MRI of the throat is relevant when other research methods turn out to be uninformative. Basically, the indication for its implementation is a suspicion of cancer. The reasons for performing the procedure may be:
- anatomical abnormalities of the throat structure;
- voice change;
- the need to visualize a foreign object;
- problems with food passing into the stomach;
- regular headaches, dizziness (may indicate disorders in the cervical vessels);
- "lump in the throat;
- periodic attacks of suffocation;
- difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- injuries to the mucous membranes of the throat;
- pronounced asymmetry, swelling of the soft tissues of the neck area;
- the need to evaluate the results of ongoing antitumor therapy;
- preparation for surgery and assessment of the results of surgical treatment.
Photo: MRI of the larynx and neck
What will an MRI of the larynx, pharynx and neck show?
Image: MRI of the neck and larynx
The magnetic resonance imaging image shows:
- larynx;
- oropharynx;
- trachea;
- upper esophagus;
- cartilage;
- ligaments;
- lymph nodes;
- veins;
- arteries.
MRI of the larynx clearly shows changes in the size of organs and other abnormalities. Based on the results of scanning on a magnetic tomograph, a specialist can judge the condition of the vocal cords and mucous membranes of the throat, the functioning of the lymphatic system, the existence of inflammation, neoplasms, and metastases.
MRI of the throat helps diagnose:
- cysts of the larynx or pharynx;
- abscesses and phlegmon of soft tissues;
- pathologies of the esophagus (stenosis, Zenker's diverticulum);
- tumors in the area of interest;
- tracheal stenosis;
- swelling of the larynx caused by any abnormalities in the body;
- laryngocele (cyst-like formation on the mucous membrane).
MRI of the throat and larynx shows the consequences of neck injuries, for example, hematoma due to a fracture of the thyroid cartilage. But for detailed identification of damage, as well as for searching for a foreign body, it is better to do a CT scan, specializing in the study of dense structures.
Preparation
The procedure does not require special preparation. Ultrasound can be prescribed to patients of any age; it does not pose a threat to the fetus during pregnancy, and helps diagnose congenital pathologies in infants.
The average duration of diagnosis is 15 – 20 minutes. First, the patient is placed comfortably on the couch in a supine position. For more detailed visualization, a pillow is placed under the shoulders. The subject's head is positioned in the opposite direction from the diagnostician.
The skin is lubricated with a conductor gel. Next, using an ultrasound probe, the doctor slowly moves it across the area under study, studying the soft structures in detail. The patient should try to lie still during this time.
Laryngeal cancer on MRI
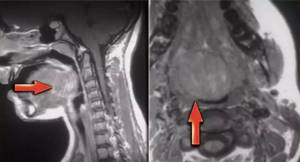
The first signs of tumors in the throat resemble the symptoms of a common cold, which complicates diagnosis at the beginning of the development of the disease. In the later stages of cancer, a person is bothered by constant laryngeal spasms, swelling appears in the neck, the voice changes, and it becomes difficult to swallow. People often attribute such symptoms to a viral infection or allergy and are in no hurry to consult a specialist, allowing the cancer to progress and deplete the body. The main risk with damage to the larynx is metastasis to the brain, lungs, heart and other important organs.
The main ways to visualize tumors are MRI and CT. Thanks to the unique opportunity to obtain the thinnest sections of the area under study, the doctor sees the volume and localization of the tumor, the degree of inclusion of various structures of the larynx and surrounding organs in the pathological process.
MRI of soft tissues of the throat in oncology is used for:
- detecting an early stage of cancer - if the images indicate the presence of a tumor, contrast is used, with which one can determine the topography and make tentative conclusions about the nature of the pathology; a biopsy is needed for a final conclusion;
- planning a surgical intervention - based on tomograms, a three-dimensional reconstruction can be carried out, allowing the specialist to think through the details of the future operation at the preparation stage;
- assessing the effectiveness of treatment - MRI of the throat and larynx shows an accurate picture of changes; the procedure is harmless and does not cause adverse reactions (this is important for patients undergoing radiation therapy);
- monitoring the state of the tumor over time - if the neoplasm is located next to vital structures, and its removal is dangerous for a person or the neoplasia cannot be removed in full - the growth process is monitored by periodic MRI scanning.
The capabilities of MRI of the larynx in diagnosing cancer directly depend on the resolution of the equipment and the professional competence of the radiologist. Images taken with low-field installations are not informative enough for early detection of pathology. Reliable information can be obtained after examination using a high-field apparatus starting from 1.5 Tesla.
Laboratory research
The list includes the following examinations - general blood test, urine test, RV test, blood test for sugar, determination of blood group and its Rh factor. During the general analysis, attention will be paid to the following indicators:
- hemoglobin level;
- leukocyte count;
- ESR is the sedimentation rate of erythrocytes.
This analysis is carried out constantly - when making a diagnosis, before surgical interventions and before each course of chemotherapy.
Any deviations from the norm are a cause for concern.
