretation is assessed at 6-8 points, a repeat study is performed, as well as ultrasound and Dopplerography. Together, these studies help to identify pathologies such as fetoplacental insufficiency, premature aging of the placenta, intrauterine infection, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, and the threat of premature birth. In such situations, the pregnant woman is offered to go to the hospital for treatment.
Therapy for unsatisfactory CTG by weeks 32-34 is aimed at improving blood supply between mother and fetus. It provides for complete rest for the woman and drug treatment. If an increase in uterine tone is recorded, antispasmodics (no-shpu, magnesia, papaverine), magne B6 (vitamin B complex), bricanil, genipral are prescribed. To improve the supply of oxygen to cells, vitamin C, E, essentiale, glutamic acid, neuroprotectors and angioprotectors, intravenous glucose, and special oxygen cocktails are used. To reduce blood clotting, aspirin, trental, chimes, actovegin are prescribed, and rheopolyglucin is injected intravenously. They also treat concomitant pathologies in women. After the CTG indicators improve, the pregnant woman can be discharged to home or left in the hospital under observation until delivery.
When CTG at 36-38 weeks shows low scores, from zero to five, the pregnant woman is immediately sent to the hospital. With such indicators, a caesarean section is indicated. If the pregnancy is less than 36 weeks, the patient may be given a short course of dexamethasone to stimulate the development of the baby's respiratory system. After the baby is born, additional surfactant is administered, immediate resuscitation may be required, and doctors must be prepared for this.
How is CTG done during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, indirect (external) CTG of the fetus is performed. To do this, one sensor with a special gel is placed on the mother’s abdomen, choosing the area where the fetal heart sounds can be heard best, and the second sensor is placed on the fundus of the uterus. The expectant mother, using a special device, records each episode of fetal movement by pressing a button. During the examination, the patient either lies on her side or is in a semi-sitting position. In order to obtain the most accurate information, the study should be carried out for at least 20-30 minutes.