+7
+7
Make an appointment
Contraindications:
- allergic reactions to the anesthetic used
- Use with caution in case of frequent nosebleeds and problems with blood clotting
Doctors:
- Zaitsev Vladimir Mikhailovich (20 years of experience)
- Magomedov Murad Magomedovich (6 years of experience)
Equipment used:
- Lore harvester ATMOS S 61
- Rigid endoscope
- Light source for endoscopic examination of ENT organs
Children suffer from nasopharyngeal diseases more often than adults. Undeveloped immunity causes frequent runny noses and colds. Only timely diagnosis allows us to identify the cause of the disease and recommend the correct treatment. To correctly make a diagnosis, 3 methods are used - standard examination, x-ray and endoscopy.
Thanks to endoscopy of the nose and nasopharynx, adenoids can be detected in a child, their size and degree of growth can be determined. Neglected adenoids in children reduce hearing, which can lead to speech delay. With the help of the study, polyps and tumors are detected at an early stage, which is important for timely treatment. When a child often suffers from sinusitis, it is necessary to have a nasal endoscopy, because with its help, the ENT doctor will see the condition of the sinus anastomosis, and the cause of frequent inflammation will immediately become clear.
Benefits of endoscopy
small age of the child: we perform ENT endoscopy for children almost from birth
Advantages of ENT endoscopy at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
- The operations are performed by surgeons with extensive experience (more than 20 years) using modern high-tech equipment.
- Minimal tissue trauma due to physiological access and no incisions.
- The use of general anesthesia with controlled hypotension allows you to minimize the risk of bleeding and perform surgery as quickly and accurately as possible.
- The procedures are painless for the patient; patients do not experience significant discomfort or pain.
- Prevention of relapse of diseases.
- In the postoperative period, instead of packing the nasal cavity, we use hemostatic sponges. This ensures normal breathing immediately after surgery.
- The hospital stay is no more than one day.
- The rehabilitation period is minimal - several times less than after operations performed in the traditional way.
You can see prices for services
The article was checked by an otorhinolaryngologist, Ph.D. Dubtsova E.A. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Indications for endoscopy
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- snoring during sleep;
- sleep apnea;
- hay fever;
- foreign bodies of the nose and nasopharynx;
- mucous, purulent, foamy or watery nasal discharge;
- hearing loss;
- delayed speech development in a child;
- complete or partial absence of smell;
- headache;
- pain or pressure in the face;
- inflammation in the nasopharynx and sinuses;
There are practically no contraindications to nasopharyngeal endoscopy, with the exception of frequent nosebleeds.
When is ENT endoscopy indicated for children?
There is a reason to diagnose a child using an ENT endoscope if the child has:
- The nose constantly “flows”, a runny nose cannot be treated with standard methods (drops, rinsing), and the discharge is mucous or mucopurulent.
- Nasal breathing is difficult for a long time or hearing is reduced - the child constantly “asks again”, asks to make the TV “louder”.
- The appetite is reduced or completely lost, the baby gets tired quickly
- There is a nasal sound, the child wheezes or snores loudly during sleep
- The child complains of a headache or ear pain. If your child does not say it, you can guess that he has an ear or headache if he presses his hand to his ear, or weakly mournful (on one note) constantly cries. Sharp pain in the ear may be indicated by sharp screaming crying.
- If your child has already been sick more than 4 times during this year.
- More rare symptoms of ENT diseases in children are night terrors and enuresis.
Preparation for endoscopic examination
Before starting the procedure, the child should be properly prepared, explaining to him that nothing terrible is happening and it will not hurt him. If the child does not cry or resist during the examination, the examination will take place in a calm atmosphere and will be more informative.
To make a child’s nasal endoscopy as comfortable as possible, parents should explain to the child in advance what the doctor will do and how this procedure occurs.
Flexible ENT endoscopy for children of the first year of life
In a child under one year of age, the ear and nose cavities are short and wide, which is why infection can penetrate there faster than in adults. Also, in newborns, especially if the child is not breastfed, immunity may be reduced, which contributes to the development of ENT diseases (otitis, sinusitis). Even a banal “runny nose” can complicate or even stop a child’s development or weight gain, because with a stuffy nose, a child cannot suckle normally from his mother’s breast, begins to eat less, and may begin to lose weight.
Young children may not respond to the doctor, be afraid, and become very capricious during examinations, which of course makes it difficult to make a diagnosis.
Even experienced parents may not always suspect that a newborn baby’s crying or refusal to eat indicates pain due to inflammation in the ear, and snoring during sleep is the first sign that a child has adenoids (hypertrophy of the adenoid tonsil).
Our flexible ENT endoscope is the best solution in this case. The procedure will be painless and quick, the child will be in the mother’s arms, the doctor will not only examine the ear and nose cavity, but will also be able to record a video on camera.
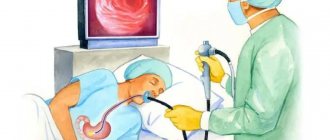
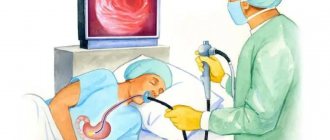
How is ENT endoscopy performed on a child?
- before starting the endoscopic examination, the doctor irrigates the nasal mucosa with vasoconstrictors (this helps reduce swelling and the endoscope will not come into contact with the mucosa, which will reduce the risk of injury);
- the child is seated in a chair (if he is worried and cannot remain still, the parent sits in the chair and picks up the child);
- the parent’s hands hold the child’s hands, and the nurse holds the head slightly tilted back;
- For a comfortable examination, the nasal mucosa is irrigated with a local anesthetic
- Before irrigation, the doctor completely collects the child’s medical history to exclude possible allergic reactions.
- the doctor turns on the endoscope, adjusts the clarity and brightness, and turns on the recording;
- the doctor carefully inserts the endoscope into the nose and slowly moves it towards the nasopharynx;
- During the examination, the doctor records various changes in the mucous membrane and structures of the nose and nasopharynx.
Treatment methods
Physiotherapeutic treatment. Used in combination for chronic forms of ENT diseases. The technique involves exposure to currents of various frequencies, ultrasound, magnetic fields and other physical energy factors. This therapy reduces the severity of nasal congestion, restores the sense of smell, eliminates headaches and other symptoms, and promotes the transition of the active stage of the disease to the remission phase.
Surgical treatment. It is used when endoscopic examination reveals tumors or other pathologies that require surgical removal. Under visual control, using low-traumatic instruments, the doctor excises damaged tissue without damaging healthy structures. This guarantees a radical solution to the medical problem, which contributes to the patient’s rapid recovery.
Endoscopy of the nasopharynx in a child
The most common reason for an endoscopic examination of the nose and nasopharynx in a child is adenoids. Nasal endoscopy for this pathology allows us to obtain the most complete picture.
You can obtain the following information:
- degree of adenoids;
- the presence and intensity of the inflammatory process on the nasal mucosa;
- the presence and nature of pathological discharge on the surface of the adenoids;
- the presence and severity of edema on the mucous membrane of the nose, nasopharynx and adenoids;
- condition of the mouths of the auditory tube;
ENT endoscopy is the best method for diagnosing adenoids in young children. I strongly recommend that you conduct this study as early as possible to make sure that everything is in order with the child’s ENT organs and that there are no adenoids or other deformities.
Types of endoscopic procedures
Endoscopy of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx
We carry out highly accurate diagnostics of nasal pathology using an endoscope. Endoscopic examination makes it possible to see areas of interest in cavities and mucous membranes that are inaccessible during normal examination. The image with high magnification is displayed on the monitor.
Endoscopy of the nasal cavity and endoscopy of the nasopharynx allows us to identify a wide range of pathologies and diseases at the initial stage of development, including:
- minimal changes in the mucous membrane (color, structure, hypertrophy);
- the presence of pathological discharge, pus;
- inflammation and hypertrophy of the adenoids;
- neoplasms (polyps, benign and malignant tumors;
- assess the condition of the nasal turbinates (hypertrophy, deformation, etc.)
- anomalies and defects of the nasal septum.
Timely identified pathology allows you to prescribe the optimal and most effective treatment.
Endoscopic polysinsotomy
Endoscopic polysinusotomy (FESS - Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery) is an endoscopic operation that is performed for chronic hypertrophic rhinosinusitis, mucocele, hemisinusitis, pansinusitis, the presence of a foreign body, cysts and other pathologies of the nasal cavity and sinuses. During the operation, the anastomosis is expanded, which makes it possible to examine the nasal sinuses.
Endoscopic septoplasty
We perform radical correction of a deviated nasal septum using endoscopic septoplasty. This is a gentle surgical method that allows, under optical control, to correct a deformed nasal septum in cases of impaired growth of facial bones, hereditary predisposition, or injuries.
Simultaneously with septoplasty, correction of hypertrophied turbinates, removal of polyps, and rehabilitation of the paranasal sinuses are possible.
Endoscopic adenotomy
At the Yauza Clinical Hospital, endoscopic adenotomy is used to remove adenoids. Indications for removal of adenoids include persistent difficulty breathing, frequent colds, snoring, hearing impairment, and deformation of the facial skeleton. Endoscopic adenotomy is performed if conservative treatment is ineffective starting from 5 years of age. During the operation, the tonsil tissue is completely removed.
Vasotomy of the nasal turbinates
For vasomotor and hypertrophic rhinitis, we perform endoscopic vasotomy of the nasal turbinates. The procedure is performed by coagulating hypertrophied areas of the inferior turbinates, which allows preserving the functional structures of the nasal passages. We perform submucosal vasotomy with lateroposition of the nasal turbinates, bipolar coagulation, and radio wave coagulation.
How is endoscopic examination performed?
Endoscopy is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia, so there is no pain during the procedure.
The study lasts only a few minutes and can be carried out directly during the consultation. Micro-instruments easily penetrate through the natural openings of the ENT organs, providing the doctor with reliable information about the condition of the mucosa and the location of tumors. The obtained data can be recorded in a computer and used for re-examination. ENT Observation by a pediatric otolaryngologist after adenotomy. Efimova Yulia Igorevna. Clinic CONSTANTA. Pediatric otorhinolaryngology.
Features of endoscopy in children
Innovative equipment and the experience of the CONSTANTA Clinic specialists minimize any risks and discomfort during the procedure, which allows its use for examining children from 2.5-3 years old. The benefits of pediatric endoscopy include:
- high information content of the method in comparison with external examination;
- the use of micro-instruments that easily penetrate the natural openings of the ENT organs;
- the use of local anesthesia, which makes the procedure painless;
- short research time (just a few minutes).
Endoscopic examination is actively used in our Clinic in Yaroslavl for children suffering from diseases of the ENT organs. It provides complete information about the condition of the ear, nose and throat, necessary to provide the most effective medical care. The received data is recorded in the computer and can be used in the future.
How is the research conducted?
Our experienced specialists carry out the procedure on an outpatient basis, setting the child up in a positive manner in a preliminary conversation, convincing the baby and parents that it will not hurt. The maximum that the child will feel is a slight tingling sensation in the area where the anesthetic was administered. An endoscopy takes only a few minutes and can be performed during a medical consultation. During the procedure, tissues and mucous membranes are not damaged, no visible marks are left on the face, and the little patient can immediately go home.
Every child who visits the Clinic receives a toy as a gift!
Clinic Constant. Information for parents of young patients.
What is upper respiratory endoscopy
Endoscopy is recognized as the most accurate, highly informative, gentle diagnostic method in the field of ENT diseases. This is the safest way to examine a patient than all types of x-ray examinations. The technique makes it possible to examine the condition of the nasopharynx, larynx and paranasal sinuses through the nasal passages or a puncture made using a trocar. You can get an enlarged image from different angles.
The examination lasts only a few minutes. Then the sick patient can go home straight away. An endoscope is a device equipped with a flexible or rigid tube. Its thickness is no more than four millimeters. At one end there is a camera with a flashlight, and at the other end there is an eyepiece. The endovideo camera records the smallest formations in the most poorly visible and inaccessible places.
In the early stages, it is usually impossible to make a diagnosis using other methods. The degree of camera magnification makes it possible to distinguish initial tissue changes. A manipulator built into the endoscope allows you to bite off a piece of tissue for a biopsy. followed by microscopy of the biopsy specimen.
The use of modern endoscopic devices in the examination of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses is a new level in identifying diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Endoscopic methods allow not only to detect diseases, but also to perform therapeutic procedures.