Posted by Andro-gynecology clinic at 2018-08-29. Published: Women, Patient Reminders
Any intrauterine intervention ( hysteroscopy, therapeutic and diagnostic curettage, induced abortion, installation and removal of intrauterine contraceptives (IUD), etc. ) is a surgical procedure, requires special training and is carried out in specialized medical institutions according to indications determined by the attending physician.
Content
- Why you need to prepare for hysteroscopy
- Examinations and tests performed before hysteroscopy
- Recommendations before hysteroscopy
- Recommendations after hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy in Krasnoyarsk
In our clinic, hysteroscopy is performed in Gynecological 106.
- Diagnostic hysteroscopy - 9500.00 rub.
- Operative hysteroscopy - RUB 13,000.00.
- Intravenous anesthesia - RUB 3,500.00.
Registration for hysteroscopy
Read more about hysteroscopy in this article
How is hysteroscopy performed?
An hour before the patient is admitted to the operating room, premedication is administered, the purpose of which is to reduce anxiety, increase tolerance to anesthesia and reduce the secretory activity of the glands. For this purpose, a combination of drugs is prescribed, containing narcotic analgesics, antihistamines, anticholinergics and sedatives.
In the operating room, the patient is placed in a gynecological chair and anesthesia is administered. The type of anesthesia is discussed in advance, taking into account contraindications, recommendations of the anesthesiologist and the wishes of the patient.
Next, proceed directly to hysteroscopy:
- The cervical canal is expanded using special instruments.
- A sterile liquid or gas is injected into the uterus through an enlarged canal. This is necessary to expand its cavity and make it accessible for inspection and manipulation.
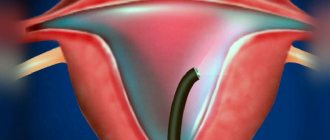
- Next, a hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix - a thin tube with a diameter of about 5 mm with an optical system that transmits an enlarged image to the monitor. As it is introduced, the cervical canal, intrauterine cavity and its angles are examined.
- After the diagnosis has been established, treatment is carried out using the same hysteroscope, which has a special channel for inserting surgical instruments. In this way, removal of polyps, submucosal myomatous nodes, dissection of synechiae, curettage of the endometrium, etc. can be carried out.
- After all interventions are completed, the hysteroscope and the injected liquid or gas are removed. The patient is sent to the intensive care ward, where she recovers from anesthesia under the supervision of medical staff.
Why you need to prepare for hysteroscopy
With any surgical procedure, including office hysteroscopy, there is a risk of infection. During intrauterine intervention, this is due to the following:
- The so-called cervical barrier is broken. The penetration of microbes into the uterine cavity is prevented by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the cervix and the mucous contents in its canal - the “mucus plug”.
- During intrauterine intervention, the mucous membrane, the endometrium, is removed from the walls of the uterine cavity. An extensive wound surface is formed, which is an “entry gate” for microorganisms.
- The proliferation of microorganisms is facilitated by an excellent nutrient medium - blood.
Surgery is a stressful situation for the patient, and stress always causes a weakening of the body's defenses. Considering all of the above, I strongly recommend following your doctor's orders. This will prevent the risk of complications.
In addition to a special examination, medication may be prescribed. The purpose of such preparation is to protect the woman’s body as much as possible from possible complications, both during the operation and in the postoperative period.
Back to contents
Hysteroscopy: description of the procedure
Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic method that allows you to completely examine the endometrium and fallopian tubes. It consists of gradually expanding the uterine cavity with a special medium (liquid or gas) and introducing a hysteroscope, which is equipped with an optical fiber, through the cervical canal. The image from the device is displayed on the monitor screen, so the doctor can carefully examine each area of the uterine cavity.
Hysteroscopy is divided into diagnostic, surgical and control, although this division is conditional, since during the manipulation the doctor may decide on the need for additional surgical procedures. Since it involves a violation of the cervical barrier and expansion of the uterine cavity, before hysteroscopy you should undergo a full examination to assess your health status and the risk of complications.
As a rule, the intervention is carried out as planned on days 5-10 of the cycle, since during this period the endometrium is thin, which makes it possible to study its structure in detail, and there are few vessels in it, so the likelihood of bleeding is minimized. But there are also emergency situations in which hysteroscopy is prescribed; in these cases, the timing of its implementation is not of fundamental importance.
Examinations and tests performed before hysteroscopy
Before performing a hysteroscopy, it is necessary to undergo an examination. The list of tests depends on the specific situation and may vary; for diagnostic purposes, the first three points are sufficient:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
. - Smear on flora and degree of vaginal cleanliness
. - Blood test for Syphilis; HIV; Hepatitis B and C
. - Detailed blood test.
- Biochemical blood test (total protein, bilirubin, creatinine, urea, sugar, Ka, Na).
