CT angiography of the vessels of the lower extremities is a non-invasive method that allows you to obtain detailed visualization of the arteries and veins of the legs. Thanks to the procedure, the doctor can comprehensively assess the condition of the blood vessels in the area under study and detect pathological processes at an early stage, including:
- congenital anomalies;
- lack of cross-country ability;
- atherosclerosis of arteries
Also, varicose veins are usually accompanied by pain and discomfort in the lower extremities. Before prescribing laser vein removal, it is necessary to carefully consider their condition.
Angiography is always performed using contrast to obtain a high-quality result.
Advantages
- Low radiation exposure (due to the use of latest generation equipment).
- The duration of the study is 20 minutes.
- Very high information content.
- Opportunity to conduct research any day of the week, from morning to evening.
- A modern device designed for patients of different sizes.
- Qualified doctors of the first and highest categories; candidates of sciences also work in medicine.
- The conclusion for each examination must be checked by the chief physician.
What does a CT scan of the lower extremities show?
Computed tomography is a non-invasive study that uses X-rays to obtain cross-sectional images and create a three-dimensional model of the circulatory system or organs. Typically, a CT scan of the lower extremities is performed using contrast to assess the condition of the vessels of the legs; this examination is also called CT angiography.
This method allows doctors to examine in detail all changes in large arteries and small vessels. At the same time, the risk of adverse effects due to radiation exposure is minimal.
Indications
A doctor may recommend a CT scan of the lower extremities in the following situations:
- swelling of the legs;
- numbness and pain;
- varicose veins;
- hematomas;
- loss of sensation;
- vascular damage due to injury;
- suspicion of arterial disease, characterized by blockage of the vessel;
- problems with blood circulation in the feet, for example, with diabetes;
- pathology of arteries and veins.
CT angiography is also used in preparation for surgical interventions and to assess the effect of the therapy received.
What does a CT scan show?
Thanks to cross-sectional images, specialists can use images to identify and enlarge pathological areas for more detailed study. As part of the examination, doctors will be able to determine:
- thrombosis;
- chronic venous insufficiency;
- atherosclerosis;
- aneurysms of various origins;
- vascular development abnormalities;
- phlebeurysm;
- angiopathy;
- acute form of arterial thrombosis;
- tumors;
- Tayakasu disease;
- rheumatic vascular lesions;
- phlebothrombosis.
How is the procedure performed?
CT scan of the lower extremities is performed with contrast. To do this, an iodine-containing drug is injected into a vein during the study, which accumulates in the circulatory system, which allows for improved visualization.
The procedure takes only 15-25 minutes. During this period, it is important to remain still so that the pictures are clear.
The examination takes place in a special room, and the doctor monitors the progress of the diagnosis through a special window. First, the specialist will help the patient lie down on a mobile table and fix the limb. When scanning begins, the frame will begin to rotate around the desired area, taking pictures.
During the tomography or before it begins, an intravenous injection is given, which may be accompanied by a feeling of heat, nausea and a metallic taste in the mouth; these side effects quickly disappear.
The images obtained during the CT scan are interpreted by a radiologist or attending physician.
Tomography is carried out in two directions - CT of veins and CT of arteries, so pay attention to what kind of research you need so that unforeseen situations do not arise later.
Get a CT angiography of the leg in St. Petersburg
Computed angiography of the leg can be done at Medical in St. Petersburg. The procedure helps in identifying pathologies and prevents the development of serious diseases. The diagnostic cost includes:
- Examination using an expert-class computed tomograph Aquilion Lightning TSX-035A (Canon Japan).
- A detailed, comprehensive conclusion made based on the images by a highly qualified radiologist. The description of the study is checked by the chief physician.
- 24/7 access to your personal account to view all your research and conclusions
- Internal research quality control
- 100% guarantee of photo quality
- Detailed information about prices can be found in the “Prices” section.
- You can find out about the benefits and ongoing promotions in the “Promotions” section.
Positive qualities of CT scan of legs
This study is prescribed in cases where doctors want to clarify the results of various non-invasive studies, such as ultrasound, Doppler sonography, and so on. The main positive quality of a CT scan of the legs is its high information content and the ability to obtain a complete picture of the condition of the lower extremities, including visualization of soft tissues, vascular bed, skeletal system and much more. Moreover, this study is non-invasive, that is, it takes place without traumatizing or compromising the integrity of the skin. At the same time, CT scan of the legs provides complete information about the vessels of the lower extremities.
Preparation for the procedure
If the study is performed without contrast, no special preparation is needed. You will need comfortable clothing without metal objects. When conducting a contrast study, a biochemical blood test for creatinine and urea is first performed. A few hours before the procedure, it is not recommended to eat; a light breakfast or dinner is allowed.
