The criteria and methods of personnel assessment that an HR specialist works with in a company depend on many factors. To develop an effective system, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of a person’s character and socio-economic parameters - you should not act according to the same algorithm for white-collar workers.
A particular difficulty in assessment arises when the task is to study not an employee, but a candidate for a position - it is necessary to thoroughly work through the database of questions so that they allow collecting enough data for analytics.
In this article, we tried to collect all possible criteria and methods for assessing specialists so that you can apply them in practice and increase the efficiency of the organization.
Summary
Prenatal CTG allows you to accurately and inexpensively determine the current condition of the fetus. Evaluation of CTG curves performed visually, i.e. subjectively, is unreliable. Computer analysis ensures consistency of results and allows, in many cases, to predict the course of pregnancy based on reliable data. This is confirmed by the results of using the oldest system (Dows-Redman) for almost 25 years. Since its introduction into practice, the Dawes-Redman system has been constantly modernized and now its database contains about 100,000 curves and, thus, this huge number of cases can be used to assess the condition of patients, i.e. the system can do things that no clinician can do. The system takes into account all the features of the cardiotocogram, discarding insignificant signs, such as short-term deviations from the norm. This work represents the latest and most complete description of the Dawes-Redman system.
Gray area
The problem with assessing prenatal fetal heart rate (FHR) is the need to decipher the many characteristics of bioelectrical activity in the gray zone between waveforms that are clearly normal and waveforms that are largely abnormal.
The most common form of fetal distress syndrome is fetal hypoxia, leading to the accumulation of lactic acid and a decrease in fetal blood pH (acidemia). In most cases, this occurs over a period of time, when the fetus still has time to compensate for this syndrome. An example of such compensation is bradycardia of heart contractions during a short period of reduced oxygen supply; its presence is evidence of the normal state of the fetus, its adaptation to a stressful, but not pathological, situation. If the fetus deteriorates to the point that it cannot cope with the lack of oxygen, distress occurs and fetal heart rate patterns indicate the need for immediate intervention.
For clinicians, this gray area is very important. This includes a small number of critically ill patients in whom risks can potentially be recognized and for whom timely intervention can ensure fetal safety. However, this group also includes many cases of healthier fetuses in which acute distress is not typical and for which urgent intervention is not necessary. Heart rate curves in these fetuses are often difficult to decipher and, although certainly not clearly normal, are not abnormal. How to distinguish normal from abnormal curves in the gray zone?
Use combined assessment methods
The key to all methods and criteria for personnel assessment is to find out whether the employee is suitable for the position he holds, in what direction he needs to grow, and whether it is worth considering his promotion to a management position.
If you want to professionally evaluate personnel, you need not only to know evaluation methods, but also to understand when and which ones are more effective to use.
It's not difficult to figure out what needs to be done. It's harder to figure out how to do it right. This is exactly what they teach in our course Personnel Assessment from A to Z. Dmitry Kuzmin Author of the media portal of the Russian School of Management
Accurate measurement
Today, the usual way to evaluate antenatal CTGs is visual assessment (subjective interpretation using vision), but this method can cause problems. An obvious and unresolved method is to use a standard curve configuration that is easily recognized by clinician A but not recognized by clinician B, and vice versa. Many recent studies (Bernardes et al, 1997; Devoe et al, 2000; Chauhan et al, 2008) repeatedly show that this is a major problem. Clinicians have conflicting views on this issue, and at times even one clinician may disagree with another when assessing the same curve.
In fact, the visual assessment method is “intuitive”, which is not always good enough. The results of each study that may lead to an intervention that is non-trivial and involves a choice between life and death must be based on valid, reproducible and accurate assessment methods. To address this problem, various clinical scoring systems have been introduced (Bracero et al, 2000). These systems work to some extent, but do not provide the required accuracy and are rather attempts to standardize different opinions. To obtain clinically significant CTG characteristics, continuous computer analysis of heart rate signals is required. Important characteristics of normality and abnormality can then be numerically scaled so that the value of a particular type of curve can be assessed equally in any country in the world.
