Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI widely entered medical practice a little later than CT - the revolutionary property of this method was the absence of the need for X-rays to obtain images.
This type of tomography is based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance - the ability of protons of the hydrogen atom (of which there are many in the human body, which is more than half composed of water) to change their orientation in space under the influence of a strong electromagnetic field. In other words, unlike all other types of tomography, MRI can be taken as often as desired without the risk of exceeding the permissible dose of radiation. This scan is not contraindicated for children or pregnant women (provided it is performed without intravenous contrast). Disadvantages include the relatively long time it takes to perform tomography (on average, about 30-40 minutes) and the ban on MRI for people whose bodies contain metal plates, foreign objects and some electronic devices - for example, pacemakers. What is it used for: for the diagnosis of tumors, vascular development abnormalities, diseases of the central nervous system, joints, and intestines.
What data does the doctor evaluate?
The results obtained after a CT scan allow us to have data on the presence or absence of many serious diseases:
- development of oncological tumors in internal organs (intestines, liver, bladder, kidneys, lungs, adrenal glands, pancreas);
- patency and location of blood vessels;
- exact shape and size of organs, possible spread of metastases;
- pulmonary pathologies;
- inflammatory processes;
- stones in the kidneys or bile ducts;
- the appearance of cysts or foreign bodies, etc.
Both the entire body and individual organs are subject to examination.
When carrying out a CT procedure, in order to save money, it is possible to study only one organ, the condition of which causes the greatest concern to the attending physician.
Shape and location of the organ
The computed tomography procedure allows you to get an accurate picture of the size, shape and location of a particular object being studied. Ultimately, an accurate three-dimensional image is simulated, which shows a picture of the location of organs and systems as if in cross-section, that is, without superimposing them on each other, as happens when conducting research using X-rays.
CT examination helps to accurately identify the presence of pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract). If a disease of the kidneys, adrenal glands, blood vessels, gallbladder and urinary system is suspected, SCT or MSCT is also often prescribed.
CT scan clearly shows various gastrointestinal pathologies
Organ density
In the CT image obtained during a CT scan, the color of certain organs varies from light to more saturated dark. Color is determined by the degree to which the organ absorbs radiation, which in turn depends on the density of the object. Thus, bone tissue in the image is displayed in light colors due to its high density, while liquids and air will have the darkest shades.
When interpreting CT scans in medicine, specialists use the Hounsfield scale to determine the density of the object being studied by color. There is a certain density range for each type of tissue, and if the actual density of an organ goes beyond the established norm, then pathologies may be present.
Classification of types of tomography
The relative position of the source of probing radiation, the object and the detector
Chest X-ray: indications for diagnostics
From the point of view of the relative position of the source of probing radiation, the object and the detector, tomographic methods can be divided into the following groups:
- transmission - the probing external radiation passing through a passive (non-radiating) object is recorded, partially attenuated at the same time (the shadow of the object);
- emission - radiation is recorded coming out of an active (emitting) object with a certain spatial distribution of radiation sources;
- combined transmission-emission (luminescent, acousto-optical and optoacoustic, etc.) - secondary radiation is recorded from sources distributed throughout the volume of the object and excited by external radiation;
- echo sounding - external probing radiation reflected from the internal structures of a passive object is recorded.
Dimensions of objects under study
- Micro level (microtomography) - objects the size of an individual cell are examined.
- The level of objects commensurate with the human body (from a single organ or laboratory mouse to an airplane).
- Macro level - atmospheric phenomena (clouds, cyclones, tornadoes), planets and stars.
Scope of application
By area of application there are:
- medical tomography
(as a type of medical imaging and medical diagnostics); - industrial (technical) tomography (as a type of flaw detection);
- tomography of macro objects.
Probing radiation
- Tomography using sound waves (including seismic): ultrasonic tomography (UT);
- seismic tomography.
- radionuclide emission tomography (gamma radiation); single photon emission tomography (SPECT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- neutron tomography;
Carrying out the procedure
CT scan is a fairly simple procedure to perform; it often does not require any effort or special preparation from the patient.
Preparation
It is necessary to prepare in advance for a CT scan only in case of examination of the abdominal organs. This procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. A few days before the procedure, you need to stop eating foods that increase bloating and gas formation. If it is necessary to use a contrast method, you must inform your doctor about the presence of allergies (if any).
Preparing for a CT scan comes down to the following steps:
- get rid of all metal objects and accessories,
- take out dentures,
- refuse to eat 2-4 hours before the procedure,
- Before CT scan of the kidneys, increase fluid intake,
- inform the doctor about the medications you are taking,
- Take a contrast agent if necessary (according to your doctor’s recommendations).
Methodology of the procedure
The procedure is carried out in specialized offices or medical clinics. The duration of the study is about half an hour.
So, how is a CT examination done? Description of the procedure:
- The patient is placed in a horizontal position on the tomograph table.
- The body is secured with straps to ensure its immobility.
- The table moves slowly through the scanner. An X-ray generator rotates around it.
- The patient's body undergoes layer-by-layer scanning. The information is transferred to the computer.
