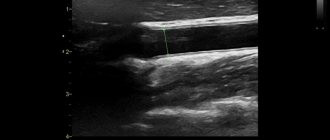
Ultrasound not only passes through tissue, but, reflected from blood cells, sends an image of the vessel to the screen, which allows one to evaluate the patency and degree of narrowing of the vessel.
There are several types of Doppler:
- Ultrasound Dopplerography (Doppler ultrasound) is a study of the vessels of the neck, head, brain or other organs, which allows you to determine the patency of the vessel, i.e. his anatomy.
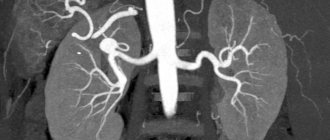
- USDS - (Duplex Ultrasound Scanning) combines two functions: In this case, the vessel is already visible on the monitor, and an image of the tissue around it is obtained, as with a conventional ultrasound. It turns out that this method, unlike Doppler ultrasound, helps in diagnosing the cause of poor vessel patency. It helps to visualize plaques, blood clots, tortuosity of blood vessels, and thickening of their walls.
- With Triplex scanning, the vessel is visible on the monitor against the background of the image of the tissues in the thickness of which it passes. In this case, the vessel is painted in different colors depending on the speed of blood flow in it.
Ultrasound scanning of head and neck vessels is recommended for the following diseases:
- congenital anomalies of the location, course or branching of blood vessels
- atherosclerosis
- injury to an artery or vein
- inflammatory change in the walls of arteries and capillaries (vasculitis)
- diabetic, hypertensive, toxic angiopathy
- encephalopathy
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck helps to understand:
- causes of repeated transient ischemic attacks, strokes
- the degree of damage to these particular arteries due to metabolic or antiphospholipid syndromes
- the degree of impairment of the patency of blood vessels in the arterial bed due to atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, and smoking.
Knowledge of the condition of extra- and intracranial arteries and veins, obtained using duplex scanning, helps in prescribing the correct treatment, objective monitoring of its effectiveness, and drawing up an individual prognosis.
How it goes
No special preparation is required to assess the condition of extracranial vessels. On the day of the examination, it is advisable not to smoke or drink alcoholic or caffeinated drinks. You must warn your doctor if you are taking any medications. Diagnosis takes place in the supine position. There may be a small cushion under the neck. In some cases, the study is carried out with functional tests: turning the head, briefly pressing the arteries, holding the breath.
After the ultrasound, a conclusion is issued, which is deciphered by the attending physician. In some cases, other types of ultrasound or vascular examination using MRI may be prescribed.
Who needs to examine cerebral vessels
Duplex scanning (or at least ultrasound scanning) of intracranial arteries and veins (that is, those located in the cranial cavity) is indicated in cases of such complaints:
- headache, noise in the ears or head
- heaviness in the head
- dizziness
- visual impairment
- attacks of impaired consciousness such as fainting or inadequacy
- unsteadiness of gait
- lack of coordination
- impairment of speech production or understanding
- limb weakness
- numbness of hands.
The examination is also performed when pathology is detected during ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck, when pathology of the neck organs is detected using CT, scintigraphy, MRI (for example, enlargement of the thyroid gland). In this case, in order to prescribe adequate therapy, a neurologist needs to know how all these diseases affect the brain, and whether its nutrition may suffer from this.
What are the advantages of ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic vessels in the neck:
Ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries and vessels is not expensive, it does not cause pain and it goes away very quickly. It provides a lot of necessary information that will help the doctor make the correct diagnosis.
Using BCA ultrasound it is possible to identify:
- Initial vascular damage;
- The very condition of the vessels;
- The presence of atherosclerosis and stenosis;
- The nature of blood flow and its speed;
- Vein thrombosis;
- Vascular injuries;
- Varicose veins.
And the same anatomical deviations in the neck vessels themselves, for example, the entwining of vessels around the neck.
Indications for examination of the vascular bed of the head and neck
Ultrasound duplex scanning of those arteries and veins that supply blood to the brain, but are located in the neck (that is, extracranial - outside the cranial cavity) should be carried out in the following cases:
- headache
- dizziness
- unsteadiness of gait
- impaired memory, attention
- coordination problems
- when planning operations on blood vessels and heart muscles
- when identifying pathology of the neck organs, due to which the vessels passing there may be compressed
- visible contraction of the blood vessels of the heart.
Duplex scanning of the main veins of the upper extremities
Thrombotic lesions of the veins of the upper extremities remain a fairly common pathology. The basis for instrumental diagnosis of pathology of the main veins of the upper extremities is duplex scanning, which is intended for diagnosing developmental anomalies of the venous system of the upper extremities; diagnosis of venous thrombosis and valvular venous insufficiency, diagnosis of arteriovenous developmental anomalies.
Duplex scanning allows you to examine the main veins of the upper extremities, determine their direction and course; identify the presence of thrombosis, its localization, duration and severity, diagnose valvular venous insufficiency along the entire length of the main veins of the upper extremities. In almost 100% of cases, the method eliminates the need for angiographic studies.
Indications for use are:
- all diseases of the veins of the upper extremities;
- pain in the upper extremities in combination with their swelling;
- the presence of symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency of the upper extremities without clear indications of a primary thrombotic lesion;
- traumatic injuries of the main veins of the upper extremities; control after surgical treatment of the main veins of the upper extremities;
- congenital anomalies of vein development;
- conditions after manipulations on the main veins of the upper extremities: intravenous injections, puncture of the subclavian veins.
When is routine Doppler sonography necessary?
