Indications for the procedure
Reasons to conduct an examination may be characteristic signs of adenoiditis:
- snoring during sleep;
- constant nasal congestion;
- nasal voice;
- sleep apnea – short-term holding of breath during sleep;
- change in the pronunciation of some sounds (“m”, “n”);
- delayed speech development;
- rhinitis, causing frequent coughing;
- wheezing and wheezing when breathing;
- decreased hearing acuity.
Endoscopy of the adenoids is sometimes prescribed to monitor drug and surgical therapy, which allows for regular monitoring of this disease and timely adjustment of treatment.
The child keeps asking questions, is inattentive, speaks poorly, why did the speech therapist in the kindergarten send him to an ENT specialist?
Insufficient nasal breathing leads to the fact that the child’s brain is constantly in a state of oxygen starvation, and this, in turn, leads to asthenic syndrome. Children experience increased fatigue, decreased attention and memory, while all mental processes suffer and change. Disturbances in physiological breathing lead to changes in speech breathing. Speech exhalation becomes short. The words are interrupted by unnecessary pauses, mostly to take an extra breath. Children with adenoids experience disturbances in the voice and its main characteristics. The voice acquires a strong nasal tint - nasality due to adenoids (the so-called closed rhinolalia). After treatment of adenoiditis, classes with a speech therapist give positive results after 6 months.
Contraindications
Before performing the procedure, the doctor assesses the condition of the child’s nasal passages and collects a detailed history to identify possible limitations for endoscopy. Contraindications may include:
- the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx are too thin, which can cause bleeding upon contact with the endoscope;
- pathologically narrow nasal passages;
- severe mental illness;
- intolerance to painkillers;
- acute infectious diseases;
- severe general condition (sepsis, shock);
- congenital anomalies of the nasopharynx that do not allow the insertion of equipment;
- severe cardiac and respiratory failure;
- oncological processes in the body;
- blood diseases.
Maybe radiography will help make a more accurate diagnosis?
X-ray examination is considered unjustified due to the fact that it does not fully reflect the volume of adenoid tissue and inflammation, but only shows shadows of lymphoid tissue and has an unnecessary x-ray effect on the child’s body.
Carrying out computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging according to indications for concomitant diseases allows otorhinolaryngologists to see the adenoid tissue in the images, its volume of filling the nasopharynx, their structure, and also assess the condition of neighboring organs.
How is endoscopy of adenoids performed in children?
The procedure is mainly performed under local anesthesia; anesthesia or light sedation is required for children under 3–4 years of age who are unable to sit still for a long time. In children, endoscopy of the adenoids is performed using pediatric equipment: this tube is smaller in diameter, which makes it easier to insert the device into the narrow nasal passages. The research algorithm is standard:
- the small patient is seated in a chair or on the parents’ lap and the head is fixed in a tilted back position (for babies under 6 months, the examination is carried out in a lying position);
- anesthesia is administered;
- the injection area and endoscope are treated with an antiseptic;
- slowly and gradually insert the tube into the nasal passage, carefully pushing the tip into the nasopharynx cavity;
- carefully rotating the endoscope, examine the adenoids and adjacent tissues, assess the amount of inflammation and other parameters of the disease;
- if necessary, a biopsy is performed during the study - taking a piece of mucous tissue for further analysis;
- After completing the examination, the endoscope is slowly and carefully removed, and the patient remains under medical supervision for several more hours.
During the diagnosis, all data is displayed on the screen in the form of a clear picture, and the doctor can take photos of individual areas or record on video the entire adenoscopy procedure, which will help monitor the treatment process in the future
Endoscopy of the adenoids is performed mainly from 6 months, but under certain indications it is indicated even for newborns. The technique is safe, the likelihood of complications is minimal.
How to prepare a child for adenoid endoscopy
The basis of an informative and child-friendly procedure is the psychological preparation of children. Parents, together with the attending physician, need to tell the child how the examination will be carried out, what sensations may appear during the diagnostic process, and why it is important to sit quietly and listen to the doctor.
There is no need to follow a special diet before adenoscopy, but to avoid food getting into the respiratory tract during the examination, you must:
- in case of general anesthesia, avoid eating before the procedure;
- When using local anesthesia, limit food 3-4 hours before the examination.
Medical preparation before adenoid endoscopy may include:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram - test for blood clotting;
- allergy tests to determine the body's reaction to anesthetic components.
The patient's parents should inform the doctor in advance if the child has a history of acute allergic reactions to medications, food, insect bites or other substances.