The second problem with the visual assessment method is the unequal degree of experience among different specialists. It is illogical and unreasonable to expect all medical professionals who analyze antenatal CTGs to be uniquely qualified to interpret them. In fact, even the most experienced transcriptionists cannot retain in their memory the sheer volume of typical examples that can be observed and remember what each one means. And, again, the problem is that computer analysis does not make a diagnosis - it only delivers to the patient’s bedside the experience accumulated in the archive, which helps in deciphering cardiotocograms.
The need for computer measurement of fetal heart rate led to the emergence of the Dawes-Redman system.
Assessment methods
There are many ways to assess employee competencies and skills. We suggest paying attention to both universal ones, which are used in almost any company and often do not even require separate human resources to carry them out, as well as specific ones. Consider the specifics of your business before implementing practices.
Quantitative methods
Such methods are directly related to numerical indicators and are easy to calculate. Data is usually collected throughout the entire work cycle - for example, using CRM or financial planning management specialists.
- A rating system is when the effectiveness of each employee is calculated and they are ranked in order. For example, in production you can rank specialists by the number of parts created. This evaluation method can be used to increase motivation by making the rating public.
- KPI is the main method for assessing staff performance. For example, a manager sets specific tasks for actions, and each of them is assigned an importance coefficient. At the end of the period, the specialist’s overall assessment is calculated. In some industries, wages depend on KPI scores. Let’s say the task is to make 100 parts. If a person made 90 parts, his salary will be 90% of the total amount.
- Combined point system - for each action performed, a reward is assigned in the form of a certain number of points. At the end of the period, the points are summed up. Let’s say the scoring system for a marketer is to bring a thousand people to the site for 5 points, make 10 sales requests for another 5 points. If 5 thousand people came to the site, and there were 200 applications, then the overall rating is 25+100, or 125 points.
- Subjective assessment - works if the staff can be assessed by several managers at once. Let's say the sales department is controlled by a top manager of a line, a department head and two senior managers. They make a rating of the most effective employees, in their opinion, based on several parameters or one at a time, depending on the specifics of the organization. Then these ratings are compared - those employees who are at the bottom of the list for most managers become outsiders. This is a reason to apply disciplinary measures to them, strengthen their work with motivation, or even make a management decision.
- Testing is a method reminiscent of conducting an exam. A list of questions with unambiguous answers is compiled, which can be used to test the specialist’s competencies.
Qualitative methods
Such methods are suitable not only for assessing existing staff, but also applicants. Basically we are talking about competencies that can be tested with tests and somehow measured.
Method of extremes
, or the method of a system of arbitrary characteristics - the manager identifies the strongest and weakest aspects of a specialist, analyzes achievements and mistakes, and then draws conclusions.
Descriptive method
- the manager also evaluates employees, but in this method he writes a characteristic for the person, trying to highlight all his strengths and weaknesses. Unlike an arbitrary system, this method strives to cover as much information as possible and be objective.
Matrix method
- often used when assessing applicants, but can also be used to study existing personnel. A list of key competencies that the person filling the position must have is compiled. They are ranked by importance, each assigned a certain percentage. The employees are then compared.
For example, this is what a matrix for a marketing specialist might look like:
| Competence | Importance | Specialist 1 | Specialist 2 |
| Using promotion channels | 50% | ||
| Web analytics | 30% | ||
| PR tools | 20% |
If this is an applicant, then by adding up the values of competencies, you can decide to hire the right person.
Group assessment is a method that requires resources. Poor when assessing linear positions, but effective when assessing a top-level employee or applicant. Suitable for studying a specialist with rare competencies. For example, this method is now used in small companies to hire IT specialists - when such an employee is needed to develop a website, and the business is in no way connected with the digital industry.
Here's how it works: a manager, a specialist and an invited expert participate in the dialogue. The employee is asked to tell how he will act within the framework of a specific case. The answers are analyzed, the expert’s resume is taken into account, not only the level of knowledge is taken into account, but also the psychological aspects of the employee’s behavior.
