Destruction of the root or tooth enamel during breastfeeding is quite common. And mothers are tormented by doubt: to go or not to go to the doctor. Doubts are well founded, since there is a fear of dental infection entering breast milk, but anesthesia and x-rays do not inspire confidence.
First of all, it is necessary to destroy the myth that X-rays have a harmful effect on breast milk. Firstly, during X-ray monitoring, a lead apron is put on the nursing mother’s body, which does not allow X-ray rays to pass through. Secondly, especially suspicious girls can refuse x-rays and use a new examination method - a radiovisiograph (recommended during pregnancy and lactation).
As for anesthesia, you should warn the dentist that the patient is a nursing mother. For breastfeeding, anesthesia is prescribed that does not penetrate into the blood, and, therefore, into breast milk. Thus, it is obvious that tooth extraction during lactation is absolutely safe for the child.
Fluorography and radiography
Fluorography and radiography are methods of radiographic examination. Fluorography is often used for mass, routine screening of tuberculosis.
Nowadays digital fluorography is mainly used . Film fluorography is an outdated research method. Digital fluorography has a lower radiation exposure to a person, but at the same time its resolution (that is, the ability to transmit a real image) is lower in comparison with x-rays of the lungs in direct projection.
X-rays contain more information and pathological changes are more clearly visible.
The radiation exposure is low for both methods (digital devices have lower radiation exposure).
What types of X-ray diagnostics are used in dentistry?
The main types of images obtained during x-ray photography of the dental system:
- Sighting. Provides information about the condition of one or more teeth and adjacent tissues. This helps the specialist assess the condition of dentin, root canals, periodontium, and blood vessels.
- Panoramic (OPTG, orthopantomogram). It is a detailed flat image of the jaws, teeth, joints, and sinuses. This image helps to detect carious areas, defects in fillings, impacted teeth, and cysts. And also draw up a correct plan for implantation, prosthetics, and treatment.
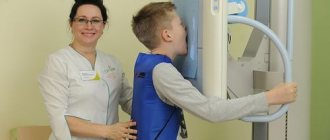
- Occlusal. This is the so-called bite radiography, which is often used when examining children, as well as when it is impossible to obtain clear results using targeted radiography.
In addition, photographs can be film or digital, when the resulting image is transmitted using a special sensor to a computer monitor. In the second case, the study is called radiovisiography.
X-ray and breastfeeding
Modern scientific research proves that there is no reason why a nursing mother should wean her baby off breast milk for some time due to X-rays.
Breastfeeding is NOT a CONTRAINDICATION for x-rays of any area of your body.
CT and MRI are also not contraindicated during breastfeeding.
If a contrast agent is administered, it is necessary to decide individually whether a particular contrast agent is compatible with breastfeeding. Mostly gadolinium-based contrast agents are used.
According to the website e-lactancia.org, X-ray examinations and gadolinium-based contrast agents are in the green (permitted) zone.
- X-ray does not affect the quality, quantity and taste of milk.
- There is no need to pump either before or after!
- There is no need to wean the baby from the breast after the X-ray examination. ⠀
X-ray is a short-term procedure (lasts a few seconds). The effect of radiation on the body stops immediately after the end of the procedure, the rays do not accumulate in it and radioactive substances are not formed.
Breast milk is not exposed to the negative effects of X-rays and its composition does not change.
Remember that any procedure must be justified and performed according to indications. Don't put off getting an X-ray if you need it! Late diagnosis worsens the prognosis of the disease!
More information: X-ray during pregnancy
Source:
Mohrbacher N., Stock J., La Leche League International, The Breastfeeding Answer Book, Third Revised Edition, 2008
Author: Tatyana Neeshpapa, @doctor_neeshpapa
Similar
Why does a dentist refer a patient for dental x-rays?
An x-ray gives the doctor the opportunity to most accurately assess the condition of the problem unit or all organs of the oral cavity. And also study the clinical picture in detail. In particular:
- detect foci of inflammation that have not yet manifested themselves;
- identify neoplasms in the bone and soft tissues of the dental system;
- establish the signs and stage of development of periodontitis or periodontal disease;
- establish linear dimensions, volume, structure of bone tissue before implantation;
- more accurately assess the correctness of occlusion (tight closure of the dentition);
- detect anomalies of the dental system organs;
- determine the position of erupting wisdom teeth.
As a rule, radiography is prescribed before the start of orthodontic treatment, when planning implantation and prosthetics, before and after filling the tooth canals. This study is also used to evaluate the results of conservative and surgical treatment.
Free consultation
30-40 minutes
inspection and diagnostics
treatment plan and cost
Make an appointment
Are there any contraindications to X-ray examination?
Dental X-rays are not performed on patients with severe bleeding in the mouth, or those who are unconscious or in critical condition.
Pregnancy is considered a relative contraindication. In this condition, women should not undergo dental procedures involving radiation until 4-5 months. But in each individual case, the expectant mother needs to personally consult a doctor, since situations are different.
A breastfeeding woman can undergo an X-ray examination. But it is advisable to resort to digital methods and skip one or two feedings after the session.
Are dental x-rays safe for human health?
In accordance with SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03, the maximum permissible annual radiation dose during diagnostic x-ray procedures is 1000 μSv (microsievert) for an adult and 300-400 μSv for a child.
To receive it, within a year you must complete:
- 500 targeted dental examinations using a radiovisiograph;
- 100 procedures of conventional x-rays with image output on film;
- 80 digital or 40 film orthopantomographies (obtaining a panoramic image).
Thus, dental X-rays for almost any purpose do not exceed the permissible doses. Therefore, it does not have a negative effect on health. Even when producing film OPTG, the radiation dose is a maximum of 30 μSv. If it is necessary to take a targeted X-ray of the teeth and use radiovisiography, you can even get several images during one appointment. Without any risk to health, since a single dose in this case is only 2-3 μSv.
