Computed tomography is a research method based on x-rays. The predecessor of a computed tomograph is a conventional X-ray machine, but with a CT scan it is possible to obtain layer-by-layer images of the area under study. Multislice computed tomography (MSCT) is considered the most modern. The advantage of this method is the following:
- reduction of radiation dose;
- obtaining a higher quality image on the monitor;
- allows you to increase the volume and speed of scanning.
What does a CT scan of the facial skull show?
Multislice CT is prescribed to evaluate almost any pathology of the facial part of the skull.
CT scan of the facial skull with 3D reconstruction
CT scan of the facial skull allows you to evaluate:
- integrity of facial bones;
- condition of the paranasal sinuses, eye sockets and nasal cavity;
- condition of soft tissues.
Preparing for a CT scan of the skull
To examine the skull using a CT machine, no special preliminary preparation is required. However, if the examination is not primary for the pathology being diagnosed, the patient is recommended to bring with him all previous medical documents. The more detailed information is provided to our specialists, the more comprehensive the diagnostician will apply to the disease. This is especially important for patients who are examined to identify the dynamics of the process - such an assessment is only possible by comparing new data with previous studies.
Indications for CT scan of the facial skull
Carrying out a CT scan of the facial skull is relevant:
- for injuries to the facial area, especially with severe bone displacements, swelling and internal bleeding or hematomas;
- with inflammatory changes in facial tissues;
- loss of tone of facial muscles;
- suspected oncological processes;
- if MRI is not possible.
Most head injuries are accompanied by fractures of the facial bones and their displacement. The facial skull is formed by the frontal, jaw bones and a number of small bones. Damage to the small bones of the facial skull cannot always be visualized using a conventional x-ray; the most informative is a CT scan of the facial skull. It is important to note that computed tomography allows you to diagnose tumors of cartilage and bone tissue even at an early stage. CT images of the facial skull clearly show the contours of the tumor, as well as their growth into the cranial space, nasal cavity and orbit. In such situations, additional intravenous contrast may be required.
Computer tomograph Siemens
There are cases that patients with claustrophobia cannot undergo magnetic resonance imaging of the soft tissues of the face, since its implementation involves a long stay in a confined space. However, if an MRI is more informative, the doctor prescribes it.
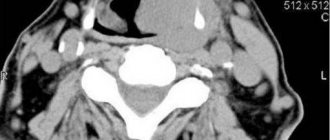
Computed tomography (CT) of the skull base
Computed tomography (CT) of the skull base reveals the following normal anatomical structures: a – pterygopalatine fossa, b – foramen ovale, c – carotid artery canal, d – incus, e – facial nerve (VII), f – clival petrosal synchondrosis, g – cochlear opening, h – notch for the sigmoid sinus.
Computed tomography (CT) of the skull base reveals the following normal anatomical structures:
- a . Pterygopalatine fossa. Communications: with the nasal cavity - through the ethmoid palatine foramen ( 1 ), with the space of the masticatory muscles - through the pterygomaxillary fissure, with the orbit - through the inferior orbital fissure, with the cavernous sinus - through the round foramen, with the middle cranial fossa - through the pterygoid canal ( 2 ) and palate – through the greater palatine canal.
- b . Oval hole. An oval-shaped hole in the large wing of the sphenoid bone (middle cranial fossa). The mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V3), the accessory meningeal artery, emissary veins, the auditory ganglion, and sometimes the lesser petrosal nerve pass through it.
- c . Carotid canal (carotid artery canal). A passage in the petrous part of the temporal bone through which the internal carotid artery and sympathetic plexus pass. Its lower part is represented by the carotid foramen (the entry point of the internal carotid artery), located anterior to the jugular fossa. The carotid canal opens into the cavity of the middle cranial fossa above the foramen lacerum.
- d . Anvil. The incus is the middle ossicle in the chain of auditory ossicles, which is connected to the head of the malleus (anterior to the center) ( 3 ) and the stapes (inferior to the center) through a long process ( 4 ). It is identified as the most externally located among the auditory ossicles, because its short process is directed outward and posteriorly.
