Installations for MRI and X-ray examinations Visualization diagnostic methods (radiography, fluorography, CT, MRI, etc.) are actively used in all branches of medicine. With their help, you can examine the internal tissues of the body without damaging the skin and unnecessary risks. X-rays or MRIs provide images of areas hidden from the naked eye. Thanks to the methods discussed, doctors can impartially assess the patient’s condition, make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. However, the information content of these procedures differs significantly in different clinical situations.
What is fluorography?
It often happens that a person who needs to examine his lungs thinks about how fluorography differs from an x-ray of the lungs. It is worth knowing that fluorography, just like radiography, is based on obtaining an image based on the passage of ionizing radiation through the human body. However, the radiation dose, the technique, and the information content of these methods vary significantly.
The difference between lung radiography and fluorography is that the latter method is considered much more gentle and safe, since the radiation dose at a time is 0.015 mSv. For problems to arise due to excessive radiation exposure, you need to undergo such diagnostics about a thousand times a year.
The history of fluorographic research
Before you understand what fluorography and X-ray of the lungs are, how the methods differ from each other and which one is better, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the history of the fluorographic diagnostic method. It appeared in 1930 and was actively promoted by the Soviet scientist S. A. Reinberg.
The first fluorography devices still required a fairly high radiation dose, up to 2.5 mSv, and such an examination required significant effort on the part of doctors. If you want to know what the difference is between fluorography and x-rays of the lungs, then keep in mind that modern fluorography machines have become much safer and allow you to obtain very high-quality images.
How is MRI different from X-ray?
The main difference between the procedures lies in the underlying physical phenomena. MRI is based on the ability of a high-intensity magnetic field to change the orientation of hydrogen atoms in water molecules in cells. Radio frequency waves sharply return them to their original position, and energy is released. The device records the resonant response, and a computer program makes an image from the recorded vibrations. The structure of the image in the photographs is determined by the intensity of energy release, which in turn depends on the number of hydrogen atoms, so loose, liquid-rich formations are clearly visible.
X-rays are based on the ability of radio rays to pass through tissue and be retained in the denser ones. The part of the body being examined is placed between two surfaces, one of which emits the rays, and the second captures them. The results are recorded by an X-ray machine. Depending on the change in the density of radiation passing through the body, a picture is obtained that is printed on film.
Focusing on the mechanism and features of the study, you can compare them and say how MRI differs from X-ray:
- Goals. Magnetic resonance imaging is a more universal procedure, as it provides information about the condition of soft tissues, nerves, blood vessels, lymph nodes, and joint elements.
- Safety. Diagnostics using an MRI scanner does not carry radiation exposure and does not provoke the formation of free radicals. Allowed for pregnant women from the second trimester, as it is not harmful.
- Possibility of repeated research. MRI can be done as many times as necessary for an objective assessment of changes in the patient’s body.
- Image quality. As a result of tomography, images are obtained in three mutually perpendicular projections. That is, the area under study can be viewed in any plane.
- Information content. MRI is used to detect the slightest changes in the body and diagnose diseases at the earliest stages of development.
Despite the potential danger of ionizing radiation, x-ray studies have their advantages compared to MRI:
- Speed of diagnosis and results. The procedure takes a couple of seconds, and preparing images takes a few minutes. Immediately after receiving the result, you can go to your doctor. MRI diagnostics lasts from 15 minutes to one and a half hours (including interpretation of images).
- Restrictions. Exposure to X-rays is not recommended for children and pregnant women, however, the procedure can be performed if there are metal or electronic implants in the body, which are a contraindication for MRI.
- Price. X-ray examination costs much less than magnetic tomography diagnostics.
- X-ray radiation more clearly visualizes solid foreign bodies, stones, and bone structures.
The disadvantages of using ionizing radiation are the low information content of the study with relatively small changes in soft tissues, and there is also a limit on the number of procedures (no more than 2 per year).
Types of fluorography
You can understand the difference between X-rays of the lungs and fluorography after familiarizing yourself with the main types of the latter. They are widely used to diagnose inflammation and tuberculosis.
Digital fluorography
Lung X-ray or fluorography: what is the difference and advantages of modern research methods? Digital fluorography is a more advanced method and provides minimal stress on the body. As a result of such a study, an image of the shadow of the organs will appear on the computer equipment monitor, which is created thanks to a special chip located in the receiver. The produced beam will linearly pass through the entire examined area, after which special software will reconstruct the image. When choosing between whether fluorography or x-ray of the lungs is better, we can say that the digital research method is much safer.
