During pregnancy and after the birth of a baby, women try not to do anything that could harm it. All thoughts and actions are aimed exclusively at meeting the needs of the little person. There are even cases where young mothers refuse the necessary treatment. There is an opinion that after childbirth the body is renewed and metabolic processes are activated.
A woman with a baby in her arms is responsible not only for her own life. During this period, it is especially important to monitor your health. During the first weeks after childbirth, a woman in labor needs to visit an antenatal clinic and have a chest x-ray taken. Tests should be taken as early as possible. Fluorography (FLG) of the lungs during breastfeeding (BF) causes concern among patients. Experts agree that such fears are unfounded. Using X-rays, lung lesions can be quickly and easily identified. Tuberculosis lesions are especially dangerous. Examination of the internal organs of the chest using X-rays is still a minor exposure to radiation. Let's figure out how dangerous it is and whether it carries a risk of changing the composition of breast milk.
Why do fluorography after childbirth?
The main purpose of the examination is to detect pulmonary tuberculosis in the early stages. In addition, the image will show possible abnormalities in the body: neoplasms of the mammary glands, lungs, mediastinum, disorders of the structures of the pleura and diaphragm.
The epidemiological threshold for tuberculosis incidence has been exceeded in many regions of the Russian Federation. The disease has long become widespread. All social strata of the population are at risk. Koch's bacillus is transmitted by airborne droplets. The danger of infection is present in any public place. Fluorography of the lungs is part of any routine examination. Often a certificate of examination is required when applying for a job that involves communicating with people.
Fluorography should be carried out after childbirth, because during this period there is a high risk of any disease for the mother and child. X-rays of the lungs are recommended every year. During pregnancy, X-ray exposure is prohibited. The immune system is greatly suppressed during pregnancy. Preconditions for infectious and bacterial diseases arise. And, since pregnancy is a contraindication to any ionizing effects, it turns out that the lungs of the woman who gave birth were examined a long time ago. No one has the right to oblige a woman in labor to undergo fluorography. This procedure is voluntary. If the patient does not want to undergo a chest x-ray, she simply writes a refusal. Still, it is better to take an x-ray than to expose the child to the risk of contracting tuberculosis from the mother. It is also advisable for all members of the family where a new life has appeared to do this.
Fluorography during lactation is indicated by doctors in the following cases:
- the woman who gave birth experiences symptoms of tuberculosis and lung cancer;
- people around the woman in labor have signs of infection with Koch's bacillus, a positive Mantoux test;
- it is necessary to undergo inpatient treatment with the child;
- The epidemiological threshold for the disease in the region has been exceeded.
Undiagnosed tuberculosis leads to complications, even death. Treatment will be effective in the early stages of the disease. Signs that may indicate damage to lung tissue:
- cough with sputum, blood;
- chest pain;
- weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- cough that has not stopped for more than two weeks;
- increased body temperature;
- sweating at night;
- the appearance of subcutaneous nodules;
- general weakness, constant feeling of fatigue.
The presence of at least some of the listed symptoms is a reason for immediate examination.
Selecting the type of fluorography
X-ray of the lungs is an examination of the chest area using a low dose of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays are capable of deeply illuminating tissue, which allows the doctor to “see” the internal organs and assess their condition. When undergoing fluorography, the resulting image is first visible on a small screen and subsequently transferred to film. During a regular X-ray, the rays project an image directly onto photographic film.
There is no need to be afraid of performing fluorography during breastfeeding. In modern devices, a beam of X-rays penetrates the body like a fan. This reduces the level of radiation. The dose of radiation that a person receives is equivalent to several days in the sun. Equipment is regularly tested to ensure compliance with radiation standards. The effect itself lasts no more than a few seconds.

Two methods are used - traditional film and modern digital. In the first case, beams of rays pass through the organs of the human body and fall on a special photosensitive film. Depending on the intensity of absorption of X-rays, light and dark areas appear in the image, clearly depicting bones and tissues. X-rays pass well through the soft structures of the chest, but not through the ribs, collarbones, and other bones. It takes time to develop the negative and dry the photograph. The conclusion can usually be received the next day.
The digital survey method is more expensive, but more informative. Disease diagnosis statistics are 15% better. The X-ray beam passes through the area of interest linearly, reconstructing the image on the computer screen. The digitally captured image is stored indefinitely. You can zoom in on any area on the monitor, allowing you to better see possible tissue damage.
Advantages of digital diagnostics:
- better information content of the image;
- lower dose of radiation received;
- increased throughput.