- e . Facial nerve (VII). In this image, the facial nerve passes under the lateral semicircular canal, where the descending or mastoid portion is located. The facial nerve innervates the facial muscles, is responsible for taste recognition in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue, and supplies the salivary and lacrimal glands with parasympathetic fibers.
- f . Slope-stony synchondrosis. Synchondrosis between the top of the petrous part of the temporal bone and the clivus, which is the anterior part of the occipital bone. This interosseous joint is a classic site for the formation of specific types of tumors (chondrosarcomas) of the skull base. Knowledge of this anatomical feature can help in formulating the diagnosis.
- g . Cochlear opening. This is the opening of the distal internal auditory canal through which the cochlear nerve passes into the cochlea. The nerve follows approximately the path indicated by the arrow and is one of four bundles of the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII), within the internal auditory canal.
- h . Notch for the sigmoid sinus. The sigmoid sinus (venous sinus of the dura mater) is a continuation of the transverse sinus. It descends medially in an S-shaped notch posterior to the mastoid air cells into the jugular foramen. In the case of a deeper notch, unilateral dominant venous drainage of venous blood through the sigmoid sinus located in it is often noted.
Safety of the CT method of the facial skull
During the examination, the patient is in a specialized room, under the constant supervision of a radiologist, who is in the next room during the procedure. Communication is carried out via a special microphone. Single radiation exposure to MSCT is minimal and absolutely safe for the patient. For clearer visualization of soft tissues, focal inflammatory processes and differential diagnosis of cysts from soft tissue formations, iodine-based contrast agents are used, which practically do not cause side effects. Occasionally, after their use, mild dizziness occurs, which quickly passes. The procedure itself lasts several minutes, minimizing patient exposure to radiation.
Advantages of the method
The good spatial resolution of computed tomography allows for very thin “slices” of tissue. For a multislice tomograph, the slice thickness is 0.5 mm, and for a spiral one – 1 mm.
CT is not too sensitive to artifacts and errors due to random movements of the patient; modern devices minimize these phenomena as much as possible due to the speed of the procedure. As a result, the pictures are very clear.
The radiation dose a patient receives from a CT scan is much lower than from an X-ray.
If you don’t know where to get a computed tomography scan of the facial bones in Moscow, then we will provide you with all the information over the phone. We have available data on all medical centers that conduct diagnostics using modern equipment with an advanced software and hardware module.
How is a CT scan of the facial bones performed?
There is no need for special preparation to perform a CT scan. If you decide to have a CT scan of the facial bones, then you need to take with you a referral from your doctor, as well as the results of previous examinations and tests performed in the early stages of diagnosis. Before the procedure, it is necessary to temporarily remove all metal objects from the head and neck. Clothing should be light, comfortable, not causing discomfort, without metal locks, zippers or buttons.
If you are going to do a CT scan of the facial skull using a contrast agent, you need to do a creatinine level analysis. This can be done in advance or immediately before the procedure. If the creatinine level is higher than normal, a computed tomography scan with contrast is not possible. The sequence of actions when performing a CT scan of the facial skull:
- The radiologist places the patient in a comfortable position on the mobile tomograph table and gives a brief instruction. Then he performs the necessary settings of the device - selects the required operating mode - and goes to the next room to control the device.
- The tomograph automatically moves the table along with the patient’s body, plunging the head into the apparatus tunnel.
- X-rays, penetrating through the tissues of the head, are captured by special sensors, undergo computer processing and are displayed on a computer monitor.
The duration of the CT scan of the facial skull is several minutes; if injection of a contrast agent is required, the preparation time will take 10-15 minutes. The basic rule is that the subject should not move while the tomograph is operating - even too much swallowing of saliva can interfere with the construction of an image of the area under study. In most cases, the contrast agent is well tolerated and is eliminated from the body within 24 hours.
Purpose
A CT scan of the skull bones is prescribed in the following case.
- If x-rays do not provide reliable information about the existing disease.
- If it is necessary to clarify the presence or refute the absence of anomalies or deviations from the norms.
- If the patient cannot undergo an MRI because his body has an insulin pump, pacemaker or other fixed metal prostheses.