360 method
We have specifically included this and the following methods in separate subsections - these are new methods that should be used carefully, only after understanding their specifics.
The 360 degree method is a way to evaluate an employee using his environment. Accordingly, it should be used not only to assess competencies, but also to study the psychological characteristics of a specialist, his communication and leadership qualities. It is widely used in the West after the publication of the book of the same name by Peter Ward. In Russia, references to this practice have been found since the 2000s.
What's the point? The assessment of a specialist is carried out not only by managers, but also by all his colleagues - superiors, subordinates, employees from other departments with whom the person interacts. The result should be a rating of “properties-characteristics”, the list of which is compiled based on the profession - that is, for a manager it will be the level of communication skills, for a logistician - the ability to quickly make decisions and be able to build routes.
The survey is usually conducted anonymously, only the level of relationship is set - colleague, subordinate, manager. The assessment is carried out in points, then the average value is calculated for each competency.
Sometimes partners, clients and other persons are involved in the method - then the method is renamed method-540.
Assessment center
This is a method of comprehensive personnel assessment that uses complementary methods of checking employees. Focused both on the study of competencies and on the psychological and professional characteristics of employees. There is an opinion in the scientific community that this method is one of the most accurate and reliable today. In addition, this method is presented in the Russian assessment center standard and in international standards.
Assessments using this method are usually carried out either by invited organizations or by internal HR specialists who have undergone special training. Moreover, if there is a risk of bias, it is better to invite people from outside. If the specifics of the organization are such that employees must have special competencies, then it is better to entrust the analysis to your own HR service, due to the difficulty of finding external contractors with the necessary expertise.
A specialist conducting personnel assessment using the Assessment Center method must have the appropriate skills - be able to observe the behavior of participants, describe processes in as much detail as possible, classify behavior, assess competencies and related skills, and also give qualified feedback to participants in a timely manner.
Most often, assessment procedures consist of three stages - business games, interviews, tests. The maximum data is obtained from simulated situations, since it is in them that one can study not only the employee’s competencies, but also his teamwork skills, communication skills, and leadership abilities. In addition, the assessment is also given during feedback sessions - how the specialist reacts to criticism, in what form he better perceives data from experts, and how he reacts to the opinion of outside specialists.
All this allows you not only to understand the employee’s abilities, but also to draw up a detailed psychological portrait of him. These assessments can be used to prepare a summary of the employee's suitability for the position.
Dawes-Redman system for assessing antenatal CTG
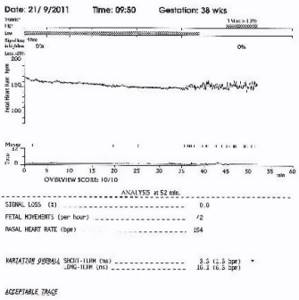
Development of the system began in 1978, and the first commercial system was released to the market by Oxford Instruments in the late 1980s. It was designed to work with any monitor, and the purpose of the system was to determine, given sufficient information, whether the fetus was normal and monitoring was no longer required. The norm was determined by the number of criteria, now called the Dawes-Redman criteria, with a minimum recording duration of 10 minutes. If, however, the recording was made at the end of the 1 hour period, the conclusion was that the fetal condition was not normal (“recording results did not meet the criteria”).
Deciphering CTG begins with finding the isoelectric line, which, unexpectedly, can be difficult. Visually, this is an intuitive and approximate solution. It is unlikely that for two people the isoelectric line will be at the same level. After determining the isoline, characteristics such as increased or slowed heart rate in the fetus can be found and measured. There are many nuances to this process that will not be discussed here. In some cases, CTGs may be so unstable that the isoelectric line cannot be detected visually; For others, the signal drops out so often that decoding is unreliable or even impossible.