The radiation dose depends on the technical characteristics of the device. The latest models provide exposure equal to 10 hours in the sun.
How to properly prepare for the procedure
The main rule when undergoing the procedure as a young mother is not to worry. The danger from X-rays is greatly exaggerated, in contrast to the serious consequences of an undetected disease and subsequent intensive antibiotic therapy, especially since the list of medications approved for use during lactation is limited. X-ray anxiety is more likely to affect breast milk. Due to stress, its production may even temporarily stop. The baby feels the mother’s condition, which affects his well-being. The baby may become fussy and have difficulty eating and sleeping.
If a young mother is undergoing fluorography and wants to maintain breastfeeding, the following precautions when preparing for the examination will help:
- attach the baby to the breast before undergoing the procedure;
- wear a lead apron for nursing women during the examination;
- prefer digital diagnostics;
- Remember to avoid X-ray exposure if it causes excessive anxiety.

These tips will help you calm down. Their implementation will maximally protect mother and baby during diagnostics.
Taking X-rays with contrast agents
Bronchography during lactation with contrast agents allows you to obtain detailed information about the condition of the tissues and blood vessels of the internal organs.
Iodine-based drugs are often used, which can provoke an allergic reaction. Contrast radiography is used exclusively according to the indications of the attending physician, to clarify the diagnosis.
Radiocontrast agents are typically used for X-ray-based CT scans.
For this reason, the risk of contrast agents passing into breast milk remains high.
After undergoing diagnosis, breastfeeding women are advised to stop breastfeeding until the body is completely cleansed. The time ranges from several hours to days.
Iodine-containing contrasts
Preparations containing iodine increase the intensity of the image of organs and vascular structures. This type of contrast is administered orally, less commonly through other routes.
Iodine-containing drugs have some degree of nephrotoxicity, so they are prescribed with caution to patients with renal failure.
The bioavailability of the contrast is almost zero, there is no need to stop breastfeeding.
Gadopentetic acid
It is a paramagnetic contrast agent used in MRI. When performing CT or X-rays, it is practically not used; preference is given to iodine-containing drugs.
It is mainly excreted from the body by the kidneys within 6-24 hours. The amount of the drug that penetrates into milk is no more than 0.25% - the minimum indicator that does not require stopping breastfeeding after the study.
Today, X-ray examinations are carried out using modern digital machines. This reduces radiation exposure to a minimum and produces high-quality images.
Fluorography is recommended to be performed once a year, including during lactation.
Pros and cons of the method
Using fluorography, serious diseases such as cancer and tuberculosis are detected. In the early stages they are practically asymptomatic. The more advanced the disease, the more difficult the treatment and the greater the impact on the body.
In addition to the importance of diagnosing dangerous diseases, fluorography and x-ray of the lungs have the following advantages:
- the ability to choose a gentle digital examination method;
- relative safety;
- painlessness;
- efficiency;
- rapidity.
The disadvantages include receiving a small dose of radiation. Having assessed the possible risk of untimely diagnosis, it becomes clear that fluorography is the lesser evil and does not have a negative impact on breastfeeding. The method has relative contraindications:
- age up to 15 years;
- period of bearing a child.
Is there any harm
Most doctors say that X-rays are not dangerous for breastfeeding. The effect of irradiation does not change the composition of mother's milk and does not affect the baby. Sometimes pediatricians advise putting the baby to the breast before the procedure, and after it, expressing the first milk. This recommendation is more aimed at reassuring mothers.
The radiation dose during fluorography is minimal. It is not harmful to human health and does not affect the quality of breast milk during feeding. For X-rays to become harmful to your health, you need to be exposed to them more than 100 times in a year. Significantly greater harm to breast milk from fluorography will be caused by excessive excitement and nervousness of the woman. If you can’t calm down, you can postpone the examination and do it immediately after stopping breastfeeding.

Preparing for the examination
If, despite the arguments presented above, you are still worried about your health and the health of your child, then you can try to minimize all dangers. To do this, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Give preference not to fluorography, but to x-rays. Despite the fact that this procedure is slightly higher in cost, it is also safer.
- Do not do fluorography unless necessary and prescribed by a doctor.
- On the eve of the examination itself, it is still better to feed the child so that after the procedure he does not want to eat for two to three hours.
- In order to eliminate the risk of contracting tuberculosis, almost every maternity hospital offers young mothers vouchers for fluoroscopy. And, if you are sure that during pregnancy you were not at risk of contracting this disease, then you can legally refuse the examination.
