Diseases that begin with the letter "P": Panaritium, Panaritium, Panic attack, Pancreatitis, Papillomas, Paralysis, Bell's palsy, Paranoia, Paraproctitis, Facial nerve paresis, Periodontitis, Periodontal disease, Paroxysm, Paroxysmal tachycardia, Scab (favus), Pediculosis, Torsion of the spermatic cord, Bone fracture, Fractured ribs, Fracture of the femoral neck, Post-term pregnancy
A rib fracture is understood as a destructive change in the chest caused by external factors and circumstances. In children, such fractures are extremely rare, since the level of elasticity of bone structures is quite high compared to older people.
Causes of rib fractures
The causes of rib fractures can be external mechanical influences with different pressure forces. Basically, a rib fracture can be caused by the following factors:
- chest injury as a result of a traffic accident;
- chest injury during sports;
- severe blow with a blunt object to the chest area;
- falling from height;
- applying symmetrical pressure on the body with objects from both sides.
In road traffic accidents, the driver’s chest is often damaged, since during a collision or sudden braking at high speed there is a strong impact on the steering wheel. In such a situation, the bones in the area of the subclavian artery often break. If a pedestrian's chest is struck in an accident, multiple fractures are usually diagnosed.
The severity of injury from a fall depends on the speed of the fall and the properties of the surface on which the victim lands.
In addition, it is possible to break the ribs of the chest with minimal use of force. The reasons for this lie in the patient having the following diseases that reduce the elasticity of the bone structures of the sternum:
- presence of primary bone marrow and tissue tumors;
- rheumatoid type arthritis;
- the presence of metastases in the bones;
- osteoporosis;
- congenital abnormal development of the chest or pathological absence of a rib.
What is a rib x-ray?
Content:
- What is a rib x-ray?
- Features of the study
- X-ray for a fracture
- Indications for the study
- Preparation for the procedure
An X-ray is a test that uses small amounts of radioactive radiation to produce images that allow doctors to view the inside of the body. The exposure level is considered safe for adults. However, this method is not considered safe for the developing fetus, so it is very important that the pregnant patient informs the doctor about her pregnancy before undergoing X-ray diagnostics.
X-rays pass through skin and soft tissue, but do not pass through bone or metal. Because different tissues in the body absorb different amounts of radiation, images will show different shades of black and white.
One of the most common uses of x-rays is to check for bone damage after an accident, as well as in many other circumstances.
Radiography is used to identify, diagnose and treat many types of diseases. This is a basic type of diagnosis, and is often performed during the patient’s first visit.
Symptoms
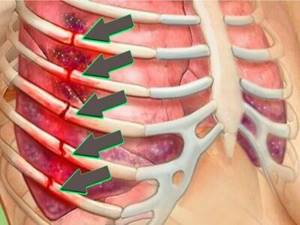
If you suspect a chest injury, it is important to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Symptoms of damage to one or more ribs are as follows:
- Severe pain in the area where the bone structure is damaged. Bone and bone particles can irritate nerve endings and also damage muscle tissue.
- Adopting a certain posture to reduce pain. As a rule, the victim sits bent over or presses his chest, which reduces the frequency of the respiratory reflex.
- Possibility of tactile identification of a fracture.
- Coughing, sneezing, deep breathing and speech provoke increased pain.
- Swelling of the area of the sternum that received the blow. Swelling may appear and a hematoma will be noticeable.
- Only frequent and shallow breathing is possible.
- Inability to take a slow, deep breath due to severe and sharp pain.
- Open wounds.
- External deformation and change in the structure of the chest, that is, on the side of the damage you can see a small depression or depression.
- An unusual sound appears when moving.
X-ray for a fracture
Rib fractures are a common consequence of trauma and can cause life-threatening complications. Ribs 4-10 are the most susceptible to fracture. Fractures of the 1st to 3rd ribs are associated with trauma that involves high-energy force.
When a rib is cracked twice, a "dangling rib" is a loose crack fragment, and when three or more adjacent dangling ribs are present, it can make breathing very difficult.
Etiology of rib fractures:
- blunt and penetrating trauma: for example, road traffic accidents, falls, assaults;
- pathological fractures;
- stress fractures: more common in athletes;
- cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR);
- skeletal dysplasia;
Rib fractures are often associated with other injuries, and the greater the number of fractures, the greater the likelihood of brachial plexus injuries or damage to the infraclavicular part of the plexus (fractures of the 1st-3rd rib), pneumothorax/hemothorax, injury, pulmonary hernia, liver injury, kidney injury and spleen (fractures of the 10-12th rib).
In addition to the immediate traumatic complications described above, complications such as atelectasis and pneumonia can develop mainly due to weak respiratory movements caused by pain, leading to increased morbidity and mortality due to rib fractures.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the chest is carried out to distinguish a fracture from a bruise. A traumatologist deals with this issue. To make an accurate diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Visual examination of the victim using tapping and listening to the chest. The doctor tries to determine whether there are accumulations of air, blood and other fluid in the lungs and pleural area.
- X-ray.
- Computed tomography or ultrasound diagnostics.
Preparation for the procedure

X-rays of the ribs and chest require minimal preparation. It consists in the fact that the day before the procedure the patient must exclude from the diet foods that cause excessive gas formation in the intestines. This is necessary because a swollen intestine can lift the diaphragm and put pressure on the lungs.
Immediately before the x-ray, you need to remove your outer clothing, all jewelry, and accessories so that there are no extraneous stains on the image of your ribs when developed. It is better to put long hair up so that it does not fall into the shooting area.
To protect the lower part of the body, which does not fall into the study area, the patient is put on a special lead apron, which will prevent the penetration of ionizing radiation.
Treatment methods
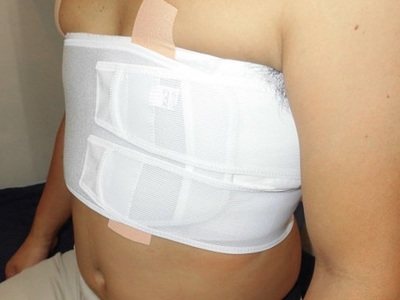
When a victim seeks medical help, first of all, doctors give an anesthetic injection. The most commonly used is 2% Promedol. If transportation to the hospital is required, the chest is tightly bandaged.
The treatment of fractured thoracic ribs itself consists of the following procedures:
- Injection of local anesthetic into the damaged area. The most commonly used is Novocain. After the anesthetic wears off, it is re-administered.
- Applying a bandage or plaster corset to the rib area. Thus, pain is reduced and breathing is normalized by switching to the abdominal type.
- If a patient is admitted to the hospital with a bilateral fracture, then plates may be installed. This is done in order to keep the bones in the right condition for further proper fusion.
Treatment for rib injuries does not involve bed rest. The patient needs to sit more often, practice breathing exercises and exercises. However, physical activity should be excluded.
In terms of the use of medications, the patient may be prescribed the following drugs: Nimesil, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Morphine. If there is congestion and pneumonia of the pulmonary tract, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial drugs (for example, Amoxiclav).
If the chest is damaged in particularly difficult cases, the patient will be prescribed surgical intervention:
- Treating an open wound. The surgeon cleans the wound, removes dead pieces of tissue, ligates ruptured blood vessels and administers an antibiotic.
- Pneumothorax. Excess oxygen is removed by inserting a medical tube connected to a vacuum pump.
- Hemothorax. A medical tube is inserted into the pleural cavity to remove excess blood.
- Abdominal surgery is performed in the presence of internal bleeding or damage to internal organs.
- In case of severe destruction of bone fragments, the surgeon compares them and fixes them for further fusion.
- If there is a foreign object in the chest, open surgery is also performed.
The healing time of broken ribs depends on several factors:
- age of the injured patient;
- number of broken ribs;
- timeliness of medical care;
- the presence of fragments and the degree of bone displacement;
- general health and medical history of the patient.
Under standard conditions, in an adult patient, the ribs can grow together in 3-5 weeks, and in a child – in 2-3 weeks. Complete rehabilitation and full restoration of physical capabilities occurs within 2 months.