Possible negative consequences of the procedure
The likelihood of complications after endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx and adenoids is extremely low. In most cases, adverse events are limited to short-term numbness of the tongue, larynx and difficulty swallowing. More dangerous complications include:
- allergic reactions to anesthetics, local or general anesthesia;
- bleeding caused by damage to the mucous tissues of the nasopharynx;
- development of inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract.
The likelihood of identifying these consequences is minimal, especially if the child is psychologically prepared for the examination and behaves calmly during the procedure.
What to do after endoscopic diagnosis of adenoids
There are no special rules of behavior after the examination. During the first 2-3 days after endoscopy, parents need to change the child’s usual diet to a menu consisting of soft dishes that do not require thorough chewing - purees, broths, soups, boiled vegetables. For a while you will have to exclude:
- nuts and seeds;
- hard fruits with thick skin and seeds;
- coarse cereals;
- crackers and dryers.
For the first few days, it is advisable to limit children’s physical activity, active games, running, bending, jumping. For 2–4 days, you should avoid overheating, prolonged exposure to the sun, and possible hypothermia.
We are worried about frequent otitis, tubo-otitis, what does adenoids have to do with it?
The condition of the adenoids plays a significant role in the normal functioning of the auditory tube and middle ear in children. In most cases, blocking of the mouths of the auditory tubes by inflamed adenoids leads to their dysfunction and pathology of the middle ear, which is manifested by the clinic of tubootitis and otitis media.
With chronic adenoiditis, in most cases, clinical signs of tubo-otitis and exudative otitis can be observed: the child complains of congestion, pain in the ears, a feeling of fluid in the ear, asks the parents again, turns up the TV volume or sits closer to it. Upon examination, changes in the eardrums are revealed, and the level of fluid (mucus) in the middle ear is observed. It is advisable to conduct a study of the patency of the auditory tubes and hearing, in which, as a rule, conductive hearing loss is noted, which is reversible with complete treatment of the pharyngeal tonsil and middle ear.
Causes of the disease
To prevent the development of the disease and its transition to a chronic form, you should understand why it occurs. Among the most common causes of adenoiditis are the following:
- Development against the background of acute respiratory infections (activation of microbial flora contributes to inflammatory processes);
- Hypothermia;
- Prolonged exposure to allergens;
- Lack of vitamin D and predominantly carbohydrate diet;
- Insufficient development of the immune system (this is why children are more often than adults susceptible to this disease).
Additional information on the topic “Adenoids”
Dear visitors, I invite you to familiarize yourself with additional resources on the site on this topic. They provide both text and video materials. Where the aspects of both treatment and recovery after surgery are discussed in detail, as well as more in-depth data, this may be useful to you for a better understanding of issues related to problematic adenoid vegetations.
Be healthy. Sincerely, otorhinolaryngologist Ph.D. Boklin A.K.
Introductory information about the page “Adenoids in a child”
Despite the fact that in previous materials I have already described the definition, causes, features of the course, and symptoms of enlarged adenoids, this page combines all available data, supplemented by new information from evidence-based medicine.
I am also convinced of the need to identify this pathology taking into account age, since adenoids can also occur in adults. Additional material will be devoted to this in the future due to its peculiarities of both the clinic and the treatment.
I am grateful in advance for the questions you asked in the online chat or on the service page: “Yandex.Connoisseurs”.
The child has a malocclusion, the orthodontist sent him for a consultation to an ENT doctor, why?
When examining a child suffering from chronic adenoiditis, an orthodontist can identify signs of deformation of the dental system in the form of a distal bite, high hard palate, narrowing of the upper jaw, lack of space in the dental arches, which, in combination with oral breathing, form the “adenoid” type the child's face. If conservative or surgical treatment of chronic adenoiditis is not started in a timely manner, the permanent bite is subsequently disrupted. In this regard, the orthodontist refers the patient to an otorhinolaryngologist to restore nasal breathing in order to further effectively correct the child’s malocclusion.
Can the disease go away on its own?
Adenoids usually shrink with age - towards the onset of puberty. With slight proliferation of lymphoid tissue, conservative, drug treatment helps well. However, as the disease progresses with increasing severity of symptoms, the question arises about the need for surgical intervention.
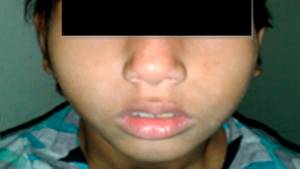
“Adenoid face” in a 9-year-old girl. Photo: Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care / Open-i (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported)
What kind of rehabilitation is needed after surgery?
After surgery, the child needs special care. He should not be allowed out of the house and left alone.