Convincing confirmation of the normal state of the fetus is the episodic change in heart rate characteristic of different phases of sleep in the fetus. During deep sleep, the fetal heart rate curve is relatively flat with a small number of short-term deviations. During periods of fetal activity, as is well known, the fetal heart rate increases repeatedly and the fetus is considered “reactive.” One of the main purposes of the Dawes-Redman system is to detect this reactivity, regarded as a “high heart rate episode” (i.e., a period of large deviation of the fetal heart rate from the norm). Once one of these events is detected, and in the absence of other adverse events, the fetus can be considered to meet the Dawes-Redman criteria and monitoring can be discontinued. The advantage of this system is that it minimizes the time required to monitor normal infants. However, the duration of deep sleep can last up to 40 or 50 minutes, therefore, to confirm the normal state of the fetus, it may be necessary to decipher a longer period.
Why do you need a specialist assessment?
Personnel assessment is a system of clear indicators by which you can determine whether a person is suitable for the position he holds, whether he is effective enough, and which aspects he needs to “tighten up” to become even better.
Competent personnel assessment is useful for both managers and employees:
- It helps to determine the level of specialists, their skills and competencies. It’s easier to decide who to promote and who needs to be more motivated to do the job or fired.
- Managers understand what personnel changes are needed in the organization and where to direct the efforts of HR specialists.
- Based on assessment data, the motivation system and KPIs are improved.
- There is more order in the organization, chaos and disorganization disappear.
Correctly developed criteria and assessments of employee performance help the manager keep his finger on the pulse and understand how effectively human resources are used in the organization.
Here are some strategic decisions you can make by reviewing the assessment results:
- Develop a personnel planning system - determine a matrix for employee promotion.
- Create a system of grades and checklists based not on a universal system of competencies, but on the real level of knowledge and skills of employees in the organization.
- Think over the training system - draw up a plan for courses for employees, understand with which contractors to enter into long-term contracts to send specialists for advanced training.
- Create a personnel reserve, understand which employees in the future can move from line positions to management positions.
- Conduct an analysis of the effectiveness of work processes, understand the motivation system, identify leaders and bottlenecks in the organization’s business logic.
Waveform with fast sinusoidal rhythm
This phenomenon is rare, but very significant, indicating fetal anemia. This could be due to a number of reasons. If the anemia is severe enough to cause this change in the curve, the safety of the fetus may be seriously compromised. This case is easily detected by specialists visually, but many studies are carried out by workers with insufficient experience, who are unlikely to quickly recognize such an anomaly and decide what it means. In these cases, the Dawson-Redman system is also very useful. It detects the problem with confidence and alerts the clinician to the severity of the case. (Picture 1).
Rice. 1. Rapid sinusoidal rhythm, indicating severe fetal anemia. Please note that a short-term deviation is normal, but pathology is detected through computer analysis.
Validation of the Dawson-Redman system.
During its existence, the system was continuously modernized and improved. It has been enriched with a number of new features, many of which are unfamiliar to users, and some of which allow you to avoid mistakes when deciphering difficult, but unusual or rare patterns.
The algorithm for recognizing the rare but dangerous sinusoidal rhythm is unique in its design and testing method (Reddy et al, 2009), and only works in the authentic Dawson-Redman system. To make it possible to use the system in non-standard, but clinically important cases, the method for finding the isoelectric line has been improved several times. The system considers borderline characteristics as a whole, and not separately, generating, if necessary, a special alarm message. The system was developed based on a database containing about 100,000 records. Every new event is now checked against this database, the largest in the world. Archived records are linked to detailed clinical outcome data over the past 20 years. No improvements are made to the system as it functions reliably with a comprehensive set of data making it trouble-free and unique.
The current version of the system is marketed exclusively by Huntleigh, having acquired the rights from Sonicaid in 2006, and is the only analysis method that contains all the improvements and a more powerful algorithm. There are currently a number of systems on the market that mimic our analysis method, but they are based on published material and do not include many of the improvements we have made to the system over the past 20 years.