- Coagulogram.
- ECG.
- Consultation with a therapist.
Based on the results of the examination, the woman consults a gynecologist; if there are no contraindications, she is sent for the procedure.
If acute inflammatory processes and STDs are detected, hysteroscopy is contraindicated!
Back to contents
What are the types of hysteroscopic surgeries?
If intrauterine pathology is detected, the following surgical interventions are performed:
- removal of myomatous nodes;
- lysis of intrauterine synechiae (adhesions);
- dissection of the intrauterine septum;
- polypectomy;
- targeted endometrial biopsy;
- myomectomy;
- removal of remnants of the intrauterine contraceptive device;
- removal of foreign bodies;
- preparation for the IVF program.
Recommendations before diagnostic hysteroscopy
- Stop sexual intercourse two days before hysteroscopy.
- The day before the procedure, cut or shave the pubic hair, labia and perineum short.
- On the eve of the intervention, go to bed no later than 22:00. You can take a sedative: tinctures of motherwort, peony, valerian, etc., according to the instructions included with the medications.
- In the morning, on the day of the procedure, take a shower and thoroughly clean the external genitalia, and put on clean knitted underwear.
- Hunger - last meal three hours before hysteroscopy.
- Immediately before the procedure, empty your bladder.
- HAVE WITH YOU:
- Referral for hysteroscopy, examination results (ultrasound, smear for flora, RW, HIV, Hepatitis B and C).
- A clean shirt (robe) and socks, sanitary pads, slippers.
Leave jewelry (earrings, rings, etc.) at home.
Back to contents
When is a hysteroscope examination necessary?
Direct indications for hysteroscopy, both diagnostic and therapeutic, are determined only by a doctor. The procedure is prescribed for:
- An abnormal result of a Papanicolaou smear (PAP or PAP test). In this case, the hysteroscopy procedure helps to study the condition of the cervix, detect or exclude signs of oncological processes or the development of dysplasia.
- Uterine bleeding recognized as pathological. Often such bleeding occurs in the presence of benign formations in the uterine cavity.
- Infertility or inability to bear a child. Using a hysteroscope, you can detect adhesions, as well as developmental anomalies of the fallopian tubes and uterus - frequent causes of frequent miscarriages and difficulties with conception.
- Asherman's syndrome - multiple adhesions, polyps, disruption of the integrity or location of intrauterine devices.
In addition, indications for hysteroscopy are small fibroids, the need for biopsy or endometrial ablation. In such cases, a hysteroscope relieves the patient of the need to perform open abdominal surgery.
Recommendations after diagnostic hysteroscopy
For 2-3 days after the procedure, moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen and moderate bleeding may persist. It is possible to increase body temperature to 37.0 - 37.2 degrees. To minimize the risk of complications, try to follow the recommendations of the gynecologist.
- If an antibiotic was prescribed, it should be continued for 5 days.
- If necessary, use painkillers and antispasmodics. The frequency of administration depends on the intensity of pain, but should not exceed that indicated in the instructions for the drug.
- Use only sanitary pads; tampons interfere with the normal flow of blood, which contributes to the development of an infectious process.
- Avoid sexual activity, physical activity, and thermal procedures for up to 10 days, until the bleeding stops. Change gaskets as needed.
- Take a shower. Avoid bathing, swimming in pools and ponds for the same period.
- Toilet the external genitalia with warm water as needed, at least twice a day.
- Monitor body temperature, the nature and amount of discharge from the genital tract, and timely emptying of the intestines and bladder.
If your body temperature rises above 37.5°C, acute pain in the lower abdomen appears, a change in the nature of discharge from the genital tract, or a deterioration in your general health, you should immediately contact your doctor or an ambulance!
After 10 days, you should make an appointment with your doctor for consultation on the results of histological examination!
READ SUMMARY
Hysteroscopy in our clinic is performed by:
What else do you need to know about the examination?
Hysteroscopy is an absolutely painless procedure. It is performed under general anesthesia and takes 30-40 minutes. After it, a woman may experience slight discomfort in the lower abdomen, and slight bleeding, which is normal, is also common. After the manipulations, for three to four days you must refrain from:
- sex;
- using tampons;
- douching;
- saunas, baths or hot baths.
Hysteroscopy of the uterus today is perhaps one of the simplest gynecological manipulations, and also the most frequent and necessary. There is no way to do without it in diagnosing diseases and treating them. Thanks to the active development of medicine, this procedure is carried out comfortably and does not cause pain or discomfort for the woman.
The specialists at the ART clinic are very familiar with this procedure. But in order not to have to resort to it, it is strongly recommended to visit a medical facility regularly once or twice a year. This will allow you to detect problems in time. An appointment with a gynecologist is made both by phone and when visiting the clinic. In addition, you can use the clinic website.