Mode. On the first day - strict bed rest, and in the next 7-10 days - at home. For at least 2 weeks, it is necessary to exclude any physical activity, etc. For a week, the child should not take a hot bath or undergo any thermal procedures (inhalations, compresses, warming).
Diet. Feed the child regular, non-rough food, excluding hot, very cold, spicy, salty, and sour foods. The duration of such a diet is from 3 to 10 days, depending on the doctor’s instructions.
When is surgery needed?
Surgical removal should be performed only if there are clear indications, which depend, first of all, on the degree of enlargement of the adenoids. This is the main condition, but not the only one. Under certain conditions and with the second degree of hypertrophy, such indications may occur. The decision to operate must be made by an experienced surgeon, and the parents must give their consent if they do not doubt the doctor’s correctness. It is always possible to obtain the opinion of several specialists who may or may not advise surgical treatment. So if in doubt, don't waste your time. And remember, if there is no positive dynamics within 3 months of conservative treatment, you need to change either the treatment methods or the doctor.
There are many adenotomy methods, which one to choose?
These methods are preferable because they have minimal risks of relapse (1%):
- Endoscopic adenotomy using the shaver technique: adenoid tissue is gradually and evenly removed using a microdebrider (special attachment) under strict endoscope control over the volume of adenoid tissue removal.
- Laser adenotomy: during this technique, lymphoid tissue is coagulated and valorized (evaporated). The advantage of this method is coagulation of blood vessels, i.e. bloodlessness, the ability to choose the intensity of exposure.
- The coblation method using a cold plasma beam is the most modern adenotomy method in our time. “Cold plasma” (electric current in a sterile saline electrolyte solution forms a narrowly focused destructive cloud) is characterized by a minimal depth of impact (hundredths of a millimeter), while healthy tissues are not injured. “Cold plasma” has analgesic and coagulating properties, as a result there is no risk of bleeding after surgery.
In most cases, operations are performed under anesthesia without causing psychological trauma to the child.
Classic adenotomy using a Beckmann adenotomy is performed “blindly,” which means there is a high risk of leaving a piece of hypertrophied tissue.
Symptoms of the disease
If you pay attention to the corresponding ailments at an early stage, this will significantly facilitate the treatment process and reduce the likelihood of the disease becoming chronic. One of the main symptoms is a violation of the process of nasal breathing, as a result of which headaches may develop and sleep patterns may be disrupted (in some cases, it can lead to hearing loss and chronic apathy). Due to such disorders, the habit of walking with an open mouth may appear (after all, breathing through the nose is problematic) - the so-called “adenoid face”. As complications progress, the voice changes, urinary incontinence and coughing at night, as well as asthmatic attacks, may occur. Acute adenoiditis is accompanied by an increase in temperature (up to 38 and above) and a burning sensation in the nasopharynx.
On the issue of the dangers of X-ray irradiation.
It all depends on the dose. The natural background radiation on the surface of our planet is not dangerous to health. In the city this background is somewhat higher. The total average annual dose in Moscow is 3 mSv per year, the permissible dose is 15 mSv. A single irradiation, subject to accepted standards for any diagnostic studies, is absolutely safe. “Dose accumulation” during repeated irradiation is dangerous. And this needs to be monitored. That is why in our clinic you cannot do an X-ray examination at your own request. Technological progress makes it possible to reduce the required dose with each new generation of devices. With tomography, the radiation dose ranges from 1 to 7 mSv, and with radiography of the nasopharynx using modern equipment – 0.8-1 mSv. Thus, you gain several times more in the city.
Complications
This operation is usually well tolerated with no adverse effects. However, removal of the pharyngeal tonsil can still cause the following complications:
- allergic reaction to the anesthetic used;
- bleeding requiring repeated intervention, the use of general and local hemostatic procedures;
- infection of a postoperative wound with the development of purulent foci in the lymph nodes, retropharyngeal space, mediastinum; in severe cases - sepsis;
- inhalation of removed tissues with the development of asphyxia (suffocation) or aspiration pneumonia;
- injury to the soft palate or root of the tongue, which leads to changes in voice, difficulty swallowing, and heavy bleeding.
To avoid such adverse effects, the operation should be done only in a well-equipped clinic by an experienced surgeon.
What if the tonsils are still enlarged?
Sometimes, along with the adenoids, the palatine tonsils, which are popularly called “tonsils,” grow. They are clearly visible when examining the pharynx. Unfortunately, in this situation there may be indications for additional surgical intervention. If both the tonsils and adenoids are enlarged, it is advisable to solve both of these problems at the same time, i.e. during one operation, remove the adenoids and partially remove the tonsils (to a physiologically normal size). In our clinic, this operation is performed using a bloodless technique, using radiosurgical instruments.