- During this event, you can ask a specialist to give you a protective apron, which is offered to pregnant women. This will also help protect yourself from additional radiation.
Take care of yourself and the people close to you!
Is it possible to do fluorography while breastfeeding?
Radiologists say that fluorography and other x-ray examinations for nursing mothers are allowed. The study does not in any way compromise the quality of breast milk. Breastfeeding specialists and pediatricians advise playing it safe and feeding the baby before FLG, and expressing the first milk immediately after the procedure. There are recommendations to skip one feeding or even not give the baby breastfeeding for 2-3 days.
For the timely detection of serious pathologies of the respiratory system, FLG can and should be done. When asked whether it is necessary to undergo examination if there is a risk of disease for a woman, the answer is absolutely positive. Such risks include the illness of someone from the immediate environment, or the appearance of symptoms in a young mother. You will have to present a certificate of fluorography and, if necessary, go to work if it involves communicating with people.
Features of the diagnostic event
Until now, fluorography remains an informative method for diagnosing the early development of pulmonary tuberculosis. The study is a routine examination procedure, which is closely related to the high prevalence of the disease.
Passing fluorography is a mandatory condition for further employment. Thanks to modern technologies and the availability of specialized centers with high-quality equipment, X-ray diagnostics becomes safe and also minimizes radiation exposure.
Is it necessary to express milk after fluorography?
There is a misconception that x-ray radiation somehow accumulates in breast milk and thereby can affect the development of the child. There are no medically justified prerequisites for skipping feeding, pumping, or temporarily switching to artificial formula. The radiation is effective only during a few seconds of passage of the FLG. As soon as the device is turned off, the effect of X-rays on the body also stops. This means that you can feed the baby immediately after the procedure is completed.
Expressing in the first days after childbirth can lead to congestion, lactostasis, a decrease in the amount of milk, and even cessation of lactation. A newborn baby, after eating from a bottle for a day or two, may refuse to breastfeed. It will be extremely difficult to restore a normal feeding system after this.
Indications and contraindications
Fluorography has indications and contraindications. Self-medication cannot be carried out; you must follow the doctor’s recommendations. The procedure is recommended for women:
- A routine examination is required after childbirth.
- A woman's complaints about her health.
- The attending physician has doubts regarding making the correct diagnosis.
We recommend reading: Episiotomy during childbirth
There are no contraindications to the procedure as such. If there are no obvious signs of the development of any disease, it is realistic to postpone the procedure until the end of breastfeeding, or the first months after childbirth.
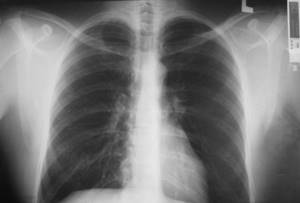
Photo interpretation
To diagnose pathologies, a specialist deciphers the film, which shows:
- focal shadows - darkening up to 10 mm, indicating pneumonia or tuberculosis;
- compacted, enlarged roots with general normal health indicate chronic inflammation, bronchitis;
- stringy roots are visible in smokers and in acute bronchitis;
- calcifications indicate contact with a patient with tuberculosis, but immunity was sufficient to preserve the Koch bacillus in a shell of calcium salts;
- fibrous tissue appears as a result of injuries, pulmonary diseases, surgical interventions;
- changes in the diaphragm occur due to obesity, gastrointestinal diseases, pleurisy;
- pleuroapical layers accumulate after tuberculosis;
- an increase in the vascular pattern will indicate bronchitis, heart problems, pneumonia, and the initial stages of cancer;
- sinuses (cavities between the pleural folds) in healthy lungs are free, but sealed ones require treatment;
- displacement and expansion of the mediastinum - the space between the lungs and other organs of the chest - are detected;
- adhesions and layers do not require treatment; they indicate previous inflammation.
Alternative diagnostic methods that are safe during and after breastfeeding
If a woman refuses to undergo examination due to uncertainty that fluorography is safe during or after breastfeeding, they resort to alternative methods for detecting tuberculosis and other hidden pathologies:
- general, biochemical blood test;
- culture of sputum;
- listening with a phonendoscope;
- urine test - general and for the presence of microplasma;
- tapping the chest;
- throat swab;
- Ultrasound of the heart and lungs.
Possible harm from fluorography can be reduced by undergoing a digital examination. Unlike traditional film, radiation exposure during this procedure is 4-5 times less.