- If a severe traumatic brain injury is received and there is a suspicion of unclear consequences due to bone displacement, hematomas or internal swelling.
- With a sharp deterioration in vision and hearing for no apparent reason.
- For headaches, nausea, fainting that occur after a strong blow to the head.
- For frequent dizziness of unknown origin.
- In order to differentiate malignant and benign formations.
- To determine the depth, contours and severity of bruises and injuries to the facial part of the head.
- If a stroke is suspected.
- With cerebral hemorrhage.
- Diagnosis: hydrocephalus.
These are not all the indications for which a CT scan of the skull bones can be performed. Before prescribing the procedure, the doctor interviews the patient, performs a visual examination, and records symptoms. Only a doctor can decide whether such a procedure is necessary. This may be a specialist in the field of ophthalmology, otolaryngology, traumatology and more.
Is it possible to do a CT scan of the facial skull for children?
Computed tomography at the medical center is performed only on children over the age of five and strictly with a referral from the attending physician. It is prohibited to perform a CT scan of the child’s facial skull only at the request of the parents, without appropriate compelling reasons. In exceptional cases, a CT scan of the facial skull is prescribed from the age of five, if the specialist comes to the conclusion that this procedure cannot be avoided and the benefits of the examination are much greater than the potential harm from the radiation dose received during its passage.
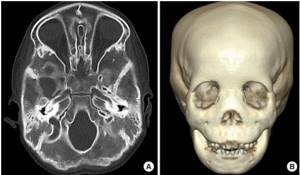
CT scan of the child's facial skull
Our medical center uses a multislice computed tomography machine to minimize the child’s exposure to radiation.
Contraindications
A CT scan exposes the human body to a small amount of radiation. In this regard, a session can be prescribed for a pregnant and lactating woman, a child, but only with the permission of the doctor. It is important to determine the degree of risk and the expected benefit.
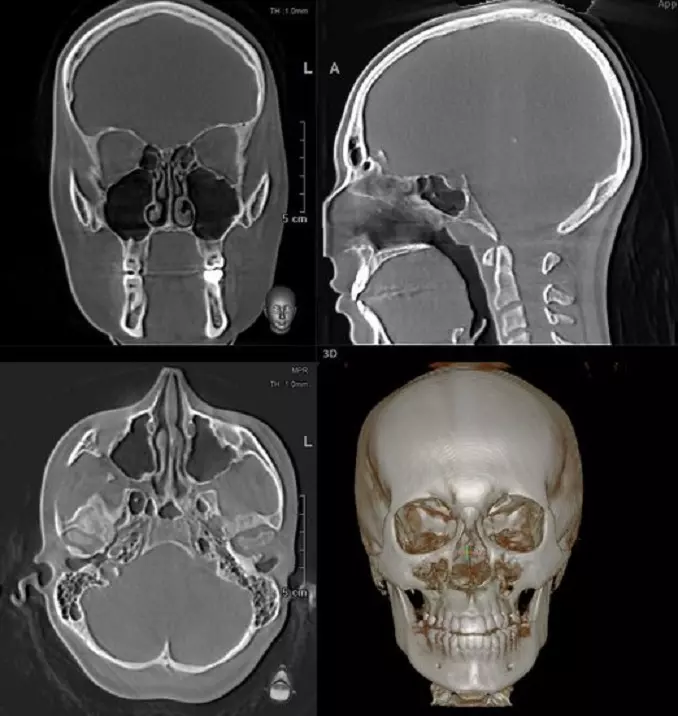
Those who weigh more than 150 kg are prohibited from undergoing the study. Such a load can negatively affect the equipment and cause it to fail. Conducting a CT scan of the skull with contrast is contraindicated in the following cases:
- allergic reaction to an iodine-containing substance;
- obvious renal failure;
- thyroid diseases;
- the presence of other diseases that, in the doctor’s opinion, cannot be combined with examination using contrast.
Features of scanning for pregnant women
Although the upper part of a pregnant woman's body is exposed to x-rays, the developing baby may be negatively affected by the rays. When performing a CT scan of the facial skull, the level of radiation exposure exceeds what is relatively safe for the fetus, which negatively affects the development of the fetus. The cells of the embryo are actively dividing; when they are exposed to radioactive radiation, developmental defects may form, and in severe cases, fetal rejection.