During the procedure, the doctor is in another room. During the study, communication with the patient is carried out via audio communication.
Patients may have a question: how is CT diagnostics of the back performed? This examination is carried out similarly to other organs and parts of the body. In some cases, it may be necessary to change the position of the patient's body: he may be placed on his stomach or side.
What is CT of organs - features
Ascites - methods of diagnosis and treatment, prevention and prognosis
All images obtained from tomography are black, white or various shades of gray.
Air and gas on CT scan are black, bone tissue is white. The color of other organs and tissues is gray. Its intensity and brightness depends on the density of the tissue being studied.
Metastatic foci, cysts, abscesses, tumors, etc. have their own specific features that allow them to be differentiated from normal tissues. IMAGES
Indications for the study
The CT procedure is indicated if the patient has:
- head injuries;
- spinal injuries, intervertebral hernias, spinal anomalies, osteochondrosis, bone destruction;
- sinusitis (sinusitis, ethmoiditis, etc.);
- fainting states and seizures of unspecified etiology;
- developmental anomalies, vascular injuries, aneurysms;
- various neoplasms, metastatic foci;
- echinococcal cysts in the liver, lungs, etc.;
- unspecified pathologies in the abdominal or chest organs.
Also, if necessary, computed tomography can be performed during screening examinations in patients with a high risk of developing tumors or the appearance of metastatic foci.
Additionally, the study is used if necessary, CT control of the biopsy being performed.
CT scan – contraindications
There are contraindications during pregnancy and breastfeeding (if there is no alternative, breastfeeding is stopped for 48-72 hours after the study). Also, if an alternative is available, CT is not recommended for young children.
To reduce the level of radiation exposure to the body, for children and patients of small stature (and low body weight), the dose of X-ray radiation is reduced by 50%.
CT with contrast is contraindicated in patients with individual intolerance to the contrast used, as well as in persons with severe somatic pathologies (the presence of diabetes (diabetes mellitus), renal failure, decompensated thyroid diseases, etc.).
Patients with convulsive symptoms, mental illness, claustrophobia, etc. CT scanning can be performed under general anesthesia.
Also, tomography is not performed on patients weighing more than 150 kilograms, since tomographs are not designed for such a load.
What does a CT scan show?
Computed tomography can be used to detect and visualize:
- metastatic foci,
- tumors,
- bone destruction,
- foci of osteochondrosis,
- anomalies and aneurysms of blood vessels,
- bone abnormalities,
- intervertebral hernias,
- fluid in the nasal and paranasal sinuses,
- abscesses in the liver, lungs, etc.
Tomographic examination of the paranasal sinuses is effective for traumatic damage to the eye sockets, the bony part of the nasal septum, and sinusitis (ethmoiditis, sinusitis, sphenoiditis, frontal sinusitis).
CT scan of the neck is indicated for developmental anomalies, traumatic injury or atherosclerosis of neck vessels, neck tumors, pathologies of the cervical spine (developmental anomalies, osteochondrosis, etc.), pathologies of the thyroid gland.
Computed tomography of the spine allows you to detect displacement of the vertebrae, intervertebral hernias, destruction of bone tissue and intervertebral discs, spinal deformities, abnormalities of the spine, etc.
Examination of the chest organs allows us to identify pathologies of the thoracic aorta, neoplasms and metastatic foci in the lungs, abscesses and fluid in the lungs.
Abdominal CT is effective in diagnosing aneurysmal vascular lesions and atherosclerotic plaques of the abdominal aorta, identifying abscesses, inflammatory changes in organs, diverticula in the intestine, neoplasms of the liver, pancreas, etc.
Characteristics of the method
What is computed tomography? This is a method that allows you to determine the condition of any internal organ without entering the body. Belongs to the non-invasive group. Used since 1988. Over the course of three decades, it has gained great popularity due to the high information content of the results.
CT scan involves the use of a tomograph - a special device that produces X-rays. They penetrate the body and are absorbed by tissues from different angles. The degree of absorption depends on the density of the tissue - this is the basis for the examination mechanism.
Special sensitive sensors record the slightest changes in tissues and transmit this information to the computer. It processes the received data and turns it into a three-dimensional image, which the diagnostician sees on the monitor. The method works on the principle of radiography. However, it is more advanced and accurate. Its second name is X-ray computed tomography.
False PET results
Choosing a pillow for the driver's back in the car
Both false positive and false negative results are possible. Sometimes PET scans reveal foci of radiopharmaceutical accumulation in organs that are considered tumorous, although they are not. This is primarily due to improper preparation for the study.
Before PET, it is important to adhere to a diet low in simple carbohydrates and avoid physical activity. If these conditions are not met, unreliable results may occur.
In addition, intense accumulation of glucose is typical of inflamed tissues. Such an inflammatory focus can mimic a malignant tumor.
False positive results are observed when:
- granulomatous diseases;
- postoperative changes;
- inflammatory diseases (abscess);
- metformin therapy (in the intestines);
- reactions to foreign bodies;
- fat necrosis.
A false negative result is the absence of radiopharmaceutical accumulation in the tumor. This situation can be observed with low-grade tumors of a non-aggressive nature. Some tumors may be hidden due to high physiological accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals in certain organs.
It is difficult to interpret PET results against the background of normal accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals in the brain, tonsils, muscles (especially after physical exercise), bone marrow, and thymus. To visualize the tumor, another radiopharmaceutical, for example, based on amino acids, may be required.
Contrast enhancement
The need to constantly improve examination results complicates the diagnostic process. Increasing information content due to contrast is based on the ability to distinguish tissue structures that have even slight differences in density, which are often not determined during conventional CT.
It is known that healthy and pathological tissue have different intensities of blood supply, which causes a difference in the volume of incoming blood. The introduction of an X-ray contrast agent allows for increased image density, which is closely related to the concentration of iodine-containing X-ray contrast agent. Injection into a vein of 60% contrast agent in an amount of 1 mg per 1 kg of patient weight can improve the visualization of the organ under study by approximately 40–50 Hounsfield units.
There are 2 ways to introduce contrast into the body:
- oral;
- intravenous.
In the first case, the patient drinks the drug. Typically, this method is used to visualize hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Intravenous administration makes it possible to assess the degree of accumulation of the drug in the tissues of the organs being studied. It can be carried out by manual or automatic (bolus) administration of the substance.
Important! The rate of bolus administration of the drug fully corresponds to the operating mode of a modern tomograph, so it is almost impossible to obtain a similar result using a manual one.
What types of CT scans are there?
Medical technologies are progressing all the time, and therefore diagnostic devices are also being improved. The following types of CT scans are available:
- spiral;
- multilayer;
- contrasting;
- angiography;
- perfusion.
Spiral computed tomography
This form of devices has been used in diagnostic practice for 30 years. A spiral computed tomograph consists of 3 main parts:
- rotating X-ray tube;
- one row of ultra-sensitive sensors along the circumference of the ring;
- couch moving across the gantry.
Multislice computed tomography
This type of device provides the most informative and most accurate research. Multislice computed tomography (MSCT) differs from standard diagnostics in the increased number of detectors and tubes. In the devices described, the sensors are installed in 2-4 rows. Not one, but two X-ray tubes can rotate around the gantry circumference, which significantly speeds up the examination and reduces the radiation dose.
Other advantages of MSCT:
- the latest software;
- high resolution images;
- optimal contrast of images;
- the ability to record dynamic processes in real time;
- maximum detail of the cut;
- large area of anatomical coverage;
- construction of 3D models of all systems and organs.
Computed tomography with contrast
To enhance the differentiation of organs located nearby and to clarify small physiological structures, such as blood vessels, special types of CT studies are used. They involve the introduction of drugs that increase tissue contrast when absorbing x-rays. This type of computed tomography is performed in 2 ways:
- Orally.
The patient drinks a solution with a contrast agent. The volume of liquid, the sequence and frequency of its intake is calculated by the doctor. - Intravenously.
The contrast solution is administered by injection or using an automatic dropper.
CT angiography
This type of study is designed specifically for studying the circulatory system. CT angiography of the vessels of the neck and head helps to identify any circulatory disorders in these areas, including ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, assess the severity of their consequences, and detect neoplasms of any quality. To increase the information content of the procedure, a contrast agent containing iodine is first injected into the cubital vein.
One of the most modern and impressive achievements of medicine is multislice computed tomography of the head, neck, limbs and other parts of the body. Thanks to advanced software, this manipulation allows you to create a three-dimensional model of the entire human circulatory system with the ability to display it in detail from any angle.
CT perfusion
The presented version of the study is considered the most advanced and accurate way to diagnose dangerous circulatory disorders. Perfusion computed tomography differs from the standard procedure in the minimum slice thickness, which ensures a more detailed 3D model of the organs as a result. This manipulation is carried out with intravenous administration of a contrast agent under the control of an automatic dropper.
In medicine, CT perfusion of the brain and liver is used exclusively. It helps not only to create a highly accurate three-dimensional image of these organic structures, but also to evaluate the intensity and efficiency of blood flow through their tissues, large and small vessels. With modern devices, these processes can be observed in real time.
CT device: principle of operation
Computer tomography is a software and hardware complex that allows you to create high-definition images of the area under study. Directed beams of X-rays pass through the patient's body at different angles, after which their parameters are recorded by ultra-sensitive sensors. Processing and analysis of the received data is carried out by a powerful software package. The result of the scan is a series of layer-by-layer images with a step of 0.5 mm, the study of which allows you to make an accurate diagnosis.
What types of CT machines are there?
Regardless of the type of equipment, it includes the main components:
- the body is cylindrical (less often cubic) in shape;
- ray tubes;
- table moving through the gantry frame.
Depending on how the CT machine works, the following types of such equipment are distinguished:
- Step-by-step - outdated tomographs, rarely used for diagnostics due to high radiation exposure to the body, low information content and long examination time. They scan only one slice at each step.
- Spiral - the movement of the table and the rotation of the emitter occur simultaneously. This allows you to obtain more information in less time and reduce radiation exposure.
- Multispiral is a type of spiral tomograph, the main difference of which is that several tomographic slices are obtained during one revolution of the gantry. The greater the number of slices the device produces for each step, the clearer the images are, and the smaller the volume of defects and the magnitude of the x-ray load. For example, the MSCT power of 64 slices means that 64 data streams are processed simultaneously.
Unlike magnetic resonance scanners, open-type CT does not exist. This is due to the impossibility of preventing the spread of X-rays into the surrounding space in the absence of a closed circuit.
Which CT machine is better?
Currently, most clinics use spiral and multispiral tomographs. Most often, patients are offered to undergo examination on 8-, 16-, 32- and 64-slice devices. Some specialized medical centers have installed 128-slice equipment. As is clear from the previous explanations, more detailed information is provided by multispiral installations with a number of sections from 32.
You should check with your doctor about which equipment is best for diagnostics. So, to study bone tissue injuries, it is enough to sign up for an examination at a clinic where a 16-32-slice device is installed. If we are talking about studying blood vessels, the heart, and internal organs, the best option would be MSCT with 64 slices.
What a CT machine looks like: photo
So that the appearance of the device does not come as a surprise to you, you can see what a CT machine looks like in a photo on the Internet. On our portal you can also find photo and video information about the CT examination.
Literature
Wiktionary has an entry for "tomography"
- Vazhenin A.V., Vaganov N.V. Medical and physical support of radiation therapy. - Chelyabinsk, 2007.
- Levin G. G., Vishnyakov G. N. Optical tomography. - M.: Radio and communication, 1989. - 224 p.
- Tikhonov A. N., Arsenin V. Ya., Timonov A. A. Mathematical problems of computed tomography. - M.: Science, Ch. ed. physics and mathematics lit., 1987. - 160 p.
- Tikhonov A. N., Goncharsky A. V., Stepanov V. V., Yagola A. G. Numerical methods for solving ill-posed problems. - M.: Science, Ch. ed. physics and mathematics lit., 1990. - 232 p.
- Natterer F. Mathematical aspects of computed tomography. - M.: Mir, 1990. - 288 p.
- Vasiliev M. N., Gorshkov A. V. Hardware-software complex GEMMA and tomographic method for measuring multidimensional distribution functions in trajectory and phase spaces when diagnosing charged particle beams. // Instruments and experimental techniques. - 1994. No. 5. - P.79-94. // Translation into English: Instruments and Experimental Techniques. - V.37. No. 5. Part 1. 1994. -P.581-591.
- Gorshkov A. V. REIMAGE software package for significantly improving image resolution when processing physical experiment data and a method for finding an unknown hardware function. 01/26/94. // Instruments and experimental techniques. - 1995. No. 2. - P.68-78. // Translation into English: Instruments and Experimental Techniques. - V.38. No. 2. 1995. - P.185-191.
- Moskalev I. N., Stefanovsky A. M. Diagnostics of plasma using open cylindrical resonators. - M.: Energoatomizdat, 1985.
- Hermen G. Restoring images from projections: Fundamentals of reconstructive tomography. - M.: Mir, 1983. - 352 p.
- Weinberg E.I., Klyuev V.V., Kurozaev V.P., Industrial X-ray computed tomography, in the book: Instruments for non-destructive testing of materials and products. Handbook, ed. V.V. Klyueva, 2nd ed., vol. 1, M., 1986
Where is the best place to get a CT scan?
The correctness of the computed tomography result directly depends on two factors: the professionalism of the radiologist, the quality and technical capabilities of the tomograph itself. Multislice, multispiral, multidetector computed tomographs are used for research.
All manufacturers of these devices want to reduce the radiation dose to a minimum with each new model.
The doctor conducting the examination must know exactly the purposes and subtleties of each examination. Therefore, those who do not know where to get a CT scan can be advised: only in serious diagnostic centers specializing in the required disease profile. They have the latest equipment that will give a high-quality image with a minimum of radiation, and a staff of experienced and qualified specialists will help make the correct diagnosis.
Price
In Moscow, studies are carried out by several private and public medical centers. The price for PET/CT ranges from 10 (Russian Academy of Sciences Hospital) to 77 thousand rubles (European Medical Center).
In St. Petersburg, you can undergo the study at the Main Clinical Complex of the Almazov National Medical Research Center for 7,500 rubles, the Clinic of the Brain Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences for 15,500 rubles, and other medical institutions.
In Kazan, PET CT is performed at the Republican Clinical Oncology Center for 38 thousand rubles, and in Yekaterinburg at the Sverdlovsk Regional Oncology Center for 39,200 rubles.
note
You can undergo the study for free under your compulsory medical insurance policy. To do this, you need to get a referral from an oncologist after a preliminary examination.
Often you have to go to other regions where such a tomograph is available, after waiting in line for several weeks.
Important!
Please prepare in advance and bring with you all extracts, protocols or recordings (disks) of previous studies. The more information the doctor has before the study, the clearer the task assigned to him. In addition, previous results will allow us to assess the dynamics of the disease.
Before the procedure, be sure to notify your doctor if you have:
- Pregnancy
- Are you allergic to medications, including iodine in the contrast agent?
- Cardiovascular disease (eg, heart failure)
- Diabetes mellitus or you are taking metformin (Glucophage). You may need to avoid taking this medication the day before and for the day after your procedure.
- Kidney diseases
- Bronchial asthma
- A pacemaker or insulin pump is installed
- Multiple myeloma.
- You have had an X-ray examination within the previous 4 days using a barium contrast agent (irrigoscopy) or you have used medications containing bismuth. Barium and bismuth, appearing on X-ray film, reduce image quality.
- There is a fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia). Because you will have to lie still inside the scanner during the procedure, you may need sedatives. In this case, you should ask someone to take you home after the procedure.
The Department of Radiation Diagnostics of the University Clinical Hospital No. 2 operates within a multifunctional clinic, therefore, if any possible complications are suspected, the decision on conducting the study, its type and methods of preparation is made together with medical specialists (nephrologist, endocrinologist, etc.).
Which is better - MRI or CT scan of the sinuses?
Many patients are interested in the question of which is better – CT or MRI of the paranasal sinuses. These diagnostic methods solve different problems, so the choice of examination method depends on the specific case.
MRI is based on the effect of radiofrequency pulses on an object placed in a high-intensity magnetic field. This technology is best used to study solid soft tissues. CT uses X-rays that most clearly visualize bones and hollow organs. The latter include the nasal sinuses.
Magnetic tomography is done:
- to confirm/exclude perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus as a result of trauma or dental diseases;
- if you suspect a tumor, polyps, cysts;
- to assess the condition of the mucous membranes of the sinuses;
- for headaches of unknown origin.
MRI also shows inflammation and hemorrhages in the paranasal cavities.
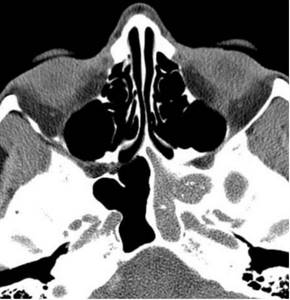
Magnetic tomography of the paranasal sinuses: left-sided sphenoiditis
CT diagnostics of the paranasal sinuses is done for acute inflammation and recurrent sinusitis. A computed tomography scan will show cracks and fractures of the facial bones, osteomyelitis complicating an injury or dental disease, metastases that have spread from neighboring anatomical areas.
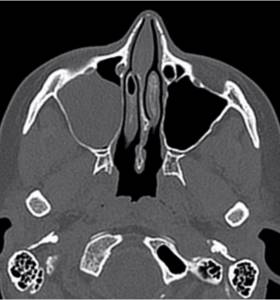
Computed tomography scan of the nasal sinuses: right-sided sinusitis
When giving preference to a magnetic resonance examination or CT scan of the nose, the doctor takes into account the limitations. MRI is not performed if there are metal elements on (in) the body. The processes occurring in the tomograph can cause damage to these structures and the device itself. A CT scan of the sinuses is not a magnet, but an x-ray. Metal objects do not interfere with the operation of the device, but may appear in the photo and cause errors in the description.
Due to radiation, pregnant women are not allowed to undergo CT examinations of the maxillary sinuses (any dose of radiation is harmful to the fetus). In such a situation, the best option is MRI; diagnostics are carried out strictly according to indications.
CT scan – indications and contraindications
The technology in question is widely used in medicine for several purposes. Computed tomography may be prescribed as:
- screening;
- emergency diagnostics;
- routine inspection;
- assessing the effectiveness of treatment;
- monitoring the implementation of therapeutic and diagnostic manipulations.
CT – indications for:
- fainting;
- headache;
- dry prolonged cough;
- fever;
- convulsive syndrome;
- mental status changes;
- head injuries;
- bleeding disorders;
- focal neurological deficit;
- paralysis;
- cognitive disorders;
- high blood pressure;
- hypoventilation of the lungs;
- meningism;
- pain in any part of the body of unknown origin;
- sustainable change in the consistency and quality of stool;
- digestive disorders;
- deterioration of mobility of the spine and joints;
- myalgia;
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- internal bleeding;
- diseases of the teeth and oral cavity;
- suspicions of the presence of neoplasms of any quality;
- severe paresis and other conditions.
Contraindications to manipulation without the use of a contrast agent:
- pregnancy;
- body weight exceeding the permissible maximum for the existing device.
CT with the use of iodine-containing drugs has similar contraindications; it should not be done in the following cases:
- multiple myeloma;
- allergy to contrast agent;
- diabetes mellitus in a severe stage;
- renal failure;
- unsatisfactory general condition of a person;
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
Negative effects of the technique on the body
SCT is considered a relatively safe examination method. A potential threat to the patient’s health and life is associated with the effect of ionizing radiation on the body’s cells.
The risk of developing cancer increases over the next 10-20 years when using one or more x-ray techniques whose annual dose exceeds 5 mSv.
When the fetus is exposed to rays during intrauterine development, the likelihood of disruption of the formation and maturation of organs and tissues increases, which leads to anomalies and developmental defects. In children under 18 years of age, physical development may be delayed during the period of active growth.
Acceptable frequency of diagnostic procedures
For each patient who has been exposed to radiation for diagnostic purposes, a dose load recording card is created.
It records the types of x-ray procedures performed during the year and the individual effective doses used.
When making a primary or repeated referral for tomography, the doses received from the previous diagnosis are taken into account.
According to vital indications, the frequency of diagnosis is increased at the discretion of the attending physician and radiologist.
Comparison of surveys
There are several differences in the operation of MSCT and CT scanners. During the CT procedure, the table stands motionless, while during SCT it moves at a speed programmed by the doctor. The X-ray tube makes a spiral motion, collecting information and transmitting it to detectors. The time spent and the amount of contrast required for scanning with the SCT method are required less. Accordingly, below.
The difference between SCT and CT:
- Minimal radiation exposure (one third less than CT).
- Speed of examination.
- The ability to take many pictures in different projections.
- Minimum interference during research.
- The sensors are positioned in such a way that a thin slice of the area being examined is visible.
- Contrast is more effective.
- Tumors measuring 1 mm are visible.
Diseases of the pancreas, liver, and aortic pathologies are visually determined. Using precise tomograph settings, the specialist adjusts the slice size: the minimum value is 0.5 mm.
Indications and contraindications
CT is good at diagnosing pathologies of bone structures of all parts of the spine, lower and upper extremities, and skull. MSCT is prescribed to detect tumors and neoplasms, study cracks and fractures, as well as diagnose the abdominal cavity: pathologies of the stomach, lungs and other hollow organs. MSCT is often used to clarify or confirm the diagnosis after CT. Cases in which MSCT is needed:
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- Internal bleeding of unknown origin.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
- Pulmonary and renal failure.
- Determination of bone density.
- Confirmation of the presence of tumor processes or metastases.
- Pathologies of the jaw.
There are absolute and relative contraindications:
Absolute ones include: allergy to gadolinium (contrast agent); pregnancy (harm to the fetus); renal failure; the patient's weight exceeds 130 kg.
Relative: preschool age, weakened physical condition (illness, malaise); psycho-emotional disorders that do not allow the patient to maintain a stationary position; metal implants, prostheses in the body; tattoos that contain iron particles in the ink.
The procedure is hampered by the patient's Parkinson's disease. Severe tachycardia and vasoconstriction due to arterial calcification create difficulties during scanning.
How to prepare
If there is an examination of joints, soft tissues, spine, or brain, special preparation is not required; it is enough to have clothes that do not restrict movement. Tomography of the abdominal organs using contrast occurs as follows: a test for allergy to iodine is done; exclude gas-forming foods from the diet the day before the procedure; stop eating 4 hours before the examination. 2 hours before the scan, drink a contrast drug and do a cleansing enema.
3 days before the tomography with contrast agent, a blood and urine test is done. If a high level of urea is detected in the urine and the presence of creatinine, the procedure is contraindicated.
How often can scanning be carried out and the permissible radiation dose?
MSCT has gained popularity due to the minimal risk of a large dose of radiation that the patient may receive during scanning. This effect is achieved due to the short examination time. You can take the necessary pictures in a few seconds. However, the procedure is not recommended more than once a year. The doctor prescribes a repeat CT scan in an emergency. The permissible radiation dose is 150 mSv per year.
Applicable radiation doses to some organs:
- head - 2 mSv;
- spine - 6 mSv;
- pelvic area - 9 mSv;
- OGK - 11 mSv.
Harmful to young children and pregnant women
Children need to undergo MSCT according to strict indications, since the child is undergoing an intensive development process, radiation exposure stimulates unwanted cell division and provokes oncology. The procedure is not recommended for children under 14 years of age.
For pregnant women, MSCT is performed in emergency cases when it is impossible to do an MRI and the need for urgent diagnosis. The scan takes place under general anesthesia to immobilize the fetus.
Types of computed tomography
Types of computed tomography according to research methods:
- Spiral - with this research technique, the X-ray emitter and the table on which the patient is located rotate. In this case, the rays are arranged in a spiral.
- Multislice – differs from spiral tomography in the location of the sensors that record the rays. In such a study, they are placed in several rows, which reduces the irradiation time. This tomograph is also equipped with two X-ray emitters. In one revolution of the tube, it is possible to completely examine the heart or brain.
- Using a contrast agent - when examining nearby organs, a contrast agent containing iodine can be used. Such a study allows you to obtain clearer images and accurately distinguish between healthy and diseased tissue.
CT results facilitate the diagnosis process and allow timely treatment of the patient’s pathologies.
A CT scan of the chest is aimed at detecting tumors or metastases in the chest. It allows you to accurately determine the location of tuberculosis foci and check the integrity of blood vessels.
An abdominal CT scan can detect changes in organs located in this area.
Using a CT scan of the brain, one can confirm or refute a violation of the integrity of blood vessels, intracranial hemorrhages and tumor formations. A tomogram of the head accurately indicates the location of tumors.
Tomography of the nose and sinuses is performed before plastic surgery or after serious injuries to the nose. It allows you to determine the presence of inflammatory processes in the paranasal sinuses.
A kidney examination with a CT scanner is prescribed in the presence of urolithiasis, cysts, or renal development disorders.
Before surgery in the oral cavity, the patient is advised to undergo a tomography of the jaw and teeth. A tomography examination helps assess the health of the oral cavity and the structure of bone tissue. With its help, the location of foci of inflammation is determined.
CT scan of the musculoskeletal system allows you to determine changes, damage and pathological conditions of the skeletal systems. Sometimes patients ask: what do CT images of the cervical spine show? They depict a layer-by-layer section of the human body. With the help of such an examination, a number of diseases of bone tissue and the musculoskeletal system can be identified.
Preparatory activities
In most cases, CT does not require special preparatory measures. You should make sure that there are no contraindications, and also prepare yourself mentally for the procedure.
The patient has the right to know all the details, to become familiar with how the diagnosis is carried out, and what side effects it may have. If you experience severe nervousness, you can take a sedative.
A couple of hours before the test, it is recommended to refrain from eating and drinking. This is especially important when the planned administration of a contrast agent. Before the procedure itself, you need to take off all metal objects and change into something comfortable. Many diagnostic centers provide special clothing for performing computed tomography. Young children are often given a light anesthesia to ensure immobility.
If a CT scan of the abdominal cavity is performed, the preparation may be somewhat more thorough. The patient should, a few days before the study, refuse food that can cause fermentation in the intestines:
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- mushrooms;
- fatty, spicy foods;
- carbonated drinks.
The day before the procedure, it is advisable not to eat anything solid at all. Only puree soups, juices, fruit drinks, compotes. A CT scan of the abdomen is performed on an empty stomach. The patient is first given a laxative or an enema to cleanse the intestines.
Computed tomography of the pelvic organs also has its own nuances. In this case, the patient should strengthen the drinking regime a few days before the procedure. From the evening of the day preceding the study until the time of its conduct, it is advisable to take at least four liters of liquid. It is usually recommended to dilute 76% Urografin or 60% Triomblast in this amount of water.
It is necessary to tell the treating doctor about all serious diseases that you have had before or currently have, about the medications you are taking, and whether you are allergic to specific irritants.
How the research works
In the CT room, the patient receives information about the procedure and signs informed consent. Jewelry, dentures, and hearing aids are removed from the head and body. The patient changes into clothes without metal buttons or hooks, which cause artifacts to appear.
Patients suffering from fear of confined spaces and emotional instability are pre-administered sedatives.
The patient, with the help of an x-ray laboratory assistant, takes a horizontal position on the back, side or stomach on a movable conveyor table.
The body and limbs are secured with belts that restrict movement. Communication with the doctor, who will be in another room during the study, is maintained through an intercom. After moving the table inside the gantry, scanning and computer processing of data begins.
During the examination, to improve the clarity and quality of the image, commands are received from the doctor to hold your breath for 20-30 seconds or limit swallowing movements.
The scanning duration is 5-20 minutes. When using contrast enhancement, the time is doubled.
Within 24 hours after completion of the study, the patient receives a conclusion with a protocol describing the identified changes, photographs or electronic media with images.
Development of CT scanners
Over the course of two decades, tomographs have been improved by making changes to their design.
The angle of rotation of the X-ray tube was expanded, and the number of detectors was increased.
As a result, high-precision devices were created that are capable of detecting organic, functional changes in the early stages of the disease:
- 1st generation computed tomographs were designed in 1973. The device consisted of one tube emitting X-ray radiation in the form of a narrow beam, and a receiving detector located on the opposite side. During scanning, the tube moved 160 positions with a rotation angle of 10˚. As a result, it took 4.5 minutes to obtain one image, and processing the data and recreating the image on a computer took 2.5 hours.
- The 2nd generation devices were equipped with additional detectors, and the tube was configured for fan-shaped X-ray emission with a rotation angle of 30˚. This reduced the time to measure data and obtain one image of the scanned area to 20 seconds.
- For 3rd generation devices, 500-700 detectors are placed on the arc. Emitting a fan-shaped beam of radiation, the tube, together with the sensors, rotates around the subject’s body 360˚. This creates conditions for the study of moving organs, in addition to other structures of the human body. It takes 10 seconds to process one image.
- The 4th generation of tomographs is equipped with 1088 sensors located along the periphery of the ring. Inside the latter, a tube with a fan-shaped distribution of the beam rotates around the patient’s body. The new design has improved image quality. The time to obtain one slice was reduced to 0.7 seconds.
- The 5th generation of tomographs is used to study the structure of the heart. Their work is based on the action of an electric beam gun. It emits electrons that are directed by electromagnetic coils through the patient's body to tungsten targets located under the CT scanner table, which convert the signal into an image.
What magnetic field strength is preferable when choosing a tomograph?
The term “Magnetic resonance imaging” itself reflects the essence of the diagnostic method. If a human body is placed inside a machine (tomograph) with a constant magnetic field and electromagnetic waves are applied to it, this will lead to a change in the orientation in space of hydrogen atoms, which are part of all living cells. As a result, the atoms first absorb and then resonantly release a certain amount of energy, which is captured by sensors and, using computer processing, displayed in the form of an image of a section of the tissue under study. Such cuts can be obtained at any angle and direction.
It is the magnetic field, or rather its power, that plays a leading role in obtaining high-quality images.
The power of the magnetic field is measured in Tesla (T); in medicine, devices with a power of 0.1 to 7.0 Tesla are used.
Tomographs, depending on the strength of the magnetic field, are divided into several groups:
- Low-field - from 0.1 to 0.5 T
- Mid-field - from 0.5 to 0.9 T
- High-field - from 1.0 to 2.9 Tesla
- Ultra-high field - 3.0 and 7.0 Tesla
In clinical practice, low-field and high-field tomographs are more often used. Low-floor
scanners are usually installed on open-type devices. The power of the magnetic field of the tomograph from 0.23 to 0.5 Tesla does not allow obtaining a good quality image and on average 2 times more time is spent on the study compared to more powerful devices.
| Comparison of images of the abdominal organs using low-field (left) and high-field (right) tomographs |
But these tomographs also have advantages:
- can be used for claustrophobia and children, because in open-type tomographs there is no closed space;
- there are no restrictions on body weight and size of patients;
- Fewer breathing artifacts
- can be used in the presence of implanted metal products,
- good monitoring of patient behavior and equipment condition.
High-floor
scanners with a power of 1 to 3 Tesla are more often used in closed-type tomographs. These scanners provide high resolution, so images are obtained with greater contrast and less time is spent on research compared to low-field scanners. Such tomographs can be used to study any organ and tissue for any pathology. Devices of this type make it possible not only to distinguish foci of inflammatory, tumor, degenerative lesions measuring 1 mm, but also to determine their structure and clearly localize the boundaries of the lesion.
|
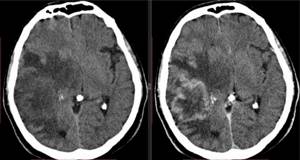
| Images of the brain obtained using a high-field tomograph clearly show small foci of tumor lesions |
The main disadvantages associated with the fact that high-field scanners are installed in closed-type tomographs are claustrophobia, restrictions on the patient’s body weight and size, and the inability to conduct research in the presence of back pain, when the patient cannot lie still for a long time.
The thickness of the tissue sections under study depends on the strength of the magnetic field. The greater the power, the smaller the distance between the layers of cuts, which reduces the risk of missing a damaged area.
On a high-field tomograph, sections are obtained with a thickness of 1.5 mm, which makes it possible to examine small lesions. This is of great importance in oncology for early diagnosis of the disease and timely treatment, in neurosurgery when analyzing the consequences of a stroke or before an upcoming operation.
| A series of layer-by-layer thin sections of brain tissue in different projections obtained on a high-field tomograph |
With a low-field tomograph, slices are obtained every 6 mm; this is not enough for early diagnosis of tumors. Therefore, if the doctor needs to determine the cause of the disease, the study on a low-field tomograph should be abandoned, because You will have to repeat the scan on a more powerful device. But such images can be used in cases where it is necessary to confirm a previously established diagnosis (for example, when passing an MSEC commission).
Ultra-high-field
Tomographs with a power of 3 Tesla are rarely used for diagnostic purposes, only when indicated in emergency cases, when it is necessary to minimize the examination time. Such tomographs are used for scientific purposes or in studying brain function (suspected epilepsy or Alzheimer's disease).
Which tomograph to choose - low-field or high-field - depends on the specific purpose of the study, because everyone has positive and negative sides.
Preparation
Most often, the study does not require special preparation. However, in any case, it is carried out on an empty stomach.
- Before a CT scan of the kidneys, abdomen, and pelvis, doctors recommend drinking more fluids and 2-3 days before stopping eating foods that increase the formation of gases in the intestines. The day before 21:00 you need to have a light dinner, and then you can only drink liquids. After dinner, take enterosorbent to reduce the risk of gas formation. Empty your bowels naturally in the morning. Enema is used only in extreme cases. If you are constipated, it is better to take a laxative. Half an hour before the CT scan, you can take 2 antispasmodic tablets to relax the intestinal muscles.
- A CT scan of the kidneys and bladder will require some simple preparation. Your doctor will recommend filling your bladder, but do not overfill it. An hour before the examination, you need to urinate and drink 2 glasses of water. Next, go to the toilet after the CT scan.
- Before a CT scan with contrast, it is necessary to exclude contraindications from the kidneys, since it is this organ that removes the radiopaque substance from the body.
How many CT scans can be done per year and how often?
There should be 6-12 months between scheduled studies, depending on the radiation exposure. If a clinical case requires frequent tomography, this period can be reduced to 2-12 weeks, but taking into account the total annual radiation dose.
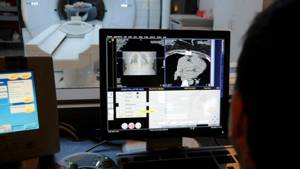
Using a 3D image taken by a tomograph, the doctor can study the structure of the organ both as a whole and in individual layers. Photo: US Navy photo/DVIDS