If the hemoglobin level and the number of leukocytes are minimal, then you first need to bring the indicators back to normal.
- Characteristic signs of bone pain due to cancer
Biochemistry
It is necessary to assess the performance of internal organs. The results will indicate the affected organ and where the metastases are located. But how can you recognize cancer based on the results of biochemistry:
- the concentration of albumin and total protein levels decreases as the tumor grows;
- if metastases have affected the gallbladder and gastrointestinal tract, then there will be an increase in the level of alkaline phosphatase;
- when metastases spread to the liver, bilirubin and ALT increase;
- the concentration of urea in the blood increases with the disintegration of the tumor and intoxication of the body;
- metastases have affected the liver, lungs, reproductive organs - this can be recognized by an increase in sugar levels.
Tumor markers
This method is relatively new and, compared to a biopsy, is not as traumatic. But the accuracy is somewhat reduced. The procedure is carried out as follows:
- over several months, blood is taken from a vein from the patient;
- Also, during this time, studies are carried out to identify protein compounds in the patient’s blood that are characteristic of laryngeal cancer.
More than a hundred tumor markers are known, but about thirty are used in practice. They are specific bodies produced by cancer cells. In a healthy person they are absent or present in small quantities. When determining laryngeal cancer, the following types of tumor markers are used:
- CSS is present in the blood of a healthy person in an amount of no more than 1.5 ng/ml. a slight increase in level is evidence of the onset of cancer. A doubling of the concentration already indicates existing cancer. This tumor marker is also examined after surgery - if it shows an elevated level, this means that not all cancer cells have been removed and a relapse of the disease is possible.
- CYFRA 21-1 - normally does not exceed the following indicators - 2.3 ng/ml. if its value is above 3, then this is already evidence of cancer. An even greater increase in indicators means that almost all internal organs are infected with metastases.
Another tumor marker is used - CA 19-9. However, to diagnose laryngeal cancer, its indicators alone are not enough. Confirmation from other sources is also needed.
Biopsy
The most informative study that helps reliably confirm the diagnosis. A piece of tissue is examined under a microscope. Which is usually obtained from the larynx by direct laryngoscopy. Also, material for examination can be obtained as a result of other procedures. The collection is made using a special needle.
If, as a result of examining the material, atypical cells were found in it, then we can confidently speak about a malignant process in the body.
This study also allows us to clarify the specific form of cancer. In this case, it will be easier to predict the further development of the disease.
For example, in the third stage of laryngeal cancer, metastases are found in regional lymph nodes. This allows not only to confirm the previously announced diagnosis, but also to determine the stage of the disease.
This procedure is mandatory when diagnosing malignant diseases.
- Stage 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 of throat cancer, stage classification according to the TNM system, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and life prognosis
MRI of the esophagus
The esophagus is a hollow tube that pushes the bolus of food towards the stomach. With pathologies of the organ, a person has problems with swallowing. In such cases, to clarify the cause, X-rays, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are prescribed.
During an MRI of the throat, the cervical esophagus is scanned. The doctor sees in the pictures:
- acute and chronic inflammatory processes;
- areas of ulceration;
- perforation (perforation);
- stenosis;
- violation of peristalsis (esophagospasm);
- obstruction;
- developmental anomalies;
- benign tumors;
- malignant neoplasms at different stages.
The greatest danger is esophageal cancer. At first, the disease is asymptomatic, and only after a significant narrowing of the canal does it become difficult to swallow food. It is possible to prevent cancer if an ulcer, inflammation of the mucous membrane (esophagitis), polyps, or a condition called Barrett's esophagus is detected in time. MRI of the larynx provides comprehensive information about the localization of the pathological process, changes in tissues and organ walls, making it possible to accurately recognize the disease and choose the optimal treatment tactics.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
, an ultrasound diagnosis of the thyroid gland should be performed . This procedure is invasive, fairly cheap, fast and provides accurate results.
Ultrasound is a study of the body using ultrasonic waves. The echo signals reflected from the internal organs, after certain transformations, create on the monitor screen an image of a section of the gland in different shades of gray.
A specialist can determine the condition of the organ: geometric dimensions, state of borders, lymph nodes, blood vessels. Ultrasound determines the acoustic density of an organ, called echogenicity.
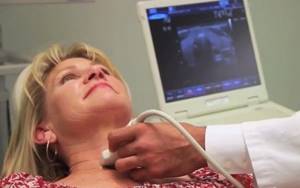
May be:
- normal;
- reduced;
- increased;
- echonegativity.
The condition of the organ being studied is determined by the types of echogenicity.
Reduced (hypoechogenicity) is characteristic of liquid formations (dark gray areas on the screen). Perhaps it is a cyst, liquid formations, vascular formations and cancer in 5% of cases. A doctor cannot always reliably determine the nature of these formations, so other diagnostics, such as a biopsy, will be required.