All information is for informational purposes only. If you have any health problems, you need to consult a specialist.
Forms of endometrial hyperplasia
Depending on the proliferation of endometrial elements, several types of disease are distinguished:
Fig.2. Certificate of the Russian Federation for registration of a program for selecting the correct algorithm for identifying and treating patients with endometrial hyperplasia.
- glandular form - there is a proliferation of glandular tissue that is not prone to malignancy; the probability of developing cancer is only 2-6%.
- glandular-cystic - the proliferation of glandular tissue and the formation of cysts, this is a benign formation that can in some cases turn into cancer.
- atypical - this type of hyperplasia is classified as a precancerous condition, it is the most severe form, pathological changes are observed both in the functional layer and in the basal layer. Without treatment, the risk of progression to cancer reaches 40%.
- focal - the cells of the inner layer grow unevenly, forming individual foci with a diameter of 2-3 mm to several centimeters; cells in these zones are more sensitive to the action of hormones, which contributes to more active division. If cell proliferation occurs in a polyp, then it noticeably increases in size.
Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia
To minimize the risk of developing the disease, it is necessary to promptly treat genital diseases of an inflammatory and infectious nature. In addition, great importance should be given to concomitant diseases: in case of diabetes mellitus - constant monitoring of glucose levels, in case of hypertension - timely reduction of blood pressure, women with excess body weight should normalize their weight. You also need to stop having abortions and uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives. It should be remembered that often the disease at the initial stage occurs without any symptoms. Therefore, regular visits to the gynecologist twice a year will help to promptly recognize any disease.
What alternatives are there to hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy can be replaced by some other diagnostic procedures, but not in all cases:
- Transabdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs through the anterior abdominal wall helps to identify diseases that lead to pelvic pain, menstrual irregularities, vaginal bleeding, and infertility.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is performed with a special probe inserted through the vagina. It allows you to obtain more informative images of the uterus and its appendages.
- Aspiration biopsy of the myometrium. This procedure does not require hysteroscopy: using vaginal speculum, the cervix is visualized and a tube connected to an aspirator is inserted through it.
All these studies are not as informative as hysteroscopy. However, if you start the diagnosis with them, in some cases endoscopic examination of the uterus may not be required. Sometimes these diagnostic methods are used as an alternative if there are contraindications for hysteroscopy for one reason or another.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Causes of endometrial hyperplasia
A variety of unfavorable factors can trigger the development of the disease.
- Hormonal disorders, usually present in patients with gynecological diseases: fibroids, polycystic disease, mastopathy, endometriosis. Also, uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives affects hormonal levels.
- Diseases of the endocrine glands: thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, which have an adverse effect on the endometrium or the functioning of the ovaries.
- Abortions, diagnostic curettages, as a result of which the endometrial receptors lose sensitivity to the action of hormones, while the cells continue to multiply, despite the fact that the hormones are normal.
- Hereditary predisposition, when the disease is diagnosed in close relatives.
Treatment
Treatment tactics for endometrial hyperplasia are prescribed individually and depend on the woman’s age, the severity of the disease, and the type of disease. For some forms of hyperplasia, after receiving the results of histological analysis, drug treatment is possible, the purpose of which is to suppress further growth of the endometrium and restore hormonal balance.
If conservative methods are ineffective, as well as if the disease recurs, surgical treatment is indicated. Today, thanks to the use of modern techniques, it is possible to cure the disease without removing the uterus. One of the well-proven methods is hysteroscopy; the technique is indicated for patients of reproductive and premenopausal age. This method is also used in cases of large blood loss, in an emergency, or in the presence of polyps. Among the advantages of this method, it is worth noting that it is less traumatic, the procedure is short and the recovery period is short. In the presence of cysts and polyps, a combination of surgical treatment and drug therapy is practiced.
Also a very effective method is endometrial ablation - a minimally invasive procedure during which it is possible to achieve total removal of the endometrium (both basal and functional layers), as well as part of the underlying myometrium. Electrosurgical and laser ablation methods are used, but all of them are performed under the control of a hysteroscope, which allows visual control of all the doctor’s actions.
If an atypical form of hyperplasia is detected during menopause, removal of the uterus is recommended. In the absence of pathological changes in the ovaries, only the uterus is removed; in case of adenomyosis or if malignant cells are detected, a hysterectomy with appendages is indicated.
Why perform hysteroscopy before in vitro fertilization (IVF)
Gynecologists prefer to prescribe hysteroscopy before IVF, since this way the woman gets rid of several invasive procedures necessary to prepare for IVF. As a rule, before IVF, a diagnostic (office) hysteroscopy is prescribed, which allows you to provide additional information about the condition of the endometrium - the presence or absence of polyps, tumors and nodes, and this information will prompt the doctor to take the necessary actions for further in vitro fertilization.