Doppler of both extra- and intracranial arteries and veins should be performed at least once a year as a routine study (even before the appearance of any complaints):
- all women over 45 years old
- all men over 40 years old
- those who have close relatives suffering from hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease
- for diabetes
- smoking
- antiphospholipid syndrome
- for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
- metabolic syndrome
- arterial hypertension
- if you have had a stroke or transient cerebrovascular accident
- if a person suffers from rhythm disturbances (the likelihood of cerebral thromboembolism with subsequent stroke is increased)
- increased levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoproteins in the blood (signs of atherosclerosis)
- had surgery on the spinal cord or brain
- before planned heart surgery.
Duplex scanning of the main arteries of the upper extremities
The method of duplex scanning of the main arteries of the upper extremities is intended for the diagnosis of anomalies in the development of the arterial system of the upper extremities; diagnosis of arterial thrombosis.
The method allows you to examine the main arteries of the upper extremities, determine their direction and course; if necessary, measure the diameter, determine the presence of thrombosis of the main arteries of the upper extremities, its location, and assess the condition of the vascular wall.
Indications for the use of duplex scanning are:
- all diseases of the arteries of the upper extremities;
- suspected pathology of the main arteries of the upper extremities;
- absence of pulse in any of the main arteries of the upper extremities;
- traumatic injuries of the main arteries of the upper extremities;
- control after surgical treatment of the main arteries of the upper extremities.
Ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the lower extremities
A doctor may recommend ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the lower extremities for the following diseases and conditions:
- Atherosclerosis, endarteritis and diabetic angiopathy of the vessels of the lower extremities
- Atherosclerosis of the visceral branches of the abdominal aorta (vessels supplying the gastrointestinal tract, liver, spleen and kidneys)
- Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta and other vessels
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities
- Vasculitis (inflammatory vascular disease)
- Vascular diseases of the brain and neck
- Control of performed surgical intervention on blood vessels
- Postthrombophlebitic disease
- External vessel compression syndrome
- Screening examination (a study to identify asymptomatic forms of the disease)
- Thrombophlebitis and phlebothrombosis of the veins of the extremities
- Thrombosis of intestinal vessels
- Vascular trauma and its consequences
Ultrasound of neck vessels
Ultrasound is a simple, informative, painless and safe method for diagnosing diseases and pathologies of the brachiocephalic arteries and vessels of the neck that supply blood to the brain.
Ultrasound of neck vessels at the Rehabilitation Clinic in Khamovniki
In our clinic, all services are provided at a highly qualified level, and diagnostic accuracy plays a primary role in this. Moreover, we are not limited to just one examination: if it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, the patient can undergo an MRI of the cervical spine or an MRI of the soft tissues of the neck; all recommended tests can be taken in the treatment room.
You can get detailed information about the procedure, find out the cost, and make an appointment on our website or with the help of our specialists. Appointments are made even on weekends, so patients from Moscow and the region can receive qualified assistance from our doctors at a time convenient for them.
How does the procedure work?
There are three types of ultrasound: Doppler (Doppler ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound), duplex scanning and triplex scanning. As a rule, this study is carried out as prescribed by a doctor. The procedure takes about half an hour: the patient frees the neck and shoulder area, and the specialist uses a sensor to study the condition of the blood vessels. Deciphering the results takes a few minutes.
Special preparation for an ultrasound is not needed, but it is recommended to give up alcohol and smoking on the eve of the procedure, and inform the doctor about all medications you are taking, as they may affect the result.
What does an ultrasound scan of the neck vessels show?
During ultrasound, various structures are examined: carotid, ophthalmic, subclavian, supratrochlear and vertebral arteries, brachiocephalic trunk (large main vessel), jugular veins, veins of the vertebral plexus. Ultrasound examination allows:
- assess the condition of even small vessels (from 1-2 mm in diameter), see obstacles that impede the normal flow and outflow of blood to the brain (plaques, blood clots, etc.), calculate the speed of blood flow, vascular patency, the condition of the vascular walls and other important options;
- determine the possibility of developing cerebral ischemic stroke, as well as diagnose a whole range of diseases (atherosclerosis of extracranial arteries, aortoarteritis, dissection of the arterial wall, etc.).
Indications for ultrasound of neck vessels
- Headaches, dizziness and pain in the cervical spine.
- Decreased vision, including periodic vision, the appearance of spots before the eyes, etc.
- Deterioration of memory, attention, forgetfulness, absent-mindedness.
- Hearing loss, ringing or noise in the ears.
- Loss of coordination of movement, unsteadiness of gait.
- Sleep disorders.
- A sharp causeless increase or decrease in blood pressure.
- Loss of consciousness, especially repeated.
- Prevention: for preventive purposes, people over 45 years of age, smokers, patients with diabetes mellitus, high blood cholesterol, hypertension, heart disease, after a stroke, heart attack, and operations on the blood vessels of the head and neck should be examined at least once a year. We recommend not to ignore such examinations, since the cost of any prevention is significantly lower than the cost of treatment.
Methodology for performing the examination
First of all, the patient lies on his back with his head facing the doctor. The specialist begins the diagnosis with the carotid arteries. First on the right side, tilting the sensor down so that its head passes along the neck to the corner of the lower jaw. This allows you to determine the direction of the artery, the depth and the point of division of the artery into two parts.
Then Doppler is used, and the picture turns out to be in color, which allows you to separately examine each branch of the blood vessels, their walls and damaged areas. When a pathological vessel is detected, it is carefully examined, the degree of damage and the progress of the disease are determined. The left side is diagnosed in a similar way.
Afterwards, the patient receives the test results and can go home.