The method is based on obtaining layer-by-layer images by irradiating the study area with X-rays. In our clinic, the study is carried out using modern equipment that reduces radiation exposure. According to indications, the study can be carried out several times a year.
5. Why should a CT scan be done at the State Clinical Hospital named after. S.P.Botkina
At the Botkin Hospital, CT and MSCT examinations are carried out in the radiology department. The department has at its disposal five modern multispiral multislice computed tomographs, including those from Philips and Toshiba, with a capacity of 128 and 160 slices.
There are 17 doctors in the radiology department, of whom one is a professor, 2 doctors of medical sciences, 5 candidates of medical sciences, 11 doctors of the highest qualification category, 3 doctors of the first category, 14 x-ray technicians of the highest category, one of the first and two of the second category. A number of employees underwent internships in Germany, Austria, and Israel. The head of the department is a specialist of the year in radiation diagnostics, laureate of the “Formula of Life” competition, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Andrei Vladimirovich Arablinsky, a doctor of the highest qualification category with 32 years of experience. When you contact the Botkin Hospital, we guarantee you an accurate and reliable research result.
Veterans of labor and disabled people of groups 1 and 2 are provided with a 10 percent discount on the computed tomography procedure.
6. CT scan with contrast (CT angiography)
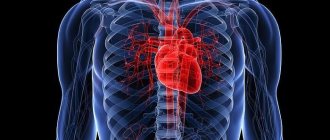
Along with routine studies of the brain, lungs, and abdominal cavity, the Botkin Hospital performs CT scans with bolus contrast enhancement in patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system, including dynamic monitoring of patients after coronary artery bypass surgery, angioplasty and coronary stenting arteries.
CT diagnostics using a contrast agent is carried out to increase information content. Such a study allows the doctor to clearly see blood vessels or hollow organs, and detect even very small tumors, hematomas or blood clots. CT with contrast is prescribed to identify cardiovascular pathologies and clarify the location and size of tumors.
For contrast studies, a relatively recent (no more than 2 months old) biochemical blood test (creatinine, urea, glucose) is required. In addition, an allergy to iodine or a polyvalent allergy is a contraindication for contrast studies.
7. Indications for CT scan by organ
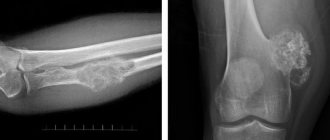
- A CT scan of the head (skull) is necessary for skull fractures or severe bruises. The examination will clearly show the picture of the fractures, the condition of the brain and the need for further operations.
- A CT scan of the nose and larynx will help determine inflammation of the tear ducts, tumors, and identify chronic sinusitis.
- A CT scan of the brain allows the doctor to diagnose hemorrhagic strokes, clarify the presence and/or location of hematomas, hemorrhages, and identify even small tumors of the brain and meninges, and vascular pathologies. In diseases of the brain, CT is promising in examining patients with vascular aneurysms and malformations.
- A CT scan of the chest cavity is prescribed to diagnose pathological changes and neoplasms that affect the bronchi, lungs, heart (including pericardium), esophagus, and mammary glands.
- A CT scan of the lungs will make it possible to detect various pathologies at an early stage: pneumonia, tumors, and clarify doubtful cases of “pulmonary emphysema.”
- An abdominal CT scan will reveal pancreatitis, cysts, appendicitis, other inflammations, blood clots, fluid accumulation, pathologies of the liver (in addition to the usual data on tissue density and neoplasms, CT will allow you to evaluate the iron content in it), spleen, and adrenal glands.
- CT scan of the intestine is considered one of the most gentle, but most effective diagnostic methods for problems with this digestive organ.
- CT scan of the spine (cervical, thoracic, lumbar) allows you to clarify or remove suspicions of osteoporosis, osteochondrosis, hernia, scoliosis. A CT scan of the spine is prescribed in complex cases when an X-ray examination is not enough to fully clarify the problem.
- A CT scan of the knee, hip, and shoulder joints will help determine the causes of pain during movement, the presence of fluid in the joint, arthritis or arthrosis, and identify the degree of degenerative changes in the joint.
- The capabilities of multislice CT are widely used in urological patients , namely, with suspected prostate tumors and vascular diseases of the kidneys, as well as with tumors of the pancreas and liver. CT scan of the urinary tract, CT scan of the kidneys.
8. How to prepare for research
The CT scan procedure does not require any special preparation from the patient. Only when examining certain areas, for example, the abdominal cavity, you need to give up certain foods a few days before, and follow a strict diet a few hours before. Most importantly, before the procedure, the doctor must know about all the diseases and medications that you are taking.
9. How the procedure works
A CT examination takes from one to 30 minutes (depending on the area of the body, the method and the power of the tomograph). All this time, the patient lies on a special table inside the tomograph, without moving. This is necessary in order to obtain accurate data. The capsule is closed, but well lit, there is ventilation. The doctor is in touch with the patient and gives him instructions on holding his breath. Sometimes it is suggested to fix the patient’s arms and legs to prevent involuntary movements.