Traditional fluorography
It is an outdated technique that differs little from x-rays. The photograph is taken on small film. If you have an x-ray or fluorography of the lungs (which is better in this case, it is unlikely to be determined) of the traditional type, the radiation exposure will be the same.
Fluorography
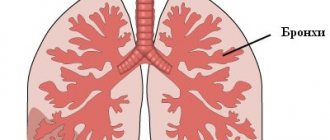
The study involves the use of x-rays, their effect on the body is negligible. Only organs located in the chest are examined, namely the lungs, large bronchi, and the heart. As a result, an image is obtained (often digital), but its size is quite small, it is 11 by 11 cm. Today, the devices with which the study is carried out are divided into 2 types:
- film devices;
- digital.
The technique is used for prevention purposes and is distinguished by the presence of contraindications, including: age under 14 years, pregnancy.
What is a lung x-ray?
It is not possible to say unequivocally which is better, x-ray or fluorography of the lungs. Although the latter method is more gentle, the resulting images are of lower quality. On an x-ray, shadows measuring two millimeters can be detected, while on a fluorographic image – at least five centimeters.
The difference between X-ray of the lungs and fluorography is also that the X-ray rays pass through the tissue and the film is illuminated accordingly. This type of research creates a high, but very short-term radiation load on the human body.
What is the difference between x-ray and fluorography
Both diagnostic methods relate to x-ray diagnostics, and it may seem that there is no fundamental difference between them. But, as already mentioned, fluorography is mandatory for the purpose of preventive detection of pathologies. X-rays are not prescribed without serious indications, or to monitor the dynamics of treatment. As you can see, the goals of these examination methods are different. With X-rays, the image quality will be much higher; it is widely used in a variety of fields of medicine, including neurology, traumatology, pediatrics, surgery, and cardiology.
Fluorography has a narrow scope; it will demonstrate only the organs that are located in the chest. X-rays may be prescribed several times, especially if it is necessary to track the dynamics of recovery. If we talk about cost, then x-rays are more expensive, but the image of the lines will be clearer, you can better examine the structure of the tissues, and see pathological areas. The dose of radiation received is lower, but sometimes it is necessary to take several photographs in different projections; in total it will be equal.
No preparation is needed in either case unless a contrast agent is used. It is recommended to do fluorography once a year. Doctors try not to prescribe procedures such as chest x-rays and fluorography too often; their differences and frequency of use lie in the purpose of the procedure. There are categories of people who should not refuse timely fluorography, these are:
- people living in a house with pregnant women;
- persons with HIV;
- teachers, hazardous workers, medical staff;
- patients with chronic diseases.
Such an examination should be replaced with an x-ray when doctors suspect pneumonia, pneumothorax, hemothorax, lung abscess, the presence of tumors, or the patient has pain in the chest.
Important! Radiography is an optional procedure. It is used under certain circumstances when there is pathology or damage to some organs.
How often can I undergo radiography and fluorography?
When a doctor prescribes a diagnosis, he must assess the benefits and risks to the body. Often patients themselves exaggerate the harm that can be caused in this case. What is the real negative impact on the body? Firstly, the composition of the blood may change for a short time; radiation exposure is dangerous for pregnant women and young children.
If digital technology is used, then the harm is minimal, which in no way indicates a possible negligent attitude towards the intended purpose. Fluorography is usually used once a year. In the case of x-rays, everything is different; there are moments in life when you cannot do without x-rays. Such a deep procedure is extremely necessary and can be carried out several times a year, when without it a correct diagnosis is impossible.
Doctors try to approach this issue wisely and prescribe examinations only when absolutely necessary. Remember, if the device is modern, then you should not be afraid of radiography; such devices are not as dangerous as old film ones.
Is X-ray examination of the OGK safe?
Trying to understand the difference between chest x-rays
and fluorography, it is worth knowing that in domestic clinics the radiation dose is several times higher than that permitted in more developed countries. The reason is that Russian clinics often use very old devices. In Europe, the annual dose of X-ray radiation is no more than 0.6 mSv, but in Russia it is more than twice as high - 1.5 mSv.
However, in the event of a threat to the patient’s life, for example from acute pneumonia, doctors will not have to choose whether to do a fluorography or an x-ray of the lungs; they will simply use the available equipment for a speedy diagnosis. Typically, in such a situation, an X-ray examination is performed directly and from the side, and often a targeted X-ray is also needed.