Conducting a CT scan of the facial skull during pregnancy is strictly contraindicated; it is permitted only in cases of extreme necessity in the later stages, as prescribed by the attending physician, using special means of protecting the fetus and setting the MSCT to a minimum radiation dose. It is optimal to postpone the procedure, carry it out after delivery, or prescribe an alternative examination method - magnetic resonance imaging.
Why do doctors often prescribe the CT procedure to their patients?
This manipulation attracts doctors for four reasons:
- safe (it does not imply any harm to the patient’s health);
- may involve the introduction of a contrast agent, which will help to obtain clear outlines of the organ being examined and thereby obtain an accurate result;
- takes very little time;
- offered at a low price.
Before the procedure, the doctor will ask the patient to remove earrings and piercings. No special preparation is needed if the procedure is performed without contrast. If a contrast agent is administered, the patient will be asked to fast 7 hours before the procedure.
Where can I get a bone CT scan?
Today there are many organizations that offer bone CT scans. The free piter-mrt service is ready to help with choosing a clinical diagnostic center. Here is a list of clinics where computed tomography of bone tissue is performed.
The proposed list of organizations includes:
- all centers in the locality of interest (only those centers that offer a diagnostic procedure are reflected in the list);
- address of the organization indicating the nearest metro station;
- the company's phone number, which you can call at any time to make an appointment;
- organization rating (the rating is displayed as the number of positive and negative reviews from patients of the clinic).
Thanks to a convenient list of companies, a citizen will be able to choose the most suitable organization based on price and proximity to home or work.
Indications
The reasons for ordering an examination are:
- Injuries, bruises.
- Pain in bones and joints.
- Limited natural range of motion.
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases.
- Suspicion of neoplasms.
- Bone tumors.
- Bone destruction.
- Age-related changes.
- Developmental anomalies.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Stroke.
- Congenital pathologies.
- Brain hemorrhage.
- Decreased hearing and vision of unknown origin.
- Pain and discharge in the ear.
- Impaired mobility of the upper jaw.
- Dizziness.
- Otosclerosis.
- Preparation for surgery.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of conservative or surgical therapy.
Computed tomography of the brain at the Miracle Doctor clinic is:
Minimal radiation exposure
Computed tomography is comfortable and safe for the patient. The Toshiba Aquilion RXL tomograph allows you to control the level of radiation exposure without loss of image quality. The risk associated with X-ray exposure is completely eliminated.
High diagnostic accuracy
The Japanese tomograph Toshiba Aquilion RXL allows you to obtain 32 slices per revolution lasting 0.5 s. The detector completely covers the area under study. This allows you to obtain the most accurate, high-resolution images.
Many types of research
In our medical center you can perform not only classical, but also modern diagnostic procedures. We perform CT with the introduction of a contrast agent, MSCT angiography of pulmonary and cardiac structures, CT of coronary calcium and much more.
Convenient solution for overweight patients
The CT scanner installed in our clinic allows diagnostics for people weighing up to 200 kg. Also, the examination is as comfortable as possible for elderly patients.
Profitable price
In our clinic you can do a CT scan of the brain at an average cost in Moscow. A price list with current prices in rubles is presented on the website.
Quality service
You can do a CT scan of the head and neck at any convenient time: our medical center is open seven days a week. If necessary, you can immediately make an appointment with a doctor of the required specialization.
Purpose of a head CT scan
Since the brain is intensively supplied with blood, computed tomography allows one to detect even minimal pathological changes and foci of inflammation of the structure under study.
The procedure is prescribed to determine the detailed clinical picture of traumatic brain injuries. Research shows:
- minor violations of the integrity of bone tissue;
- fractures of the base of the skull;
- condition of the wound channel;
- presence of foreign objects in the scanned area;
- degree of cerebral edema (in case of concussion);
- the presence of hematomas and hemorrhages;
- displacement of internal structures and much more.
This examination method is also used to diagnose various pathological processes:
- cysts and brain tumors;
- cerebrovascular accidents (ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes);
- abscesses.