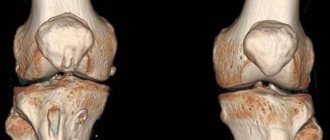
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most modern and accurate instrumental diagnostic methods. MRI is also used for examination of diseases of the eyes and orbital region. Tomography is prescribed for inflammatory processes, tumors, and injuries. Thanks to the examination, you can make an accurate diagnosis and select the most effective treatment. The main difference between MRI and similar methods is that magnetic resonance imaging is not associated with x-rays, like radiography.
MRI of the eye orbits and optic nerves
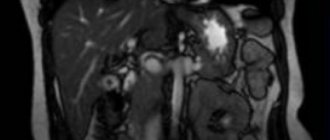
The complexity of the anatomical structure of the visual system often makes it difficult to detect pathologies when using diagnostic methods such as ultrasound or computed tomography (CT). High-resolution MRI of the eye orbits shows all changes in the tissues and structures of the eyeball, optic nerves and lacrimal glands.
Compared to CT, magnetic resonance imaging is more informative because it better visualizes soft tissue and blood vessels. In addition, MRI eliminates radiation exposure to the patient’s body. MRI images of thin sections of the eye orbits are performed with high clarity and allow the specialist to draw conclusions about the degree of development of the pathology and evaluate the dynamics of treatment.
General characteristics of tomography
MRI allows you to study the human body based on the saturation of tissues with hydrogen and the characteristics of their magnetic properties. Let's look at the magnetic resonance imaging technique. The human body consists almost entirely of water. Water, in turn, consists of 2 protons. The peculiarity of the proton is its back. This is the intrinsic angular momentum (indicator of motion) of an elementary particle, which is equal to ½.
If you place this proton in a strong alternating magnetic field, it will begin to emit a radio wave. Each of these radio waves will be located and transmit a different frequency/intensity, depending on the location. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner detects these radio waves, thereby finding the location of the proton itself. The equipment records the signal from protons, processes them using special mechanisms and turns them into an image of the area under study. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner can be called a large magnet, but the “source” of protons will be the patient himself.
Contrast-enhanced tomography is placed in a separate category. The patient is injected intravenously with a special contrast agent, which spreads through the bloodstream and stains the organs/vessels. What does this give? Contrast improves the information content/clarity of the picture, helping the specialist to navigate the diagnostic results easier and faster. This type of MRI takes longer than the standard procedure.
Content:
- General characteristics of tomography
- What do you need to know about the study area?
- Preparation and performance of MRI
- Evaluation of results
Advantages of MRI over X-rays and computed tomography
The price and demand for MRI is much higher than that of CT or X-ray. What is the reason for this?
Firstly, magnetic resonance imaging is considered an absolutely safe diagnostic method. CT scans and X-rays rely on x-rays, which can be harmful to the human body. The radiation exposure of an X-ray is much higher, so it is permissible to do it only a few times a year. With modern computed tomography scanners, the radiation dose is reduced, and therefore the time frame between diagnostics is shorter.
Secondly, MRI gives a more informative result. An x-ray is a flat image that visualizes only dense tissue. Magnetic resonance and computed tomography scanners cover absolutely all tissues, produce a three-dimensional image, and allow you to evaluate a specific section in detail.
Some experts prefer CT in terms of information content. Layer-by-layer photography using complex algorithms really gives a complete understanding of what is happening inside a living organism. But the selection of diagnostics depends on a number of characteristics of the patient, the disease and the area being examined. In general, MRI is considered the safest and most informative method. Its only drawback is the price. It is justified by the high cost of the equipment and the need for its constant maintenance.
Why do an MRI of the eye orbits and optic nerves?
High-precision diagnostics using MRI makes it possible to identify neoplasms, retinal detachment, and inflammatory processes at an early stage, assess the integrity and homogeneity of the structures of the ocular orbit, avoid complications during treatment and determine its effectiveness. Ophthalmologists prescribe MRI of the eye orbits
and optic nerves if metastases of malignant tumors are suspected. For optic atrophy, MRI is required to determine the extent of degenerative changes.
Magnetic resonance imaging with contrast makes it possible to examine the blood vessels of the eye and diagnose thrombosis and aneurysm.
Why contrast is needed
The dye injected through a vein has the ability to stain blood vessels. In addition, it accumulates in the soft tissues of the body. Moreover, healthy cells are weakly capable of accumulating contrast, or do not do this at all. But cells with a malignant process “glow” on the tomograph brighter than others. Therefore, when making an oncological diagnosis, the patient is prescribed an MRI with contrast.
The dose of contrast injection depends on the body weight of the subject. Modern drugs are safe for the patient and do not cause side effects. Within 24 hours, the drug will be excreted from the body through the kidneys.
Indications
MRI of the eye orbits shows minute changes in their structure and is performed for the following indications:
- eye injury or foreign body entry into it;
- blurred vision of unknown origin;
- causeless pain and pain in the eyes;
- inflammatory process in the area of the eye orbit;
- pre- and postoperative period;
- pathological changes in the retina and cornea;
- infection of the tissues of the eye orbits;
- suspicion of the development of neoplasms in the eye area or the appearance of metastases.
Alternative research methods
- Ophthalmological research methods - ophthalmoscopy, electrophysiological study, exophthalmometry, etc.
- Ultrasound of the orbits is a simple, painless and safe method of objective examination.
- CT scan of the orbits—diagnosis of bone abnormalities, traumatic, inflammatory or tumor processes.