10. Contraindications to CT
Unnecessarily, CT is not prescribed to young children, pregnant women, or patients with a general serious condition. Claustrophobia or increased physical activity are also contraindications, since during the examination the patient must lie motionless for some time inside the device. However, the Botkin Hospital has an open tomograph that will solve this problem.
Note that computed tomography can be performed on patients with pacemakers and implants - this is not a contraindication, as is the case with magnetic resonance imaging.
Also, a patient’s weight of more than 130 kilograms can become an obstacle - most tomograph models are designed for a lower weight of the subject. However, there are several models with a limit of up to 200 kg.
A contraindication for CT examination with contrast would be an allergy to iodine or a polyvalent allergy.
11. Ask a question
Would you like to make an appointment for a CT scan? Do you have any questions? Don't know what to choose? Call the Botkin Hospital contact center by phone. We will help you!
Interpretation of CT scan of the arteries of the upper extremities
As a rule, diagnostic data is immediately handed over to the patient for transfer to the attending physician. Although computed tomography is more expensive than a conventional ultrasound or x-ray, it provides much more detailed data. Clear visualization of small arteries, veins and even capillaries allows the attending physician to recognize pathologies that are not visible using other diagnostic methods, and this is a significant advantage of arterial CT. Diagnostics allows us to identify the following diseases:
- blockage of veins or arteries - during the study, the contrast agent does not spread along the desired path;
- congenital structural anomalies or endarteritis - the lumen of the vessel is seriously reduced;
- varicose veins or aneurysms - CT scans show dilation, protrusion of the walls or excessive tortuosity of the vessels;
- malformations - manifested by excessive branching of veins and arteries, leakage of contrast material into nearby vessels and even lymph nodes.
How is a CT scan performed?
The procedure is carried out in several stages:
- Preparation. The patient enters the office. Before the examination, you need to remove metal objects and lie down on the tomograph table.
- Scanning. During this stage, the tomograph table moves into the tomograph’s working area (gantry) in which the area under study is scanned. Important! The patient should lie still. To increase the information content, CT can be performed with contrast administered into the patient’s body. It allows you to show pathological changes in the scanning area in more detail.
- Diagnosis. From the resulting numerous images, the thickness of which can be less than 1 mm, multiplanar images (in different planes), a volumetric 3D model are created to determine foci of inflammation, injuries, identify and evaluate tumor processes, and better visualize the vascular network. Based on the results of the study, the attending physician can select the optimal treatment method.
Orthopantomography
This type of CT scan is used for:
- detection of dental diseases (including in the early stages);
- assessing the bite, identifying the consequences of injuries;
- assessing the condition of soft and hard tissues of the dental system (gums, teeth, sinuses);
- diagnostics of the condition of the jaw joints;
- assessing the quality of dental treatment (fillings, installation of implants, prosthetics);
Abdominal CT scan
carried out for:
- Diagnosis of tumors of the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, kidneys, ureters.
- Clarification of ultrasound results (differential diagnosis of cysts, hemangiomas, metastases, angiomyolipomas, etc.).
- Detection of stones in the gall bladder, kidneys, ureters and bladder.
- Diagnosis of inflammatory and infectious diseases - abscesses, pancreatitis, diverticulitis.
- Assessment of diseases of the aorta and other vessels - aneurysms, thrombosis and occlusion.
- Rapid diagnosis of internal organ damage during trauma.
- Planning operations and assessing their effectiveness.
- Determining the stage of the tumor, planning and assessing the results of radiation and chemotherapy.
CT angiography with the introduction of a contrast agent allows you to visualize the vessels of the brain, kidneys, pelvis, limbs, lungs, heart, neck, and abdominal cavity.
Indications and contraindications for CT scan of arteries with contrast
Indications
The study is prescribed if the patient complains of the following clinical manifestations:
- pain symptoms localized in the muscle tissue of the arms;
- absence of vascular pulsation;
- feeling of weakness in the upper limbs after physical activity;
- regular sensations of numbness in the hands;
- feeling of chilliness even in warm weather.
The procedure is mandatory for patients who have been diagnosed with:
- narrowing of blood vessels - stenosis;
- the formation of blood clots inside the vessels - thrombosis;
- local expansion of the vessel due to damage to its walls or pathologies - aneurysm;
- a number of pathological diseases of blood vessels or anomalies of their development.
Contraindications
The procedure is not performed on pregnant patients and patients during breastfeeding. It is also not suitable for patients in serious condition, as well as patients who suffer from:
- individual intolerance to the components of contrast agents;
- severe renal and liver failure;
- severe forms of diabetes mellitus;
- multiple myelomas;
- OSN;
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland.