What is this?
FGDS of the stomach is a highly informative diagnostic method that makes it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract through probing. The probe is a long tube equipped at the end with a light source and a small camera that transmits the image to the doctor’s screen. Thanks to this it is possible to:
- Determine the actual amount and size of damage to the stomach wall, as well as the nature and depth of the wound.
- Identify the source of bleeding and eliminate it (gastroscopy allows minor surgical interventions to be performed in parallel with diagnosis).
- To evaluate the effectiveness of prescribed medical therapy for peptic ulcer disease.
- Monitoring the growth and changes of benign neoplasms and timely detection of malignant degeneration.
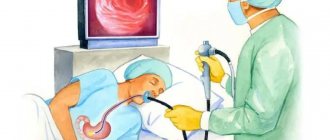
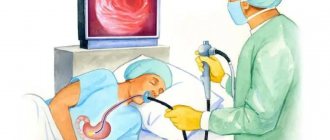
To carry out this diagnostic procedure, the patient must lie on his left side and hold the mouthpiece with his teeth. After this, the doctor inserts an endoscope into his oral cavity, smoothly moving along the esophagus into the stomach cavity, simultaneously examining the surrounding tissues for the presence of any defect. As a rule, no anesthesia is used for this procedure. However, if there are indications or the patient’s personal desire, local and even general anesthesia can be used.
The results of the examination, in most cases, are reported immediately. But if it is necessary to take biological material for additional microscopic examination, the announcement of the diagnosis may be postponed.
FGDS (gastroscopy)
Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (or FGDS) is an instrumental examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a flexible optical endoscope. The endoscope is equipped with a camera, illuminator and a working channel through which probes with forceps are inserted to take a biopsy. FGDS is an informative and safe, although not very pleasant, study for the patient.
How long does gastroscopy (FGDS) last?
The procedure lasts about 5 minutes from the moment the endoscope is inserted. During this time, the doctor manages to take all the necessary photographs of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, as well as perform a biopsy. The examination is carried out under local anesthesia: the gag reflex is weakened and the patient feels only slight discomfort. The whole process, including preparation, takes from 10 to 15 minutes.
When is FGDS performed?
Typically, a gastroenterologist prescribes an FGDS to a patient for the following symptoms:
- Pain in the pit of the stomach after eating
- Frequent heartburn, sour belching
- Vomiting blood
- Attacks of nausea, vomiting
- Frequent feeling of heaviness, fullness in the stomach.
What are the contraindications to FGDS?
- Severe respiratory failure
- Heart rhythm disturbances
- Serious forms of mental illness (eg, advanced Alzheimer's disease)
- Recently suffered a stroke.
Preparation for FGDS and actions after the procedure
- If you are taking aspirin, iron-containing drugs, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, you should stop taking them 2 weeks before FGDS. This is associated with the risk of bleeding.
- Before the procedure, you should not eat for at least 12 hours. A planned study is most often carried out in the morning, so the last meal should be the night before at 18-19 hours.
- After the procedure, you should also refrain from eating and drinking for 1-2 hours.
- You must not smoke on the day of the examination.
- If sedation or anesthesia was used during FGDS, you should not drive on this day.
How is FGDS performed?
During FGDS, the patient lies on his left side, holding a mouthpiece in his teeth. The doctor inserts an endoscope through the mouth and sequentially penetrates the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, examining them. If necessary, the procedure is performed under general or local anesthesia. Diagnostic results are usually communicated to the patient immediately, except in cases where the doctor takes tissue samples for examination.
Meet the endoscopist at Euromed Clinic
Features of FGDS for pregnant women and children
FGDS can be done in pregnant women and children, but its benefits must exceed the expected harm of the study. Pregnant women should not be given the anesthesia used in such cases, and for children during FGDS, anesthesia, on the contrary, is required. During FGDS in young children, surgical anesthesia with artificial ventilation is used, so this study is prescribed to children only when absolutely necessary.
Possible discomfort after FGDS
Common: sore throat, slight numbness, hoarseness. They occur as a result of slight mechanical damage during the passage of a gastroscope. They do not require treatment and go away on their own within 1-3 days. You can alleviate the condition by sucking softening lozenges and warm (but not hot) drinks.
Sometimes: stomach pain. They arise due to air that is pumped into the stomach to smooth out the mucous membrane. They disappear within a few hours after the procedure and do not require treatment.
EGDS or FGDS?
Now in our clinic we carry out the procedure esophagogastroduodenoscopy (or EGDS), it is also called video gastroscopy, which in essence is practically no different from FGDS, but nevertheless has a number of important advantages. And our patients are always interested in the question: what is the difference between them? The fact is that with FGDS, only the stomach and duodenum are examined, while with video gastroscopy (EGDS), the esophagus is also examined.
Moreover, with video gastroscopy, the entire process is recorded on a special camera located in the endoscope. This allows the doctor to visualize the condition of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum on a computer monitor, while controlling the moving camera. There is one more advantage over FGDS: the entire video protocol of the study can be saved, and this makes it possible to confirm the diagnosis and can save the patient from repeating the procedure.
If you have any questions, call us at the clinic’s 24-hour phone number, the contact center specialists will definitely answer them.
Duration of the procedure?
FGDS is done after special preliminary preparation, including diet, giving up bad habits and stopping taking certain medications. As a rule, it is necessary to adhere to these preparatory measures several days before the scheduled day of the diagnostic procedure. This is a mandatory measure to obtain the most informative and accurate data. If we talk directly about gastroscopy, then its duration is approximately 5-10 minutes. This medical procedure is carried out exclusively by a qualified diagnostician in a specially equipped office with the necessary amount of endoscopic equipment.
This time is enough to assess the condition of the esophagus and gastric wall. If it is necessary to perform a biopsy (taking biomaterial for further microscopic examination) or obtain images, the duration of diagnosis may increase. Since FGDS involves swallowing and further advancement of the probe, some patients may experience discomfort and activation of the gag reflex. To prevent unwanted effects or pain, local anesthesia may be used. Taking into account pain relief, the procedure takes about 15-20 minutes.
.
Is there an alternative to FGDS?
There is no complete alternative to this study. Ultrasound, x-rays and other methods provide only partial information about the functioning of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum. There is currently no more informative and safe method than FGDS.
With proper preparation and adequate behavior during the procedure, FGDS is as painless as possible. The fears and horror stories of patients who have undergone the procedure are due to a lack of proper preparation and failure to follow the doctor's instructions.
What affects the time of gastroscopy?
Despite the fact that the average duration of an endoscopic examination of the stomach is 5-10 minutes, this period can be extended under the influence of several internal and external factors.
Among them:
- Psychological mood
. Most patients (especially those undergoing this examination for the first time) associate endoscopy with painful sensations. This creates a persistent fear in them, which negatively affects the formation of contact with the doctor. - Failure to comply with proper preparation
. If the patient did not adhere to the diet and consumed any food within a few hours or minutes, performing an FGDS may be difficult or even canceled. In this situation, active digestion of incoming food will occur in the stomach cavity, as a result of which it becomes impossible to assess the condition of the walls of the organ. - Use of anesthesia
. As mentioned above, if there are indications or personal desire, endoscopic examination of the stomach is possible under local or general anesthesia. This will require the involvement of an anesthesiologist, who individually selects the optimal drug and its dosage.
Indications for FGDS
Endoscopic examination of the stomach is one of the safest and most informative examinations in medicine. It is prescribed to provide a clear picture of the pathological process for the following patient complaints:
- with persistent attacks of heartburn, belching;
- with pain in the epigastric region, heaviness and sensations of bloating;
- with attacks of nausea, frequent vomiting;
- for problems with bowel movements (bowel movements).
FGDS is prescribed for suspected oncology, esophageal stenosis, gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastric bleeding and other diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopic examination, if necessary, is combined with:
- with treatment of the pathological focus with a drug (for example, chemical coagulation of a bleeding vessel);
- with testing for Helicobacter (analysis);
- with stopping bleeding (tamponade, application of ligatures/clips);
- with biopsy and subsequent histology (if cancer is suspected);
- with removal of polyps;
- with bougienage of the esophagus (expansion of the stenotic area).
Indications
Gastroscopy (EGD) is performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The study is carried out to identify and confirm a number of diseases of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum and some general somatic pathologies. In particular, we are talking about inflammatory processes (esophagitis, gastritis, bulbitis, etc.) of toxic, infectious and other origins. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is one of the main methods for diagnosing gastric and duodenal ulcers. With this diagnosis, the procedure is also prescribed for therapeutic purposes; gastric endoscopy is used to administer various drugs that promote ulcer healing.
Another indication for endoscopy is tumor formations of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. These can be benign processes (polyps) and malignant neoplasia. It is on the conclusion of the biopsy performed during the study that further tactics of patient management are based. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy allows you to visualize specific changes in the mucous membrane of the duodenum and collect material for histological examination in Whipple's disease, Crohn's disease and some other pathologies. Endoscopy makes it possible to reliably confirm the presence of esophageal or gastrointestinal bleeding. During the procedure, mechanical and chemical methods are used to stop bleeding, and hemostatic agents are administered.
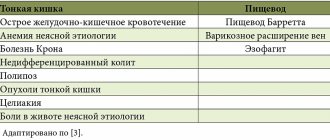
Hematemesis and melena are observed in many nosologies, therefore esophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed for the purpose of differential diagnosis of diseases of the esophagus, stomach and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract that can provoke bleeding. In addition, endoscopy is used in some cases to identify the cause of intestinal obstruction (duodenal obstruction of various natures). The study is widely used for surgical removal of polyps, precancerous formations, bougienage in the presence of stenoses, removal of foreign bodies, etc. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is also prescribed in the preparation of patients for surgical treatment of a number of diseases.