Nutrition
It is important to include foods high in calcium in your regular diet if you have a rib fracture. The following products are suitable: salmon, milk, yogurt, sour cream, homemade cheese, tofu, herbs, almonds, oatmeal, oranges.
Features of the study
Features of the study include:
- the chin should not cast a shadow on the photo;
- it is important to minimize the overlap of the boundaries of the scapula with the lung fields;
- the collarbones should be in the same horizontal plane;
- the vascular pattern of the lungs should be clearly visible.
- the patient is directly in front of the X-ray tube, the back resting on the vertical detector;
- the chin is raised so as to be outside the image field;
- hands are placed on the patient's sides
Health risks from rib fractures
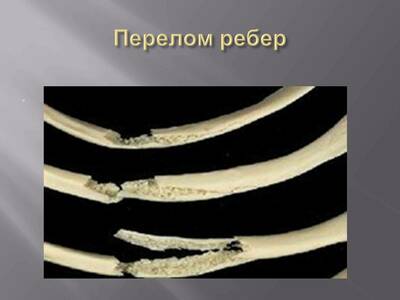
Multiple rib fractures pose a serious health hazard, as this can cause the following conditions:
- pleuropulmonary shock;
- the likelihood of damage to internal organs and the respiratory system;
- impaired ability to breathe independently;
- the occurrence of stagnation and accumulation of fluid in the lungs;
- development of post-traumatic pneumonia;
- penetration of fragments of bone structures into the heart and large blood vessels.
Indications for the study
X-rays of the ribs are used for a variety of reasons. The doctor may order an x-ray to rule out cancerous formations in different parts of the chest, in the area of the ribs.

X-rays are used to examine a part of the body in which the patient is experiencing pain, swelling, or other complaints that require a visual examination of the organs.
X-rays can help your doctor find the cause of problems. X-rays of the ribs can be used to diagnose the disease, monitor the course of the disease, determine a treatment plan, as well as dynamic changes during treatment. Doctors use this method to detect foreign objects in the chest. X-rays can diagnose conditions affecting the lungs, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, emphysema, or lung cancer.
This diagnostic method can be used to diagnose symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, persistent cough or chest pain. X-rays of the ribs can detect breast tumors. X-rays may reveal an enlarged heart, a sign of congestive heart failure.
A chest X-ray may detect cancer, infection, or air accumulation in the space around the lung (pneumothorax). It may also show chronic lung diseases such as emphysema or fibrosis, as well as complications associated with these conditions.
A chest x-ray may show changes or problems in the lungs that are due to heart problems. For example, fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema) may result from congestive heart failure.
Heart size and configuration. Changes in the size and shape of the heart may indicate heart failure, fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion), or problems with the heart valves.
Blood vessels. Because X-rays show the outline of large vessels near the heart—the aorta and the pulmonary arteries and veins—they can reveal aortic aneurysms, other blood vessel problems, or congenital heart defects.
A chest x-ray can detect the presence of calcium in the heart or blood vessels. Its presence may indicate damage to the heart valves, coronary arteries, heart muscle, or the protective sac that surrounds the heart. Calcium deposits in the lungs most often occur from an old, resolved infection.
Fractures. Fractures of the ribs or spine or other bone problems can be seen on a chest x-ray.
Postoperative changes. A chest x-ray is useful for monitoring recovery after surgery on the chest, such as the heart, lungs, or esophagus. The doctor may look at any lines or tubes that were placed during surgery to rule out any post-operative complications.
Pacemaker, defibrillator, or catheter. Pacemakers and defibrillators have wires attached to the heart to make sure the heart rhythm is normal. Catheters are small tubes used to deliver medications or for dialysis. A chest x-ray is usually taken after such medical devices are placed to ensure everything is in place correctly.
A rib x-ray is essentially an x-ray of the chest that allows you to visualize the heart, lungs, blood vessels, airways, bones of the chest and spine. A chest X-ray may also detect fluid in the lungs or tissues surrounding the lungs.
If a patient goes to the doctor or emergency room with chest pain, chest injury, or shortness of breath, they will usually be sent for a chest X-ray. A chest x-ray helps a doctor determine whether a patient has heart problems, pneumonia, broken ribs, emphysema, cancer, or any other disease.