Increased (hyperechogenicity) indicates a lack of iodine (endemic goiter), damage to the organ by poison (toxic goiter), autoimmune thyroiditis, subacute thyroiditis, oncology, areas of sclerosis. Visualized on the monitor as white spots. Hyperechogenicity may occur in a healthy gland, or it may indicate serious pathologies, therefore, to obtain a reliable diagnosis, it is advisable to conduct additional research.
Echonegativity (anechoicity) is displayed as black areas. Perhaps it is a cyst, pseudocyst, colloid cyst, adenoma. It is also recommended to undergo other examinations to make a more accurate diagnosis.
With normal echogenicity, the silhouette of the gland is smooth and clear. A benign tumor has smooth edges, while a malignant tumor has curved edges.
Since the frequency of ultrasound is not high, there is no harmful effect on the body.
How to do an MRI of the larynx
To do an MRI of the throat and larynx, no special preparation is required. You just need to follow a few simple recommendations:
- It is better to come to the examination with a doctor’s referral, which will clearly indicate what you should pay attention to and for what reason;
- all metal objects and electronic devices are left outside the door of the diagnostic room; if such elements or life support devices are present in the body, it is necessary to inform the radiologist in advance;
- During the procedure, it is important to remain still, then the pictures will be as clear as possible.
To perform an MRI of the larynx, a person lies down on a transport table. If necessary, the head is secured with straps to prevent spontaneous movements. Then the table is moved into the ring-shaped frame of the tomograph and scanning begins. There are no uncomfortable sensations for a person, only the noise and crackling of equipment can be heard. Medical staff watches the process through glass from an adjacent office. If the patient for some reason wants to interrupt the procedure, he can use the speakerphone.
When prescribing an MRI of the throat with contrast, regular (native) images are first taken, then a drug is injected into a vein to enhance the clarity of the image and the session is continued. When using additional agents, blood vessels and soft tissues are better visible, which is of great importance if a tumor is suspected.
After the examination, the radiologist deciphers the data and draws up a conclusion. To make a final diagnosis and select a treatment option, you should contact an observing specialist.
Indications for the procedure
The examination of the larynx is carried out as prescribed by the ENT specialist. The main indication for its implementation is unusual sensations or discomfort in the throat:
- hoarseness or lack of voice;
- pain when swallowing;
- feeling of a foreign object;
- pain symptoms of unknown etiology;
- the appearance of a cough with blood inclusions.
The procedure is mandatory for patients diagnosed with:
- laryngitis;
- obstruction of the respiratory tract;
- dysphonia;
- vocal cord paresis.
There are also contraindications
. The procedure is not performed on patients diagnosed with epilepsy, heart disease, or inflammatory processes in the larynx or nasal cavity.
Children's ENT
Prevention and treatment of ENT diseases in children is one of our main areas of activity. The clinic is adapted to receive the youngest patients; modern medical equipment is equipped with special means for providing medical care to children (for example, special children's attachments for endoscopic equipment, etc.). The clinic's pediatric ENT doctors have extensive experience in treating children of all age categories, have special communication skills with children and are able to provide timely and highly qualified medical care, taking into account the age-related characteristics of the diagnosis and treatment of the child.
Our specialists
- Oganesyan Tigran Sergeevich
otorhinolaryngologist, rhinosurgeon
experience: 18 years
ENT pathology expert
- Sokolova Alla Vasilievna
otorhinolaryngologist, otosurgeon, doctor of the highest category
experience: over 35 years
Candidate of Medical Sciences
- Galkin Alexey Vladimirovich
otorhinolaryngologist, rhinosurgeon
experience: 14 years
ENT pathology expert
- Chuprikov Roman Sergeevich
otorhinolaryngologist, rhinosurgeon, phoniatrist, doctor of the highest category
experience: 19 years
ENT pathology expert
- Sadykhov Rahim Agalarovich
otorhinolaryngologist, rhinosurgeon, audiologist
experience: 6 years
ENT pathology expert
- Starosvetsky Andrey Borisovich
otorhinolaryngologist, rhinosurgeon
experience: 22 years
Candidate of Medical Sciences
- Moseikina Liliya Alekseevna
otosurgeon
experience: 29 years
Candidate of Medical Sciences
- Yakushev Anatoly Andreevich
otorhinolaryngologist, otosurgeon
experience: 8 years
leading doctor of the clinic
doctorAll specialists
Our ENT doctors have extensive and unique experience in treating ENT diseases, both adult patients and children. We have a highly professional team of otolaryngologists of the highest qualification category
, rhinosurgeons and otosurgeons, including 40% of our doctors have an academic degree of
candidate of medical sciences
. Our specialists solve complex problems every day and perform unique surgical operations of the ENT organs.
Operations in the ear, nose and throat clinic
The clinic performs a wide range of surgical operations, such as adenoid removal, tonsil removal, tympanoplasty, septoplasty, rhinoplasty, vasotomy, etc. We have an operating room and a hospital at our disposal, which are equipped with the most modern medical equipment. The team of surgeons is represented by a wide range of specialists in their field who have extensive experience in performing complex surgical operations using modern technologies for operating and rehabilitating patients.