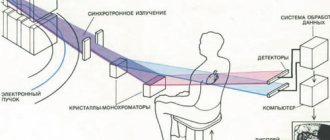
Impact of X-rays on the human body
Modern medicine often resorts to x-ray examinations. They are widely used to obtain detailed information about internal health problems such as diseases of the musculoskeletal system and internal organs. Experts say that X-ray examination is not at all dangerous when used rationally. During such a procedure, the human body receives a tiny dose of radiation, the benefits of which largely outweigh the possible risks.
It has been proven that the body experiences quite a lot of X-ray-like effects every day. However, his immune system neutralizes their harmful destructive effect. The softest X-ray radiation is used when undergoing fluorography, which is so important during the period of rising incidence of tuberculosis. In this regard, there is no particular reason to doubt whether it is possible to do fg while breastfeeding.
A real health hazard from X-rays arises only in the case of powerful, unregulated exposure. Doctors say that the real probability of causing harm to the body from undergoing an x-ray is normally no more than 0.001%. Such figures can reassure even particularly suspicious patients.
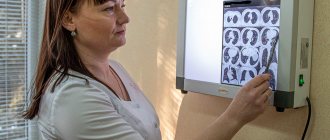
How is dental x-ray examination performed?
The photo is taken in a special room with lead-protected walls and floors. The doctor asks the patient to remove metal jewelry and accessories, as they may distort the results of the study. The vital organs of the body are protected by an apron with lead inserts. Features of the study depend on the method used.
When receiving a targeted image, the doctor directs an x-ray beam to the area of the jaw being examined from the side of the face or to an area of the oral cavity. An orthopantomogram is obtained in a different way. The patient fixes his head in a special device, grabs the plate in a disposable cover with his teeth and remains motionless while the mobile part of the device makes a full revolution around the head.
Dental problems after childbirth
It should be noted that it is during the postpartum period that many women begin to notice that the condition of their teeth has worsened. There is such a popular expression “teeth flew”, which describes how quickly dental problems arise in young mothers. And this is along with the fact that severe hair loss also begins, and sometimes skin problems.
Dental problems after childbirth are common
Indeed, such unpleasant changes are not uncommon. During lactation, the female body is significantly depleted - reserves of calcium, various vitamins and minerals are spent first on carrying a child and then on feeding him. This is why dental pathologies arise – caries, gum disease.
Usually the problem is noticeable already during pregnancy. But for some irrational reasons, expectant mothers are in no hurry to treat their teeth, postponing this moment until later. Meanwhile, if pregnancy gingivitis, serious gum inflammation, and the risk of premature birth are not treated, the risk of premature birth increases significantly. Therefore, teeth and gums can be treated during pregnancy; the most favorable period is the second trimester.
The hypertrophied form of gingivitis affects all gums
It has been noted that untreated teeth during pregnancy, a predisposition to dental problems, bleeding gums - all this around the middle of lactation becomes an imminent threat of urgent treatment. And in order not to lead to the removal of teeth or the formation of large carious cavities, you need to go to the doctor, without fear of either the treatment itself or anesthesia.
Is it possible to visit the dentist during breastfeeding?
Often women encounter dental problems even during pregnancy, this is due to the fact that all valuable microelements are spent on the formation and development of the fetus, and calcium deficiency begins in the mother’s body. Lactation continues to aggravate the situation, but the woman is afraid to go to the dentist so as not to harm the child. In fact, it is not only possible to treat teeth, but also necessary! Here are several reasons for this.
Constant pain affects a person’s psycho-emotional state. The mother becomes nervous and irritable, which can directly affect the amount of milk, up to its complete disappearance.
Komarovsky's opinion
The famous pediatrician Evgeniy Olegovich also touched upon the topic of dental treatment during pregnancy and lactation. He is sure that if the mother took insufficient amounts of calcium-containing medications, then the dental problem will worsen during lactation.
It is necessary to treat teeth, especially if a woman is overcome by severe pain, it promotes the production of adrenaline, which can adversely affect the fetus and the availability of milk. Komarovsky also draws attention to the need to inform your attending physician about your situation.
Indications for orthopantomogram
An orthopantomogram (or “OPTG”, “panoramic image of the dental system”) is one of the types of diagnostic radiography. In dentistry, OPTG is of key importance - many types of treatment cannot be started without this diagnostic method.
Method of performing an orthopantomogram:
Technically, it is carried out as follows: the beam source (X-ray tube) and its receiver (film or digital sensor" move around the object under study in opposite directions. As a result, a very limited part of the object of study is in focus, everything else is blurred. Panoramic views are made photographs using orthopantomographs.The volume of radiation is such that panoramic photographs can be taken every day for a month without significant harm to health.
Before the procedure, the patient is put on a special lead apron to protect him from unwanted exposure to X-rays. An orthopantogram is performed from a standing position. A disposable cover is put on a special tube. The tube is clamped by the patient himself with his front teeth. The X-ray tube will rotate around the patient's head for a few seconds. Information from the sensor will be sent to a computer, corrected using special programs, and then this image can be printed on paper or film, and also saved in digital format. No other preparation is required.
Contraindications: first and second trimester of pregnancy, lactation.
How often can I have x-rays?
A diagnostic x-ray is prescribed by the attending physician in case of suspicion of the presence of any disease, in order to confirm or refute them. SanPiNom limits are not established in such cases; radiation examination in this case is dictated by vital indications.
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to undergo a chest x-ray (fluorography) once a year, and a breast examination (mammography) once every two years. In medicine, the maximum permissible radiation dose is 1 mSv/year.