A chest x-ray is a common way to diagnose the disease. But it can also be used to determine whether a certain treatment is working. Some people have a series of chest X-rays taken over time to track whether a health problem is improving or worsening.
A chest x-ray is a common type of examination. A chest X-ray is often among the first procedures a patient will undergo if a doctor suspects they have heart or lung disease. It can also be used to check how a patient is responding to treatment.
Causes
Any impact can provoke a fracture, such as a direct blow aimed at the ribs or a fall; in addition, excessive compression of the chest area can be a possible cause. The most common type of fracture is a fracture within the area of greatest bending, that is, along the lateral surfaces of the chest.
Pathological rib fractures can also occur in the presence of the following concomitant ailments:
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is a common connective tissue disease that affects internal organs, bones and joints. Rib fractures are the most common
- Metastases of malignant tumors in bones. Most malignant tumors are capable of metastasizing - forming a tumor focus distant from the original localization of the pathological process due to the migration of cancer cells with the blood or lymph flow. Metastasis to the bones of the chest can occur with the development of prostate cancer, breast cancer, kidney cancer and some other organs. In a metastatic focus, the structure and function of the bone are disrupted, and normal tissue is replaced by pathological tissue. This causes the bone to weaken significantly and lose its resistance to external stimuli.
- Primary tumors of bone tissue or bone marrow. When cancer occurs in the bone or bone marrow, which is found in the structure of most bones, the nutrition and function of the bone is disrupted.
- Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a pathological condition in which, for some reason, the functional and structural properties of bones are disrupted, which undergo a number of changes and become more fragile. In most cases, this pathology is associated with impaired calcium metabolism, hormonal disorders, and genetic abnormalities. Osteoporosis often develops in old age, thereby representing one of the forms of physiological aging of bones.
- Congenital or acquired absence of the sternum. For the normal functioning of the chest, its anatomical integrity is necessary. In the absence of the sternum, the element that holds the anterior ends of the ribs together, the chest becomes much less resistant to mechanical stress. The sternum may be absent due to congenital anomalies or after certain surgical interventions.
- Genetic abnormalities of skeletal development. Some genetic abnormalities are accompanied by inadequate development of skeletal structures, which leads to bones becoming more fragile and breaking even under the influence of relatively small forces.
Research methodology
An X-ray of the ribs is prescribed by a traumatologist after the initial examination. Next, the patient is sent to the radiography room, where the procedure is performed based on the following rules:
- During the examination, the patient should not have objects containing metal with him. This hinders the acquisition of clear images and makes it difficult for the traumatologist to study the finished data.
- The chest must be pressed against the X-ray screen, and the image itself is taken while holding the breath. At the doctor's request, several images can be taken in different projections.
- To obtain a picture of the anterior ribs, it is necessary to take an x-ray from the side of the abdomen. The posterior sections of the ribs will be visible in the image if the X-ray machine captures an image from the patient’s back. The lateral projection of the ribs is removed from the side - the person additionally raises his arms up.
- Oblique projections are obtained when taking the picture in a supine position. They are somewhat more difficult to perform, since the patient’s body must be fixed in an atypical position.
A medical apron is provided in the radiography room and is used to protect the body from radiation. The photo itself will be ready within 15 minutes.
X-rays of the ribs can be performed in a medical office. It has all the necessary equipment and qualified doctors. And the prices are quite affordable compared to other competitors.
Contraindications
X-rays of the ribs are not recommended for pregnant women. At this stage, such a study should be abandoned, choosing an alternative diagnostic option - ultrasound, MRI or CT. Ionizing radiation can become a prerequisite for miscarriage or the development of radiation sickness in a baby. Also, X-rays are undesirable during the feeding period of the child. The radiation used in diagnosis can affect hormonal levels, which will cause problems with milk production.
X-rays of the ribs should not be prescribed to those people who are in serious condition. The study may have a negative impact on the recovery phase. Ultrasound is most often prescribed as an alternative diagnosis. For children under 15 years of age, chest x-rays can be prescribed only in the most extreme cases, since ionizing radiation affects the formation of the supporting skeleton.