X-rays of teeth
What is a visiograph and how does it differ from an x-ray?
This is one of the most common questions, like what is the difference between a car and a traffic light. It seems that both concepts have some kind of connection, but it is quite difficult to compare them. Also here. A radiovisiograph is a system that receives x-ray radiation, transforms it into digital form and displays the image on a computer screen.
Roentgen (who was Wilhelm Conrad) was a German physicist who gained worldwide fame for his discovery of short-wavelength rays with enormous penetrating power. The physicist himself called these rays X-rays (in English today they are called exactly that - X-ray), but now we often call them X-rays, and in everyday life simply “X-rays”. The unit of radiation power was also called the x-ray. Now it is clear that a visiograph and an x-ray are completely different things. If you compare the visiograph with anything, it’s with x-ray film, which it is universally replacing from all areas of medicine.
X-ray of teeth
Is it true that a visiograph is safer than a regular film photograph?
When asked about such a comparison, they mean the radiation exposure that the patient receives when using different techniques. In this sense, indeed, a visionograph is better, since its sensor is much more sensitive compared to film. Therefore, to obtain a high-quality image using a visiograph, you need significantly less shutter speed. To take a picture on film, the shutter speed is 0.5-1.2 seconds. To obtain the same image using a visiograph sensor – 0.05-0.3 seconds, that is, 10 times less. As a result, the radiation exposure received by the patient when using a visiograph is reduced to an insignificant minimum.
How many pictures can you take at one time? And in general, isn’t it harmful that when treating a large number of teeth, you have to take a lot of X-rays?
This is the most pressing of questions. This is an echo of the Chernobyl tragedy and life safety lessons that emerge in memory. But in our society there is still a very strong phobia towards everything that is even remotely connected in our heads with radiation. Any extra photo often raises questions about radiation sickness, or “will I glow in the dark?” Therefore, we will try to explain in more detail here. First from a scientific point of view.
To measure the amount of radiant energy applied to living tissue, various units are used - joule per kilogram, gray, rem, sievert, etc. In medicine, X-ray procedures typically measure the dose received by the entire body during one procedure—the effective equivalent dose, measured in sieverts. According to SanPiN 2.6.1.8-38-2003, when carrying out preventive medical x-ray procedures and scientific research, this dose should not exceed 1000 μSv (microsievert) per year. Moreover, here we are talking specifically about preventive studies, and not about therapeutic ones, where this bar is much higher.
What is 1000 µSv? Is it a lot or a little?
Remembering the famous cartoon, the answer is simple - depending on what you measure it in. 1000 μSv is approximately:
- 500 targeted images (2-3 μSv) obtained using a radiovisiograph
- 100 of the same images, but using good X-ray film (10-15 µSv)
So, apparently, even if we take 1 picture on a visiograph every day for the whole year, and also a couple of 3D computed tomograms per year, and the same number of orthopantomograms, then even in this case we will not get out beyond the limits of safe permitted doses.
there is no need to be afraid of receiving a significant dose of radiation during dental procedures . Even if you want to go beyond the permissible values, it is unlikely to be possible. To be clear, here are the doses needed to cause any serious health effects:
- 750000 μSv - short-term minor change in blood composition
- 4,500,000 μSv - severe radiation sickness (50% of those exposed die)
All these figures are incomparable in their significance with the doses we receive in everyday life. So even if, for some reason, several pictures are taken at once in a row, and the day before you were already “exposed” by doing an orthopantomogram, you don’t need to panic and run to the store to buy a Geiger counter or search on the Internet for “the first symptoms of radiation sickness.” To calm yourself down, it’s better to “detoxify” with a glass of red wine. There will be no point in this, but the mood will immediately improve.
Let us clarify that, for example, with one-stage basal implantation, control targeted images are taken before and after installation of implants (when installing 1-3 implants). And also after final prosthetics (7-8 days).
Is it possible to do x-rays for pregnant women?
We will not remind you that before pregnancy it is better to take care of your health in advance, including “preparing” your own teeth at the dentist. In order not to run away later with acute pain and doubts whether this or that manipulation will harm the development of the fetus... Therefore, you should leave the lyrics and pay attention to the facts and common sense. Without phobias, prejudices, speculations and myths. So, is it possible to do x-rays for pregnant women?