Short-term variability, fetal brain and fetal health
Short-term variability (STV) is an important, but by no means the only, indicator of the normal condition of the fetus. This is not the same as a change in the duration between heartbeats, which cannot be detected by Doppler sonography. However, STV is measured by external Doppler sonography devices, which are widely used throughout the world. A low STV value is most often observed in fetuses with slow growth and those in a state of chronic stress. An STV value of less than 4 ms is considered low, less than 3 ms is considered abnormal, and less than 2 ms is considered extremely abnormal. These thresholds are only valid if measurements are taken for a full 60 minutes. There may be cases where an operator, concerned about a low STV, stops recording prematurely, which is a bad decision. Such a recording may occur if the child has been quiet for a long time, then awakens and exhibits normal reactivity before the end of one hour, although it may be concluded that the recording does not meet the Dawes-Redman criteria (Figure 2).
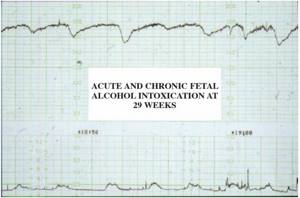
However, not all flat graphs are the result of chronic stress resulting from placental dysfunction. The appearance of the normal curve is determined by the normal activity of the fetal brain. With complete asphyxia of the fetus, it falls into a coma, with severe suppression of brain function. However, there are other cases of fetal coma, one of which is alcohol intoxication, as shown in the drawing of a fetus from an alcoholic mother (Figure 3). Another case of a congenital anomaly of the central nervous system is that in anencephalic fetuses very flat graphs are observed.
It would be a mistake to assume that STV is the only characteristic of interest. The effectiveness of the Dawes-Redman system is that its criteria relate to several different aspects of the fetal condition. Recent research into the outcome of mothers' claims against the NHS (the largest monetary proportion of NHS claims worldwide) shows the importance of correct CTG interpretation (NHS Litigation Authority, 2012). While the interpretation of CTG during labor is very important, the same can be said about issues associated with the analysis performed by the antenatal monitoring system, where the Dawes-Redman system is the gold standard when it comes to data interpretation.
|
Rice. 2. Unusual duration of the fetal restful sleep phase during a normal pregnancy. Note that the normal state is not determined until the last 6 minutes of recording, when the fetus becomes active and an episode of large deviation in heart rate is detected. The curve is normal, but the short-term deviation is small and does not reflect any problem, but is caused by the fact that the recording was started at the beginning of a long period of restful sleep. If recording was stopped earlier, the transient abnormality may be erroneously attributed to fetal distress.
|
Rice. 3. The state of the fetal brain determines the nature of the heart rate curves. A mother in a state of intoxication and the effect of this intoxication on the fetus. The curve is abnormal in nature, but returns to a completely normal appearance after the cessation of alcohol intake into the body.
Basic provisions
• Antenatal CTG reliably detects severe cases of fetal distress.
• In the “gray zone” between normal fetal condition and fetal depression, interpretation of indications is difficult and diagnostic accuracy is reduced.
• Subjective visual interpretation of the obtained CTG data gives contradictory and inaccurate results.
• The only way to overcome these shortcomings is computer analysis.
• The latest version of the Dawes-Redman system has been improved many times over the years, and is now the most reliable and efficient of its kind in existence.
• The system minimizes registration time.
• Short-term deviations in heart rate are a useful measure of fetal well-being. However, this criterion is only useful after 60 minutes from the start of recording and relates to only one aspect of the fetal condition.
• This Dawes-Redman system has features and enhancements not found in other similar systems on the market.
Methods of personnel assessment
There are hundreds of methods and criteria for assessing the work of specialists, but in any case it all comes down to three:
- Manual receipt and processing of data - most often this means interviews with employees, group or personal. The advantage of this method is a careful assessment of the skills and abilities of specialists. Disadvantages - it requires a lot of resources to carry out, there is a possibility of errors in assessment and personal factors.
- Automatic assessment - tests are carried out, often using computer programs. The data is analyzed by the system. This is a fast and effective method; moreover, it is enough to develop tests once and then the system can be scaled to an indefinite number of participants. The downside is that it is difficult to assess individual characteristics. Well suited for positions with formalized responsibilities.
- A combined method is when competencies are tested using tests, and additionally, using interviews and other methods, the individual characteristics of the object being assessed are assessed.