Contraindications Preparation
the prices for services in the price list or check by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Contraindications
MRI is not performed if the patient’s body contains metal implants or medical electronic devices that cannot be removed or temporarily removed. These could be pacemakers, metal vascular clips, implanted hearing aids, or braces. The examination is also excluded if the patient is in serious condition and there is a need for constant use of a cardiac monitor or endotracheal tube.
Pregnant women can be examined with a magnetic resonance imaging scanner in the second and third trimester if there are serious indications for the examination and the administration of contrast is not expected. MRI with contrast is contraindicated at any stage of pregnancy, as well as in cases of chronic renal failure and allergy to the contrast agent.
The patient's heavy weight can also become an obstacle to the procedure - most devices are designed for body weight not exceeding 120 kilograms.
What do you need to know about the study area?
The human visual system is not limited to just the eyeball. This is a whole multi-component system that functions like a well-coordinated mechanism. The optic nerve and eye orbits also belong to this mechanism.
The optic nerve is the second pair of cranial nerves. They are the ones who transmit the signal from the retina to the brain and help us navigate the outside world. The nerve itself has an atypical structure and development. It is more like cerebral white matter, which is connected with the nuclei of the diencephalon and the cerebral cortex.
What clinical manifestations should be diagnosed? Even a slight decrease in vision may indicate problems with the optic nerve. Perhaps its conductivity is impaired, or a certain area of the fibers is affected, which limits the field of vision. Visual hallucinations, regardless of etiology, should also be the reason for contacting a specialist.
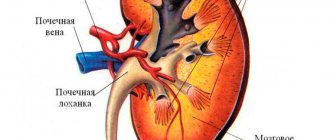
The eye sockets or orbits are a paired cavity in the skull.
It is in it that the eyeball with appendages is located. The volume of the orbit of an average adult person is 30 ml, of which 6.5 ml is reserved for the eyeball. MRI will help monitor the condition of the orbits and diagnose congenital or acquired disorders. Among them are various defects, the result of mechanical damage, cancer, inflammatory processes, etc. Indications/contraindications for the procedure
| Indications | Relative contraindications | Absolute contraindications |
| Mechanical injuries to the eyeball (for example, foreign objects or the consequences of a blow) | The presence of tattoos, permanent makeup, which may be based on metal particles | The presence of a pacemaker (can affect the magnetic waves of MRI equipment, distorting the diagnostic result) |
| Inflammatory/infectious process in one or more elements of the visual system | Decompensated heart failure | Presence of ferromagnetic/electronic middle ear implants |
| Suspicion or diagnosis of thrombosis | First trimester of pregnancy | Presence of ferromagnetic Ilizarov apparatus |
| A sharp decrease in visual acuity, pain/discomfort in the eyes, regardless of etiology | Claustrophobia | Excessive excess weight (depending on the maximum weight that the equipment can support) |
| Diagnostics before and after surgery on the organs of the visual system | Severe or extremely serious condition of the subject | |
| Suspicion or diagnosis of cancer | Patient's mental illness | |
| Problems with blood supply that affect the functionality of the visual organs | Presence of fixed dentures or braces | |
| Diagnosis of the optic nerve condition | Hemostatic clips, prosthetic heart valves, insulin pumps | |
| Diagnosis of the development of metastases that have penetrated into the tissues of the organs of vision |
Contrast MRI is contraindicated during pregnancy (in the first trimester), chronic renal failure, hemolytic anemia and individual intolerance to contrast agents.
Why are tattoos, braces and metal devices considered contraindications?
An MRI is a large magnet that is capable of attracting metal elements. The person inside whom these elements are located may feel extremely unpleasant sensations - from minor discomfort to serious pain. It depends on the amount and characteristics of the metal inside. In addition to implanted iron, before diagnosis it is necessary to remove all metal objects and design elements - earrings, belt, etc.
What's wrong with tattoos? Until 20 years ago, ink tattoos contained small pieces of metal. In modern tattoo parlors, this practice has become the exception, not the rule, which the client is always warned about. A patient who has a metallic tattoo on their body will experience tingling, pain, or itching during diagnosis. Magnetic fields literally pull metal enzymes out of the ink, which leads to unpleasant symptoms. The reaction of patients can be specific - some do not feel pain, others interrupt the procedure due to an unbearable feeling.
Metallized substances can distort MRI results. In order not to waste time and material resources, be sure to inform your doctor about the presence of a tattoo. He will determine the presence/absence of metal particles and select an alternative diagnostic method.
How is the procedure done?
The patient is placed on a mobile tomograph table. A contrast agent is injected into the vein after the first series of images. The examination lasts from 20 minutes to an hour, you cannot move during this time, so it may be necessary to fix the head. Eyes should be kept closed during the examination. The space inside the device is well ventilated, and communication with the doctor and his assistant is possible (call button, signal bulb).
Patients who cannot remain still for a long time (severe pain, motor agitation due to mental illness), as well as young children, may be offered medicinal sedation if other research methods that do not require complete immobility are excluded. The Energo clinic does not provide sedation; the information is provided for informational purposes.
Images and a specialist’s report are issued within 30-60 minutes after the examination; in case of controversial issues, issue may be issued the next day
Is it possible to do MRI for children?

In clinics, MRIs are performed on children from the age of 7 years. If a younger child needs diagnosis, he should be taken to an institution that specializes in pediatric scanning.
Parents of babies are allowed to be present with them during the scanning period. Since they are unable to maintain a quiet body position for a long period, they are examined under anesthesia or light sedation.