Here's what they write to us about this in the documents (SanPiN 2.6.1.8-38-2003):
7.16. Pregnant women are prescribed for X-ray examination only according to clinical indications. Studies should, if possible, be carried out in the second half of pregnancy, except in cases where it is necessary to decide on termination of pregnancy or the need for emergency or emergency care. If pregnancy is suspected, the question of the admissibility and necessity of an x-ray examination is decided based on the assumption that there is a pregnancy...
7.18. X-ray examinations of pregnant women are carried out using all possible means and methods of protection so that the dose received by the fetus does not exceed 1 millisievert for two months of detected pregnancy. If the fetus receives a dose exceeding 100 mSv, the doctor is obliged to warn the patient about the possible consequences and recommend terminating the pregnancy.”
In general, the conclusion from these two main points is simple and clear. It’s definitely not worth taking pictures in the first half of pregnancy, but in the second half - 1 mSv for a visiograph - this is practically unlimited.
I would also like to add that one often encounters bellicose stubbornness: an X-ray at the dentist during pregnancy is an absolute evil. It’s better, they say, to screw up a tooth, to cure crooked canals... there are a lot of teeth, pregnancy is more important. Moreover, such sermons are given not only by lay patients who have little understanding of the essence of things, but also often by dentists themselves who have forgotten their school physics course.
To resolve this doubt, we must understand that sources of ionizing radiation are not only found in medical offices. And it doesn’t have to be near Chernobyl (and now Fukushima) to receive some doses from the environment. After all, every second we are influenced by both natural sources (sun, water, earth) and man-made ones. And the doses received from them are much greater than those received from an x-ray of a tooth.
For clarity, we can give one simple example. As you know from a school physics course, the sun emits electromagnetic energy in a wide range, not only in infrared (heat), visible (light), ultraviolet (tan), but also in x-rays and gamma radiation. Moreover, the higher the earth's surface, the more rarefied the atmosphere and, therefore, the weaker the protection from sufficiently strong radiation from the sun.
After all, while “fighting” radiation at the dentist, the same people often calmly fly south to bask in the sun and eat fresh fruit. Moreover, during a 2-3 hour flight in a “healthy” climate, a person receives 20-30 μSv, i.e. the equivalent of approximately 10-15 images on a visiograph. In addition, 1.5-2 hours in front of a cathode ray monitor or TV gives the same dose as 1 picture... How many pregnant women sitting at home, watching TV shows and surfing the Internet, think about how many pictures they “took”? while watching another program, and then discussing it with friends on the forum and social networks? Almost no one, because people do not associate all this with ionizing radiation, unlike a picture in a doctor’s office.
And yet, dear expectant mothers, prepare for pregnancy in advance. For many people, visiting the dentist still remains stressful. And it’s not so much that anesthesia or x-rays can be harmful during this period, but what is important is your peace of mind and the absence of unnecessary worries (of which many already have more than enough during this period). You can study more information on this topic in our article “Can teeth be treated during pregnancy.”
What is the best protection to use if you need to take a photo while pregnant?
The number of aprons does not matter. In contact radiography, the apron essentially protects not from direct radiation, but from secondary, that is, reflected. For X-rays, the human body is an optical medium, like a glass cube for a flashlight beam. Point the beam of a flashlight at one of the faces of a large glass cube and, regardless of the thickness and direction of the beam, the entire cube will be illuminated. It’s the same with a person - you can swaddle him completely in lead and shine only on his head - at least a little, but it will reach every heel. So even under two aprons with a good lead equivalent, a pregnant woman will, at most, simply have a harder time breathing.
Is it possible to do x-rays for breastfeeding mothers? And if possible, then what about feeding the child after the procedure?
Can. X-rays are not the same as radioactive waste. By itself, it does not accumulate in the biological environment. If you irradiate a loaf of bread with a lethal dose, it will not mutate, get radiation sickness, or begin to “foul.”
X-rays differ from light rays only in wavelength and have a direct damaging effect only under certain conditions. If you shine a flashlight into a bucket of water and turn off the flashlight, the light won't stay in the bucket, right? The same is true in a protein-fat solution, which is what many biological fluids are (including breast milk) - the radiation passes right through. So, with such a load that is necessary to work with a visiograph, it is unlikely that anything will happen to the milk itself.
As a last resort, to reassure yourself, you can skip one regular feeding. Another thing is that the breast tissue itself during lactation is, of course, more susceptible to the harmful effects of radiation. But, again, we are talking about doses much more powerful than is necessary for digital radiography (of course, subject to all protective measures and without “shooting” 20 times anywhere).